- Article
Pharmacological Treatments and Adverse Reactions Following Snake Antivenom Therapy: A Collaborative Study by Healthcare Professionals in the Southernmost Region of Thailand
- Panuwat Promsorn,
- Wittawat Chantkran and
- Janeyuth Chaisakul
- + 1 author
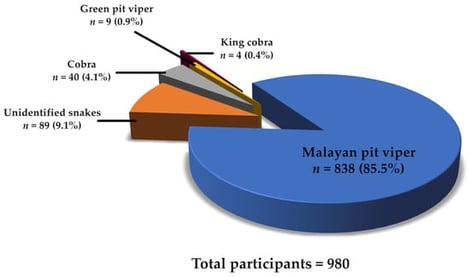
The administration of specific immunoglobulin G-based antivenoms is a key strategy for treating snakebite envenoming victims. However, serious adverse reactions, such as anaphylaxis or serum sickness, are frequently observed following such administration. In addition, inflammation associated with delayed wound healing considerably drives the irrational use of antibiotics or anti-inflammatory agents, which may be linked to adverse reactions following antivenom treatment. In this study, we evaluated the factors contributing to adverse effects following the administration of snake antivenom, especially pharmacological treatment and premedication intended to prevent adverse reactions. Our retrospective study was conducted by healthcare professionals in Narathiwat, the southernmost province in Thailand, and it involved 980 patients confirmed to have been snakebitten from 2016 to 2021. Of these cases, 513 were treated with antivenom. Prevalence rates and 95% confidence intervals were calculated, and univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to determine the correlation between adverse reactions and medications. Following antivenom administration, the majority of the patients exhibited no adverse reactions (86.7%). Nevertheless, skin rash, itching, wheezing, angioedema, chest tightness, and fever were observed in 13.3% of those receiving snake antivenom. After the administration of antivenom for Malayan pit viper bite, adverse reactions occurred in 11.7% of the sample, especially among referral patients (p < 0.001). Epinephrine and antihistamines were prescribed as prevention and treatment for hypersensitivity due to antivenom administration. Antibiotics, Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and acetaminophen were not associated with antivenom-induced adverse reactions. Interestingly, tramadol and antihistamines significantly reduced the occurrence of adverse reactions after antivenom administration (p < 0.05). Well-trained staff, close monitoring alongside resuscitation equipment and medications that can minimise the severity of anaphylactic reactions must be promptly available whenever antivenom is administered.
12 March 2026