-
 Probiotic Potential of Pediococcus acidilactici SWP-CGPA01: Alleviating Antibiotic-Induced Diarrhea and Restoring Hippocampal BDNF
Probiotic Potential of Pediococcus acidilactici SWP-CGPA01: Alleviating Antibiotic-Induced Diarrhea and Restoring Hippocampal BDNF -
 Tracing Zoonotic Pathogens Through Surface Water Monitoring: A Case Study in China
Tracing Zoonotic Pathogens Through Surface Water Monitoring: A Case Study in China -
 An Insight into Strain-Specificity of Streptomyces chrestomyceticus ADP4 and Identification of a Novel Peptide with Potential Antiviral Activities Against Significant Human Viruses, Including SARS-CoV2, HCV, and HIV
An Insight into Strain-Specificity of Streptomyces chrestomyceticus ADP4 and Identification of a Novel Peptide with Potential Antiviral Activities Against Significant Human Viruses, Including SARS-CoV2, HCV, and HIV -
 The Growing Antibiotic Resistance of Campylobacter Species: Is There Any Link with Climate Change?
The Growing Antibiotic Resistance of Campylobacter Species: Is There Any Link with Climate Change?
Journal Description
Microbiology Research
Microbiology Research
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal published monthly online by MDPI (from Volume 11, Issue 2 - 2020).
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), Embase, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 20.2 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 5.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
2.2 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.1 (2024)
Latest Articles
Gamsia batmanii sp. nov. Isolated from a Common Bent-Wing Bat and the Review of the Genus Gamsia
Microbiol. Res. 2026, 17(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres17010009 (registering DOI) - 3 Jan 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Cave ecosystems represent environmentally constrained habitats that host diverse and highly specialized fungal communities. Many cave-dwelling fungi act as decomposers, transient colonizers, or cave fauna symbionts. During a mycological survey of Sesalačka cave (Serbia), a previously undescribed species was isolated from the skin
[...] Read more.
Cave ecosystems represent environmentally constrained habitats that host diverse and highly specialized fungal communities. Many cave-dwelling fungi act as decomposers, transient colonizers, or cave fauna symbionts. During a mycological survey of Sesalačka cave (Serbia), a previously undescribed species was isolated from the skin of a Miniopterus schreibersii. The aim of this study was to characterize this isolate using an integrative taxonomic approach combining morphology, physiology, and multilocus phylogenetics. The fungus was cultured on different media under and its morphophysiological traits were recorded. DNA sequences of ITS, LSU, SSU, and TEF1α were compared with existing Gamsia species and phylogenetic analysis placed the isolate within the Gamsia clade, forming a well-supported lineage the most closely related to G. aggregata, but differing from it by 8–12 base pairs across loci. Distinctive morphological features of this species include obovoid to pyriform polyblastic conidia, hyaline to pale-brown annelloconidia, and reduced conidiophores, clearly separating the species from described congeners. It is psychrotolerant and does not grow at 37 °C, suggesting it is a cave-associated saprobe rather than a mammalian pathogen. This study expands the known diversity of Gamsia species and contributes to the growing evidence that subterranean habitats harbor numerous undescribed fungal kingdom members.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Bacterial Resistance in the ICU: A Comparative Analysis of Pre-Pandemic and Pandemic Periods and the Impact on Clinical Outcomes
by
Geane Andriollo Paradynski, Ronaldo dos Santos Machado, Lucas Machado Sulzbacher, Maicon Machado Sulzbacher, Vítor Antunes de Oliveira, Pauline Brendler Goettems Fiorin, Mirna Stela Ludwig, Thiago Gomes Heck and Matias Nunes Frizzo
Microbiol. Res. 2026, 17(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres17010008 - 30 Dec 2025
Abstract
Inappropriate use of antibiotics can stimulate antimicrobial resistance, since bacteria are capable of circumventing pharmacological action through various resistance mechanisms. Recently, during the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been an increase in the use of antimicrobials. This is an analytical, quantitative, and retrospective study
[...] Read more.
Inappropriate use of antibiotics can stimulate antimicrobial resistance, since bacteria are capable of circumventing pharmacological action through various resistance mechanisms. Recently, during the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been an increase in the use of antimicrobials. This is an analytical, quantitative, and retrospective study on bacterial resistance and mortality in Intensive Care Unit (ICU) patients from 2017 to 2022. This study analyzed sociodemographic aspects, clinical, and laboratory parameters in patients admitted to the ICU. A total of 221 medical records of patients with multidrug-resistant bacteria in the ICU were included, with an outcome of 95 discharges (42.98%) and 126 deaths (53.01%). An increase in the prevalence of bacterial resistance in the ICU was identified during the Pandemic period, when compared to the Pre-Pandemic period. It was identified that the increase in bacterial resistance of some pathogens was associated with death. It was also observed that age was a factor for an increased risk of mortality in the ICU, no matter the sex of the patient. Importance of careful analysis in the use of antimicrobials, as well as in the care of ICU patients and in the surveillance of bacterial infections by health professionals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Multidrug Resistance Across Pathogens: Fungi, Bacteria, Parasites, and Viruses)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Salivary Oral Microbiota in Patients with Prediabetes Undergoing Intragastric Balloon Surgery
by
Rabab A. D. Meshan, Norah Ahmed AlOsaimi, Abdulmohsen Redha and Maribasappa Karched
Microbiol. Res. 2026, 17(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres17010007 - 30 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Kuwait faces a significant public health challenge from obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), conditions known to disrupt the natural balance of oral bacteria. This imbalance, or dysbiosis, can promote gum disease and may worsen metabolic health. While the intragastric balloon (IGB)
[...] Read more.
Kuwait faces a significant public health challenge from obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), conditions known to disrupt the natural balance of oral bacteria. This imbalance, or dysbiosis, can promote gum disease and may worsen metabolic health. While the intragastric balloon (IGB) is a common, less invasive weight-loss procedure, its specific effect on the community of bacteria in saliva remains unclear, especially for high-risk groups. The objective of this study was to investigate changes in the salivary microbiota of obese prediabetic patients following IGB placement. We recruited 20 obese patients (11 female, 9 male; average age 31.5) from a clinic in Kuwait. Saliva samples were collected just before IGB (Allurion™) insertion and again 6 weeks after that. Using 16S rRNA gene sequencing, we identified the bacterial species present and used bioinformatic tools to analyze diversity and abundance. Our analysis revealed that the overall diversity and structure of the salivary microbial community remained stable after the procedure. However, we detected notable changes in specific types of bacteria. The relative abundance of several genera, including Veillonella, Porphyromonas, and Fusobacterium, shifted significantly. At the species level, Porphyromonas pasteri and Haemophilus parainfluenzae became less abundant, while certain Veillonella and Streptococcus species increased in number after the IGB was placed. In conclusion, for obese prediabetic patients in Kuwait, the salivary microbiome demonstrates remarkable stability in the weeks following IGB surgery. The procedure did not drastically alter the overall ecosystem, but it did trigger specific, subtle changes in certain bacterial populations. This suggests the oral microbiota is resilient, adapting to the new physiological conditions without a major upheaval.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Identification and Characterization of a Proteinaceous Antibacterial Factor from Pseudomonas extremorientalis PEY1 Active Against Edwardsiella tarda
by
Hyun-Sol Jo, Youl-Lae Jo and Sun-Mee Hong
Microbiol. Res. 2026, 17(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres17010006 - 30 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Pseudomonas extremorientalis PEY1, isolated from the intestinal contents of marine fish, was evaluated for the production and properties of antibacterial proteins active against Edwardsiella tarda, a major pathogen in aquaculture. Antibacterial production was maximized in a minimal medium supplemented with 1% yeast
[...] Read more.
Pseudomonas extremorientalis PEY1, isolated from the intestinal contents of marine fish, was evaluated for the production and properties of antibacterial proteins active against Edwardsiella tarda, a major pathogen in aquaculture. Antibacterial production was maximized in a minimal medium supplemented with 1% yeast extract and 1% galactose under stationary cultivation at 25 °C and pH 7.0. Growth and bioactivity assays were conducted under varying carbon and nitrogen sources, temperatures, and pH levels. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis revealed a distinct ~37 kDa protein band corresponding to antibacterial activity, exhibiting an inhibition zone of 2.4 ± 0.1 cm against E. tarda. The activity was completely abolished by papain digestion but remained detectable after exposure to 55 °C and pH 8, indicating that the active compound is a moderately heat-stable, proteinaceous antibacterial molecule. LC–MS/MS analysis identified the protein as a putative disulfide reductase with ~40% sequence coverage. The antibacterial factor exhibited strong physicochemical stability, retaining activity in the presence of surfactants and metal ions. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that P. extremorientalis PEY1 produces a thermostable, papain-sensitive antibacterial protein with selective activity against E. tarda, highlighting its potential as a promising natural biocontrol or postbiotic candidate for sustainable aquaculture.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Growth of Ectomycorrhizal Fungi on Inorganic and Organic Nitrogen Sources
by
Burenjargal Otgonsuren, Hangyu Lan and Douglas L. Godbold
Microbiol. Res. 2026, 17(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres17010005 - 25 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In forest soils, nitrogen (N) is present in inorganic and organic forms. The organic forms include monomeric amino acids, but also polymers such as chitin. Ectomycorrhizal fungi are known to take up both inorganic and organic N forms, and to depolymerize large organic
[...] Read more.
In forest soils, nitrogen (N) is present in inorganic and organic forms. The organic forms include monomeric amino acids, but also polymers such as chitin. Ectomycorrhizal fungi are known to take up both inorganic and organic N forms, and to depolymerize large organic compounds; however, it is unknown if the compounds are used for growth. The aim of this investigation was to determine the growth of a range of ectomycorrhizal fungi on inorganic and organic N sources. Seven ectomycorrhizal fungi and one endophyte originating from mountain regions either in Austria, Mongolia, or Slovenia were grown in in-vitro cultures containing ammonium, nitrate, or chitin. Four ectomycorrhizal fungi were used to investigate growth on amino acids. All fungi, except Paxillus involutus, utilized nitrate as a N source. All fungi also grew on both chitin and N-acetylglucosamine, the amino sugar precursor of chitin. Paxillus involutus and Melanogaster broomeanus showed enhanced growth on chitin-containing media. Amanita muscaria, Rhizopogon roseolus, and Suillus granulatus, but not Paxillus involutus, were able to utilize the amino acids glycine and glutamate, as well as the tripeptide triglycine. The ability to utilize the different N sources was independent of the origin of the fungi.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Regulatory Mechanisms of Fumonisin Biosynthesis and Applications in Food Safety and Biotechnology
by
Lei Fan, Yuqing Lei, Zhihui Qi, Haiyang Zhang, Lin Tian and Fang Tang
Microbiol. Res. 2026, 17(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres17010004 - 24 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Fumonisins, a major class of mycotoxins, pose significant health risks to humans and animals due to their widespread contamination and potent toxicity. Recent advances in molecular biology, biochemistry, and enzymology have greatly enhanced the understanding of fumonisin biosynthesis and its genetic regulation. The
[...] Read more.
Fumonisins, a major class of mycotoxins, pose significant health risks to humans and animals due to their widespread contamination and potent toxicity. Recent advances in molecular biology, biochemistry, and enzymology have greatly enhanced the understanding of fumonisin biosynthesis and its genetic regulation. The key biosynthetic genes are typically organized in clusters and regulated by specific transcription factors; increasing evidence also highlights the involvement of complex transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms. Environmental factors such as nitrogen, carbon, and pH also modulate these regulatory networks. Despite substantial progress, critical gaps remain in fully elucidating the regulatory pathways that control fumonisin production. This review synthesizes current knowledge regarding fumonisin biosynthesis, gene clusters, and multi-level regulatory mechanisms, while emphasizing recent trends, existing challenges, and potential applications in food safety and biotechnology to enhance food security and promote sustainable development.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Ureaplasma Species and Human Papillomavirus Coinfection and Associated Factors Among South African Adolescent Girls and Young Women
by
Sinazo Kondlo and Zizipho Z. A. Mbulawa
Microbiol. Res. 2026, 17(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres17010003 - 23 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Ureaplasma species are associated with various reproductive health issues, while human papillomavirus (HPV) is associated with cervical, vaginal and vulvar cancers. Data on the association between Ureaplasma species and HPV are limited in South Africa. This study investigated the prevalence of Ureaplasma urealyticum
[...] Read more.
Ureaplasma species are associated with various reproductive health issues, while human papillomavirus (HPV) is associated with cervical, vaginal and vulvar cancers. Data on the association between Ureaplasma species and HPV are limited in South Africa. This study investigated the prevalence of Ureaplasma urealyticum (U. urealyticum), Ureaplasma parvum (U. parvum), and HPV coinfection and their associated factors, among adolescent girls and young women (AGYW) in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. A total of 214 participants were retrospectively recruited, and secondary data on HPV, U. urealyticum, U. parvum, demographics, and sexual behavior were used. HPV was detected using the Roche Linear Array HPV Genotyping Test, while U. urealyticum and U. parvum were detected using Allplex™ sexually transmitted infection (STI) essential Assay. Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism Version 8.0.1.244. The prevalence of U. urealyticum was 43.9% (94/214) and increased significantly with age (p = 0.036, R2 = 0.8497); while U. parvum prevalence was 68.7% (147/214) and was not influenced by age. Having four to six lifetime sexual partners (PR: 1.77, 95% CI: 1.04–3.00, p = 0.043) was associated with increased risk of U. urealyticum. A proportion of 36.3% (77/212) had HPV-U. urealyticum coinfection and its risk was increased among those with 3–6 lifetime sexual partners (PR: 1.59, 95% CI: 1.10–2.53, p = 0.017), 2–4 new partners past three months (PR: 2.14, 95% CI: 1.19–2.42, p = 0.021); vaginal sexual intercourse frequency past 1-month (2–3 vaginal intercourse: PR: 1.54, 95% CI: 1.06–2.53, p = 0.037; 4–10 vaginal intercourse: PR: 1.91, 95% CI: 1.83–1.91, p = 0.005) and alcohol consumption (PR: 1.85, 95% CI: 1.20–3.28, p = 0.004). U. urealyticum positives had a significantly higher risk of HPV types targeted by Cervarix® HPV vaccine than negatives (PR: 2.56, 95% CI: 1.23–5.37, p = 0.013), Gardasil®4 (PR: 2.16, 95% CI: 1.25–3.75, p = 0.006) and Gardasil®9 (PR: 1.70, 95% CI: 1.25–2.32, p = 0.001). AGYW of Eastern Cape Province, South Africa had high prevalence of U. urealyticum-HPV and U. parvum-HPV coinfections. Ureaplasma species coinfection was associated with HPV prevalence and distribution of genotypes. The U. urealyticum prevalence and its coinfection with HPV were associated with sexual behavior. Data from this study could contribute to the design of sexual health and STI interventions and could serve as a baseline for future epidemiological studies, which include ongoing surveillance of HPV genotype prevalence to evaluate the impact and effectiveness of HPV vaccination programs in the population.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Spatio-Temporal Presumptive Identification of Enterococcus spp. and Vibrio spp. in Water from the Veracruz Reef System National Park in the Central Gulf of Mexico
by
Fátima Jael Olvera-Muñoz, Martina Hilda Gracia-Valenzuela, Fabiola Lango-Reynoso, Olaya Pirene Castellanos-Onorio, Jesús Montoya-Mendoza, Christian Reyes-Velázquez, María de Lourdes Fernández-Peña, Bani Mariana Ruesgas-Ramon and María del Refugio Castañeda-Chávez
Microbiol. Res. 2026, 17(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres17010002 - 21 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The Veracruz Reef System National Park (VRSNP), located in the central Gulf of Mexico, is one of the country’s most ecologically and economically significant coral systems. Despite its high biodiversity and ecosystem functionality, it is affected by anthropogenic inputs such as fluvial discharges,
[...] Read more.
The Veracruz Reef System National Park (VRSNP), located in the central Gulf of Mexico, is one of the country’s most ecologically and economically significant coral systems. Despite its high biodiversity and ecosystem functionality, it is affected by anthropogenic inputs such as fluvial discharges, urban effluents, and port and tourism activities that contribute organic and bacteriological loads. This study aimed to identify the presence of Enterococcus spp. and Vibrio spp. during three climatic seasons—dry, rainy, and north winds—at two water column depths (surface and bottom) across three reefs (Enmedio, Chopas, and Gallega) within the VRSNP during the 2022 annual cycle. Samples were analyzed according to national and international standards. Results showed that Vibrio spp. were influenced mainly by temporal factors, with higher values during north winds and the dry season (>1100 MPN/100 mL); otherwise, rainy conditions reported the lowest load (184.89 ± 15.00 MPN/100 mL). While Enterococcus spp. exhibited greater spatial influence, particularly in surface waters, Enmedio Reef recorded the highest load (478.34 ± 37.28 CFU/100 mL); in addition, Chopas Reef reported the lowest at the bottom (12.43 ± 1.26 CFU/100 mL). The findings highlight the need to strengthen microbiological monitoring protocols in marine coastal ecosystems to assess water quality, public health risks, and the ecological integrity of coral reef environments, as well as the implementation of molecular identification techniques.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Lysinibacillus as Microbial Nanofactories: Genomic Mechanisms for Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs)
by
José Luis Aguirre-Noyola, Gustavo Cuaxinque-Flores, Jorge David Cadena-Zamudio, Marco A. Ramírez-Mosqueda, Lorena Jacqueline Gómez-Godínez and Juan Ramos-Garza
Microbiol. Res. 2026, 17(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres17010001 - 19 Dec 2025
Abstract
The green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) by bacteria is a strategic route for sustainable nanobiotechnology; however, the genomic and biochemical mechanisms that make it possible remain poorly defined. In this study, bacteria native to silver-bearing mine tailings in Taxco (Mexico) were isolated,
[...] Read more.
The green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) by bacteria is a strategic route for sustainable nanobiotechnology; however, the genomic and biochemical mechanisms that make it possible remain poorly defined. In this study, bacteria native to silver-bearing mine tailings in Taxco (Mexico) were isolated, capable of tolerating up to 5 mM of AgNO3 and producing extracellular AgNPs. Spectroscopic (430–450 nm) and structural (XRD, fcc cubic phase) characterization confirmed the formation of AgNPs with average sizes of 17–21 nm. FTIR evidence showed the participation of extracellular proteins and polysaccharides as reducing and stabilizing agents. Genomic analyses assigned the isolates as Lysinibacillus fusiformis 31HCl and L. xylanilyticus G1-3. Genome mining revealed extensive repertoires of genes involved in uptake, transport, efflux and detoxification of metals, including P-type ATPases, RND/ABC/CDF transporters, Fe/Ni/Zn uptake systems, and metal response regulators. Notably, homologues of the silP gene, which encode Ag+ translocator ATPases, were identified, suggesting convergent adaptation to silver-rich environments. Likewise, multiple nitroreductases (YodC, YdjA, YfKO) were detected, candidates for mediating electron transfer from NAD(P)H to Ag+. These findings support the role of Lysinibacillus as microbial nanofactories equipped with specialized molecular determinants for silver tolerance and AgNP assembly, providing a functional framework for microorganism-based nanobiotechnology applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Exploring Nanoparticle-Based Antivirals for a Virus-Free Future)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Non- and Medium-Polar Fractions from Trametes villosa Inhibit Staphylococcus aureus Growth, Virulence, and Biofilm Formation
by
Hernando Maldonado-Pérez, Juan Pablo Pinzón-Esquivel, Gloria María Molina-Salinas, Avel Adolfo González-Sánchez, Haziel Eleazar Dzib-Baak, Ángel Dzul-Beh, Carlos Javier Quintal-Novelo and Andrés Humberto Uc-Cachón
Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16(12), 263; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16120263 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus are a health problem worsened by antibiotic resistance. New drugs, including those inhibiting virulence and resistance mechanisms, are needed. This study aimed to evaluate the anti-growth, anti-virulence, and anti-biofilm activities of Trametes villosa. (2) Methods: Fractions
[...] Read more.
Background: Infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus are a health problem worsened by antibiotic resistance. New drugs, including those inhibiting virulence and resistance mechanisms, are needed. This study aimed to evaluate the anti-growth, anti-virulence, and anti-biofilm activities of Trametes villosa. (2) Methods: Fractions were obtained from the basidiomata of T. villosa. Anti-growth, anti-hemolysis, and anti-biofilm activities were tested against S. aureus strains using resazurin microtiter, blood cell lysis, and crystal violet assays, respectively. Cytotoxicity was evaluated in Vero and HaCaT cells using sulforhodamine B. The active fractions were subjected to GC-MS analysis and molecular docking with S. aureus quorum-sensing receptors. Results: The n-hexane and ethyl acetate (EtOAc) fractions exhibited anti-growth activity against all strains (MIC: 31.2–2000 µg/mL). These fractions also displayed anti-hemolysis (IC50 = 33.8 ± 1.1–53.8 ± 5.1 µg/mL) and anti-biofilm formation activity (IC50 = 106.6 ± 4.8–383.4 ± 31.4 µg/mL), while exhibiting low cytotoxicity in Vero and HaCat. GC-MS analysis revealed that both active fractions mainly contained alkanes, aldehydes, and fatty acids. Molecular docking revealed that isovanillic acid, identified in the EtOAc fraction, exhibited optimal interactions with S. aureus quorum-sensing receptors AgrA and SarA. (4) Conclusions: Our research highlights the potential of T. villosa as a source of bioactive compounds effective against S. aureus.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Structure-Based Identification of Ponganone V from Pongamia pinnata as a Potential KPC-2 β-Lactamase Inhibitor: Insights from Docking, ADMET, and Molecular Dynamics
by
Himanshu Jangid, Chirag Chopra and Atif Khurshid Wani
Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16(12), 262; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16120262 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CREs) pose a critical threat to global public health, largely driven by the enzymatic activity of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-2 (KPC-2), a class A serine β-lactamase that hydrolyzes most β-lactam antibiotics. While β-lactamase inhibitors like avibactam offer temporary relief, emerging KPC variants
[...] Read more.
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CREs) pose a critical threat to global public health, largely driven by the enzymatic activity of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-2 (KPC-2), a class A serine β-lactamase that hydrolyzes most β-lactam antibiotics. While β-lactamase inhibitors like avibactam offer temporary relief, emerging KPC variants demand novel, sustainable inhibitory scaffolds. This study aimed to identify and characterize potential natural inhibitors of KPC-2 from Pongamia pinnata, leveraging a comprehensive in silico workflow. A curated library of 86 phytochemicals was docked against the active site of KPC-2 (PDB ID: 3DW0). The top-performing ligands were subjected to ADMET profiling (pkCSM), and 100 ns molecular dynamics simulations (GROMACS) to evaluate structural stability and interaction persistence, using avibactam as control. Ponganone V exhibited the most favorable binding energy (−9.0 kcal/mol), engaging Ser70 via a hydrogen bond and forming π–π interactions with Trp105. Glabrachromene II demonstrated a broader interaction network but reduced long-term stability. ADMET analysis confirmed high intestinal absorption, non-mutagenicity, and absence of hERG inhibition for both ligands. Molecular dynamics simulations revealed that Ponganone V maintained compact structure and stable hydrogen bonding throughout the 100 ns trajectory, closely mirroring the behavior of avibactam, whereas Glabrachromene II displayed increased fluctuation and loss of compactness beyond 80 ns. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) further supported these findings, with Ponganone V showing restricted conformational motion and a single deep free energy basin, while avibactam and Glabrachromene II exhibited broader conformational sampling and multiple energy minima. The integrated computational findings highlight Ponganone V as a potent and pharmacologically viable natural KPC-2 inhibitor, with strong binding affinity, sustained structural stability, and minimal toxicity. This study underscores the untapped potential of Pongamia pinnata phytochemicals as future anti-resistance therapeutics and provides a rational basis for their experimental validation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Probiotic Potential of Pediococcus acidilactici SWP-CGPA01: Alleviating Antibiotic-Induced Diarrhea and Restoring Hippocampal BDNF
by
You-Zuo Chen, Chieh-Ting Chen, Tsung-Wei Shih, Wei-Hsuan Hsu, Bao-Hong Lee and Tzu-Ming Pan
Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16(12), 261; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16120261 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Gut microbiota dysbiosis is increasingly being recognized as a major contributor to host metabolic imbalance, immune dysfunction, and neurophysiological disorders. Probiotics are known to modulate intestinal metabolism and exert systemic effects through the gut–brain axis. Herein, we evaluated the safety and probiotic potential
[...] Read more.
Gut microbiota dysbiosis is increasingly being recognized as a major contributor to host metabolic imbalance, immune dysfunction, and neurophysiological disorders. Probiotics are known to modulate intestinal metabolism and exert systemic effects through the gut–brain axis. Herein, we evaluated the safety and probiotic potential of Pediococcus acidilactici SWP-CGPA01 (SWP-CGPA01) under antibiotic-induced microbiota dysbiosis. Genomic and phenotypic analyses verified its safety profile, supporting its suitability for use in food and nutritional applications. In a mouse model of antibiotic-induced dysbiosis, SWP-CGPA01 supplementation alleviated diarrhea and restored hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression. These findings demonstrate that SWP-CGPA01 is a safe and functionally active probiotic with the potential to maintain gastrointestinal and neurotrophic homeostasis under gut microbiota dysbiosis.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of the Antibiofilm Activity of Clove Essential Oil in the Development of Bioactive Coatings for Arterial Sampling Devices
by
Ikram Markaoui, Meryem Idrissi Yahyaoui, Abdeslam Asehraou, Abdelkrim Daoudi, Brahim Housni and Houssam Bkiyar
Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16(12), 260; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16120260 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Multidrug-resistant (MDR) pathogens and biofilm-associated infections represent a major global health concern, particularly in the context of medical devices such as catheters, tubing, and blood sampling devices. Biofilms, responsible for up to 85% of human infections, confer a high level of microbial resistance
[...] Read more.
Multidrug-resistant (MDR) pathogens and biofilm-associated infections represent a major global health concern, particularly in the context of medical devices such as catheters, tubing, and blood sampling devices. Biofilms, responsible for up to 85% of human infections, confer a high level of microbial resistance and compromise device performance and patient safety. In this study, the antibiofilm potential of Syzygium aromaticum (clove) essential oil was investigated through an in vitro assay. GC–MS analysis revealed eugenol (72.77%) as the predominant compound, accompanied by β-caryophyllene (14.72%) and carvacrol (2.09%). The essential oil exhibited notable antimicrobial activity, producing inhibition zones of 30.5 ± 4.5 mm against Staphylococcus aureus, 24.5 ± 0.5 mm against Micrococcus luteus, 16.0 ± 2.0 mm against Escherichia coli, 13.0 ± 1.0 mm against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, 23.5 ± 1.5 mm against Candida albicans, and 24.0 ± 2.0 mm against C. glabrata. A marked reduction in biofilm biomass observed on polyvinyl chloride (PVC) surfaces. The application of clove essential oil as a coating for PVC-based medical devices remains a future possibility that requires formulation and in vivo testing. This strategy is proposed as potentially eco-safe, although environmental toxicity and biocompatibility have not yet been evaluated. It could contribute to the prevention of biofilm formation in arterial sampling systems and other healthcare-related materials, thereby enhancing device safety and longevity.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Taxonomic and Genomic Characterization of Enterococcus alishanensis JNUCC 77 Isolated from the Flowers of Zinnia elegans
by
Kyung-A Hyun, Ji-Hyun Kim, Min Nyeong Ko and Chang-Gu Hyun
Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16(12), 259; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16120259 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Enterococcus alishanensis JNUCC 77 (=BLH10) was isolated from the flowers of Zinnia elegans collected at Ilchul Land, Jeju Island, Republic of Korea. Whole-genome sequencing was conducted to clarify its taxonomic position, genomic composition, and adaptive metabolic potential. The assembled genome comprised five contigs
[...] Read more.
Enterococcus alishanensis JNUCC 77 (=BLH10) was isolated from the flowers of Zinnia elegans collected at Ilchul Land, Jeju Island, Republic of Korea. Whole-genome sequencing was conducted to clarify its taxonomic position, genomic composition, and adaptive metabolic potential. The assembled genome comprised five contigs totaling 3.86 Mb, with a G + C content of 35.6% and 100% completeness. Genome-based phylogenomic analyses using the Type Strain Genome Server (TYGS) and digital DNA–DNA hybridization (dDDH) confirmed that strain JNUCC 77 belongs to E. alishanensis. Functional annotation revealed enrichment of genes related to transcriptional regulation, carbohydrate metabolism, replication, and DNA repair, suggesting a lifestyle adapted to oxidative and UV-exposed floral habitats rather than pathogenic competitiveness. Genome mining with antiSMASH identified two putative biosynthetic regions associated with terpenoid and isoprenoid metabolism, which are commonly linked to redox regulation and cellular protection. These genomic features indicate that E. alishanensis JNUCC 77 has evolved a metal-assisted, redox-regulated survival strategy suitable for floral microenvironments. Given its origin from vibrant flowers and its genomic potential for redox-protective metabolism, this strain represents an attractive microbial resource for future development of nature-inspired postbiotic and cosmeceutical ingredients that align with the clean and eco-friendly image of flower-derived biotechnologies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Chemical Profiling and Biological Evaluation of Matricaria pubescens as a Promising Source of Antioxidant and Anti-Resistance Agents
by
Elhasnaoui Abdelhadi, Janah Iman, Ait-El-Mokhtar Mohamed, Sellam Khalid, Bouadid Ismail, Eddouks Mohamed, Lahrach Nadia and El-Haidani Ahmed
Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16(12), 258; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16120258 - 9 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Matricaria pubescens (Desf.), a medicinal plant belonging to the Asteraceae family, is traditionally used in southeastern Morocco but remains insufficiently studied. In this study, samples collected from the Zagora region (Morocco) were subjected to the preparation of aqueous, methanolic, and petroleum ether extracts,
[...] Read more.
Matricaria pubescens (Desf.), a medicinal plant belonging to the Asteraceae family, is traditionally used in southeastern Morocco but remains insufficiently studied. In this study, samples collected from the Zagora region (Morocco) were subjected to the preparation of aqueous, methanolic, and petroleum ether extracts, followed by qualitative phytochemical screening. Total phenolic, flavonoid, and condensed tannin contents were quantified. Antioxidant activity was assessed using DPPH, RPC, and ABTS assays, whereas antimicrobial activity was evaluated against eight bacterial and fungal species, including antibiotic-resistant strains, using disc diffusion and microdilution techniques. Qualitative analysis revealed the presence of alkaloids, polyphenols, flavonoids, tannins, sterols, and sesquiterpenes, with notable variation across extracts. The aqueous (AqE) and methanol–water (MT-H2O) extracts were particularly rich in phenolics and flavonoids, recording 9.15 ± 0.29 mg GAE/g DW and 17.1 ± 0.55 mg QE/g DW, respectively. Antioxidant assays showed strong activity, with IC50 values ranging from 3.15 to 5.48 µg/mL (DPPH) and 9.10 to 14.40 µg/mL (ABTS). The MT-H2O extract also displayed potent antimicrobial effects against eight microbial species (bacteria and fungi), with minimum inhibitory concentrations between 0.93 and 30 mg/mL, except for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. These findings highlight the untapped potential of M. pubescens from Zagora as a source of antioxidant and anti-resistance agents, providing new insights for green medicine and future pharmacological research.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Microbiological and Physical–Chemical Quality of Pickled Vegetables Produced by Rural Family Agribusinesses
by
Priscila Endlich Lozer, Rhaiza Marcia Passos Leal and Jackline Freitas Brilhante de São José
Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16(12), 257; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16120257 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The aim of the present study was to assess the microbiological and physical–chemical quality of pickled vegetables produced by rural family agribusinesses in the mountainous region of Espírito Santo State, Brazil. This descriptive, observational and cross-sectional study was carried out on the basis
[...] Read more.
The aim of the present study was to assess the microbiological and physical–chemical quality of pickled vegetables produced by rural family agribusinesses in the mountainous region of Espírito Santo State, Brazil. This descriptive, observational and cross-sectional study was carried out on the basis of secondary data provided by the Food Monitoring Program of Espírito Santo State, Brazil. Data were extracted from sample collection terms and from analysis reports on 58 samples of pickled vegetables produced by 37 rural family agribusinesses, which were collected between June and September 2022. The analyses applied to these samples included Salmonella sp. incidence; molds, yeasts, and Enterobacteriaceae counts; and pH, titratable acidity, and chloride content in sodium chloride determination. The microbiological limits for these products are the absence of Salmonella sp., 102 for Enterobacteriaceae, and 103 for molds and yeasts. For physical–chemical quality, these products must have a pH of 4.5 or lower. All samples were in compliance with the legislation provided for Salmonella and Enterobacteriaceae. In total, 13.79% of the samples (n = 8) presented mold and yeast counts higher than the microbiological limit of 103. The pH of 12.06% (n = 7) of the samples was higher than 4.5, which exceeded the limit established by the legislation. The titratable acidity ranged from 0.25 to 2.82 g of acetic acid/100 g; its mean value reached 0.89 g of acetic acid/100 g. The chloride values ranged from 0.10 to 5.70 g of NaCl/100 g; its mean value reached 1.85 g of NaCl/100 g. Thus, 25.86% (n = 15) of the samples did not comply with the legislation. These results suggested that microbiological and physical–chemical quality were compromised in some of the analyzed samples. This finding indicated likely flaws in good manufacturing practices and quality controls, and it can pose risks to consumer health.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prospective Yeast Species with Enzymatic, Aromatic, and Antifungal Applications Isolated from Cocoa Fermentation in Various Producing Areas in Côte d’Ivoire
by
Alfred Koffi Yao, Guy Florent Kouamé Amien, Brice Judicaël Assi-Clair, Nabounou Koné, Mai Koumba Koné, Kevin Bethune, Isabelle Maraval, Vincent Chochois, Jean-Christophe Meile, Renaud Boulanger and Simplice Tagro Guéhi
Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16(12), 256; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16120256 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This research study investigated the potential biotechnological applications of yeast species obtained from cocoa fermentation performed in Côte d’Ivoire. A total of 279 yeast isolates were molecularly identified and then screened for their antifungal ability against various Aspergillus species and for the production
[...] Read more.
This research study investigated the potential biotechnological applications of yeast species obtained from cocoa fermentation performed in Côte d’Ivoire. A total of 279 yeast isolates were molecularly identified and then screened for their antifungal ability against various Aspergillus species and for the production of aromatic compounds and extracellular enzymes. Thirty-one yeast species belonging to nineteen genera, dominated by Pichia, Candida, Hanseniaspora, and Rhodotorula, were isolated from fermented cocoa beans. All extracellular enzymes screened were produced by most yeast species, except β-glucanase and esterase activity, whereas the most common enzyme was β-glucosidase. Yeasts of the Pichia, Saccharomyces, Candida, Clavispora, and Hanseniaspora genera produced various enzymes, including xylanase, β-glucosidase, polygalacturonase, invertase, pectinase, and chitinase. The 88 aromatic compounds produced were grouped into five main chemical families, including esters, alcohols, acids, aldehydes, and ketones. Wickerhamomyces anomalus was the highest producer of major desirable aromatic compounds, including alcohols, ketones, and esters. All yeast species showed a specific antagonistic effect against the growth of various Aspergillus species, but Candida incommunis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and Torulaspora delbrueckii recorded the greatest antifungal ability. These yeast species could be used to develop promising starter cultures to improve the organoleptic quality of various fermented foods and beverages.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Genome Insights into Kocuria sp. KH4, a Metallophilic Bacterium Harboring Multiple Biosynthetic Gene Clusters (BGCs)
by
Gustavo Cuaxinque-Flores, Lorena Jacqueline Gómez-Godínez, Alma Armenta-Medina, Lily X. Zelaya-Molina, Juan Ramos-Garza and José Luis Aguirre-Noyola
Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16(12), 255; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16120255 - 7 Dec 2025
Abstract
The genus Kocuria includes Gram-positive and environmentally versatile bacteria, which are of biotechnological interest due to their ability to synthesize secondary metabolites. In this study, the genome of Kocuria sp. KH4, isolated from alkaline mine tailings (southeastern Mexico), was sequenced and analyzed to
[...] Read more.
The genus Kocuria includes Gram-positive and environmentally versatile bacteria, which are of biotechnological interest due to their ability to synthesize secondary metabolites. In this study, the genome of Kocuria sp. KH4, isolated from alkaline mine tailings (southeastern Mexico), was sequenced and analyzed to determine its taxonomic affiliation and explore its metabolic and adaptive potential. The assembled genome showed a size of 3.89 Mb, a GC content of 73.2%, and 3609 coding genes. Phylogenomic analyses and genomic relationship indices (ANI, AAI, and dDDH) confirmed that strain KH4 represents a novel genomospecies within the genus Kocuria. Functional analysis revealed broad metabolic diversity, with genes associated with the transport and metabolism of amino acids, carbohydrates, and inorganic ions. A total of 165 genes linked to metal resistance and homeostasis mechanisms were identified, including ABC-type transport systems and ATPases, as well as specific genes for Fe, Ni, Zn, Cu, As, and Hg. Forty-eight genomic islands were also identified, encoding a wide variety of functions and mobile genetic elements (MGEs). Furthermore, six biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) involved in the production of nonribosomal peptides, type III polyketides, terpenes, and siderophores were detected, suggesting a remarkable potential for the synthesis of bioactive compounds. Taken together, the results highlight this strain as a promising source of secondary metabolites with potential applications in environmental, pharmaceutical, and industrial biotechnology, underscoring the importance of Kocuria genomes as natural reservoirs of new biosynthetic pathways.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Microorganisms and Their Incredible Potential to Face Societal Challenges)
►▼
Show Figures
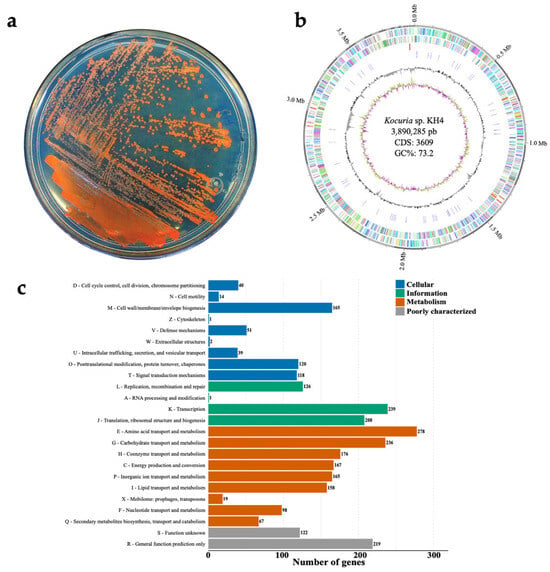
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Relapsing Visceral Leishmaniasis and Post-Kala-Azar Dermal Leishmaniasis in a Patient with Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy Under Immunosuppression: A Case Report
by
Marta Chiara Sircana, Elena Bozzi, Alfredo Caturano, Francesca Cherchi, Sergio Babudieri and Roberto Manetti
Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16(12), 254; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16120254 - 4 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Visceral leishmaniasis (VL) is a neglected vector-borne disease caused by obligate intracellular protozoa of the genus Leishmania. In immunocompromised patients, VL may present atypically, progress more aggressively, and respond less favorably to treatment. We present the case of a 62-year-old male with
[...] Read more.
Visceral leishmaniasis (VL) is a neglected vector-borne disease caused by obligate intracellular protozoa of the genus Leishmania. In immunocompromised patients, VL may present atypically, progress more aggressively, and respond less favorably to treatment. We present the case of a 62-year-old male with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) receiving long-term corticosteroids and azathioprine who developed relapsing VL complicated by post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis (PKDL). The patient initially presented with prolonged fever, pancytopenia, hepatosplenomegaly, and weight loss. Bone marrow aspirate revealed Leishmania amastigotes. Intravenous lyposomal amphotericin B (L-AMB) achieved temporary remission; however, PKDL and VL recurred one year later. Despite receiving sequential therapy with L-AMB and miltefosine, the patient experienced further relapses, likely due to severe T- and B-cell lymphopenia and marasmic-like malnutrition. VL should be considered in the differential diagnosis of prolonged fever and cytopenias in immunosuppressed patients in Mediterranean Europe, even in the absence of travel history. Chronic immunosuppression, secondary immunodeficiency, and malnutrition can significantly impair treatment response and favor recurrence, highlighting the need for integrated clinical, nutritional, and epidemiological management strategies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Molecular Identification of Escherichia coli Isolated from Street Foods: Global Evidence and Public Health Implications
by
Carmine Fusaro, Natalia Guerrero-Vargas, Yohanna Sarria-Guzmán, Nancy Serrano-Silva, Jaime E. Bernal, Karina Ríos-Montes, Haydee Eliza Romero Luna, Josué Antonio Del Ángel Zumaya, Audry Peredo-Lovillo and Francisco Erik González-Jiménez
Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16(12), 253; https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16120253 - 4 Dec 2025
Abstract
Escherichia coli (E. coli) pathotypes present in contaminated food, street food, or water are major contributors to foodborne illnesses. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods are widely applied to detect and confirm E. coli pathotypes in food samples, thereby supporting outbreak prevention
[...] Read more.
Escherichia coli (E. coli) pathotypes present in contaminated food, street food, or water are major contributors to foodborne illnesses. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods are widely applied to detect and confirm E. coli pathotypes in food samples, thereby supporting outbreak prevention efforts. The objective of this study was to provide a comprehensive and reliable review of the molecular identification of E. coli isolated from street foods and to examine its public health implications. The review followed the “Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses” (PRISMA) guidelines and included data retrieved from seven electronic scientific databases covering the period from 1 January 2015, to 15 August 2025. Relevant full-text articles were identified using the search string (“Street food”) AND (Escherichia coli), and only those that met established inclusion and exclusion criteria were selected. A total of 23 studies from Asia, Africa, Europe, and Latin America were included. These studies analyzed a wide range of street foods and beverages. MacConkey Agar and Eosin Methylene Blue Agar were the primary culture media used for the growth and isolation of E. coli. PCR was employed in 50% of the studies to amplify specific DNA segments, enabling the identification of eight E. coli pathotypes: EHEC, ETEC, EAEC (Eagg), EIEC, EPEC, UPEC, DAEC, and APEC. Additionally, a few studies reported phylogroups such as A, B1, B2, C, D, E, and Clade 1. The prevalence of E. coli in street foods varied widely, ranging from 0.5% in Chile to 100% in Mexico. Overall, this systematic review provides an updated scientific overview highlighting persistent challenges in street food safety and E. coli contamination. Across studies, three recurring issues were identified: (1) inadequate and unhygienic vending locations, (2) poor quality of food, and (3) inappropriate food preparation practices. These findings underscore the need for strategic interventions. The evidence presented could support governments and the scientific community in advancing research on E. coli in street foods and implementing corrective measures at local or regional scales, such as educational campaigns for vendors and consumers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Public Health and Quality Aspects Related to Animal Productions)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Microbiology, Microbiology Research, Microorganisms, IJMS, IJPB, Plants
New Challenges on Plant–Microbe Interactions
Topic Editors: Wenfeng Chen, Junjie ZhangDeadline: 31 January 2026
Topic in
Applied Microbiology, IJMS, Microbiology Research, Microorganisms, Veterinary Sciences, Applied Biosciences
Microbiota Diversity and Its Broader Biological Implications Across Human and Animal Health
Topic Editors: Giovanna Liguori, Luc van Nassauw, Anna CostagliolaDeadline: 30 April 2026
Topic in
Microorganisms, Pollutants, Processes, Sustainability, Recycling, Waste, Microbiology Research
The Role of Microorganisms in Waste Treatment
Topic Editors: Zuotao Zhang, Tan Chen, Bing ZhangDeadline: 31 May 2026
Topic in
IJMS, Microbiology Research, Microorganisms, Nanomaterials, Pharmaceutics
Exploring Nanoparticle-Based Antivirals for a Virus-Free Future
Topic Editors: Malgorzata Krzyzowska, Marcin ChodkowskiDeadline: 31 July 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Microbiology Research
Medically Relevant Fungi: Virulence Factors, and New Diagnostic and Treatment Approaches
Guest Editor: Hector M. Mora-MontesDeadline: 31 January 2026
Special Issue in
Microbiology Research
Unveiling the Hidden World: Diversity and Ecology of Cyanobacteria and Algae
Guest Editors: Slađana S. Popović, Olga JakovljevićDeadline: 31 January 2026
Special Issue in
Microbiology Research
Probiotics, Prebiotics and Pet Health
Guest Editors: Bing Han, Lihong ZhaoDeadline: 30 April 2026
Special Issue in
Microbiology Research
Advances in Plant–Pathogen Interactions
Guest Editors: Thanyani Emelton Ramadwa, Stephen Meddows-TaylorDeadline: 30 April 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Microbiology Research
Microbiology and Technology of Fermented Foods
Collection Editor: Salam A. Ibrahim
Topical Collection in
Microbiology Research
Public Health and Quality Aspects Related to Animal Productions
Collection Editors: Beniamino T. Cenci-Goga, Massimo Zerani
Topical Collection in
Microbiology Research
Microorganisms and Their Incredible Potential to Face Societal Challenges
Collection Editor: Mireille Fouillaud








