Revisiting BPPV: Incidence and Behavior of Atypical Variants
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Posterior canal canalolithiasis (pc-BPPV);
- Horizontal canal BPPV, geotropic form (hc-BPPV-geo);
- Horizontal canal BPPV, apogeotropic form (hc-BPPV-apo).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Examination Protocol and Diagnostic Criteria
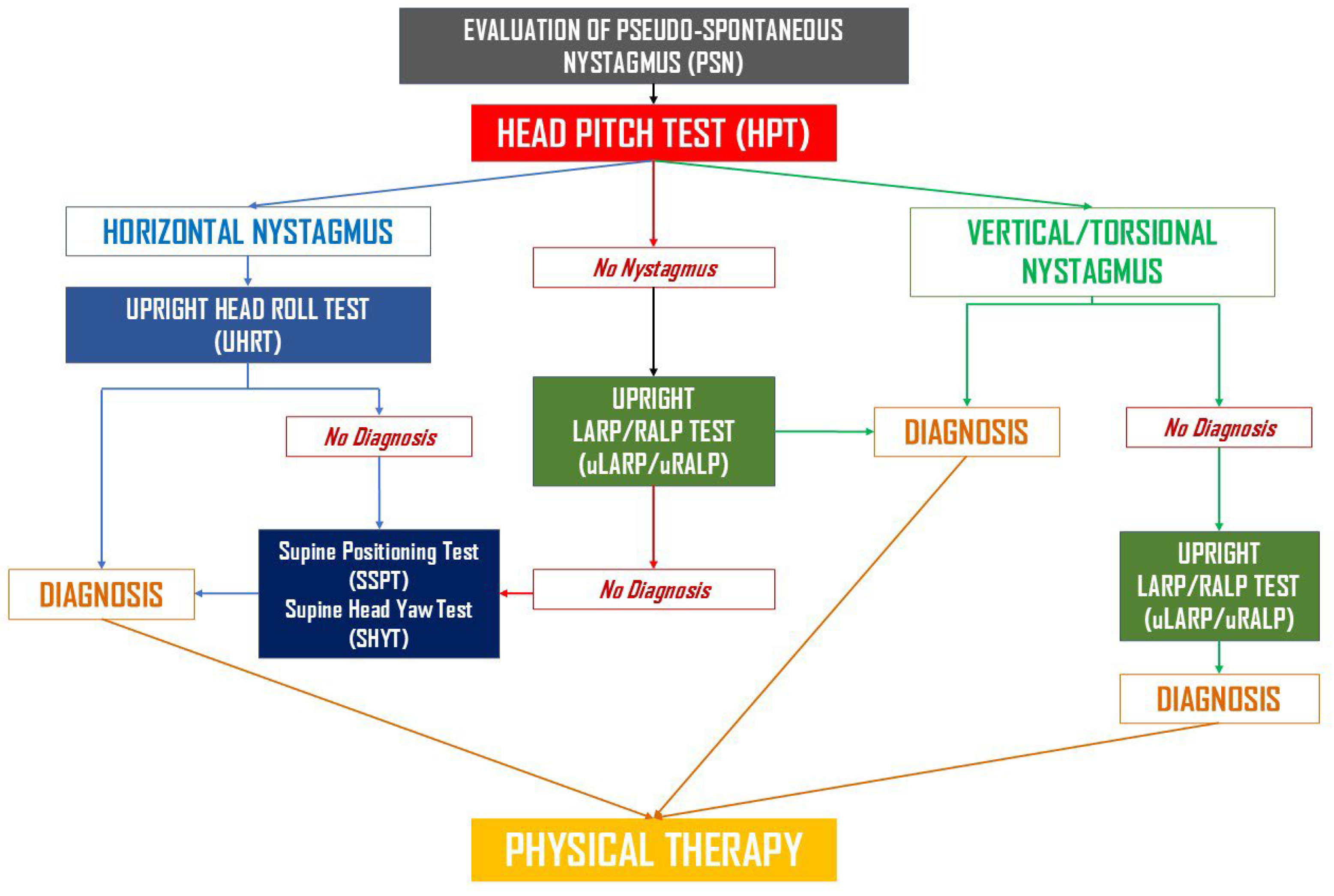
- Upright protocol (UBP): The Upright BPPV Protocol consists of a battery of diagnostic tests performed in the sitting position, with the head moved along different spatial axes to displace canaliths by gravity within the involved canals. These include the Upright Head Pitch Test (uHPT), the Upright Head Roll Test (uHRT), and the Upright LARP/RALP test (uLARP/RALP). A detailed description of UBP can be found in the corresponding publications [60,61,62,63]. If UBP yielded a conclusive diagnosis, appropriate therapeutic maneuvers were immediately performed. A schematic representation of the Upright BPPV Protocol is shown in Figure 1. This flowchart summarizes the sequence of upright and traditional positional tests used to identify BPPV variants.
- Rapid positioning maneuvers (if Step 1 was non-diagnostic): First, the Seated-to-Supine Positioning Test (SSPT), also known as the “Asprella Single Manoeuvre,” was performed [47,57,58,61,62]. If this was non-diagnostic, or if a vertical canal was suspected, the DHT was conducted. Conversely, if horizontal nystagmus was detected and lateral canal involvement was suspected, the Supine Head Yaw Test (sHYT)—also known as the Pagnini–McClure maneuver or the Supine Head Roll Test—was carried out. Traditional diagnostic maneuvers were performed in accordance with established clinical guidelines [17]. If the combination of UBP and classical positioning tests failed to establish a definite diagnosis, ancillary diagnostic procedures were employed, including the HHT (performed with the head slightly elevated from supine, approximately 30° in flexion), the Rose positioning test (supine with head and neck hyperextended), or the video Head Impulse Test (vHIT, ICS video-oculographic system, GN Otometrics, Ballerup, Denmark). The latter was used to identify the affected canal in cases of positional DBNy and in canalith jam conditions, as reported in previous studies [42,45,46,51,52,53].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ac-BPPV | anterior canal canalolithiasis |
| Apo-pc-BPPV | apogeotropic posterior canal canalolithiasis |
| BPPV | benign paroxysmal positional vertigo |
| CJ | canalith jam |
| DBNy | down-beating nystagmus |
| DBNy-BPPV-uc | BPPV with down-beating nystagmus, unspecified canal |
| DHT | Dix–Hallpike Test |
| Hc-BPPV-apo | horizontal canal bppv, apogeotropic form |
| Hc-BPPV-geo | horizontal canal bppv, geotropic form |
| HHT | Half–Dix–Hallpike Test |
| Mc-BPPV | multi-canal lithiasis |
| Pc-BPPV | posterior canal canalolithiasis |
| Pc-BPPV-cu | posterior canal cupulolithiasis |
| Pc-BPPV-suv | posterior canal BPPV with sitting-up vertigo |
| RP | Rose Position |
| SHYT | Supine Head Yaw Test |
| SSPT | Seated-To-Supine Positioning Test |
| UHPT | Upright Head Pitch Test |
| UHRT | Upright Head Roll Test |
| ULARP/RALP | Upright Larp/Ralp Test |
| VHIT | Video Head Impulse Test |
| VOR | vestibulo-ocular reflex |
References
- Epley, J.M. Human experience with canalith repositioning maneuvers. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 942, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, T.; Takeda, N.; Ikezono, T.; Shigeno, K.; Asai, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Committee for Standards in Diagnosis of Japan Society for Equilibrium Research. Classification, diagnostic criteria and management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Auris Nasus Larynx 2017, 44, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuti, D.; Zee, D.S.; Mandalà, M. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: What We Do and Do Not Know. Semin. Neurol. 2020, 40, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, S.; Jeon, E.J.; Kim, M.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, C.H.; Nam, S.I.; Kim, H.A.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, J.Y.; et al. Clinical features of secondary BPPV: A nation-wide multicenter study. J. Vestib. Res. 2025, 35, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balatsouras, D.G.; Koukoutsis, G.; Aspris, A.; Fassolis, A.; Moukos, A.; Economou, N.C.; Katotomichelakis, M. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Secondary to Mild Head Trauma. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2017, 126, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabulut, M.; Kutlu, S.; Viechtbauer, W.; Melliti, A.; Meço, C.; Mohamad, A.; Özgirgin, O.N.; Bhandari, A.; Kingma, H.; van de Berg, R. Co-occurrence of otologic disorders and benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2025; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korres, S.; Balatsouras, D.G.; Ferekidis, E. Prognosis of patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo treated with repositioning manoeuvres. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2006, 120, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güçlütürk, M.T.; Ünal, Z.N.; İsmi, O.; Çimen, M.B.; Ünal, M. The Role of Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Mediators in Benign Par-oxysmal Positional Vertigo. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2016, 12, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günizi, H.; Savaş, H.B. An evaluation of trace elements and oxidative stress in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0277960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; Kwak, S.H.; Seo, J.H. Risk Factors Associated With the Occurrence and Recurrence of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo in Koreans: A Nested Case-Control Study. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2025, 18, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.I.; Park, Y.; Lee, H.J.; Jeon, E.J. Correlation between serum vitamin D level and benign paroxysmal positional vertigo recurrence. Auris Nasus Larynx 2023, 50, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asprella Libonati, G.; Leone, A.; Martellucci, S.; Gallo, A.; Albera, R.; Lucisano, S.; Bavazzano, M.; Chiarella, G.; Viola, P.; Galletti, F.; et al. Prevention of Recurrent Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: The Role of Combined Supplementation with Vitamin D and Antioxidants. Audiol. Res. 2022, 12, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valli, P.; Botta, L.; Zucca, G.; Valli, S.; Buizza, A. Simulation of cupulolithiasis and canalolithiasis by an animal model. J. Vestib. Res. 2008, 18, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuknecht, H.F. Cupulolithiasis. Arch. Otolaryngol. 1969, 90, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.F.; Ruby, R.R.; McClure, J.A. The mechanics of benign paroxysmal vertigo. J. Otolaryngol. 1979, 8, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Kalmanson, O.; Foster, C.A. Cupulolithiasis: A Critical Reappraisal. OTO Open 2023, 7, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, N.; Gubbels, S.P.; Schwartz, S.R.; Edlow, J.A.; El-Kashlan, H.; Fife, T.; Holmberg, J.M.; Mahoney, K.; Hollingsworth, D.B.; Roberts, R.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (Update). Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 156 (Suppl. 3), S1–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnutzer, A.A.; Kerkeni, H.; Diener, S.; Kalla, R.; Candreia, C.; Piantanida, R.; Maire, R.; Welge-Lüssen, A.; Budweg, J.; Zwergal, A.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of vertigo and dizziness: Interdisciplinary guidance paper for clinical practice. HNO, 2025; epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Brevern, M.; Bertholon, P.; Brandt, T.; Fife, T.; Imai, T.; Nuti, D.; Newman-Toker, D. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Diagnostic criteria. J. Vestib. Res. 2015, 25, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertholon, P.; Bronstein, A.M.; Davies, R.A.; Rudge, P.; Thilo, K.V. Positional down beating nystagmus in 50 patients: Cerebellar disorders and possible anterior semicircular canalithiasis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 72, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.E.; Morgan, B.; Fletcher, J.C., Jr.; Krueger, W.W. Anterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: An underappreciated entity. Otol. Neurotol. 2007, 28, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichijo, H. Analysis of 30 patients with cupulolithiasis of the posterior semicircular canal. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 280, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, E.H.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, H.A.; Lee, H.; Moon, I.S.; Park, J.Y.; Yoon, B.A.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Treatment Maneuvers in Cupulolithiasis of the Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2025, 8, 250972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vats, A.K.; Kothari, S.; Khamesra, R.; Vats, S. Inversion Test and Sitting-Up Oculomotor Patterns in Patients with Graviceptive Heavy Posterior Cupula—A Case Series. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2023, 26, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helminski, J.O. Atypical PC-BPPV—Cupulolithiasis and Short-Arm Canalithiasis: A Retrospective Observational Study. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2025, 49, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, D.B.; Song, C.E.; Jung, E.J.; Ko, K.M.; Park, J.W.; Song, M.H. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo with simultaneous involvement of multiple semicircular canals. Korean J. Audiol. 2014, 18, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Kim, H.; Jung, T.; Lee, D.H.; Shin, J.E. Clinical characteristics of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo after traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2024, 38, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agus, G.; Puxeddu, R.; Demontis, G.P.; Puxeddu, P. Atypical “reversed” paroxysmal positioning nystagmus in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol. Suppl. 1995, 520 Pt 1, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucchi, P.; Pecci, R.; Giannoni, B. Posterior semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo presenting with torsional downbeating nystagmus: An apogeotropic variant. Int. J. Otolaryngol. 2012, 2012, 413603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambi, J.; Astore, S.; Mandalà, M.; Trabalzini, F.; Nuti, D. Natural course of positional down-beating nystagmus of peripheral origin. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucchi, P.; Pecci, R.; Giannoni, B.; Di Giustino, F.; Santimone, R.; Mengucci, A. Apogeotropic Posterior Semicircular Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: Some Clinical and Therapeutic Considerations. Audiol. Res. 2015, 5, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaycochea, O.; Pérez-Fernández, N.; Manrique-Huarte, R. A novel maneuver for diagnosis and treatment of torsional-vertical down beating positioning nystagmus: Anterior canal and apogeotropic posterior canal BPPV. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 88, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Califano, L.; Salafia, F.; Mazzone, S.; Melillo, M.G.; Califano, M. Anterior canal BPPV and apogeotropic posterior canal BPPV: Two rare forms of vertical canalolithiasis. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2014, 34, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Califano, L.; Mazzone, S.; Salafia, F.; Melillo, M.G.; Manna, G. Less common forms of posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2021, 41, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelli, V.; Giannoni, B.; Volpe, G.; Faralli, M.; Fetoni, A.R.; Pettorossi, V.E. Downbeat nystagmus: A clinical and pathophysiological review. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1394859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scocco, D.H.; Barreiro, M.A.; García, I.E. Sitting-up vertigo as an expression of posterior semicircular canal heavy cupula and posterior semicircular canal short arm canalolithiasis. J. Otol. 2022, 17, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scocco, D.H.; García, I.E.; Barreiro, M.A. Sitting Up Vertigo. Proposed Variant of Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helminski, J.O. Case report: Atypical patterns of nystagmus suggest posterior canal cupulolithiasis and short-arm canalithiasis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 982191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.M.; Song, M.H.; Kim, J.H.; Shim, D.B. Persistent spontaneous nystagmus following a canalith repositioning procedure in horizontal semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2014, 140, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.S.; Choi, J.; Chung, W.H. Persistent Direction-Fixed Nystagmus Following Canalith Repositioning Maneuver for Horizontal Canal BPPV: A Case of Canalith Jam. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 7, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comacchio, F.; Poletto, E.; Mion, M. Spontaneous Canalith Jam and Apogeotropic Horizontal Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: Considerations on a Particular Case Mimicking an Acute Vestibular Deficit. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, e843–e848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellucci, A.; Malara, P.; Brandolini, C.; Del Vecchio, V.; Giordano, D.; Ghidini, A.; Ferri, G.G.; Pirodda, A. Isolated horizontal canal hypofunction differentiating a canalith jam from an acute peripheral vestibular loss. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2019, 40, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, M.C.; Helminski, J.; Zee, D.S.; Cristiano, E.; Giannone, A.; Tortoriello, G.; Marcelli, V. Horizontal semicircular canal jam: Two new cases and possible mechanisms. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2020, 5, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martellucci, S.; Castellucci, A.; Malara, P.; Pagliuca, G.; Clemenzi, V.; Stolfa, A.; Gallo, A.; Libonati, G.A. Spontaneous Jamming of Horizontal Semicircular Canal Combined with Canalolithiasis of Contralateral Posterior Semicircular Canal. J. Audiol. Otol. 2022, 26, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellucci, A.; Malara, P.; Ghidini, A. Spontaneous downbeat nystagmus in posterior semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A canalith jam? Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellucci, A.; Botti, C.; Martellucci, S.; Malara, P.; Delmonte, S.; Lusetti, F.; Ghidini, A. Spontaneous Upbeat Nystagmus and Selective Anterior Semicircular Canal Hypofunction on Video Head Impulse Test: A New Variant of Canalith Jam? J. Audiol. Otol. 2022, 26, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asprella Libonati, G. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo and Positional Vertigo Variants. Otorhinolaryngol. Clin. Int. J. 2012, 4, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büki, B.; Mandalà, M.; Nuti, D. Typical and atypical benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Literature review and new theoretical considerations. J. Vestib. Res. 2014, 24, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, S.; Zalazar, G.J.; Fernández, M.; Grinstein, G.; Lemos, J. Atypical Positional Vertigo: Definition, Causes, and Mechanisms. Audiol. Res. 2022, 12, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.S. Less talked variants of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 442, 120440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellucci, A.; Malara, P.; Martellucci, S.; Botti, C.; Delmonte, S.; Quaglieri, S.; Rebecchi, E.; Armato, E.; Ralli, M.; Manfrin, M.L.; et al. Feasibility of Using the Video-Head Impulse Test to Detect the Involved Canal in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Presenting With Positional Downbeat Nystagmus. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 578588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellucci, A.; Malara, P.; Delmonte, S.; Ghidini, A. A Possible Role of Video-Head Impulse Test in Detecting Canal Involvement in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Presenting with Positional Downbeat Nystagmus. Otol. Neurotol. 2020, 41, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellucci, A.; Malara, P.; Martellucci, S.; Delmonte, S.; Ghidini, A. Fluctuating Posterior Canal Function in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Depending on How and Where Otoconia Are Disposed. Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, e193–e198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabaya, K.; Katsumi, S.; Fukushima, A.; Esaki, S.; Minakata, T.; Iwasaki, S. Assessment of semicircular canal function in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo using the video head impulse test and caloric test. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2023, 8, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, D.; Schubert, M.C. Resolution of atypical posterior semicircular canal BPPV: Evidence for putative short-arm location. BMJ Case Rep. 2023, 16, e254579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asprella Libonati, G.; Gagliardi, G.; Cifarelli, D.; Larotonda, G. “Step by step” treatment of lateral semicircular canal canalolithiasis under videonystagmoscopic examination. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2003, 23, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Asprella Libonati, G. Diagnostic and treatment strategy of lateral semicircular canal canalolithiasis. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2005, 25, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Asprella-Libonati, G. Lateral semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo diagnostic signs. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2010, 30, 222. [Google Scholar]
- Asprella-Libonati, G. Lateral canal BPPV with Pseudo-Spontaneous Nystagmus masquerading as vestibular neuritis in acute vertigo: A series of 273 cases. J. Vestib. Res. 2014, 24, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asprella-Libonati, G.; Martellucci, S.; Castellucci, A.; Malara, P. Minimum Stimulus Strategy: A step-by-step diagnostic approach to BPPV. J. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 434, 120158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malara, P.; Castellucci, A.; Martellucci, S. Upright head roll test: A new contribution for the diagnosis of lateral semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Audiol. Res. 2020, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martellucci, S.; Malara, P.; Castellucci, A.; Pecci, R.; Giannoni, B.; Marcelli, V.; Scarpa, A.; Cassandro, E.; Quaglieri, S.; Manfrin, M.L.; et al. Upright BPPV Protocol: Feasibility of a New Diagnostic Paradigm for Lateral Semicircular Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Compared to Standard Diagnostic Maneuvers. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 578305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martellucci, S.; Castellucci, A.; Malara, P.; Ralli, G.; Pagliuca, G.; Botti, C.; Gallo, A.; Ghidini, A.; Asprella Libonati, G. Is it possible to diagnose Posterior Semicircular Canal BPPV from the sitting position? The role of the Head Pitch Test and the upright tests along the RALP and LARP planes. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2022, 43, 103474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dispenza, F.; DEStefano, A.; Costantino, C.; Rando, D.; Giglione, M.; Stagno, R.; Bennici, E. Canal switch and re-entry phenomenon in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Difference between immediate and delayed occurrence. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2015, 35, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zuma e Maia, F. New Treatment Strategy for Apogeotropic Horizontal Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Audiol. Res. 2016, 6, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacovino, D.A.; Hain, T.C.; Gualtieri, F. New therapeutic maneuver for anterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J. Neurol. 2009, 256, 1851–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, H. New repositioning techniques for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: The Li repositioning manoeuvres. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2010, 124, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calheiros Cruz Vidigal, T.I.; Rando Matos, Y.; Flores Mateo, G.; Ballvé Moreno, J.L.; Peguero Rodríguez, E. Epley maneuver, performed by family doctors or emergency physicians, for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2025, 3, CD016020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoujah, D.; Naples, J.G.; Silva, L.O.J.E.; Edlow, J.A.; Gerberi, D.J.; Carpenter, C.R.; Bellolio, F. Epley maneuver for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Evidence synthesis for guidelines for reasonable and appropriate care in the emergency department. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2023, 30, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polensek, S.H.; Sterk, C.E.; Tusa, R.J. Screening for vestibular disorders: A study of clinicians’ compliance with recommended practices. Med. Sci. Monit. 2008, 14, 238–242. [Google Scholar]
- Vanni, S.; Vannucchi, P.; Pecci, R.; Pepe, G.; Paciaroni, M.; Pavellini, A.; Ronchetti, M.; Pelagatti, L.; Bartolucci, M.; Konze, A.; et al. Consensus paper on the management of acute isolated vertigo in the emergency department. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 19, 1181–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, J.E.; Miklea, J.T.; Howard, M.; Springate, R.; Kaczorowski, J. Canalith repositioning maneuver for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Randomized controlled trial in family practice. Can. Fam. Physician 2007, 53, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- White, J.; Savvides, P.; Cherian, N.; Oas, J. Canalith repositioning for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol. Neurotol. 2005, 26, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandalà, M.; Santoro, G.P.; Asprella Libonati, G.; Casani, A.P.; Faralli, M.; Giannoni, B.; Gufoni, M.; Marcelli, V.; Marchetti, P.; Pepponi, E.; et al. Double-blind randomized trial on short-term efficacy of the Semont maneuver for the treatment of posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 882–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandalà, M.; Pepponi, E.; Santoro, G.P.; Cambi, J.; Casani, A.; Faralli, M.; Giannoni, B.; Gufoni, M.; Marcelli, V.; Trabalzini, F.; et al. Double-blind randomized trial on the efficacy of the Gufoni maneuver for treatment of lateral canal BPPV. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 1782–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.D.; Shim, D.B.; Park, H.J.; Song, C.I.; Kim, M.B.; Kim, C.H.; Byun, J.Y.; Hong, S.K.; Kim, T.S.; Park, K.H.; et al. A multicenter randomized double-blind study: Comparison of the Epley, Semont, and sham maneuvers for the treatment of posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Audiol. Neurootol. 2014, 19, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, Y.; Xu, X.; Gao, L.; Li, Y.; Shao, Q.; Wang, W.; Sun, C.; et al. Minimal stimulus strategy for diagnosis and treatment of BPPV: A virtual simulation study. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2025, 282, 3525–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martellucci, S.; Attanasio, G.; Ralli, M.; Marcelli, V.; de Vincentiis, M.; Greco, A.; Gallo, A. Does cervical range of motion affect the outcomes of canalith repositioning procedures for posterior canal benign positional paroxysmal vertigo? Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2019, 40, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotto di Santillo, L.; Califano, L. Canal switch: A possible complication of physical therapeutic manoeuvers for posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2023, 43, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajguru, S.M.; Ifediba, M.A.; Rabbitt, R.D. Biomechanics of horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J. Vestib. Res. 2005, 15, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir, B.O.; Ercan, I.; Cakir, Z.A.; Civelek, S.; Sayin, I.; Turgut, S. What is the true incidence of horizontal semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo? Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2006, 134, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.W.; Park, K.N.; Ko, M.H.; Jeon, H.K.; Choi, J.Y.; Cho, Y.S.; Hong, S.H.; Chung, W.H. Incidence of horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo as a function of the duration of symptoms. Otol. Neurotol. 2009, 30, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Jeong, H.; Shin, J.E. Incidence of idiopathic benign paroxysmal positional vertigo subtype by hospital visit type: Experience of a single tertiary referral centre. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2023, 137, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korres, S.; Balatsouras, D.G.; Kaberos, A.; Economou, C.; Kandiloros, D.; Ferekidis, E. Occurrence of semicircular canal involvement in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol. Neurotol. 2002, 23, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Brevern, M. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Semin. Neurol. 2013, 33, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Brevern, M.; Clarke, A.H.; Lempert, T. Continuous vertigo and spontaneous nystagmus due to canalolithiasis of the horizontal canal. Neurology 2001, 56, 684–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, X.; Zhao, D.H.; Shen, B.; Si, L.H.; Li, K.Z.; Hong, Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Yang, X. Clinical Characteristics of Patients With Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Diagnosed Based on the Diagnostic Criteria of the Bárány Society. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, T.M.; Weidman, M.S.; Hain, T.C.; Stone, H.A. A mathematical model for top-shelf vertigo: The role of sedimenting otoconia in BPPV. J. Biomech. 2004, 37, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajguru, S.M.; Ifediba, M.A.; Rabbitt, R.D. Three-dimensional biomechanical model of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 32, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oas, J.G. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A clinician’s perspective. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 942, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, L.; Yi-Fei, Z.; Shu-Zhi, W.; Yan-Yan, Z.; Xiao-Kai, Y. Diagnosis and treatment of the short-arm type posterior semicircular canal BPPV. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 88, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Gil, Y.E.; Kim, J.S. Concomitant long-arm cupulolithiasis and short-arm canalithiasis involving the posterior canal. J. Neurol. 2025, 272, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büki, B. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo--toward new definitions. Otol. Neurotol. 2014, 35, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, N.; Martin, E.; Zubieta, J.L.; Romero, M.D.; Garcia-Tapia, R. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in patients with Ménière’s disease treated with intratympanic gentamycin. Laryngoscope 2002, 112, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balatsouras, D.G.; Ganelis, P.; Aspris, A.; Economou, N.C.; Moukos, A.; Koukoutsis, G. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo associated with Meniere’s disease: Epidemiological, pathophysiologic, clinical, and therapeutic aspects. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2012, 121, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constant Ionescu, E.; Idriss, S.; Reynard, P.; Ltaief-Boudrigua, A.; Thai-Van, H. Persistent Positional Vertigo in a Patient with Partial “Auto-Plugged” Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence: A Case Study. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2022, 18, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellucci, A.; Botti, C.; Bettini, M.; Fernandez, I.J.; Malara, P.; Martellucci, S.; Crocetta, F.M.; Fornaciari, M.; Lusetti, F.; Renna, L.; et al. Case Report: Could Hennebert’s Sign Be Evoked Despite Global Vestibular Impairment on Video Head Impulse Test? Considerations Upon Pathomechanisms Underlying Pressure-Induced Nystagmus due to Labyrinthine Fistula. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 634782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.A.; Gans, R.E.; Kastner, A.H.; Listert, J.J. Prevalence of vestibulopathy in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo patients with and without prior otologic history. Int. J. Audiol. 2005, 44, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.H.; Ban, J.H.; Lee, K.C.; Kim, S.M. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo secondary to inner ear disease. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 143, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.J.; Yoo, Y.T.; An, Y.H.; Yoo, J.C.; Kim, J.S.; Koo, J.W. Comorbid benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: An ominous sign for hearing recovery. Otol. Neurotol. 2012, 33, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, K.; Oda, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Nomura, T.; Ohbayashi, S.; Kitsuda, C. A clinical observation of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) after vestibular neuronitis (VN). Acta Otolaryngol. Suppl. 1993, 503, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandalà, M.; Santoro, G.P.; Awrey, J.; Nuti, D. Vestibular neuritis: Recurrence and incidence of secondary benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol. 2010, 130, 565–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, K.J.; Choi, H.; Choi, J.S.; Hwang, I.K. Recurrence of vertigo in patients with vestibular neuritis. Acta Otolaryngol. 2011, 131, 1172–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balatsouras, D.G.; Koukoutsis, G.; Ganelis, P.; Economou, N.C.; Moukos, A.; Aspris, A.; Katotomichelakis, M. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo secondary to vestibular neuritis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 271, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casani, A.P.; Cerchiai, N.; Navari, E. Paroxysmal positional vertigo despite complete vestibular impairment: The role of instrumental assessment. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2018, 38, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martellucci, S.; Malara, P.; Pagliuca, G.; Castellucci, A. Lindsay-Hemenway Syndrome Involving the Horizontal Semicircular Canal: Some Considerations Upon Residual Canal Afferents in BPPV Secondary to an Ipsilateral Acute Unilateral Vestibulopathy. Otol. Neurotol. 2025, 46, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Varela, A.; Rossi-Izquierdo, M.; Santos-Pérez, S. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo simultaneously affecting several canals: A 46-patient series. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 270, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Escamez, J.A.; Molina, M.I.; Gamiz, M.; Fernandez-Perez, A.J.; Gomez, M.; Palma, M.J.; Zapata, C. Multiple positional nystagmus suggests multiple canal involvement in benign paroxysmal vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol. 2005, 125, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
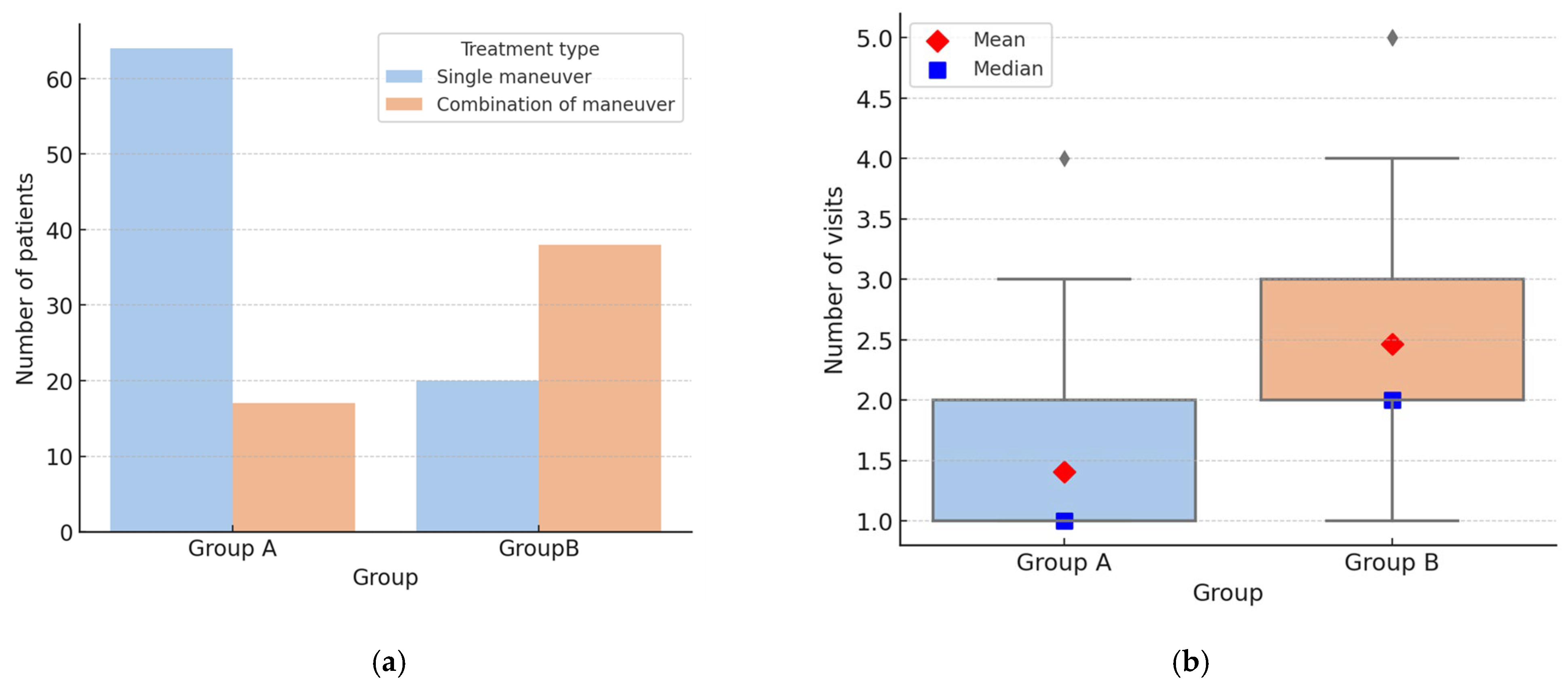
| Group A—Typical Forms |
| Posterior canal canalolithiasis (pc-BPPV) |
| Horizontal canal BPPV, geotropic form (hc-BPPV-geo) |
| Horizontal canal BPPV, apogeotropic form (hc-BPPV-apo) |
| Group B—Atypical Forms |
| Anterior canal canalolithiasis (ac-BPPV) |
| Posterior canal cupulolithiasis (pc-BPPV-cu) |
| Multi-canal lithiasis (mc-BPPV) |
| Apogeotropic posterior canal canalolithiasis (apo-pc-BPPV) |
| Posterior canal BPPV with “sitting-up vertigo” (pc-BPPV-suv): |
| Canalith Jam |
| BPPV with positional downbeat nystagmus (unidentified canal) (DBNy-BPPV-uc) |
| Form | Maneuver | Findings |
|---|---|---|
| PC canalolithiasis (pc-BPPV) | uHPT | UBNy + ipsi torsion (±parox) in extension; reversal on forward bending |
| uLARP/RALP | As above, limited to single plane (LARP/RALP) | |
| SSPT | Paroxysmal UBNy + ipsi torsion; reversal on sitting | |
| DHT | AS: paroxysmal UBNy + ipsi torsion; reversal on sitting | |
| HC-BPPV, geotropic (hc-BPPV-geo) | uHPT | Horizontal (±parox); ext → unaffected; flex → affected |
| uHRT | Horizontal geotropic | |
| SSPT | Horizontal (±parox); beats toward unaffected side | |
| sHYT | Paroxysmal horizontal geotropic (both sides); stronger on affected side | |
| HC-BPPV, apogeotropic (hc-BPPV-apo) | uHPT | Horizontal; ext → affected; flex → unaffected |
| uHRT | Horizontal apogeotropic | |
| SSPT | Horizontal (±parox); beats toward unaffected side | |
| sHYT | Horizontal apogeotropic (both sides; often non-paroxysmal); stronger on unaffected side |
| Form | Maneuver | Findings |
|---|---|---|
| AC canalolithiasis (ac-BPPV) | uHPT | DBNy; slight ipsi torsion ± |
| uLARP/RALP | Similar findings, often on BS | |
| DHT (AS/BS) + RP | DBNy + torsion → AS; ±parox; transforms into typical form (pc-BPPV) or shows ↓ VOR gain at vHIT | |
| PC cupulolithiasis (pc-BPPV-cu) | uHPT | Non-parox UBNy+ ipsi torsion in ext |
| uLARP/RALP | Similar findings on AS; may reverse on HS | |
| DHT (AS) | Non-parox UBNy + ipsi torsion | |
| DHT (HS) | DBNy + contra torsion; | |
| HHT (AS) | UBNy + ipsi torsion; > intense vs. DHT | |
| INVERSION TEST | Positive | |
| Multi-canal lithiasis (mc-BPPV) | uHPT/uLARP/RALP/uHRT | Ny compatible with canalolithiasis of >1 canal |
| DHT, sHYT | Same findings | |
| Apogeotropic PC canalolithiasis (apo-pc-BPPV) | uHPT | DBNy + contra torsion |
| uLARP/RALP | Similar findings, often on BS | |
| DHT (AS), RP | Non-parox DBNy; transforms into typical form (pc-BPPV), or shows ↓ VOR gain at vHIT | |
| PC lithiasis with sitting-up vertigo (pc-BPPV-suv): | uHPT/uLARP/RALP | Usually absent |
| Sitting up after DHT (AS) + RP | UBNy + ipsi torsion | |
| HHT | UBNy + ipsi torsion | |
| INVERSION TEST | Negative | |
| Canalith jam (CJ) | uHPT/uLARP/RALP/uHRT | Direction-fixed, omnipositional horiz ny |
| sHYT (BS) | Direction-fixed horiz ny; sometimes absent or weak reversion on one side; may convert → HC-BPPV; usually ↓ VOR gain at vHIT | |
| BPPV with downbeat ny, unspecified canal (DBNy-BPPV-uc) | uHPT/uLARP/RALP | DBNy ± ipsi torsion |
| DHT (BS), RP | Non-parox DBNy ± torsion; no conversion to typical form; non-diagnostic vHIT; resolution ≤ 4 wks |
| Group | Diagnosis | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group A | pc-BPPV | 57 | 41 |
| hc-BPPV-geo | 12 | 8.6 | |
| hc-BPPV-apo | 12 | 8.6 | |
| Group B | apo-pc-BPPV | 25 | 18 |
| ac-BPPV | 2 | 1.4 | |
| DBNy-BPPV-uc | 7 | 5 | |
| pc-BPPV-cu | 5 | 3.6 | |
| pc-BPPV-suv | 5 | 3.6 | |
| CJ | 2 | 1.4 | |
| mc-BPPV | 12 | 8.6 |
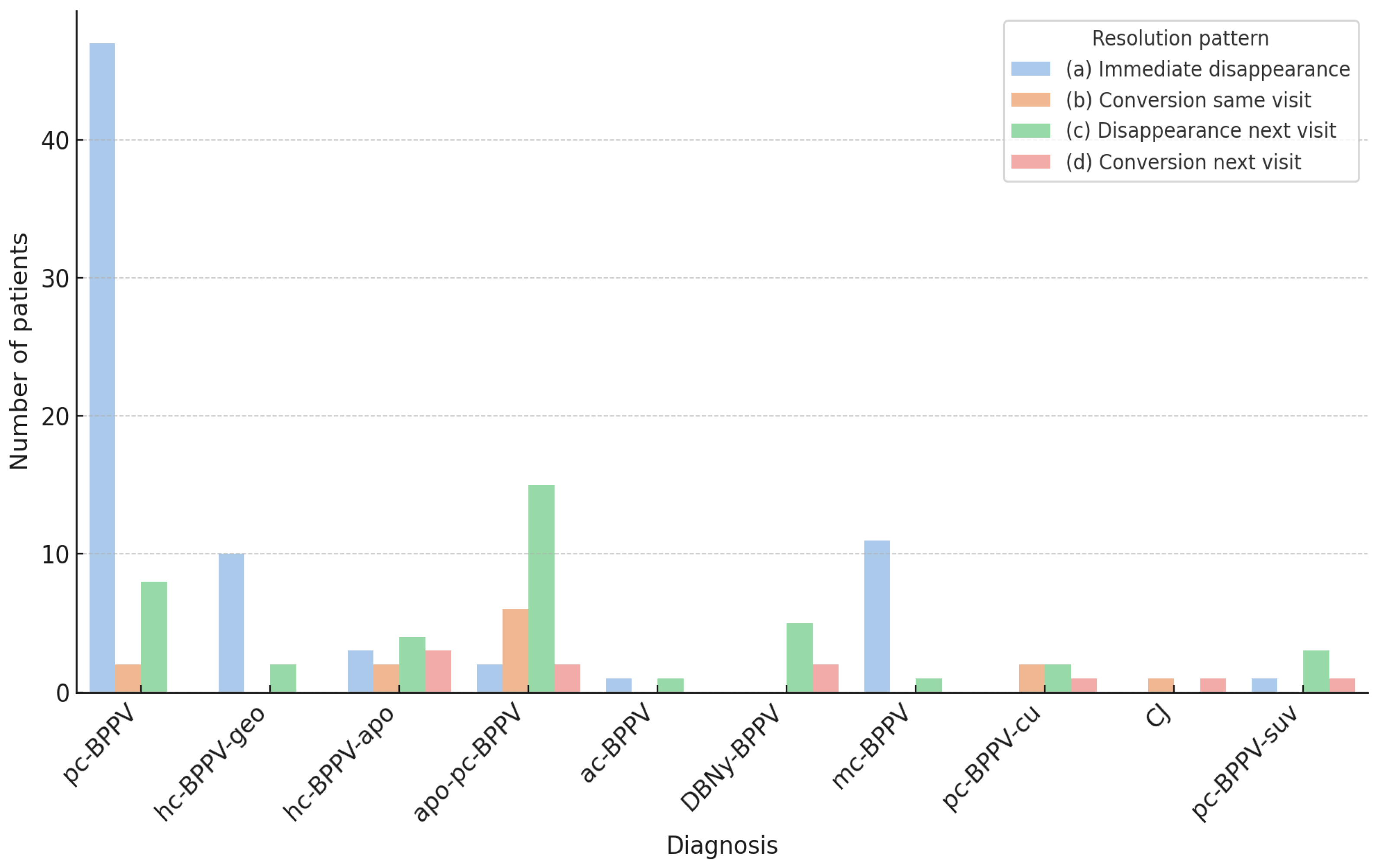
| Group | (a) Immediate Disappearance | (b) Conversion Same Visit | (c) Disappearance Next Visit | (d) Conversion Next Visit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 60 (74.1%) | 4 (4.9%) | 14 (17.3%) | 3 (3.7%) |
| B | 15 (25.9%) | 9 (15.5%) | 27 (46.6%) | 7 (12.1%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martellucci, S.; Castellucci, A.; Malara, P.; Califano, L.; Asprella Libonati, G. Revisiting BPPV: Incidence and Behavior of Atypical Variants. Audiol. Res. 2025, 15, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050140
Martellucci S, Castellucci A, Malara P, Califano L, Asprella Libonati G. Revisiting BPPV: Incidence and Behavior of Atypical Variants. Audiology Research. 2025; 15(5):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050140
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartellucci, Salvatore, Andrea Castellucci, Pasquale Malara, Luigi Califano, and Giacinto Asprella Libonati. 2025. "Revisiting BPPV: Incidence and Behavior of Atypical Variants" Audiology Research 15, no. 5: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050140
APA StyleMartellucci, S., Castellucci, A., Malara, P., Califano, L., & Asprella Libonati, G. (2025). Revisiting BPPV: Incidence and Behavior of Atypical Variants. Audiology Research, 15(5), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050140









