- Article
Underwater Electrical Explosions of Different Metal Wires on the Microsecond Timescale
- Ron Grikshtas,
- Sergey Efimov and
- Yakov E. Krasik
- + 1 author
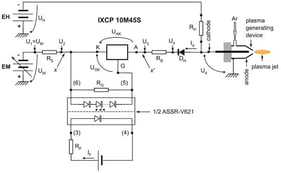
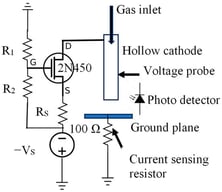
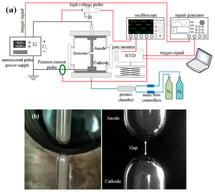
Underwater electrical explosions of single metallic wires driven by microsecond current pulses are investigated and compared with previously reported sub-microsecond experiments. Current and voltage waveforms, streak camera shadow imaging, and one-dimensional hydrodynamic simulations are employed to characterize how the energy density, energy density deposition rate, and the generated shock waves in water depend on the wire parameters. It was found that, similar to the sub-microsecond timescale, the solid–liquid phase transition occurs later than thermodynamic calculations predicted, while the liquid–vapor phase transition happens sooner than expected, leading to a two-phase coexistence. Additionally, most materials show a notable resistance peak (Ti, Fe, Ni, Zn, Ag, Sn, Ta, Au) compared to a quasi-plateau for Cu and Mo or a continuous increase for Al and Pt. Moreover, the specific action integral values are significantly smaller than those observed in wire explosion experiments in vacuum. Finally, the plasma formed at peak resistive voltage is non-ideal but exhibits lower electron density, ionization degree, and temperature compared to the sub-microsecond case.
11 February 2026