Journal Description
Scientia Pharmaceutica
Scientia Pharmaceutica
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal related to the pharmaceutical sciences, published quarterly online. It is the official journal of the Austrian Pharmaceutical Society (ÖPhG). Society members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), Embase, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Pharmaceutical Science)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 38.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.2 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Journal Clusters-Pharmaceutical Science: Scientia Pharmaceutica, Marine Drugs, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Pharmacy, Future Pharmacology, Pharmacoepidemiology, Drugs and Drug Candidates and Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry.
Impact Factor:
2.5 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.3 (2024)
Latest Articles
Nanotechnology for Metformin Release Systems: Nanostructures, Biopolymer Carriers, and Techniques—A Review
Sci. Pharm. 2026, 94(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm94010003 - 24 Dec 2025
Abstract
Currently, there are various approaches to the treatment of diabetes. Regarding type 2 diabetes (T2D), treatment focuses on blood glucose control. When changes in lifestyle do not achieve this glycemic control, the option is to start therapy with antidiabetic drugs such as metformin.
[...] Read more.
Currently, there are various approaches to the treatment of diabetes. Regarding type 2 diabetes (T2D), treatment focuses on blood glucose control. When changes in lifestyle do not achieve this glycemic control, the option is to start therapy with antidiabetic drugs such as metformin. However, long-term metformin use causes disturbances that may affect treatment approaches. This review examines recent advances in nanotechnology that have developed new forms of drug administration that can improve the efficacy of the treatment, where nanomaterials, nanostructures, and nanoparticle design are involved, so that they provide controlled and gradual release. The use of biopolymers (as drug delivery systems) has ensured biocompatibility, biodegradability, and low toxicity. There are several methods for obtaining a drug delivery system, including electrospinning, electrospraying, nanoprecipitation, etc. These systems improve drug delivery and can be used orally, transdermally, or intravenously, among means of administration. This review describes the new forms of the administration of metformin in the treatment of T2D, based on the encapsulation of metformin in polymeric matrices such as proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids, among others.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Complementary Strategies in Drug Delivery: From Particle Engineering to System Optimization)
Open AccessArticle
New Horizons in Quality Control of Enzyme Pharmaceuticals: Combining Dynamic Light Scattering, Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, and Radiothermal Emission Analysis
by
Gleb Vladimirovich Petrov, Aleksandr Andreevich Nazarov, Alena Mikhailovna Koldina and Anton Vladimirovich Syroeshkin
Sci. Pharm. 2026, 94(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm94010002 - 22 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Hyaluronidase and its modified analogs are clinically significant enzyme-based pharmaceuticals used to treat fibrosis, increase tissue permeability, and improve drug diffusion. While pharmacopeial quality control methods are well defined, scientific literature provides limited information about the physicochemical evaluation of such enzyme pharmaceuticals, necessitating
[...] Read more.
Hyaluronidase and its modified analogs are clinically significant enzyme-based pharmaceuticals used to treat fibrosis, increase tissue permeability, and improve drug diffusion. While pharmacopeial quality control methods are well defined, scientific literature provides limited information about the physicochemical evaluation of such enzyme pharmaceuticals, necessitating a more holistic analytical approach. Commercial pharmaceuticals of hyaluronidase and its modified analog were analyzed using a combination of dynamic light scattering, infrared spectroscopy, and detection of intrinsic radiothermal emission (RTE). Dimensional characteristics were studied using a Zetasizer Nano ZSP (ZetasizerNano ZSP, Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK) confirmed theoretical diameters of 5–8 nm, consistent with experimental values (6–8 nm). Fourier-Transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) (Agilent Cary 630, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) revealed characteristic transmission bands for the modified enzyme at 1464, 1448, 1326, 1158, and 1010 cm−1, confirming structural modification. RTE measurements using a TES-92 detector (TES Electrical Electronic Corp., Taipei, Taiwan) demonstrated a correlation between emission intensity and shelf life: 12.8 ± 0.8 µW/m2 for proper shelf-life samples, 8.3 ± 0.8 µW/m2 for six-month-expired, and 5.1 ± 1.0 µW/m2 for one-year-expired pharmaceuticals. The study offers a promising supplementary tool for pharmaceutical quality control of hyaluronidase-based drugs.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Crystallographic Modification of Rosuvastatin Calcium: Formulation, Characterization and Pharmacokinetic Evaluation for Enhanced Dissolution, Stability and Bioavailability
by
Deepak Kulkarni and Sanjay Pekamwar
Sci. Pharm. 2026, 94(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm94010001 - 19 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Rosuvastatin calcium is a promising lipid-lowering agent and the drug of choice in hyperlipidemia. Conventional solid oral delivery of rosuvastatin is limited by its poor solubility and ultimately poor bioavailability. An attempt was made to fabricate the cocrystals of RSC for enhancing solubility
[...] Read more.
Rosuvastatin calcium is a promising lipid-lowering agent and the drug of choice in hyperlipidemia. Conventional solid oral delivery of rosuvastatin is limited by its poor solubility and ultimately poor bioavailability. An attempt was made to fabricate the cocrystals of RSC for enhancing solubility and bioavailability. Cocrystals were prepared by a microwave synthesiser-assisted solvent evaporation technique with multiple cocrystal formers. Rosuvastatin-Ascorbic acid (RSC-AA) cocrystals showed the highest solubility (~5-fold increased) amongst all twenty drug-coformer combination (DCC). RSC-AA cocrystals (1:1 ratio) were further characterized by various analytical techniques like FTIR, DSC and XRD to confirm the formation of cocrystals. RSC-AA cocrystals also showed improved flow properties and compressibility in comparison with pure drug, and it was demonstrated using the SeDeM diagram. RSC-AA cocrystals were further formulated into an immediate-release tablet by implementing experimental optimization. Comparative dissolution study of the cocrystal and pure drug tablet revealed improved dissolution after cocrystallization. RSC-AA cocrystal tablet showed the % drug release of 95.61 ± 3.94 while RSC pure drug showed the drug release of 67.83 ± 3.29. In vivo pharmacokinetic analysis showed significant improvement in systemic availability and cumulative absorption of the drug. The peak plasma concentration (Cmax) for RSC pure drug was 13.924 ± 0.477 μg/mL, while RSC-AA cocrystals showed a peak plasma concentration of 22.464 ± 0.484 μg/mL. Area Under Curve (AUC) of RSC-AA cocrystal was also significantly greater compared to the pure drug. In the stability study analysis, the shelf life was calculated from a graphical method and was found to be around 34.58 months for RSC-AA cocrystal tablets and 19.87 months for RSC pure drug tablets, which indicates improved stability with cocrystallization. Overall, the cocrystallization resulted in significant improvement in dissolution and solubility of RSC.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Injectable Biostimulator in Adipose Tissue: An Update and Literature Review
by
Kar Wai Alvin Lee, Heesoo Kim, Jong Keun Song, Olena Sydorchuk, Wong Ka Fai, Isabella Rosellini, Hongseok Kim, Kian Hong Lau, Michael H. Gold and Kyuho Yi
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 62; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040062 - 24 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Injectable biostimulatory agents such as poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA), polycaprolactone (PCL), and calcium hydroxyapatite (CaHA) have emerged as key tools in regenerative aesthetics due to their ability to stimulate adipogenesis and adipocyte metabolic activity, enhance collagen production, and improve dermal quality. This review aimed
[...] Read more.
Injectable biostimulatory agents such as poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA), polycaprolactone (PCL), and calcium hydroxyapatite (CaHA) have emerged as key tools in regenerative aesthetics due to their ability to stimulate adipogenesis and adipocyte metabolic activity, enhance collagen production, and improve dermal quality. This review aimed to provide an updated synthesis of the role of these agents in adipocyte stimulation, focusing on their mechanisms of action, clinical efficacy, and therapeutic applications. A comprehensive search of the MEDLINE, PubMed, and Ovid databases was conducted for studies published from 2018 onward, including in vitro and in vivo experiments, randomized controlled trials, and observational studies, which were evaluated according to the Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine hierarchy. The findings demonstrated that PCL promotes adipose-derived stem cell differentiation and extracellular matrix remodeling, while PLLA exhibits dual effects on collagen synthesis and adipocyte stimulation, with clinical trials such as the SPLASH study confirming significant improvements in dermal thickness and adipogenesis. CaHA provided immediate volumizing benefits with long-term tissue regeneration, and innovative approaches including combination therapies and novel injection protocols expanded clinical applications. Overall, PLLA, PCL, and CaHA represent effective and versatile biostimulatory agents that support natural and durable outcomes in aesthetic practice. Nevertheless, the absence of large-scale trials and standardized protocols highlights the need for further research to optimize safety, efficacy, and long-term treatment strategies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Integrating 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing into Personalized Medicine for Pharmaceuticals: Opportunities, Limitations, and Future Perspectives
by
Nithin Vidiyala, Pavani Sunkishala, Preethi Mandati, Prashanth Parupathi and Dinesh Nyavanandi
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 61; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040061 - 24 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Over the last decade, additive manufacturing (AM) has been widely investigated for developing on-demand, patient-centric, and personalized medications. Among various AM techniques, fused deposition modeling (FDM), semi-solid extrusion (SSE), inkjet printing, binder jet printing, stereolithography (SLA), and selective laser sintering (SLS) have been
[...] Read more.
Over the last decade, additive manufacturing (AM) has been widely investigated for developing on-demand, patient-centric, and personalized medications. Among various AM techniques, fused deposition modeling (FDM), semi-solid extrusion (SSE), inkjet printing, binder jet printing, stereolithography (SLA), and selective laser sintering (SLS) have been most widely studied for developing simple and complex pharmaceutical medications. Implementing the AM platform enables decentralized manufacturing of medications at the hospitals and clinical sites. The dose and release profiles of the dosage forms can be tailored based on patient needs, providing flexibility to the physician. In fact, streamlining the AM process into a continuous manufacturing process equipped with process analytical technology (PAT) tools will ensure the manufacturing and delivery of safe and efficacious medications to the patient population. Complex medications, such as polypills, which are complex and time-consuming to manufacture using traditional manufacturing techniques, can be printed quickly using the AM approach. The pediatric patient population can be attracted to medication by printing the dosage forms with a geometry of interest. The AM platform can be integrated with artificial intelligence (AI) and health records to accelerate drug development and tailor medications based on patient conditions. Despite the various advantages that the AM platform brings to the pharmaceutical field, a few limitations, such as scalability, material innovation, secondary processing, and regulatory evolution, need to be addressed. This review article compares the advantages and limitations of the existing AM techniques along with a note on the recent advancements and future perspectives.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Terminological and Grammatical Study of Essential and Fatty Oils of Plants from the Austrian, Hungarian, Spanish, and Belgian Pharmacopoeias (19th Century)
by
Zsuzsanna Takáts, Attila Almási, Judit Szalai-Szolcsányi, Tünde Ambrus and Nóra Papp
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 60; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040060 - 20 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In this study, a terminological and grammatical survey of essential and fatty oils of plant origin was performed in the selected Austrian, Hungarian, Spanish, and Belgian pharmacopoeias from the 18th to 19th centuries. The Latin-language prescriptions were analysed for their content, sections, and
[...] Read more.
In this study, a terminological and grammatical survey of essential and fatty oils of plant origin was performed in the selected Austrian, Hungarian, Spanish, and Belgian pharmacopoeias from the 18th to 19th centuries. The Latin-language prescriptions were analysed for their content, sections, and indications, and then translated from Latin into English, and supplemented with the source plants. Oil types were categorised based on their preparation and origin. Most oils belong to essential oils in Ph. Austriaca I–IV, Ph. Belgica, and Ph. Hungarica I (20 in each). Cooked oils are described as having the highest number in Ph. Hispanica (21), while pressed oils are also included in a high ratio in Ph. Hisp. (18) and Ph. Austriaca V (15). At the same time, those from minerals are described only in Ph. Belg. (2) and Ph. Hisp. (5). Latin terms are used in preparation methods, including the most concise descriptions in Ph. Austriaca V and Ph. Hg. I. This comprehensive study provides new linguistic data on the oils of herbs in the selected pharmacopoeias. Studies of essential oils have recently been progressing, and this analysis might help in understanding information from old pharmacopoeias.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessPerspective
Biopharmaceuticals—Current Information and New Challenges
by
Miroslav Radenković
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 59; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040059 - 19 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Biopharmaceuticals are medical drugs produced by means of biotechnology. In contrast with small-molecule (traditional) drugs, which are usually synthesized chemically, biopharmaceuticals are derived from biological sources, including tissues, cells, or microorganisms. Biopharmaceuticals comprise a wide extent of therapies, such as vaccines, monoclonal antibodies,
[...] Read more.
Biopharmaceuticals are medical drugs produced by means of biotechnology. In contrast with small-molecule (traditional) drugs, which are usually synthesized chemically, biopharmaceuticals are derived from biological sources, including tissues, cells, or microorganisms. Biopharmaceuticals comprise a wide extent of therapies, such as vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, cell therapies, recombinant proteins, and gene therapies, as well as biosimilars. These products are designed to become important treatment options for different diseases, including cancer, autoimmune pathological disorders, andinfectious diseases. The development of biopharmaceuticals often includes multifaceted processes, involving genetic engineering and cellular culture techniques, to guarantee efficacy and safety. Accordingly, biopharmaceuticals’ legislation is a key component for ensuring the highest quality of medical products, as well as protecting public health. As a rapidly developing area inside the pharmaceutical industry, biopharmaceuticals represent a significant advancing stage in modern medicine, offering targeted therapies that can improve patient outcomes. Accordingly, this paper seeks to provide current state-of-the-art didactic information, including better insight into various challenges related to biopharmaceuticals’ development, classification, medical use, legislation and ethics.
Full article
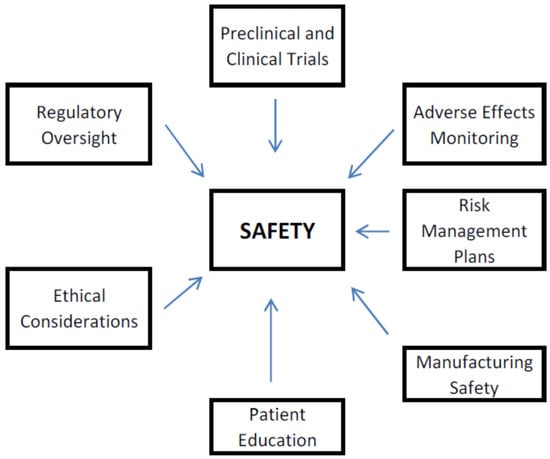
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development and Optimisation of Docetaxel-Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles for Oral Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer
by
Divya Wali, Shivakumar H. Nanjappa, Avichal Kumar and Rushikesh Shinde
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 58; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040058 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Docetaxel (DTX)-loaded polymeric nanoparticles composed of Eudragit RL and RS 100 were developed by solvent evaporation using D-α-tocopheryl polyethene glycol 1000 succinate as an emulsifier and optimised by Central Composite Design. The effects of homogenisation and sonication times on entrapment efficiency (%EE) and
[...] Read more.
Docetaxel (DTX)-loaded polymeric nanoparticles composed of Eudragit RL and RS 100 were developed by solvent evaporation using D-α-tocopheryl polyethene glycol 1000 succinate as an emulsifier and optimised by Central Composite Design. The effects of homogenisation and sonication times on entrapment efficiency (%EE) and drug release (%DR) were statistically analysed across nine batches. Particle size (PS) ranged from 302 ± 1.0 to 502 ± 2.0 nm, and zeta potential (ZP) from 25.8 ± 2.5 to 42.9 ± 1.7 mV. %EE and %DR (pH 1.2 for 2 h, then pH 7.4 for 22 h, 40 mL medium at 37 ± 0.5 °C) ranged from 69.32 ± 3.77 to 92.71 ± 0.16% and 19.24 ± 3.03 to 49.17 ± 1.98%, respectively. Optimised DTX nanoparticles (DNPs) showed EE of 78.18 ± 0.56%, DR of 46.21 ± 1.41% at 24 h, PS of 357.9 ± 2.4 nm, and ZP of 42.9 ± 3.7 mV. Scanning electron microscopy revealed ~300 nm cuboidal particles with smooth surfaces. X-Ray Diffraction and Differential Scanning Colorimetry confirmed reduced drug crystallinity in DNPs. In vitro haemolysis assays showed ~11.5-fold lower haemolytic potential (p < 0.0001) versus DTX, confirming improved safety. Fluorescence microscopy indicated enhanced cellular uptake of DNPs in MDA-MB-231 cells, while cytotoxicity assays of DNPs showed a lower IC50 (39.52 µM) compared to DTX (60.81 µM), demonstrating superior anticancer efficacy. Overall, DNPs represent a promising oral chemotherapy platform for breast cancer management.
Full article
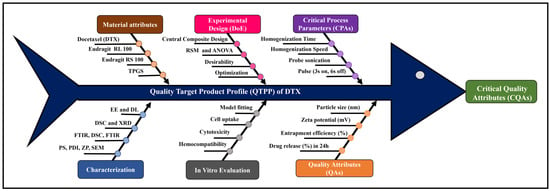
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dysphania ambrosioides as a Source of Antioxidant Candidates for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Prostatitis: A Critical Review and In Silico Prioritisation
by
Enrique Jiménez-Ferrer, Tania Abarca-Salgado, Azamar Aarón Vargas-Radilla, José de Jesús Flores-Melgar and Rodolfo Abarca-Vargas
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 57; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040057 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostatitis are multifactorial urological disorders associated with chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, and androgenic imbalance. Dysphania ambrosioides (L.) Mosyakin & Clemants contains flavonoids and phenolic acids with well-recognised antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties; however, its potential activity against the molecular
[...] Read more.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostatitis are multifactorial urological disorders associated with chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, and androgenic imbalance. Dysphania ambrosioides (L.) Mosyakin & Clemants contains flavonoids and phenolic acids with well-recognised antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties; however, its potential activity against the molecular targets of these prostatic disorders has not been systematically evaluated. A comparative quantitative analysis was performed using studies published between 2005 and 2025 that reported antioxidant activity (DPPH assay, IC50 in µg/mL) of D. ambrosioides extracts. Metabolites from extracts with IC50 values below the global mean (398.410 ± 81.810 µg/mL; n = 35) were selected for in silico prioritisation using OSIRIS, PASS, and ProTox 3.0, followed by molecular docking (CB-Dock2) against AR, 5AR2, COX-2, NLRP3, and α1A receptors. Luteolin and rosmarinic acid showed favourable binding energies (−9.5 to −7.7 kcal/mol) comparable in magnitude to reference drugs (finasteride −13.4, celecoxib −11.4, tamsulosin −7.3 kcal/mol). These metabolites, exhibited affinity for androgenic, inflammatory, and adrenergic targets, suggesting their potential to modulate key mechanisms underlying both BPH and prostatitis. This study integrates, for the first time, a quantitative assessment of antioxidant activity with a multitarget in silico analysis of D. ambrosioides, prioritising luteolin and rosmarinic acid as natural candidates with potential antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiandrogenic properties relevant to prostatic health.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Antioxidant Activity of Natural Products—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
A Score-Based Rapid Screening and Network Visualization Method Based on Bioactive Ingredient-Induced Variations in Skin Cell Gene Expression
by
Mio Ogawa, Charles W. Crawford, Ayumu Ishigaki, Iri Sato-Baran, David D. Ordinario and Tadayoshi Miyashita
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 56; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040056 - 12 Nov 2025
Abstract
Bioactive ingredients are compounds, typically derived from natural sources, that provide specific health benefits or perform certain beneficial functions. Although they can play a role in maintaining good health, their effects can vary widely based on a person’s specific genotype and phenotype, leading
[...] Read more.
Bioactive ingredients are compounds, typically derived from natural sources, that provide specific health benefits or perform certain beneficial functions. Although they can play a role in maintaining good health, their effects can vary widely based on a person’s specific genotype and phenotype, leading to situations where certain ingredients induce beneficial responses for some individuals but not others. Herein, we report a method for the rapid discovery of relationships between genes, bioactive ingredients, and physiological effects. First, RNA-Seq was performed after applying 6 plant-derived ingredients to a three-dimensional skin model. After determining expression changes for each ingredient, these changes were ranked and visualized using score-based prediction models. Based on our analysis, we were able to quickly determine and visualize the effect (or lack thereof) of the ingredients on gene expression. Our findings demonstrate the utility of combining RNA-Seq with score-based models and visualizations for screening bioactive ingredients by gene expression, visualizing their impact based on ingredient or physiological effect, and the applicability of this method to any bioactive ingredient for rapid determination of potential ingredients relevant to maintaining health and wellness.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Bioinformatics in Drug Design and Discovery—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Advancements in Encapsulation Technologies: The Potential of Polyphenols as an Antidiabetic Therapy
by
Rigoberto Cabanillas-Ponce de León, Feliznando Isidro Cardenas-Torres, Noe Ontiveros, Laura Aracely Contreras-Angulo, Cristina Alicia Elisande-Romero, Nayely Leyva-López, Manuel de Jesús Bernal-Millán, Jose Basilio Heredia and Erick Paul Gutiérrez-Grijalva
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 55; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040055 - 28 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a disease that affects over 537 million people worldwide and results in 6.7 million deaths annually. Conventional treatment of this disease focuses on lifestyle changes and drug administration. However, very few people can adhere to a healthier lifestyle, and
[...] Read more.
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a disease that affects over 537 million people worldwide and results in 6.7 million deaths annually. Conventional treatment of this disease focuses on lifestyle changes and drug administration. However, very few people can adhere to a healthier lifestyle, and drugs are difficult to access, especially in low- and middle-income countries. An alternative as an adjuvant to the treatment of DM is the phenolic compounds from plants with reported anti-diabetic effects. However, the bioavailability of these compounds is very low since they are affected by the gastrointestinal tract and xenobiotic metabolism. To improve the availability of these compounds, an emerging technology such as encapsulation is being used since it has been reported that the encapsulation of phenolic compounds improves both their bioaccessibility and bioavailability, as well as their bioactivity. In this review, we will focus on compiling the most up-to-date information on the different encapsulation processes of phenolic compounds and the antidiabetic effect of encapsulated phenolic compounds using the databases PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar. We will discuss the mechanisms, pathways, and receptors involved in the modulation of DM, especially those related to inflammation, oxidative stress, and insulin resistance.
Full article
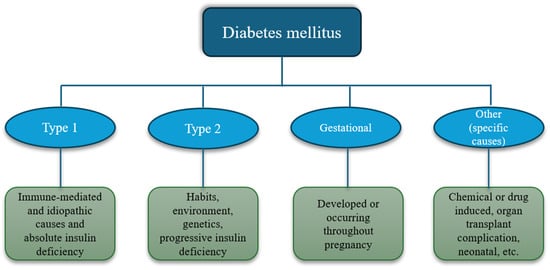
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Alpha-Mangostin Enhances Radiosensitivity in HeLa Cervical Cancer Cells
by
Pimvaree Aissara, Ausanai Prapan and Chanyatip Suwannasing
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 54; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040054 - 23 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Radiotherapy (RT) is a standard treatment for cervical cancer, but its efficacy is often limited by tumor hypoxia and low radiosensitivity. Radiosensitizers that enhance RT without dose escalation are therefore of clinical interest. Alpha-mangostin (AM), a xanthone from Garcinia mangostana, exhibits anticancer
[...] Read more.
Radiotherapy (RT) is a standard treatment for cervical cancer, but its efficacy is often limited by tumor hypoxia and low radiosensitivity. Radiosensitizers that enhance RT without dose escalation are therefore of clinical interest. Alpha-mangostin (AM), a xanthone from Garcinia mangostana, exhibits anticancer and ROS-inducing properties. This study evaluated whether AM enhances radiosensitivity in vitro. Cytotoxicity (0–35 µM) was assessed by the MTT assay, and radiation sensitivity (0–6 Gy) was assessed by clonogenic survival. γ-H2AX immunofluorescence, cell cycle distribution, apoptosis induction, and clonogenic survival assessments were used to investigate the radiosensitization effect. AM showed dose-dependent cytotoxicity in HeLa cells at an inhibitory concentration 20 (IC20) of 13.67 µM while sparing fibroblasts. The radiation lethal dose 20 (LD20) was 1.4 Gy. However, combination treatment used AM at 12 µM (IC14) combined with 2 Gy (LD30) irradiation to avoid 50% cell death. AM enhanced G2/M arrest by 21.10% (p < 0.01) versus controls. In combination treatment, AM significantly increased γ-H2AX-positive cells to 48.2% (p < 0.0001), elevated apoptosis to 39.48% (p < 0.0001), and decreased clonogenic survival to 28% (p < 0.0001) compared with control. A combination index of about 0.9 indicated synergism. Therefore, AM effectively radiosensitized HeLa cells via increased DNA double-strand breaks and G2/M arrest.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Nitazoxanide Shows an Immunomodulatory Effect in Vγ9Vδ2 T Cells
by
Ángel Daniel Campos-Juárez, Octavio Rodríguez-Cortes, Andrés Ademar Garcia-Nuñez, Mónica Adriana Rodríguez-Cadena, Jonathan B. Cortés-Serrano, Carlos Zepactonal Gómez-Castro, Itzel Pamela Torres-Avila, Damaris Priscila Romero-Rodríguez, Gamaliel Benítez-Arvizu, Dean J. Naisbitt, Mario Adán Moreno-Eutimio and José Luis Castrejón-Flores
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 53; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040053 - 22 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The γδ T cells belong to a subgroup of T cells known as non-conventional T cells due to their limited T cell receptor (TCR) repertoire and ability to recognize non-peptide antigens. They play a crucial role in combating infections and tumors. Vγ9Vδ2 T
[...] Read more.
The γδ T cells belong to a subgroup of T cells known as non-conventional T cells due to their limited T cell receptor (TCR) repertoire and ability to recognize non-peptide antigens. They play a crucial role in combating infections and tumors. Vγ9Vδ2 T cells are typically activated by molecules containing diphosphate groups, collectively known as phosphoantigens (pAgs), through a non-canonical mechanism which involves the intracellular domain of butyrofilin (BTN)3A1 protein. However, no FDA-approved drugs have yet been shown to activate them, and the underlying cellular mechanisms remain unknown. In this study, we combined high-throughput virtual screening of an FDA-approved drug database with in vitro cellular assays to identify potential γδ T cells activators. Our findings demonstrate that Nitazoxanide (NTZ) and Tinidazole induce moderate elicited a statistically significant increase in interferon (IFN)-γ production of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells by their probably interaction with the pAg binding site of BTN3A1. Additionally, NTZ induces expression of CD107a, but only at the highest concentrations tested and promotes the upregulation of HLA-DR in total PBMCs and CD14+ monocytes. Blocking BTN3A with a specific antibody led to a marked reduction in all NTZ-induced activations. This work identifies NTZ as a previously unrecognized activator of γδ T cells, highlighting its immunomodulatory potential beyond its known clinical uses. These findings broaden our understanding of γδ T cells pharmacology and suggest new opportunities for drug repurposing and the design of novel chemical scaffolds. Further mechanistic studies will be essential to fully define how NTZ engages the BTN3A–γδ T cells axis.
Full article
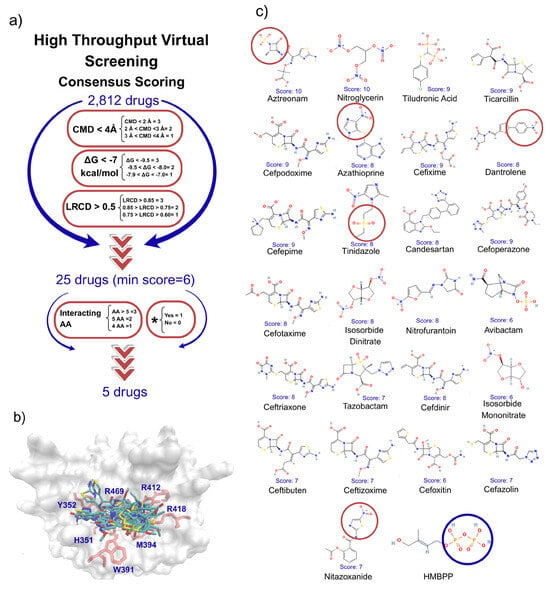
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Intranasally Administered Insulin as Neuromodulating Factor and Medication in Treatment of Neuropsychiatric Disorders—Current Findings from Clinical Trials
by
Mikołaj Grabarczyk, Aleksandra Szychowska, Sebastian Kozłowski, Kasper Sipowicz, Tadeusz Pietras, Marcin Kosmalski and Monika Różycka-Kosmalska
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 52; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040052 - 17 Oct 2025
Abstract
As a metabolism-controlling peptide, insulin affects activity of almost all tissues in human organisms, including the ones located in the central nervous system. By modifying glucose uptake and processing, as well as inducing anabolic effects, insulin alters functions of various nerve centers. Data
[...] Read more.
As a metabolism-controlling peptide, insulin affects activity of almost all tissues in human organisms, including the ones located in the central nervous system. By modifying glucose uptake and processing, as well as inducing anabolic effects, insulin alters functions of various nerve centers. Data from numerous clinical trials prove that such actions can have positive influence on cognitive processes or might be utilized as measures to control appetite, mood, and blood flow, or to prevent unfavorable mental states associated with diminished ability to maintain homeostasis. The intranasal route of administration provides an efficient and targeted delivery method, allowing insulin to be applied directly to different brain regions via the nasal mucosa. Such an approach can also reduce the risk of potential adverse effects associated with this medication, including drops in plasma glucose levels. This review gathers clinical studies’ findings on intranasal insulin’s neuromodulatory properties and its efficacy as additional treatment measure in several neuropsychiatric disease entities.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Deciphering Drug Repurposing Strategies: Antiviral Properties of Candidate Agents Against the Mpox Virus
by
Aganze Gloire-Aimé Mushebenge and David Ditaba Mphuthi
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 51; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040051 - 17 Oct 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Monkeypox (Mpox) has re-emerged as a global public health threat, with recent outbreaks linked to novel mutations that enhance viral transmissibility and immune evasion. The Mpox virus (MPXV), a double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) orthopoxvirus, shares high structural and enzymatic similarity with the variola
[...] Read more.
Monkeypox (Mpox) has re-emerged as a global public health threat, with recent outbreaks linked to novel mutations that enhance viral transmissibility and immune evasion. The Mpox virus (MPXV), a double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) orthopoxvirus, shares high structural and enzymatic similarity with the variola virus, underscoring the need for urgent therapeutic interventions. While conventional antiviral development is time-intensive and costly, drug repurposing offers a rapid and cost-effective strategy by leveraging the established safety and pharmacological profiles of existing medications. This is a narrative integrative review synthesizing published evidence on drug repurposing strategies against MPXV. To address these issues, this review explores MPXV molecular targets critical for genome replication, transcription, and viral assembly, highlighting how the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved antivirals (cidofovir, tecovirimat), antibiotics (minocycline, nitroxoline), antimalarials (atovaquone, mefloquine), immunomodulators (infliximab, adalimumab), and chemotherapeutics (doxorubicin) have demonstrated inhibitory activity against the virus using computational or experimental approaches. This review further evaluates advances in computational methodologies that have accelerated the identification of host-directed and viral-directed therapeutic candidates. Nonetheless, translational challenges persist, including pharmacokinetic limitations, toxicity concerns, and the limited efficacy of current antivirals such as tecovirimat in severe Mpox cases. Future research should integrate computational predictions with high-throughput screening, organ-on-chip technologies, and clinical pipelines, while using real-time genomic surveillance to track viral evolution. These strategies establish a scalable and sustainable framework for the MPXV drug discovery.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Challenges and Opportunities in Drug Delivery Research, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
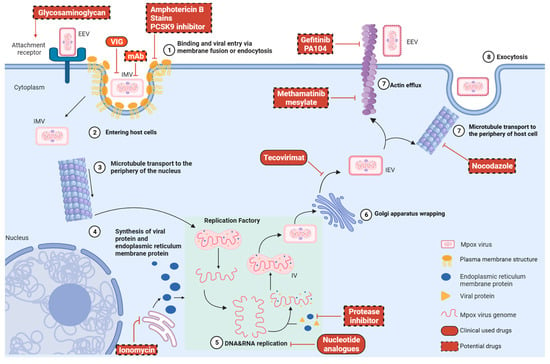
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Impact of Providing Pharmaceutical Care on Work Satisfaction of Pharmacists in Poland—A Preliminary Study
by
Patrycja Huber, Aniela Zubek-Biełuś, Paweł Lipiński and Anna Żuk
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 50; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040050 - 17 Oct 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Pharmaceutical care in European countries is at various stages of development. Although the problem of occupational burnout affects many professions, it is particularly relevant among healthcare workers, such as pharmacists. Studies assessing pharmacists’ life satisfaction and factors influencing the level of occupational burnout
[...] Read more.
Pharmaceutical care in European countries is at various stages of development. Although the problem of occupational burnout affects many professions, it is particularly relevant among healthcare workers, such as pharmacists. Studies assessing pharmacists’ life satisfaction and factors influencing the level of occupational burnout play an important role in social pharmacy. Therefore, the present study aimed to evaluate the impact of providing pharmaceutical care on the professional life satisfaction of pharmacists in Poland. This study was conducted as an anonymous online survey. It included pharmacists who are members of the professional self-government in Poland. A custom-designed questionnaire was used for data collection, and 91 completed questionnaires were obtained. The respondents were divided into four groups according to their professional experience: up to 5 years, 6–10 years, 11–20 years, and over 20 years. In response to questions regarding job satisfaction and the willingness to provide pharmaceutical care, the respondents gave affirmative answers. Pharmacists in Poland have a positive perception of the impact of pharmaceutical care on the prestige of their profession. Currently, the pharmaceutical care services most commonly provided are those financed by the State; however, pharmacists are willing to engage in such activities and expect an expansion of the scope of reimbursed services. Consequently, pharmacists express dissatisfaction with the current stage of pharmaceutical care implementation in Poland. Those who provide pharmaceutical care feel more appreciated in their profession, do not experience psychological strain, do not feel uncomfortable when communicating with patients, and are not afraid of the responsibility associated with providing such services. Nevertheless, they consider it an additional workload in their professional duties.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Modulation of Antimicrobial Peptide–Membrane Interactions by Lysyl-Phosphatidylglycerol in Staphylococcus aureus: An FTIR Spectroscopy Study
by
Andrea Vásquez, Sofía Echeverri-Gaviria and Marcela Manrique-Moreno
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 49; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040049 - 15 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Changes in membrane lipid composition constitute a key bacterial resistance mechanism. In Staphylococcus aureus, phosphatidylglycerol undergoes lysine modification to form lysyl-phosphatidylglycerol, a cationic lipid that reduces the net negative surface charge and thereby enhances resistance to cationic antimicrobial peptides. In this study,
[...] Read more.
Changes in membrane lipid composition constitute a key bacterial resistance mechanism. In Staphylococcus aureus, phosphatidylglycerol undergoes lysine modification to form lysyl-phosphatidylglycerol, a cationic lipid that reduces the net negative surface charge and thereby enhances resistance to cationic antimicrobial peptides. In this study, we examined the influence of lysyl-PG on the membrane activity of three antimicrobial peptides with distinct physicochemical characteristics: LL-37, F5W Magainin II, and NA-CATH:ATRA-1-ATRA-1. Model membranes composed of phosphatidylglycerol and cardiolipin were supplemented with increasing molar fractions of lysyl-phosphatidylglycerol, and peptide–membrane interactions were characterized using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Membrane fluidity was evaluated through shifts in the symmetric methylene stretching bands, while changes in interfacial polarity were assessed via the carbonyl and phosphate asymmetric stretching bands. LL-37 induced pronounced disruption of anionic bilayers, an effect progressively attenuated by lysyl-phosphatidylglycerol, particularly within the hydrophobic core. F5W Magainin perturbed both hydrophobic and interfacial regions across a broader range of lysyl-phosphatidylglycerol concentrations, whereas NA-CATH:ATRA-1-ATRA-1 primarily targeted interfacial domains, with minimal disruption of acyl chain order. Increasing lysyl-PG content modulated the extent of bilayer disorder and dehydration at the hydrophobic–hydrophilic interface, with each peptide exhibiting a distinct interaction profile. Collectively, these findings provide mechanistic insights into lysyl-PG-mediated modulation of peptide activity and highlight the role of lipid remodeling as a bacterial defense strategy.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pumpkin Seeds Harbor Hidden Agonists: Adenosine-Mediated A1 Receptor Activation and Antioxidant Activity
by
Adina-Elena Grasu, Roman Senn, Christiane Halbsguth, Alexander Schenk, Veronika Butterweck, Giulia Zecchin, Ionel I. Mangalagiu, Cătălina-Ionica Ciobanu and Anca Miron
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 48; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040048 - 30 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Hydroethanolic Cucurbita pepo seed extracts are traditionally used for alleviating lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), yet their mechanisms remain unclear. Adenosine, a purine nucleoside involved in neuromodulation and smooth muscle relaxation, was recently identified in C. pepo seeds. Since A1 adenosine receptors
[...] Read more.
Hydroethanolic Cucurbita pepo seed extracts are traditionally used for alleviating lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), yet their mechanisms remain unclear. Adenosine, a purine nucleoside involved in neuromodulation and smooth muscle relaxation, was recently identified in C. pepo seeds. Since A1 adenosine receptors (A1AR) suppress parasympathetic bladder overactivity by inhibiting acetylcholine (ACh) release, we investigated to which extent purines from pumpkin seed extracts contribute to A1AR activation. Complementary antioxidant capacity was assessed using the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) assay. Three hydrophilic seed extracts containing different adenosine levels (0.60–1.18 mg/g dw) were evaluated for agonist activity using a cAMP inhibition assay. The most active extract showed an EC50 of 40.22 µg/mL. Selective removal of adenosine shifted the dose–response curve rightward, while further elimination of an adenosine derivative increased the EC50 to 212.10 µg/mL, confirming adenosine as the principal active compound. Guanosine and inosine did not exhibit A1AR agonist or allosteric effects. All samples exhibited measurable but weak antioxidant activity (IC50 = 1.02–4.19 mg/mL), consistent with their low total phenolic content. These findings underscore the importance of accounting for naturally occurring agonists in plant extracts to avoid overestimating receptor-mediated effects in vitro which are not translatable in vivo.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Normalization of Immune Response via Chondroitin Sulfate and Fucoidan Targeting N-Acetylgalactosaminidase
by
Jozef Zima, Eva Nováková, Miroslava Špaglová and Miroslava Šupolíková
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 47; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040047 - 25 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This review explores the pharmacological potential of chondroitin sulfate and fucoidan as immunomodulatory agents targeting N-acetylgalactosaminidase (nagalase) to normalize immune responses. Nagalase, an enzyme produced by tumor and virus-infected cells, contributes to immune suppression by deactivating macrophage-activating factor. Both chondroitin sulfate and fucoidan,
[...] Read more.
This review explores the pharmacological potential of chondroitin sulfate and fucoidan as immunomodulatory agents targeting N-acetylgalactosaminidase (nagalase) to normalize immune responses. Nagalase, an enzyme produced by tumor and virus-infected cells, contributes to immune suppression by deactivating macrophage-activating factor. Both chondroitin sulfate and fucoidan, as representatives of glycosaminoglycans and heteropolysaccharides, exhibit significant potential in inhibiting nagalase activity, thereby restoring immune functionality. Chondroitin sulfate, a key component of the extracellular matrix, demonstrates anti-inflammatory and tissue-regenerative properties by modulating nuclear factor (NF)-κB pathways and cytokine expression. Fucoidan, a sulfated polysaccharide derived from brown seaweed, enhances immune responses through macrophage and natural killer cell activation, while also exhibiting antiviral and anticancer activities. This dual action positions these compounds as promising agents for therapeutic interventions in chronic inflammatory conditions, cancer, and infectious diseases. The synergistic effects of chondroitin sulfate and fucoidan highlight their potential to address the root causes of immune dysregulation. This review aims to elucidate the underlying mechanisms of action and explore the clinical applications of these compounds within the framework of innovative immunotherapeutic strategies. However, current evidence is limited by the predominance of preclinical studies and variability in experimental models. Well-designed clinical trials are needed to validate their efficacy for therapeutic use.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Biophysical and Computational Analysis of a Potent Antimalarial Compound Binding to Human Serum Albumin: Insights for Drug–Protein Interaction
by
Kashish Azeem, Babita Aneja, Amad Uddin, Asghar Ali, Haider Thaer Abdulhameed Almuqdadi, Shailja Singh, Rajan Patel and Mohammad Abid
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(3), 46; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93030046 - 11 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
We aimed to investigate the interaction mechanism of transport protein Human serum albumin (HSA) with a synthesized compound, QP-11, with tested antimalarial properties to monitor the changes in the protein because of QP-11 binding. The interaction between the antimalarial compound QP-11 and HSA
[...] Read more.
We aimed to investigate the interaction mechanism of transport protein Human serum albumin (HSA) with a synthesized compound, QP-11, with tested antimalarial properties to monitor the changes in the protein because of QP-11 binding. The interaction between the antimalarial compound QP-11 and HSA was thoroughly investigated through a multidimensional approach, utilizing UV-VIS spectroscopy, fluorescence, time-resolved fluorescence, and CD (Circular dichroism), alongside molecular docking techniques. Our findings unveiled a robust 1:1 binding pattern, signifying a strong affinity between QP-11 and HSA. Employing static quenching, evidenced by time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy, QP-11 was observed to induce fluorescence quenching of HSA, particularly binding to subdomain IIA. Thermodynamic parameters indicated that van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonding predominantly facilitated the binding, with increased temperature compromising complex stability. The 3D fluorescence and CD results demonstrated QP-11-induced conformational changes in HSA. Both experimental and in silico analyses suggested a spontaneous, exothermic binding reaction. The profound impact of the QP-11–HSA interaction underscores the potential for QP-11 in antimalarial drug development, encouraging further exploration for dose design and enhanced pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties.
Full article

Graphical abstract

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal MenuJournal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Bioengineering, Molecules, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Processes, Sci. Pharm.
Complementary Strategies in Drug Delivery: From Particle Engineering to System Optimization
Topic Editors: Barbara R. Conway, Hisham Al-ObaidiDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Cancers, IJMS, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Sci. Pharm., Current Oncology, Molecules
Recent Advances in Anticancer Strategies, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Hassan Bousbaa, Zhiwei HuDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
CIMB, Molecules, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Sci. Pharm.
Challenges and Opportunities in Drug Delivery Research, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Lenuta Profire, Ioana Mirela VasincuDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topic in
Cancers, CIMB, Current Oncology, Sci. Pharm., Antibodies, IJMS, IJTM
Antibody-Mediated Therapy and Other Emerging Therapies in Cancer Treatment
Topic Editors: Won Sup Lee, Yaewon Yang, Seil GoDeadline: 31 July 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Sci. Pharm.
Monoclonal Antibodies in the Treatment of Diseases: Focus on Stability, Storage, and Administration
Guest Editor: Stefano RugaDeadline: 31 May 2026
Special Issue in
Sci. Pharm.
Anticancer Potential of Natural Products
Guest Editor: Yulin RenDeadline: 31 May 2026
Special Issue in
Sci. Pharm.
Pharmaceutical Applications of Heterocyclic Compounds
Guest Editor: Thierry BessonDeadline: 31 May 2026
Special Issue in
Sci. Pharm.
Computer-Aided Drug Design and Molecular Synthesis
Guest Editors: Osvaldo Santos-Filho, Arthur Eugen KümmerleDeadline: 31 May 2026








