- Feature Paper
- Article
Quality of School and Housing Prices: A Study for the Apartment Market in Porto Alegre, Brazil
- Luiz Andrés Ribeiro Paixão and
- Carolina Barbosa Seidel da Costa
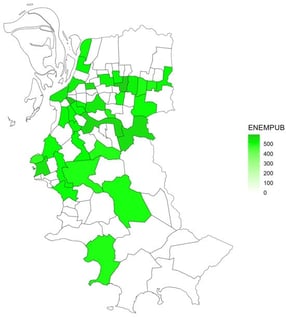
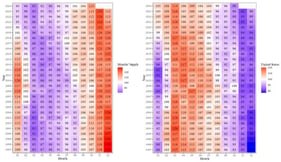
We use the hedonic price model to measure the effect of school quality on apartment rent prices in Porto Alegre, Brazil. A spatial autoregressive regression (SAR) was employed due to the spatial nature of the data. We estimated the effect of school quality on apartment prices for public and private schools separately. The results shed light on the relation between school quality and apartment prices in a Global South context. We showed that both public and private school quality is valued in Porto Alegre house markets, although the effect is quite different for each type of school. For public schools, the major effect comes from the distance of the nearest schools. An increase in test scores by one standard deviation raises apartment rent prices by 2.7% for the whole city. However, this effect is bigger for some submarkets, reaching 11.6% for the distant suburbs. For private schools, the same effect occurs but for a larger distance radius. The same increase in average test score out to a 2 km distance from private schools raised the apartment price by 1.0%. Nevertheless, this effect reaches 6.6% in one specific submarket.
27 January 2026