- Technical Note
A Facile and High-Throughput Immobilization Method for Fractionated Radiotherapy of Unanesthetized Mice Bearing Subcutaneous Tumors Using a 6 MV LINAC Clinical Facility
- Ali Nazarizadeh,
- Quy Van-Chanh Le and
- Ivan Kempson
- + 4 authors
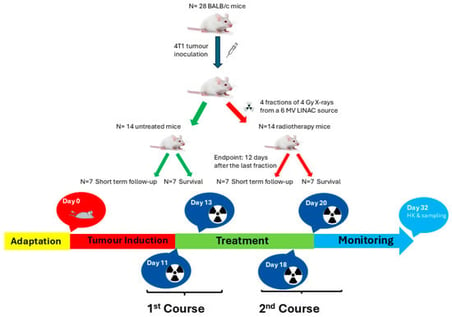
Anesthesia is the gold standard for immobilization of tumor-bearing mice before radiotherapy which potentially induces stress and distorts disease progression. Irradiation of preclinical cancer models with clinical MV linear accelerator (LINAC) beams can benefit the translation of new strategies in radiation oncology. However, logistical constraints prohibit widespread use of clinical facilities. Currently, there is no detailed protocol on how to safely introduce mice to a clinical environment to be intervened on using hospital equipment. Here, a facile and high-throughput handling method is described that eliminates anesthesia and enables fractionated radiotherapy of multiple mice simultaneously for high-throughput studies. Subcutaneous breast tumor-bearing BALB/c mice were restrained in plastic restraint cones within a containment tray and received four fractions of 4 Gy X-rays from a 6 MV LINAC source over two weeks (two fractions/week). Both short- and long-term follow-up revealed no identifiable health issues or complications associated with the restraint procedure or radiation exposure in terms of body weight loss, skin burns or body condition scores. This method not only benefits animal welfare but also data quality by reducing stress/discomfort levels and confounding effects of anesthetics. It can be applied to a broader range of studies where mice need to be immobilized before intervention.
4 February 2026