Ai-Assisted Discovery of a Direct Physical Interaction Between a Venom Serpin from the Parasitoid Wasp Liragathis javana and a Host Serine Carboxypeptidase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Transcriptomic Profiling of L. javana Venom Transcripts
2.1.1. Serpin Transcript DN708_c0_g2
2.1.2. Other Venom-Related or Highly Expressed Transcripts
2.2. Characterization of the Identified LjSPI-1
2.2.1. Sequence Characteristics of LjSPI-1
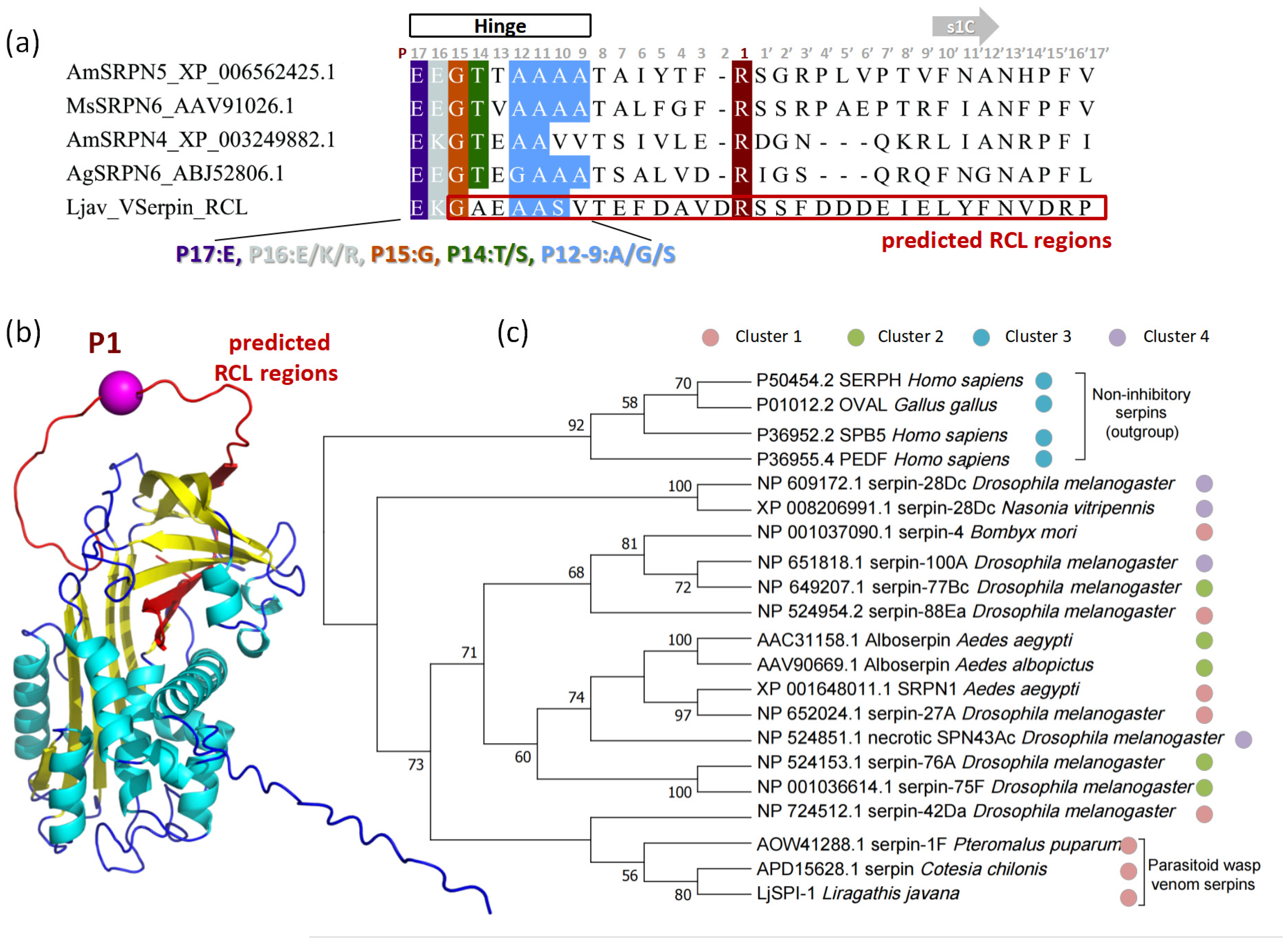
2.2.2. Structural Features and Conserved Motifs
2.2.3. Phylogenetic and Embedding-Based Placement of LjSPI-1
2.3. AI-Driven Prediction of a Novel Host Interaction Partner
2.3.1. Candidate Target Identification by D-Script and Prioritization
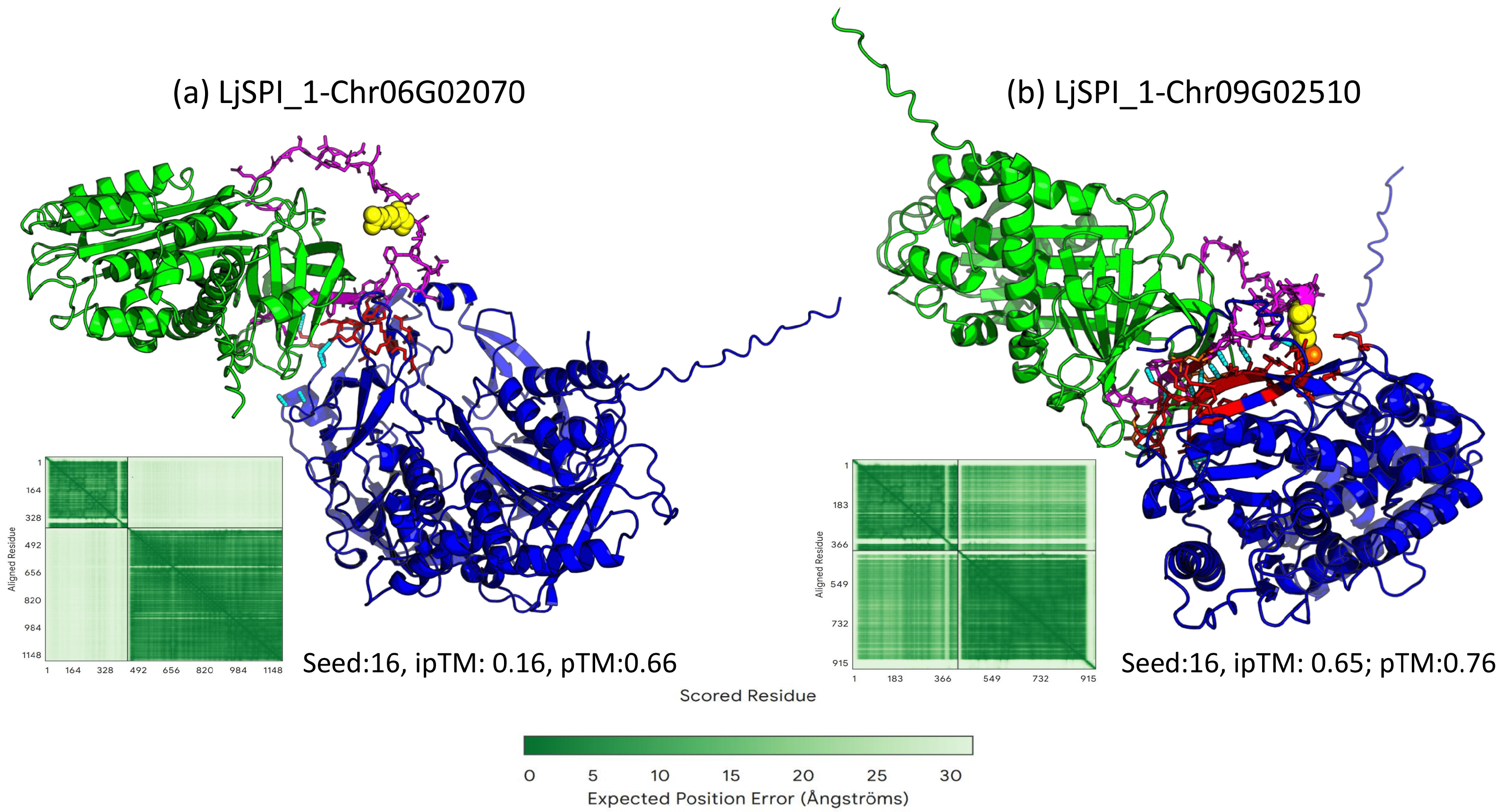
2.3.2. Structural Modeling by Alphafold3 and Binding Mode Analysis
2.4. Experimental Validation of a Physical Interaction Between LjSPI-1 and Chr09G02510
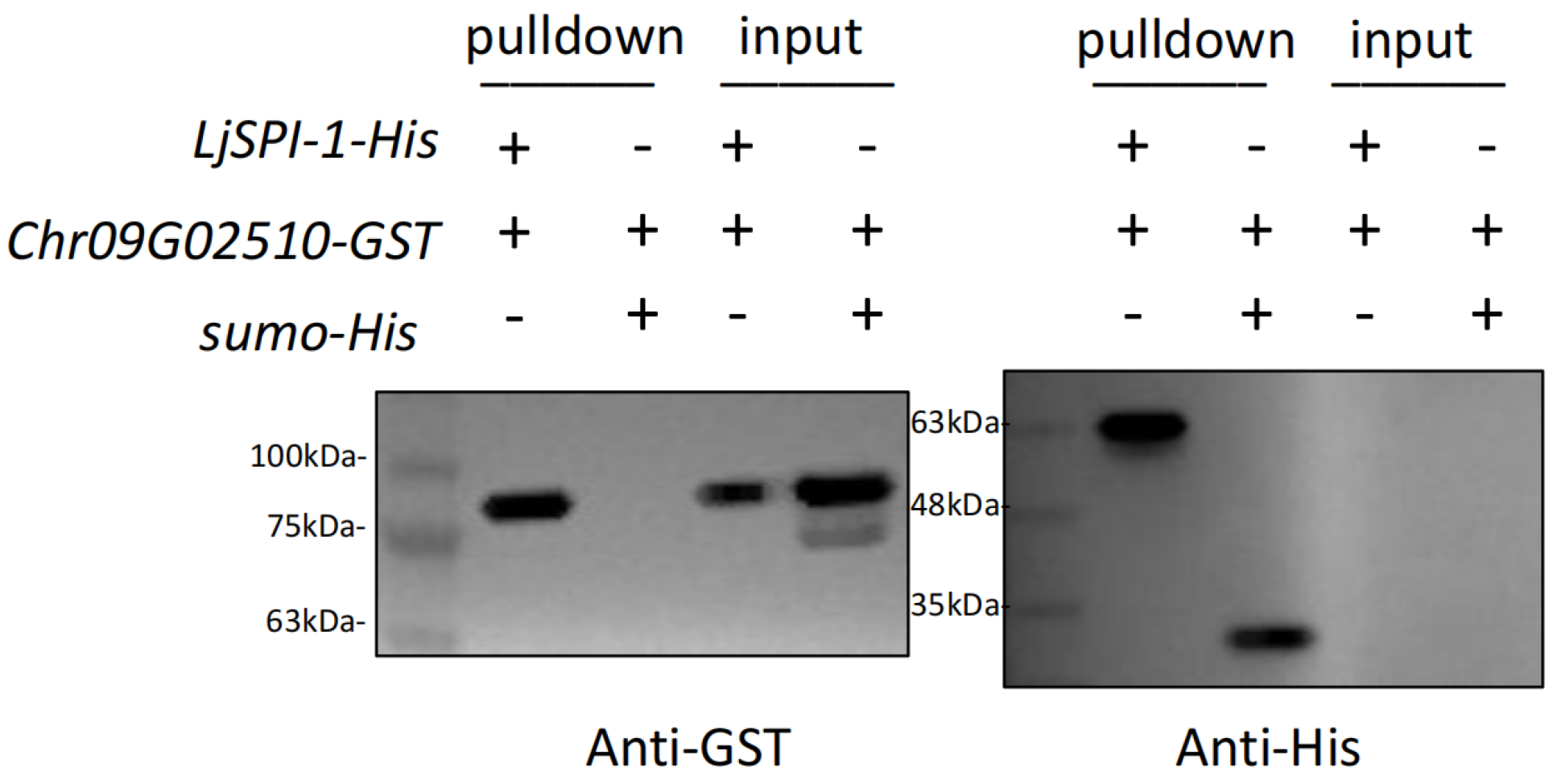
2.4.1. Pull-Down Assay Demonstrates Direct In Vitro Binding
2.4.2. Yeast Two-Hybrid Assay Confirm In Vivo Interaction
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Insect Collection and Rearing
5.2. Transcriptome and Sequence Analysis
5.3. Sequence Validation and Characterization
5.4. Structural Modeling and Phylogenetic Analysis
5.5. Interaction Protein Prediction and Structural Modeling
5.6. Embedding-Based Serpin Clustering Analysis Using ProtT5
5.7. Protein Expression, Purification, and Pull-Down Assay
5.8. Yeast Two-Hybrid Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goergen, G.; Neuenschwander, P.; Coyne, D. Conserving and exploiting biodiversity in crop cultivation in sub-Saharan Africa. In Critical Issues in Plant Health; Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 75–94. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, H. Bionomics, host plant resistance, and management of the legume pod borer, Maruca vitrata—A review. Crop Prot. 1998, 17, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Tamo, M.; Malini, P. Emergence of Maruca vitrata as a major pest of food legumes and evolution of management practices in Asia and Africa. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2021, 66, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, N.M.; Huesing, J.E.; Dabire-Binso, C.L.; Tamo, M.; Pittendrigh, B.R.; Murdock, L.L. The legume pod borer, Maruca vitrata Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Crambidae), an important insect pest of cowpea: A review emphasizing West Africa. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2019, 39, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Tamò, M.; Subramanian, S. The case for integrated pest management in Africa: Transition from a pesticide-based approach. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2022, 54, 100970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togola, A.; Datinon, B.; Laouali, A.; Traore, F.; Agboton, C.; Ojo, J.A.; Ongom, P.O.; Pittendrigh, B.R.; Boukar, O.; Tamò, M. Recent advances in cowpea IPM in West Africa. Front. Agron. 2023, 5, 1220387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, P.; Huang, C.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, J. A newly recorded species in China’s mainland, Liragathis javana, a parasitic wasp of the imoortant cowpea pest, Maruca vitrata (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Plant Prot. 2025, 51, 208–214+224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, S.; Rivers, D.B. Venom proteins from endoparasitoid wasps and their role in host-parasite interactions. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2011, 56, 313–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirié, M.; Colinet, D.; Gatti, J.-L. Insights into function and evolution of parasitoid wasp venoms. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2014, 6, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, R.H.; Zhang, Q.; McGowan, S.; Buckle, A.M.; Silverman, G.A.; Wong, W.; Rosado, C.J.; Langendorf, C.G.; Pike, R.N.; Bird, P.I.; et al. An overview of the serpin superfamily. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meekins, D.A.; Kanost, M.R.; Michel, K. Serpins in arthropod biology. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 62, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanrattana, W.; Maas, C.; de Maat, S. SERPINs-From Trap to Treatment. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yuan, R.; Gu, Q.; Wu, X.; Gu, L.; Ye, X.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X. Parasitoid serpins evolve novel functions to manipulate host homeostasis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2023, 40, msad269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.C.; Fang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, S.; Yang, L.; Wang, F.; An, C.J.; Werren, J.H.; Ye, G.Y. A venom serpin splicing isoform of the endoparasitoid wasp Pteromalus puparum suppresses host prophenoloxidase cascade by forming complexes with host hemolymph proteinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 1038–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Fang, Q.; Song, J.; Yang, L.; Xiao, S.; Wang, J.; Ye, G. A serpin gene from a parasitoid wasp disrupts host immunity and exhibits adaptive alternative splicing. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, R.; Lin, Z.; Shi, S.; Chen, C.; Jiang, H.; Zou, Z.; Lu, Z. Two venom serpins from the parasitoid wasp Microplitis mediator inhibit the host prophenoloxidase activation and antimicrobial peptide synthesis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 152, 103895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, P.C.; Carrell, R.W.; Stone, S.R. Effects of mutations in the hinge region of serpins. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 7650–7657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, J.A.; Read, R.J.; Carrell, R.W. Structure of a serpin-protease complex shows inhibition by deformation. Nature 2000, 407, 923–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gettins, P.G. Serpin structure, mechanism, and function. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4751–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huntington, J.A. Serpin structure, function and dysfunction. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, G.A.; Whisstock, J.C.; Bottomley, S.P.; Huntington, J.A.; Kaiserman, D.; Luke, C.J.; Pak, S.C.; Reichhart, J.M.; Bird, P.I. Serpins flex their muscle: I. Putting the clamps on proteolysis in diverse biological systems. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 24299–24305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Nagata, K. Biology of Hsp47 (Serpin H1), a collagen-specific molecular chaperone. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 62, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, C.; Gebauer, J.M.; Brunstein, E.; Rosenbaum, S.; Zaucke, F.; Drogemuller, C.; Leeb, T.; Baumann, U. Molecular basis for the action of the collagen-specific chaperone Hsp47/SERPINH1 and its structure-specific client recognition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13243–13247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richer, M.J.; Keays, C.A.; Waterhouse, J.; Minhas, J.; Hashimoto, C.; Jean, F. The Spn4 gene of Drosophila encodes a potent furin-directed secretory pathway serpin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10560–10565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oley, M.; Letzel, M.C.; Ragg, H. Inhibition of furin by serpin Spn4A from Drosophila melanogaster. Febs. Lett. 2004, 577, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sledzieski, S.; Singh, R.; Cowen, L.; Berger, B. D-SCRIPT translates genome to phenome with sequence-based, structure-aware, genome-scale predictions of protein-protein interactions. Cell Syst. 2021, 12, 969–982.e966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marijanovic, E.M.; Fodor, J.; Riley, B.T.; Porebski, B.T.; Costa, M.G.S.; Kass, I.; Hoke, D.E.; McGowan, S.; Buckle, A.M. Reactive centre loop dynamics and serpin specificity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patston, P.A.; Gettins, P.G. Significance of secondary structure predictions on the reactive center loop region of serpins: A model for the folding of serpins into a metastable state. Febs. Lett. 1996, 383, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvidson, R.; Kaiser, M.; Lee, S.S.; Urenda, J.P.; Dail, C.; Mohammed, H.; Nolan, C.; Pan, S.; Stajich, J.E.; Libersat, F.; et al. Parasitoid jewel wasp mounts multipronged neurochemical attack to hijack a host brain. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2019, 18, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, D.N.; Jankova, L.; Harrop, S.J.; Curmi, P.M.; Gould, A.R.; Ranson, M.; Baker, M.S. Interaction between the P14 residue and strand 2 of β-sheet B is critical for reactive center loop insertion in plasminogen activator inhibitor-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 43383–43389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankova, L.; Harrop, S.J.; Saunders, D.N.; Andrews, J.L.; Bertram, K.C.; Gould, A.R.; Baker, M.S.; Curmi, P.M. Crystal structure of the complex of plasminogen activator inhibitor 2 with a peptide mimicking the reactive center loop. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 43374–43382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, D.A.; Olson, S.T.; Palaniappan, S.; Ginsburg, D. Serpin reactive center loop mobility is required for inhibitor function but not for enzyme recognition. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 27657–27662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, P.C.; Stone, S.R. The contribution of the conserved hinge region residues of alpha1-antitrypsin to its reaction with elastase. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 15872–15879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, F.C.; Gordon, N.C.; Gettins, P.G. Formation of a noncovalent serpin-proteinase complex involves no conformational change in the serpin. Use of 1H-15N HSQC NMR as a sensitive nonperturbing monitor of conformation. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 11884–11892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Terakado, K.; Nakamura, G.; Soekmadji, C.; Masuoka, T.; Yamasaki, M.; Hirose, M. Dynamic mechanism for the serpin loop insertion as revealed by quantitative kinetics. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 348, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsui, Y.; Liu, L.; Gershenson, A.; Wintrode, P.L. The conformational dynamics of a metastable serpin studied by hydrogen exchange and mass spectrometry. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 6561–6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsters, S.I.; Goldstone, A.P.; Buxton, J.L.; Zekavati, A.; Sosinsky, A.; Yiorkas, A.M.; Holder, S.; Klaber, R.E.; Bridges, N.; van Haelst, M.M.; et al. Truncating homozygous mutation of carboxypeptidase E (CPE) in a morbidly obese female with type 2 diabetes mellitus, intellectual disability and hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawley, N.X.; Yanik, T.; Woronowicz, A.; Chang, W.; Marini, J.C.; Loh, Y.P. Obese carboxypeptidase E knockout mice exhibit multiple defects in peptide hormone processing contributing to low bone mineral density. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2010, 299, E189–E197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soisson, S.M.; Patel, S.B.; Abeywickrema, P.D.; Byrne, N.J.; Diehl, R.E.; Hall, D.L.; Ford, R.E.; Reid, J.C.; Rickert, K.W.; Shipman, J.M.; et al. Structural definition and substrate specificity of the S28 protease family: The crystal structure of human prolylcarboxypeptidase. BMC Struct. Biol. 2010, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nusbaum, M.P.; Blitz, D.M.; Swensen, A.M.; Wood, D.; Marder, E. The roles of co-transmission in neural network modulation. Trends Neurosci. 2001, 24, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yu, H.Z.; Ye, C.J.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, T.; Chen, F.S.; Xu, J.P. Bombyx mori Serpin6 regulates prophenoloxidase activity and the expression of antimicrobial proteins. Gene 2017, 610, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, L.; Lin, Z.; Zou, Z.; Lu, Z. Serpin-5 regulates prophenoloxidase activation and antimicrobial peptide pathways in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 73, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Chu, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Wang, L. Role of serpin-25 in prophenoloxidase activation and expression of antimicrobial peptide genes in the silkworm Bombyx mori. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2024, 27, 102222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qie, X.; Yan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hao, C.; Lu, Z.; Ma, L. Serpin-4 negatively regulates prophenoloxidase activation and antimicrobial peptide synthesis in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichhart, J.-M. Tip of another iceberg: Drosophila serpins. Trends Cell Biol. 2005, 15, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Tang, X.; Huang, C.; Wan, K. A chromosome-level genome assembly of the legume pod borer, Maruca vitrata Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Sci. Data 2024, 11, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; Xiao, Z.; Tang, X.; Wan, K. Ai-Assisted Discovery of a Direct Physical Interaction Between a Venom Serpin from the Parasitoid Wasp Liragathis javana and a Host Serine Carboxypeptidase. Toxins 2025, 17, 600. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120600
Wang J, Jiang X, Xiao Z, Tang X, Wan K. Ai-Assisted Discovery of a Direct Physical Interaction Between a Venom Serpin from the Parasitoid Wasp Liragathis javana and a Host Serine Carboxypeptidase. Toxins. 2025; 17(12):600. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120600
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiale, Xunyuan Jiang, Zemiao Xiao, Xuemei Tang, and Kai Wan. 2025. "Ai-Assisted Discovery of a Direct Physical Interaction Between a Venom Serpin from the Parasitoid Wasp Liragathis javana and a Host Serine Carboxypeptidase" Toxins 17, no. 12: 600. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120600
APA StyleWang, J., Jiang, X., Xiao, Z., Tang, X., & Wan, K. (2025). Ai-Assisted Discovery of a Direct Physical Interaction Between a Venom Serpin from the Parasitoid Wasp Liragathis javana and a Host Serine Carboxypeptidase. Toxins, 17(12), 600. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120600





