- Review
Microwave-Assisted Processing of Advanced Materials: A Comprehensive Review of CNR-SCITEC Genova Developments
- Maurizio Vignolo
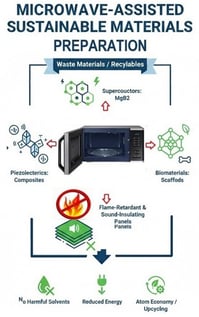
Microwave-assisted heating (MWH) has established itself as a transformative and energy-efficient paradigm for advanced materials processing. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the advances achieved at the CNR-SCITEC laboratories in Genoa. In this context, a customized microwave platform has been strategically employed for the synthesis, sintering, foaming, and melting of diverse inorganic, organic, and hybrid systems. The spectrum of materials investigated includes superconducting magnesium diboride (MgB2), hydroxyapatite-based scaffolds, polyethylene components obtained via microwave-assisted rotational molding, cork-based sound-adsorbing composites, recycled expanded polystyrene (rEPS) panels, and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) piezoelectric films. Across the case studies, MWH demonstrated a superior capacity for reducing energy consumption and processing times while maintaining—or even enhancing—the target functional properties. Furthermore, this work evaluates the technological maturity and emerging market opportunities of microwave-based processing, positioning it as a key and sustainable platform for next-generation materials development.
31 January 2026



![Self-injection-locked magnetron from reference [55].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/microwave/microwave-02-00003/article_deploy/html/images/microwave-02-00003-g001-550.jpg)