- Systematic Review
“Leave No Scale Behind”—A Pluralistic Framework for Achieving the Global Sustainable Development Goals at Every Scale
- Avit Bhowmik and
- Katharina Kalbitz
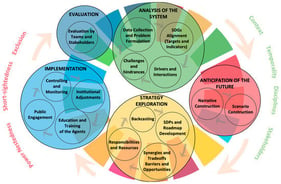
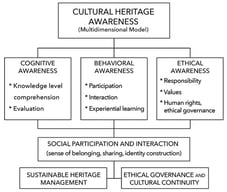
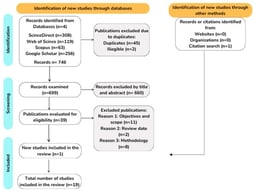
The Agenda 2030 for Sustainable Development was adopted by the United Nations (UN) to guide action towards sustainable development for humanity at every scale, as “Leave no one behind” is the central, transformative promise of the agenda. The 17 global Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide ambitious political targets for every UN member state to shape the future univocally. However, the sustainability challenges faced at regional and subnational levels, e.g., community levels, are substantially diverse and the strategies for achieving the SDGs also vary across communities based on their context, agency and resources. We developed a pluralistic framework to guide policy action and grass-root transformation at every scale, aligning with the global SDGs, by systematically reviewing 79 sustainability transformation projects reported in the published literature. We analyzed what these diverse scale projects had in common regarding sustainability strategies, collaborations among societal actors and how new narratives were transferred into guided action. The framework comprises five consequent phases for the implementation of SDGs and SDG targets through problem formulation to project evaluation and four enabling factors comprising context, temporality, disciplines and stakeholders that crucially facilitate the implementation of SDGs and SDG targets. Our framework pursues the “leave no scale behind” aspiration, focusing on multi-stakeholder processes and inter- and transdisciplinary methods to strengthen collaboration among a diverse set of actors, joint learning, and coherent implementation across all relevant areas of society.
1 February 2026