Updates on the Proposed Botulinum Toxin A Mechanisms of Action in Orofacial Pain: A Review of Animal Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
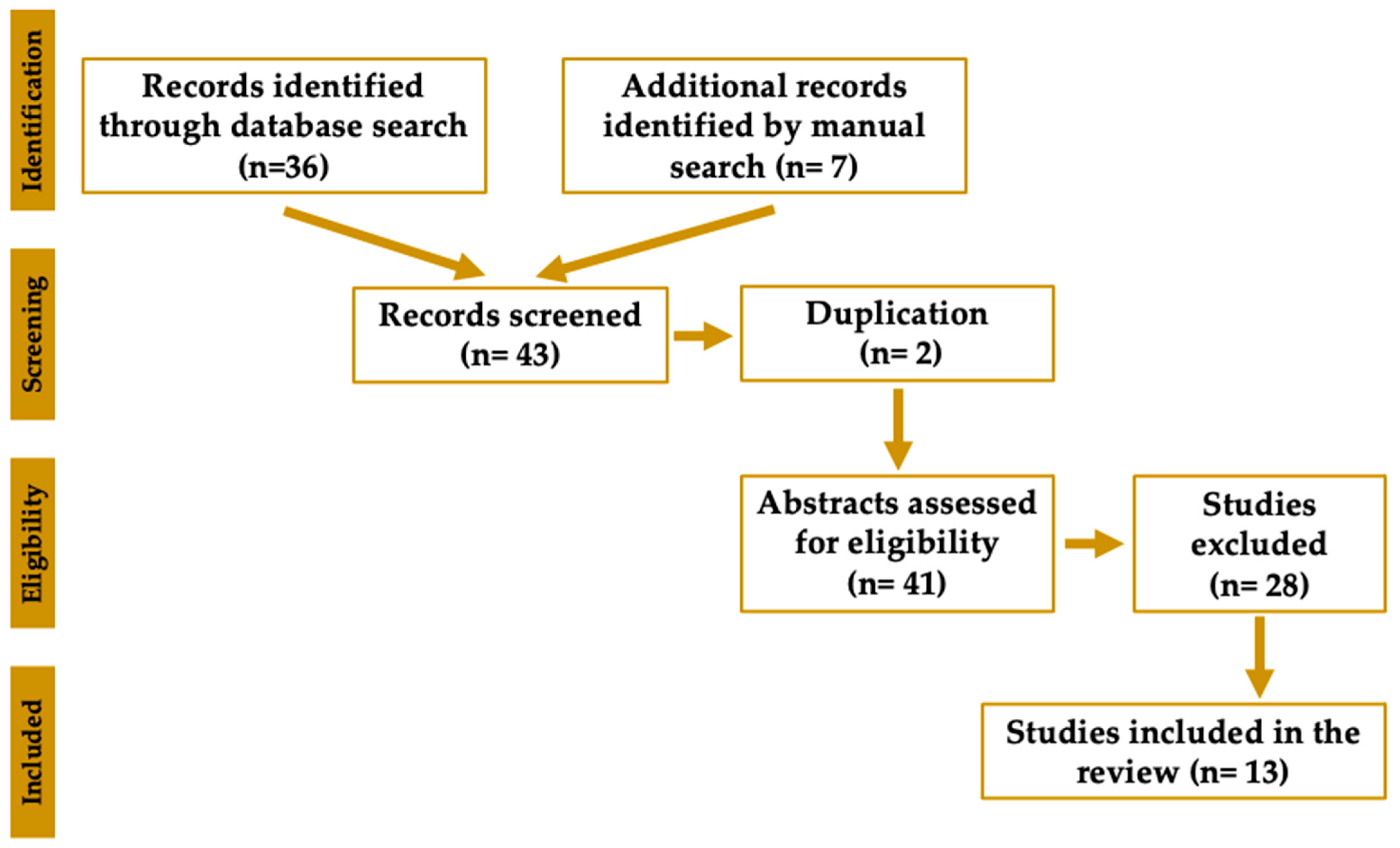
2. Methods
2.1. Study Selection
2.2. Risk of Bias Assessment
3. Proposed Mechanisms of BoNT/A in Orofacial Pain
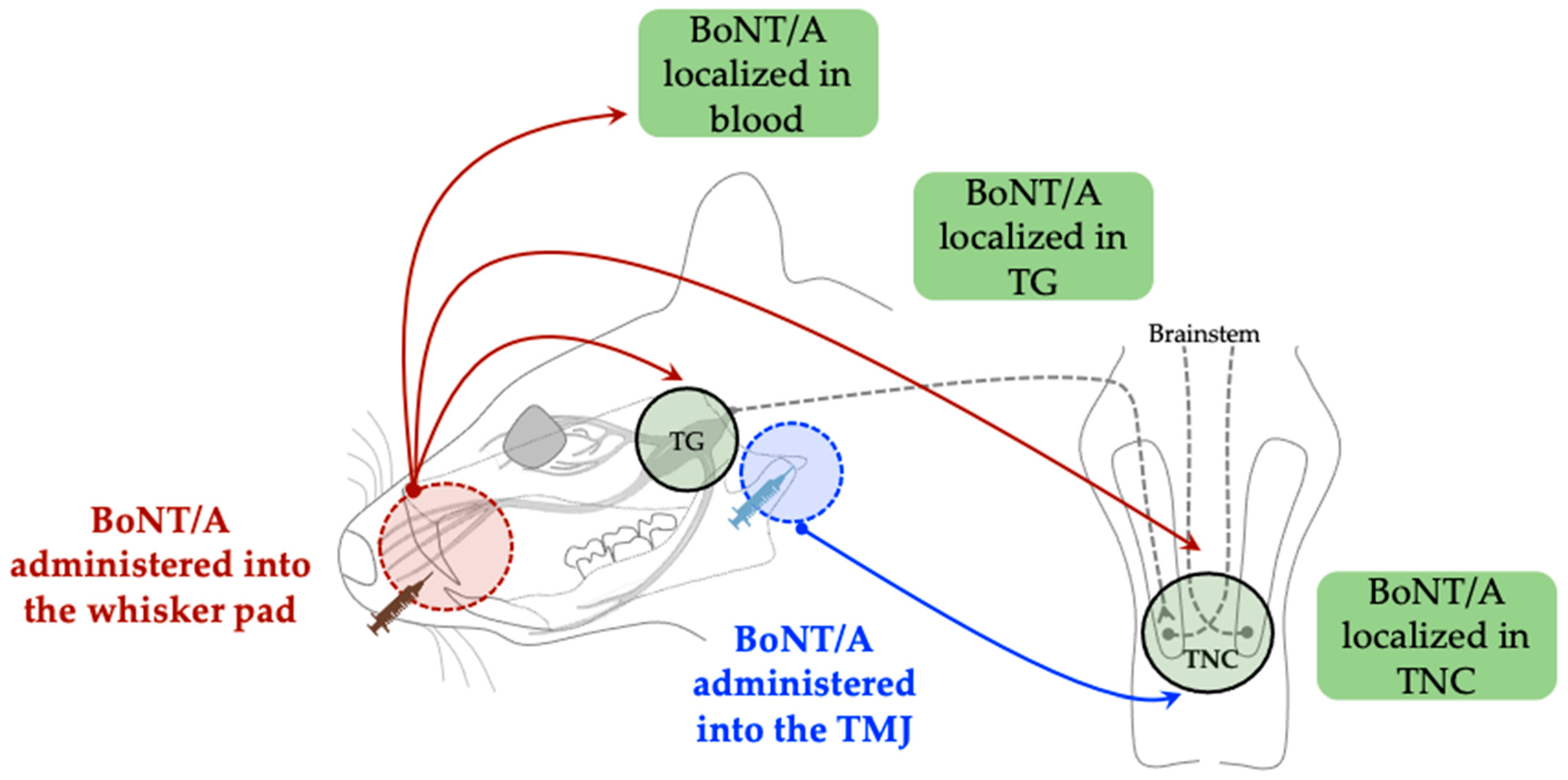
3.1. Retrograde Axonal, Transsynaptic, and Hematogenous Transport Mechanisms
3.2. Regulation of Ion Channels, and Neuronal and Glial Excitation
3.3. Inhibition of Neurotransmitter Release
3.4. Modulation of Neuroinflammation
3.5. Stimulation of the Opioid System
4. Orofacial Animal Pain Models Used to Assess BoNT/A Antinociception
5. Discussion
6. Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BoNT/A | Botulinum neurotoxin type A |
| TNC | Trigeminal nucleus caudalis |
| TG | Trigeminal ganglion/ganglia |
| cl-SNAP-25 | Cleaved synaptosomal-associated protein of 25 kDa |
| TMJ | Temporomandibular joint |
| TRPV1 | Transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 |
| TRPA1 | Transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 |
| TRPC1 | Transient receptor potential canonical 1 |
| WDR | Wide-dynamic range neurons |
| TLR2 | Toll-like receptor 2 |
| CatS | Cathepsin S |
| FKN | Fractalkine |
| P2X7 | P2X purinoceptor 7 |
| SNARE | Soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor |
| CGRP | Calcitonin gene-related peptide |
| NLRP3 | Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 |
| IL | Interleukin |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| HIF-1α | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α |
| LPA | Lysophosphatidic acid |
| N/OFQ | Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ |
| VGLUT2 | Glutamate-transporting protein |
References
- Orofacial Pain. Available online: https://www.iasp-pain.org/advocacy/global-year/orofacial-pain/ (accessed on 9 August 2025).
- Pigg, M.; Svensson, P.; List, T.; Baad-Hansen, L.; Alstergren, P.; May, A.; Ohrbach, R. International Classification of Orofacial Pain, 1st Edition (ICOP). Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 129–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Kuner, R.; Jensen, T.S. Neuropathic Pain: From Mechanisms to Treatment. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 259–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoigui, S. The Biochemical Origin of Pain: The Origin of All Pain Is Inflammation and the Inflammatory Response. Part 2 of 3—Inflammatory Profile of Pain Syndromes. Med. Hypotheses 2007, 69, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burning Mouth Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment|National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. Available online: https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/health-info/burning-mouth (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- TMD (Temporomandibular Disorders) Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment | National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. Available online: https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/health-info/tmd (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Greenbaum, T.; Emodi-Perlman, A. Headache and Orofacial Pain: A Traffic-Light Prognosis-Based Management Approach for the Musculoskeletal Practice. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1146427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.Z.; Bakri, M.M.; Yahya, F.; Ando, H.; Unno, S.; Kitagawa, J. The Role of Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) Channels in the Transduction of Dental Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oghli, I.; List, T.; Su, N.; Häggman-Henrikson, B. The Impact of Oro-Facial Pain Conditions on Oral Health-Related Quality of Life: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Rehabil. 2020, 47, 1052–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Matsuka, Y. Mechanism and Clinical Use of Botulinum Neurotoxin in Head and Facial Region. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2023, 67, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetto, O.; Pirazzini, M.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum Neurotoxins: Genetic, Structural and Mechanistic Insights. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunant, Y.; Israël, M. Neurotransmitter Release at Rapid Synapses. Biochimie 2000, 82, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, P.K.; Nigam, A. BOTULINUM TOXIN. Indian J. Dermatol. 2010, 55, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasetti-Escargueil, C.; Palea, S. Embracing the Versatility of Botulinum Neurotoxins in Conventional and New Therapeutic Applications. Toxins 2024, 16, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göbel, H.; Heinze, A.; Reichel, G.; Hefter, H.; Benecke, R.; Dysport Myofascial Pain Study Group. Myofascial pain study. Efficacy and Safety of a Single Botulinum Type A Toxin Complex Treatment (Dysport®) for the Relief of Upper Back Myofascial Pain Syndrome: Results from a Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Multicentre Study. PAIN 2006, 125, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicol, A.L.; Wu, I.I.; Ferrante, F.M. Botulinum Toxin Type A Injections for Cervical and Shoulder Girdle Myofascial Pain Using an Enriched Protocol Design. Anesth. Analg. 2014, 118, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, A.; Fontana, A.; Copetti, M.; Miscio, A.M.; d’Orsi, G. Real-World Insights into the Effectiveness and Tolerability of OnabotulinumtoxinA in Chronic Migraine: A Long-Term Evaluation of up to 11 Years. Toxins 2025, 17, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priori, A.; Berardelli, A.; Mercuri, B.; Manfredi, M. Physiological Effects Produced by Botulinum Toxin: Changes in Reciprocal Inhibition between Forearm Muscles. Brain 1995, 118, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Park, H.J. Botulinum Toxin for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain. Toxins 2017, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, Q.; Lian, Y.; Chen, Y. Botulinum Toxin Type A Reduces the Expression of Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 3 and Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid Type 4 in the Trigeminal Subnucleus Caudalis of a Rat Model of Trigeminal Neuralgia. NeuroReport 2019, 30, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Xie, N.; Lian, Y.; Xu, H.; Chen, C.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H. Central Antinociceptive Activity of Peripherally Applied Botulinum Toxin Type A in Lab Rat Model of Trigeminal Neuralgia. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piovesan, E.J.; Oshinsky, M.; Silberstein, S.; Kowacs, P.A.; Novak, E.M.; Werneck, L.C. Botulinum Neurotoxin Type-A When Utilized in Animals with Trigeminal Sensitization Induced a Antinociceptive Effect. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2016, 74, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noma, N.; Watanabe, K.; Sato, Y.; Imamura, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ito, R.; Maruno, M.; Shimizu, K.; Iwata, K. Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A Alleviates Mechanical Hypersensitivity Associated with Infraorbital Nerve Constriction Injury in Rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 637, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, Y.; Matsuka, Y.; Spigelman, I.; Ishihara, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Sonoyama, W.; Kuboki, T.; Oguma, K. Botulinum Toxin Type a (150 kDa) Decreases Exaggerated Neurotransmitter Release from Trigeminal Ganglion Neurons and Relieves Neuropathy Behaviors Induced by Infraorbital Nerve Constriction. Neuroscience 2009, 159, 1422–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović, B.; Matak, I.; Bach-Rojecky, L.; Lacković, Z. Central Action of Peripherally Applied Botulinum Toxin Type A on Pain and Dural Protein Extravasation in Rat Model of Trigeminal Neuropathy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drinovac Vlah, V.; Filipović, B.; Bach-Rojecky, L.; Lacković, Z. Role of Central versus Peripheral Opioid System in Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Botulinum Toxin Type A in Trigeminal Region. Eur. J. Pain 2018, 22, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemanić, D.; Mustapić, M.; Matak, I.; Bach-Rojecky, L. Botulinum Toxin Type a Antinociceptive Activity in Trigeminal Regions Involves Central Transcytosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 963, 176279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Lora, V.R.M.; Dugonjić Okroša, A.; Matak, I.; Del Bel Cury, A.A.; Kalinichev, M.; Lacković, Z. Antinociceptive Actions of Botulinum Toxin A1 on Immunogenic Hypersensitivity in Temporomandibular Joint of Rats. Toxins 2022, 14, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskitho, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Raman, S.; Kano, F.; Yan, H.; Raju, R.; Afroz, S.; Morita, T.; Ikutame, D.; Okura, K.; et al. Peripherally Administered Botulinum Toxin Type A Localizes Bilaterally in Trigeminal Ganglia of Animal Model. Toxins 2021, 13, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.A.; Nelson, M.; Wickware, C.; Choi, S.; Moon, G.; Xiong, E.; Orta, L.; Brideau-Andersen, A.; Brin, M.F.; Broide, R.S.; et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA Effects on Trigeminal Nociceptors. Cephalalgia 2023, 43, 3331024221141683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dux, M.; Rosta, J.; Messlinger, K. TRP Channels in the Focus of Trigeminal Nociceptor Sensitization Contributing to Primary Headaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Strassman, A.M.; Novack, V.; Brin, M.F.; Burstein, R. Extracranial Injections of Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A Inhibit Intracranial Meningeal Nociceptors’ Responses to Stimulation of TRPV1 and TRPA1 Channels: Are We Getting Closer to Solving This Puzzle? Cephalalgia 2016, 36, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Son, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shannonhouse, J.; Gomez, R.; Han, D.; Park, J.T.; Kim, S.T.; Amarista, F.; Perez, D.; et al. BoNT Injection into Temporomandibular Joint Alleviates TMJ Pain in Forced Mouth Opening Mouse Model. J. Neurosci. 2025, 45, e2035242025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo-Carrillo, A.; Strassman, A.M.; Malcolm, K.-K.J.; Adams, A.M.; Dabruzzo, B.; Briode, R.S.; Brin, M.F.; Burstein, R. Exploring the Effects of Extracranial Injections of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Activation and Sensitization of Central Trigeminovascular Neurons by Cortical Spreading Depression in Male and Female Rats. Cephalalgia 2024, 44, 3331024241278919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-J.; Niu, J.-Q.; Chen, Y.-T.; Deng, W.-J.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Liu, J.; Luo, W.-F.; Liu, T. Unilateral Facial Injection of Botulinum Neurotoxin A Attenuates Bilateral Trigeminal Neuropathic Pain and Anxiety-like Behaviors through Inhibition of TLR2-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Mice. J. Headache Pain 2021, 22, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuel Muñoz-Lora, V.R.; Abdalla, H.B.; Del Bel Cury, A.A.; Clemente-Napimoga, J.T. Modulatory Effect of Botulinum Toxin Type A on the Microglial P2X7/CatS/FKN Activated-Pathway in Antigen-Induced Arthritis of the Temporomandibular Joint of Rats. Toxicon 2020, 187, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummel, A. The Long Journey of Botulinum Neurotoxins into the Synapse. Toxicon 2015, 107, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reducha, P.V.; Bömers, J.P.; Edvinsson, L.; Haanes, K.A. The Impact of the Migraine Treatment onabotulinumtoxinA on Inflammatory and Pain Responses: Insights from an Animal Model. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2024, 64, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhu, X.; Xia, L.; Shang, J.; Wei, M.; Han, Q. Effects of Botulinum Toxin Type a on Nucleotide Binding Oligomerization Domain-like Receptor 3 Inflammasome in Trigeminal Ganglion of a Rat Migraine Model. Cytokine 2025, 190, 156934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Torres, R. Role of Interleukin-1β during Pain and Inflammation. Brain Res. Rev. 2009, 60, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinon, F.; Burns, K.; Tschopp, J. The Inflammasome: A Molecular Platform Triggering Activation of Inflammatory Caspases and Processing of proIL-β. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-K.; Son, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.-M.; Ju, J.-S.; Ahn, D.-K. BTX-A Inhibited Trigeminal Neuralgia by Blocking the NLRP3 Pathway in Rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2025, 225, 111344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Son, J.Y.; Ju, J.S.; Kim, Y.M.; Ahn, D.K. Cellular Mechanisms Mediating the Antinociceptive Effect of Botulinum Toxin A in a Rodent Model of Trigeminal Irritation by a Foreign Body. J. Pain 2022, 23, 2070–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Wen, J.; Guo, R.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, H.; Gao, M.; Wang, H.; Lai, W.; Long, H. Botulinum Toxin A Alleviates Orofacial Nociception Induced by Orthodontic Tooth Movement through Nociceptin/Orphanin-FQ Pathway in Rats. Arch. Oral Biol. 2020, 117, 104817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R. Therapeutic Use of Botulinum Toxin in Pain Treatment. Neuronal Signal 2018, 2, NS20180058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabillar, J.; Perdana, L.P.; Raman, S.; Dalanon, J.; Oshima, M.; Baba, O.; Matsuka, Y. Bilateral Transport of Neuronal Tracer after Unilateral Administration: Investigation of Potential Peripheral Mechanism. Neurosci. Lett. 2025, 854, 138219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skerratt, S.E.; West, C.W. Ion Channel Therapeutics for Pain. Channels 2015, 9, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yao, J.; Rong, M. Editorial: Role of Ion Channels in Pain. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 884665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, C.R.; Andriessen, A.S.; Chen, G.; Wang, K.; Jiang, C.; Maixner, W.; Ji, R.-R. Central Nervous System Targets: Glial Cell Mechanisms in Chronic Pain. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 846–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, K.R. Evidence for Antinociceptive Activity of Botulinum Toxin Type A in Pain Management. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2003, 43 (Suppl. S1), 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omoto, K.; Maruhama, K.; Terayama, R.; Yamamoto, Y.; Matsushita, O.; Sugimoto, T.; Oguma, K.; Matsuka, Y. Cross-Excitation in Peripheral Sensory Ganglia Associated with Pain Transmission. Toxins 2015, 7, 2906–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumada, A.; Matsuka, Y.; Spigelman, I.; Maruhama, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Neubert, J.K.; Nolan, T.A.; Watanabe, K.; Maekawa, K.; Kamioka, H.; et al. Intradermal Injection of Botulinum Toxin Type A Alleviates Infraorbital Nerve Constriction-Induced Thermal Hyperalgesia in an Operant Assay. J. Oral Rehabil. 2012, 39, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinovac, V.; Bach-Rojecky, L.; Matak, I.; Lacković, Z. Involvement of μ-Opioid Receptors in Antinociceptive Action of Botulinum Toxin Type A. Neuropharmacology 2013, 70, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinovac, V.; Bach-Rojecky, L.; Lacković, Z. Association of Antinociceptive Action of Botulinum Toxin Type A with GABA-A Receptor. J. Neural Transm. 2014, 121, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
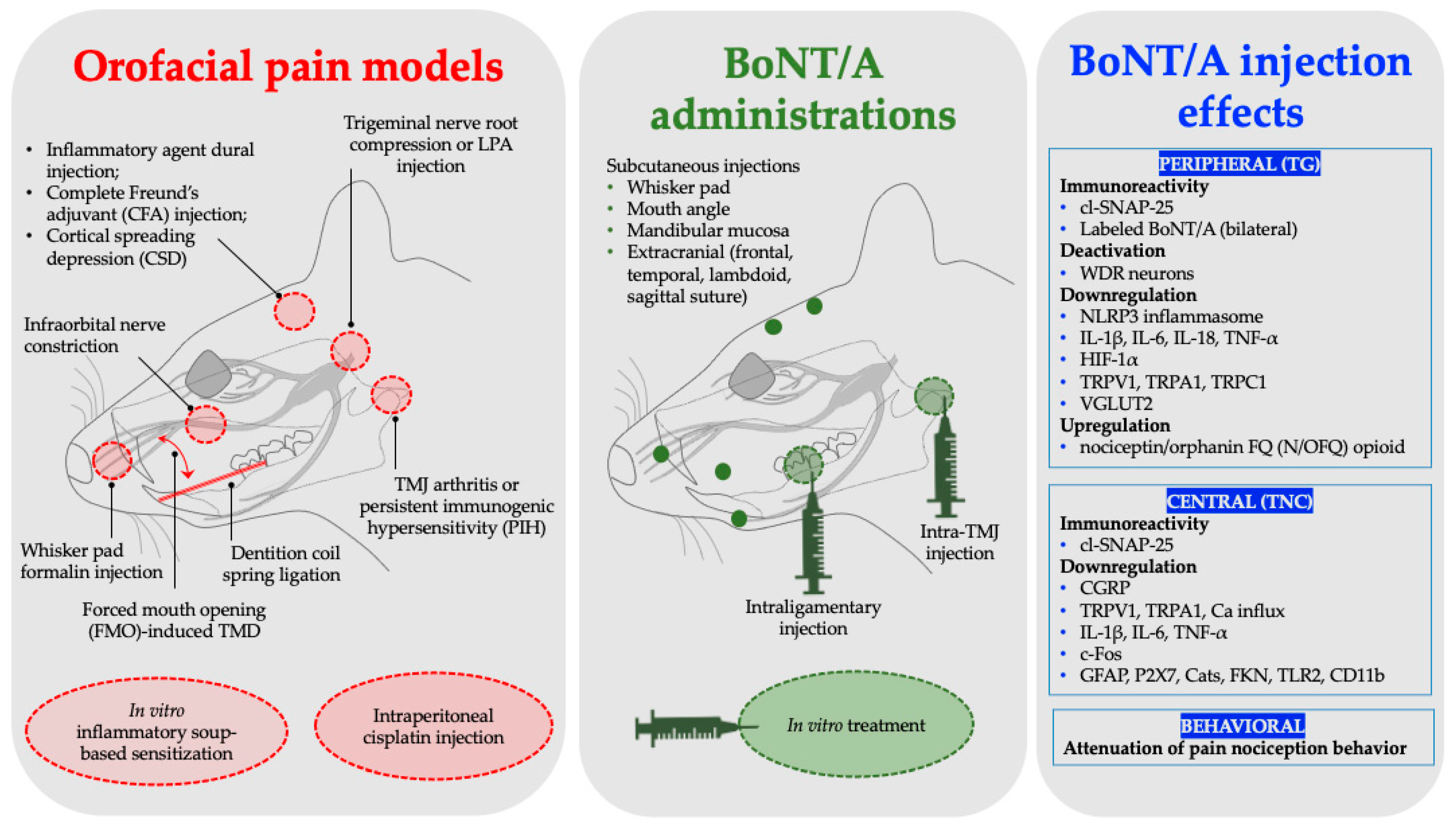
| Orofacial Pain Models | Animal Species | BoNT/A Administration | BoNT/A Dosage Administered | BoNT/A Effect Key Findings | Representative Studies | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Migraine | Inflammatory agent dural injection | Sprague Dawley (SD) rats (male) | Subcutaneous (frontal and temporal) | 10 U/Kg | Synthesis inhibition of NLRP3 and IL-1β | Shen et al., 2025 [39] |
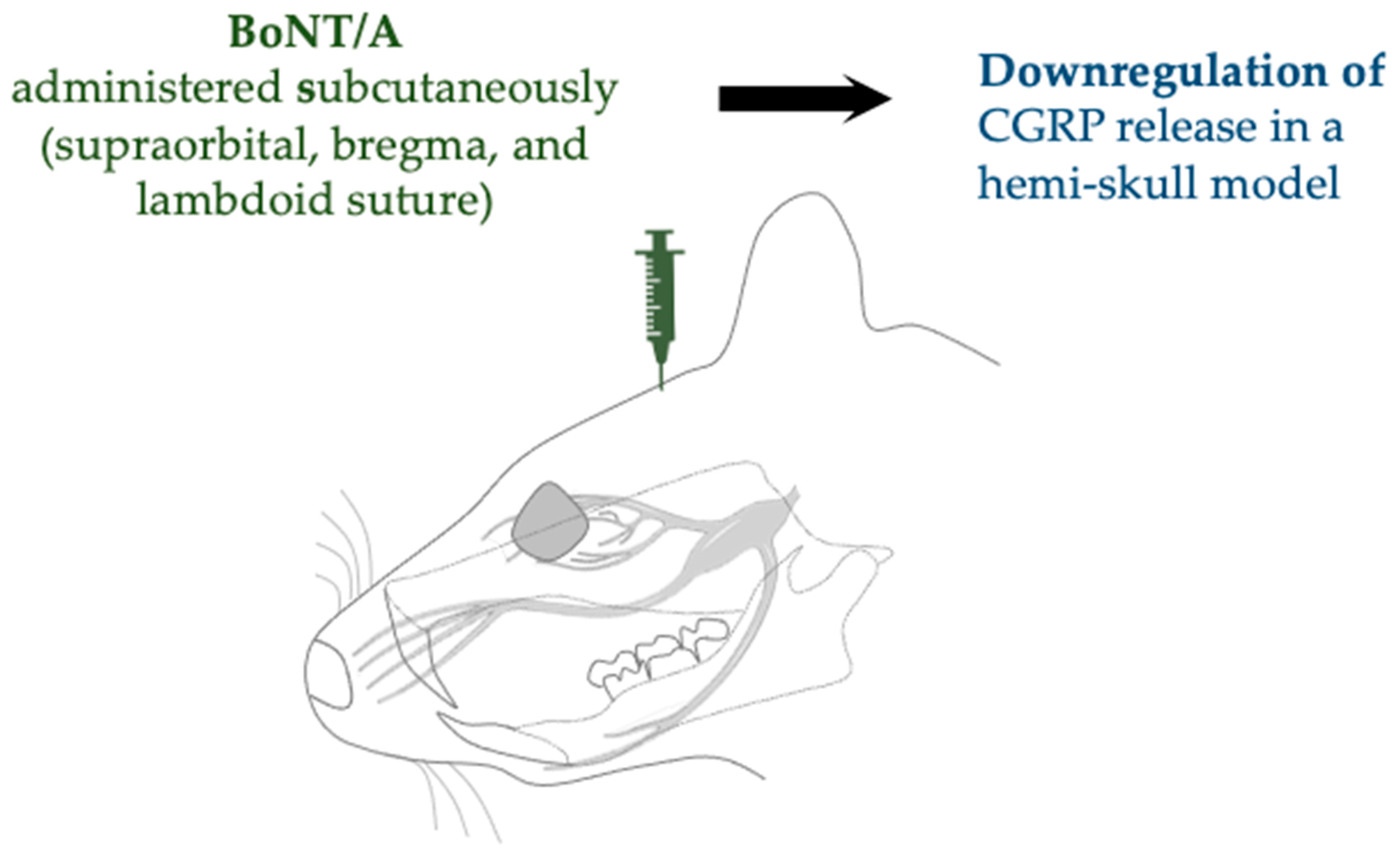
| Complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA) model of inflammation | SD rats (male) | Subcutaneous (supraorbital, bregma, and lambdoid suture) | 10 µL of 125 U/mL | Increased cleavage of SNAP-25 and downregulated expression of CGRP | Reducha et al., 2024 [38] | |
| Cortical spreading depression (CSD) | SD rats (male and female) | Extracranial injections (lambdoid and sagittal suture) | 5 U/5 μL | Inhibition of activation and sensitization of WDR neurons | Melo-Carrillo et al., 2023 [34] | |
| Inflammatory pain | Formalin injection | Wistar rat (male) | Subcutaneous (whisker pad) | 7 U/Kg | Peripheral and central immunoreactivity of cl-SNAP-25 | Nemanić et al., 2024 [27] |
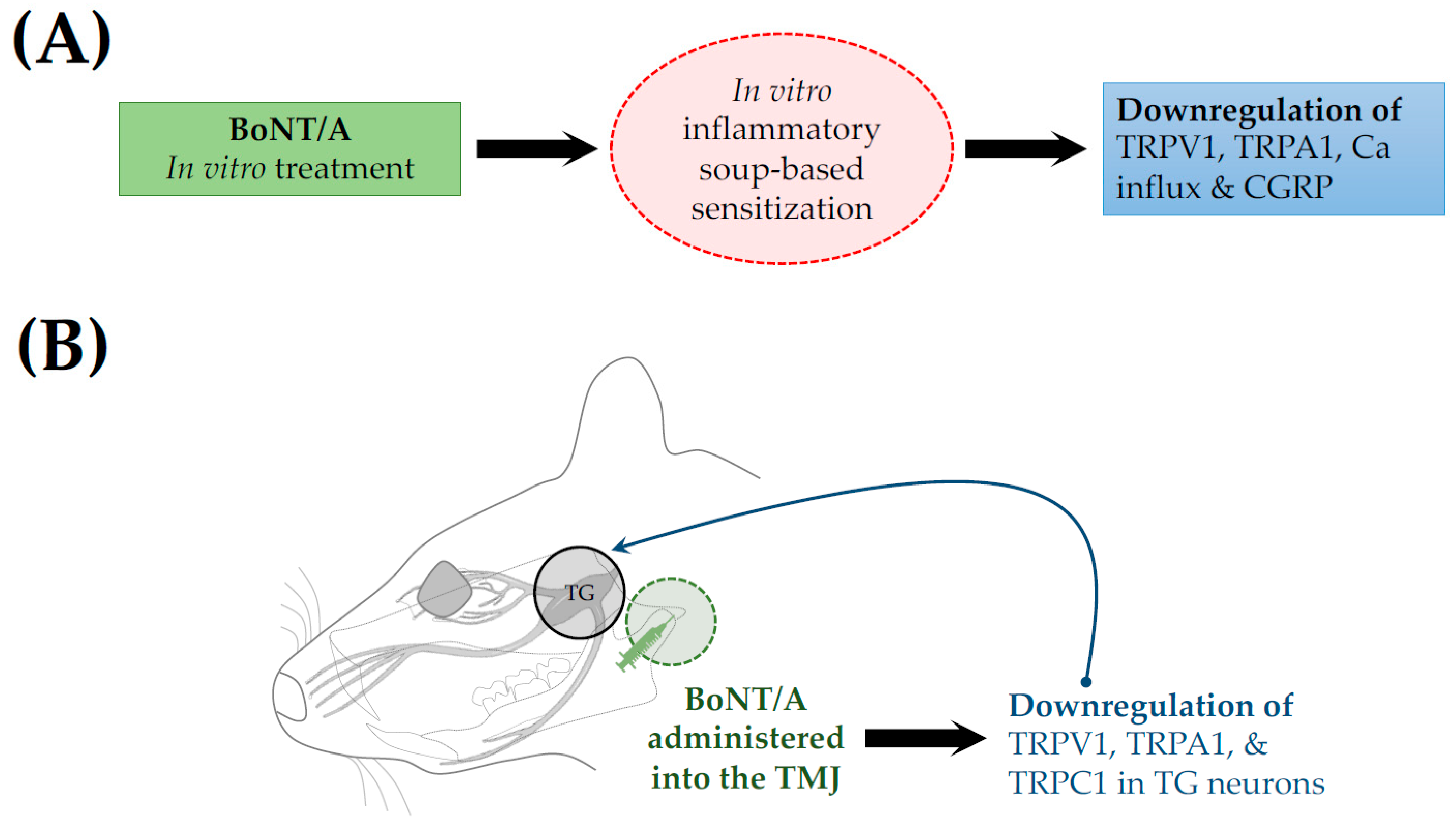
| Inflammatory soup-based sensitization model (in vitro) | C57BL/6J mice (males and females) | In vitro treatment | 2.75 pM [50 U/mL; 2.5 ng/mL] | Reduction in TRPV1 and TRPA1 surface expression, decreased calcium influx, and inhibition of CGRP release | Moore et al., 2023 [30] | |
| Temporomandibular joint pain | Persistent immunogenic hypersensitivity (PIH) | SD rats (male) | TMJ injection | 7 & 14 U/Kg | cl-SNAP-25 immunoreactivity and neuronal and glial deactivation, inhibition of CGRP release | Muñoz-Lora et al., 2022 [28] |
| Arthritis (Antigen-induced) | Wistar rats (male) | TMJ injection | 7 U/Kg | Downregulated expression of P2X7, CatS, FKN, TNF-α, and IL-1β | Muñoz-Lora et al., 2020 [36] | |
| Forced mouth opening (FMO)-induced TMD | C57BL/6 & Pirt-GCaMP3 mice (male) | TMJ injection | 20 µL [0.5 or 1 U] | Down regulated expression of vesicular glutamate transporter 2 (VGLUT2) protein, and TRPV1, TRPA1, and TRPC1 | Kim et al., 2025 [33] | |
| Trigeminal neuralgia | LPA trigeminal nerve root injection | SD rats (male) | Subcutaneous (whisker pad) | 3 U/Kg | Downregulated expression of NLRP3, IL-1β, IL-18, and TNF-α | Park et al., 2025 [42] |
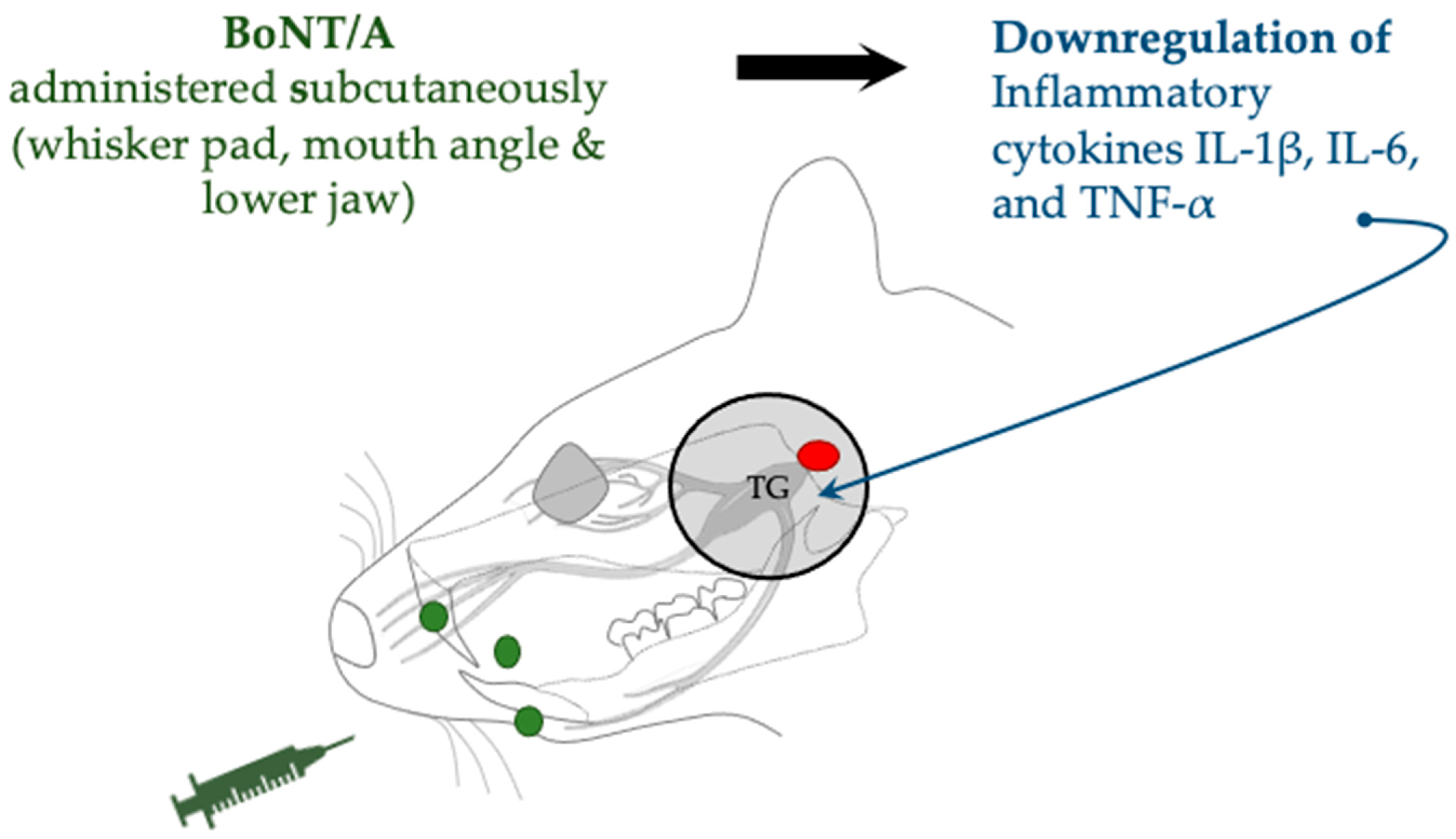
| Trigeminal nerve root compression | SD rats (male) | Subcutaneous (whisker pad, mouth angle, and lower jaw) | 1 or 3 U/kg | Expression downregulation of HIF-1α and IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α | Cho et al., 2022 [43] | |
| Distal infraorbital nerve-chronic constriction injury (dION-CCI) | C57BL/6 mice (male) | Subcutaneous (whisker pad) | 0.18 U | Downregulated expression of TLR2, CD11b, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α | Chen et al., 2021 [35] | |
| Infraorbital nerve constriction (IONC) | SD rats (male) | Subcutaneous (whisker pad) | 10 MLD in100 µL saline | BoNT/A in the bilateral TG | Waskitho et al., 2021 [29] | |
| Chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain | Cisplatin injection | SD rats (male) | Subcutaneous (whisker pad) | 10 MLD in100 µL saline | Behavioral pain attenuation | |
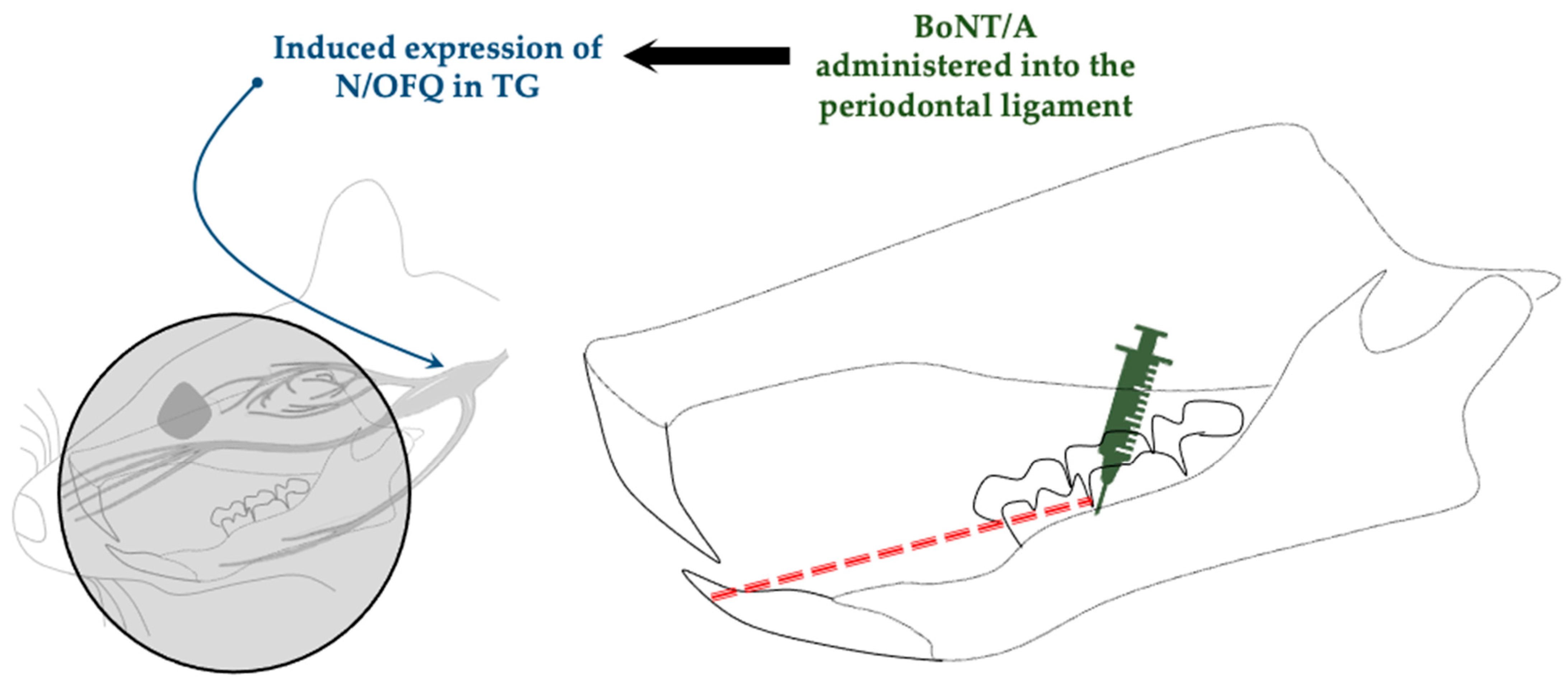
| Orthodontic movement- induced pain model | Dentition coil spring ligation | SD rats (male) | Intraligamentary injection (periodontal ligament) | 1 U/6 µL | Promotes expression of nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) | Lyu et al., 2020 [44] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fabillar Jr, J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Koike, K.; Ikutame, D.; Matsuka, Y. Updates on the Proposed Botulinum Toxin A Mechanisms of Action in Orofacial Pain: A Review of Animal Studies. Toxins 2025, 17, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120567
Fabillar Jr J, Yamamoto Y, Koike K, Ikutame D, Matsuka Y. Updates on the Proposed Botulinum Toxin A Mechanisms of Action in Orofacial Pain: A Review of Animal Studies. Toxins. 2025; 17(12):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120567
Chicago/Turabian StyleFabillar Jr, Jaime, Yumiko Yamamoto, Kazuyuki Koike, Daisuke Ikutame, and Yoshizo Matsuka. 2025. "Updates on the Proposed Botulinum Toxin A Mechanisms of Action in Orofacial Pain: A Review of Animal Studies" Toxins 17, no. 12: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120567
APA StyleFabillar Jr, J., Yamamoto, Y., Koike, K., Ikutame, D., & Matsuka, Y. (2025). Updates on the Proposed Botulinum Toxin A Mechanisms of Action in Orofacial Pain: A Review of Animal Studies. Toxins, 17(12), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120567






