- 4.1Impact Factor
- 7.6CiteScore
- 18 daysTime to First Decision
Calcium Signaling in Plant Biotic Interactions and Defense
This special issue belongs to the section “Plant Protection and Biotic Interactions“.
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
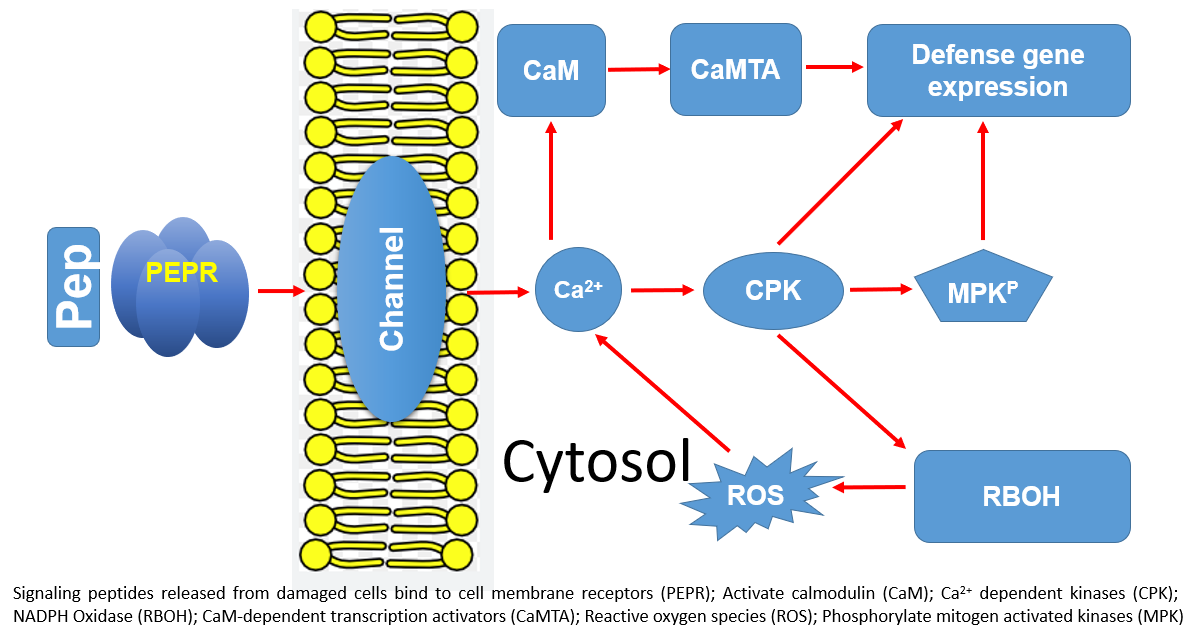
Ca2+ signaling is important in every organism and is involved in numerous signal cascades initiated by many different stimuli and stresses. In plants, transient increases in the concentration of Ca2+ serve to transduce signals received by membrane receptors in the form of ligand binding. These transitory signals are translated into downstream responses in the cytosol and membrane-bounded organelles after perception by Ca2+sensor proteins. Ca2+-binding proteins such as Ca2+-dependent kinases, calmodulins (and calmodulin-like proteins), and calcineurin B-like proteins are all involved. The responses to Ca2+ signaling include short-term effects such as reactive oxygen species generation, MAP kinase activation, gene expression regulation, and extracellular pH changes. Longer-term effects include structural changes, e.g., the formation of root nodules associated with Rhizobium spp, production of defensive compounds (in the case of biotic threats), and alteration of the growth–defense tradeoff. Advances in elucidating the mechanisms of Ca2+ signaling, including the “decoding” of this ubiquitous ion by sensor proteins, will lead to a greater understanding of the roles of Ca2+ in biotic interactions. This requires studying each stage in plant-signaling cascades. Assessing biotic interactions between plants and other organisms (and viruses) is becoming even more important. In light of both the intensification of disease/herbivory pressures faced in agriculture and conservation and the popularity of sustainable agriculture that makes use of plant innate signaling and biocontrols.
This Special Issue aims to offer new insights into how Ca2+ signaling affects plant biotic interactions. Contributions are welcomed from scientists working at all system levels, including molecule, cell, organism, and environment/ecological perspectives. Studies addressing any of the above aspects of plant Ca2+ signaling would be appropriate contributions.
Prof. Dr. Gerald A. Berkowitz
Dr. Mang Ma
Dr. Alice Kira Zelman
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Plants is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Ca2+ ion channels
- Ca2+-binding proteins
- Ca2+ protein kinase
- Ca2+ ATPase
- calcium signal transduction
- plant–biotic interactions
- plant defense responses
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- e-Book format: Special Issues with more than 10 articles can be published as dedicated e-books, ensuring wide and rapid dissemination.

