- Review
Review of the Cumulative Ecological Effects of Utility-Scale Photovoltaic Power Generation
- Bo Yuan,
- Yuan Li and
- Shuguang Xie
- + 3 authors
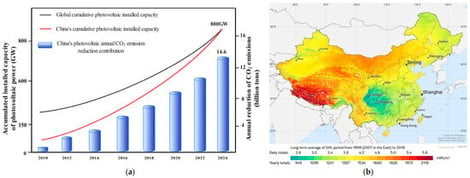
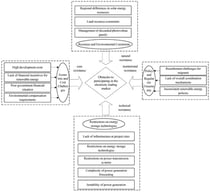
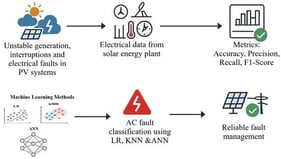
CPVG (Utility-scale photovoltaic generation) is expanding rapidly worldwide, yet its cumulative ecological effects remain insufficiently quantified. This review synthesizes current evidence to clarify how CPVG influences ecosystems through linked mechanisms of energy redistribution, biogeochemical cycling disturbance, and ecological responses. CPVG alters surface radiation balance, modifies microclimate, and disrupts carbon–nitrogen–water fluxes, thereby driving vegetation shifts, soil degradation, and biodiversity decline. These impacts accumulate across temporal scales—from short-term construction disturbances to long-term operational feedbacks—and propagate spatially from local to regional and watershed levels. Ecological outcomes differ substantially among deserts, grasslands, and agroecosystems due to contrasting resilience and limiting factors. Based on these mechanisms, we propose a multi-scale cumulative impact assessment framework integrating indicator development, multi-source monitoring, coupled modelling, and ecological risk tiering. A full-chain mitigation pathway is further outlined, emphasizing optimized siting, disturbance reduction, adaptive management, and targeted restoration. This study provides a systematic foundation for evaluating and regulating CPVG’s cumulative ecological impacts, supporting more sustainable solar deployment.
3 February 2026