Studies of Volatile Organic Compounds Emission from Bottom Sediments of Mid–Forest Eutrophic Lake with the Use of Proton Transfer Reaction Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Laboratory Analyses of Volatile Organic Compounds
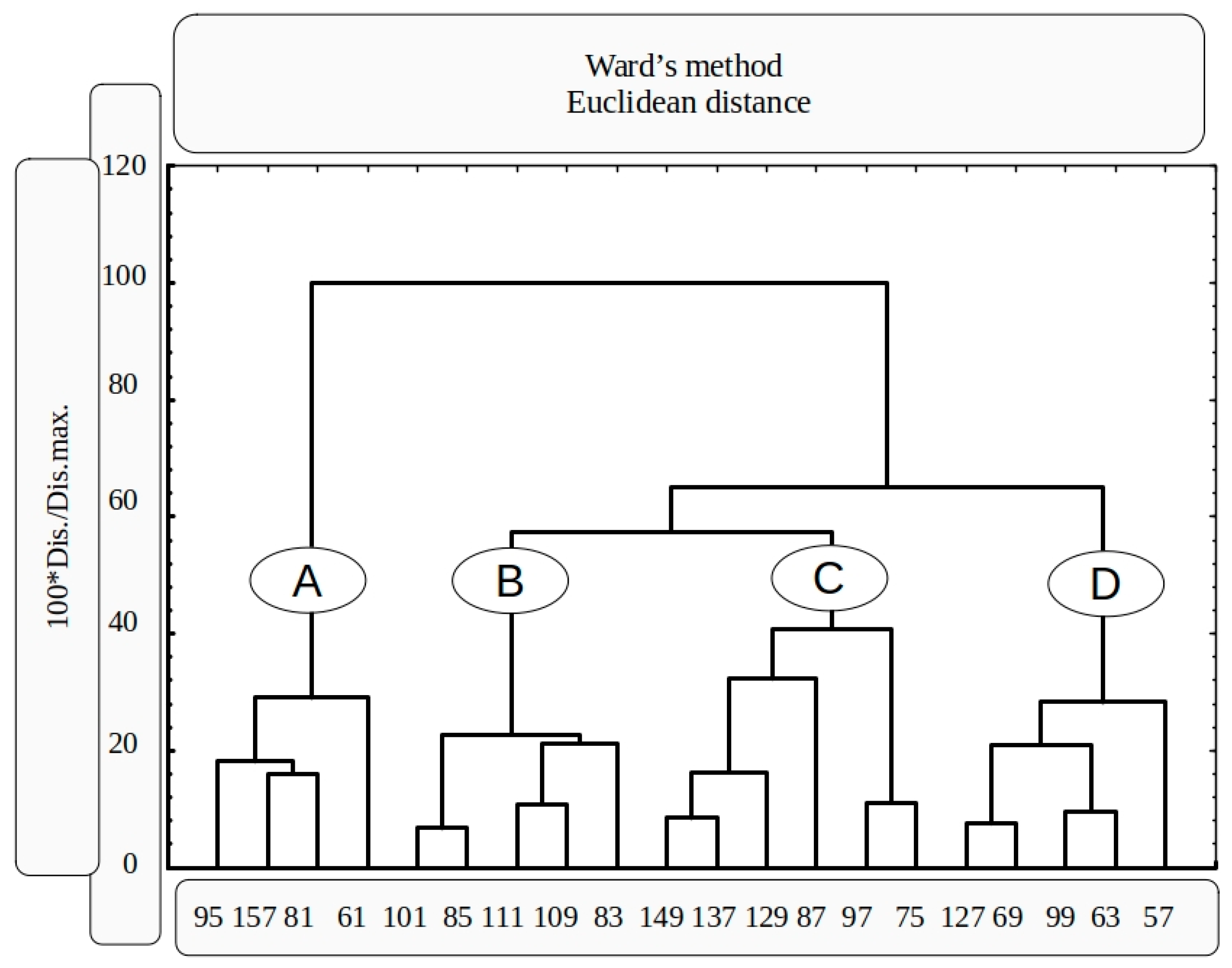
2.4. Statistical Anaysis
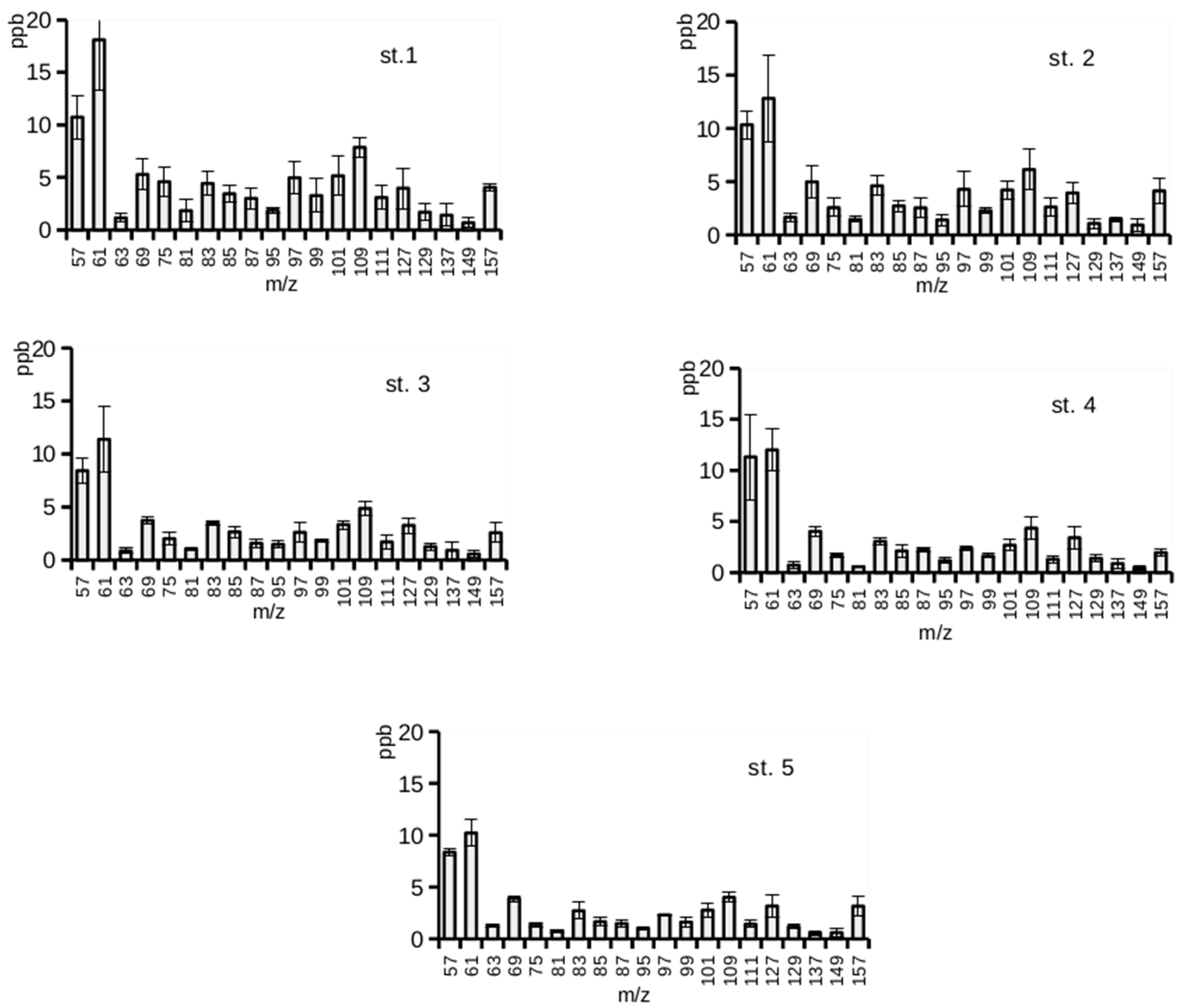
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antonowicz, J.; Wróblewski, T. Study of Volatile Organic Compounds in Emission from Bottom Sediments of Three Lakes with Impact of Anthropopression Using the ProtonTransfer Reaction Mass Spectrometry. Limnol. Rev. 2024, 24, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayrhofer, S.; Mikoviny, T.; Waldhuber, S.; Wagner, A.O.; Innerebner, G.; Franke-Whittle, I.H.; Märk, T.D.; Hansel, A.; Insam, H. Microbial community related to volatile organic compound (VOC) emission in household biowaste. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1960–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojakowska, I.; Dobek, P.; Kucharzyk, J. Geochemical characteristics of sediments of reservoir Zadebie in Skierniewice. Biul. Państwowego Inst. Geol. 2017, 470, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanowski, J.; Trojanowska, C. Balance and circulation of nutrients in a shallow coastal lake Gardno (North Poland). Arch. Environ. Prot. 2007, 33, 45–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wróblewski, T.; Kamińska, A.; Włodarkiewicz, A.; Ushakou, D. Studies of volatile organic compounds emission from Fragaria vesca and Fragaria ananassa using proton transfer reaction mass spectrometry. Acta Phys. Pol. B Proc. Suppl. 2020, 12, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesa, F.; Höller, I.; Guerra, W.; Berger, J.; Dalla Via, J.; Oberhuber, M. Chemodiversity in the Fingerprint Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) of 35 Old and 7 Modern Apple Cultivars Determined by Proton-Transfer-Reaction Mass Spectrometry (PTR-MS) in Two Different Seasons. Chem. Biodivers. 2015, 12, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslund, K.; Lehto, M.; Pussinen, P.; Hartonen, K.; Groop, P.H.; Halonen, L.; Metsälä, M. Identifying volatile in vitro biomarkers for oral bacteria with proton-transfer-reaction mass spectrometry and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, R.S.; Monks, P.S.; Ellis, A.M. Proton-transfer reaction mass spectrometry. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 861–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuzwieser, J.; Cojocariu, C.; Jüssen, V.; Rennenberg, H. Elevated atmospheric CO2 causes seasonal changes in carbonyl emissions from Quercus ilex. New Phytol. 2002, 154, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, J.; Wisthaler, A.; Hansel, A.; Kleist, E.; Miebach, A.; Niinemets, Ü.; Schurr, U.; Wildt, J. Ozone induced emissions of biogenic VOC from tobacco: Relationships between ozone uptake and emission of LOX products. Plant. Cell. Environ. 2005, 28, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezra, D.; Jasper, J.; Todd, R.; Knighton, B.; Grimsrud, E.; Strobel, G. Proton transfer reaction–mass spectrometry as a technique to measure volatile emissions of Mucodor albus. Plant Sci. 2004, 166, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.; Guenther, A.; Spirig, C.; Hansel, A.; Fall, R. Seasonal variation of biogenic VOC emissions above a mixed hardwood forest in northern Michigan. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabmer, W.; Graus, M.; Lindinger, C.; Wisthaler, A.; Rappenglück, B.; Steinbrecher, R.; Hansel, A. Disjunct eddy covariance measurements of monoterpene fluxes from a Norway spruce forest using PTR-MS. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 239, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schade, G.W.; Custer, T.G. OVOC emissions from agricultural soil in northern Germany during the 2003 European heat wave. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 6105–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, D.; Penuelas, J.; Filella, I.; Llusià, J. On-line screening of soil VOCs exchange responses to moisture, temperature and root presence. Plant Soil. 2007, 291, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, D.; Penuelas, J.; Llusià, J.; Ogaya, R.; Filella, I. Interannual and interseasonal soil CO2 efflux and VOC exchange rates in a Mediterranean holm oak forest in response to experimental drought. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2471–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byliński, H.; Barczak, R.J.; Gębicki, J.; Namieśnik, J. Monitoring of odors emitted from stabilized dewatered sludge subjected to aging using proton transfer reaction–Mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 5500–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodzińska, B.; Jańczak, J.; Kowalik, A.; Lamparska, A.; Rekowska, J.; Sziwa, R. Atlas Jezior Polski; Tom II [The atlas of Polish Lakes; Volume II]; Jańczak, J., Ed.; Scientific Publisher: Poznań, Poland, 1997; p. 256. [Google Scholar]
- Ptak, M. Changes in the area and bathymetry of selected lakes of the Pomeranian Lake District. Geogr. Works 2013, 133, 61–76. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Sobczak, B. Forest Management Plan for the Period 1.01.2019 to 31.12.2028. Nature Conservation Plan; Regional Directorate of State Forests in Szczcinek: Szczecinek, Poland, 2018; p. 293. (In Polish)
- Żółkoś, K.; Meissner, W.; Kalisiński, M.; Górska, E.; Mellin, M.; Ibron, I.; Wysocki, D. Liczebność i rozmieszczenie kolonii czapli siwej Ardea cinerea w północnej Polsce [Number and distribution of the Grey Heron Ardea cinerea colonies in northern Poland]. Ornis Polonica 2010, 51, 30–42. (In Polish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Municipality of Sławno, Poland. Official Website of the Sławno Commune Office. 2024. Available online: www.gminaslawno.pl (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Hansen, M.J.; Adamsen, A.P.S.; Feilberg, A. Recovery of Odorants from an Olfactometer Measured by Proton-Transfer-Reaction Mass Spectrometry. Sensors 2013, 13, 7860–7871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasioli, F.; Gasperi, F.; Aprea, E.; Mott, D.; Boscaini, E.; Mayr, D.; Märk, R.D. Coupling proton transfer reaction—mass spectrometry with linear discriminant analysis: A case study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 7227–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological Statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, Ø. PAST. In Paleontological Statistics. Reference Manual; Natural History Museum, University of Oslo: Oslo, Norway, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- TIBCO. Statistica (Data Analysis Software System), Version 13.3; TIBCO Software Inc.: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Trojanowski, J.; Trojanowska, C. Stan zanieczyszczenia jezior człuchowskich. Arch. Environ. Prot. 1999, 25, 91–109. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, A.P.; Varney, M.S.; Phillips, J. Analysis of volatile organic compounds in estuarine sediments using dynamic headspace and gas chromatography—Mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 1991, 542, 413–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, A.; Haidacher, S.; Hanel, G.; Hartungen, E.; Märk, L.; Seehauser, H.; Schottkowsky, R.; Sulzer, P.; Märk, T.D. A high resolution and high sensitivity proton-transfer-reaction time-of-flight mass spectrometer (PTR-TOF-MS). Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 286, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feilberg, A.; Bildsoe, P.; Nyord, T. Application of PTR-MS for Measuring Odorant Emissions from Soil Application of Manure Slurry. Sensors 2015, 15, 1148–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, S.; Taiti, C.; Bazihizina, N.; Costa, C.; Menesatti, P.; Giagnoni, L.; Arenella, M.; Nannipieri, P.; Renella, G. Soil volatile analysis by proton transfer reaction-time of flight mass spectrometry (PTR-TOF-MS). Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 86, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardine, K.; Wegener, F.; Abrell, L.; Van Haren, J.; Werner, C. Phytogenic methyl acetate. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaser, L.; Karl, T.; Schnitzhofer, R.; Graus, M.; HerdlingerBlatt, I.S.; DiGangi, J.P.; Sive, B.; Turnipseed, A.; Hornbrook, R.S.; Zheng, W.; et al. Comparison of different real time VOC measurement techniques in a ponderosa pine forest. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2893–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Märk, J.; Pollien, P.; Lindinger, C.; Blank, I.; Märk, T. Quantitation of furan and methylfuran formed in different precursor systems by proton transfer reaction mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2786–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.; Anderson, B.E.; Beyersdorf, A.J.; Crawford, J.H.; Diskin, G.S.; Eichler, P.; Fried, A.; Keutsch, F.N.; Mikoviny, T.; Thornhill, K.L. In situ measurements and modeling of reactive trace gases in a small biomass burning plume. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 3813–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyysalo, T.; Honkanen, E.; Hirvi, T. Volatiles of wild strawberries, Fragaria vesca L., compared to those of cultivated berries, Fragaria x ananassa cv. Senga Sengana. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1979, 27, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warneke, C.; Roberts, J.M.; Veres, P.; Gilman, J.; Kuster, W.C.; Burling, I.; Yokelson, R.; de Gouw, J.A. VOC identification and intercomparison from laboratory biomass burning using PTR-MS and PITMS. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 303, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, E.A.; Slowik, J.G.; El Haddad, I.; Kilic, D.; Klein, F.; Dommen, J.; Temime-Roussel, B.; Marchand, N.; Baltensperger, U.; Prévôt, A.S.H. Characterization of gas-phase organics using proton transfer reaction time-of-flight mass spectrometry: Fresh and aged residential wood combustion emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 705–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leff, J.W.; Fierer, N. Volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions from soil and litter samples. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 1629–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insam, H.; Seewald, M.S.A. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in soils. Biol. Fertil Soils 2010, 46, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
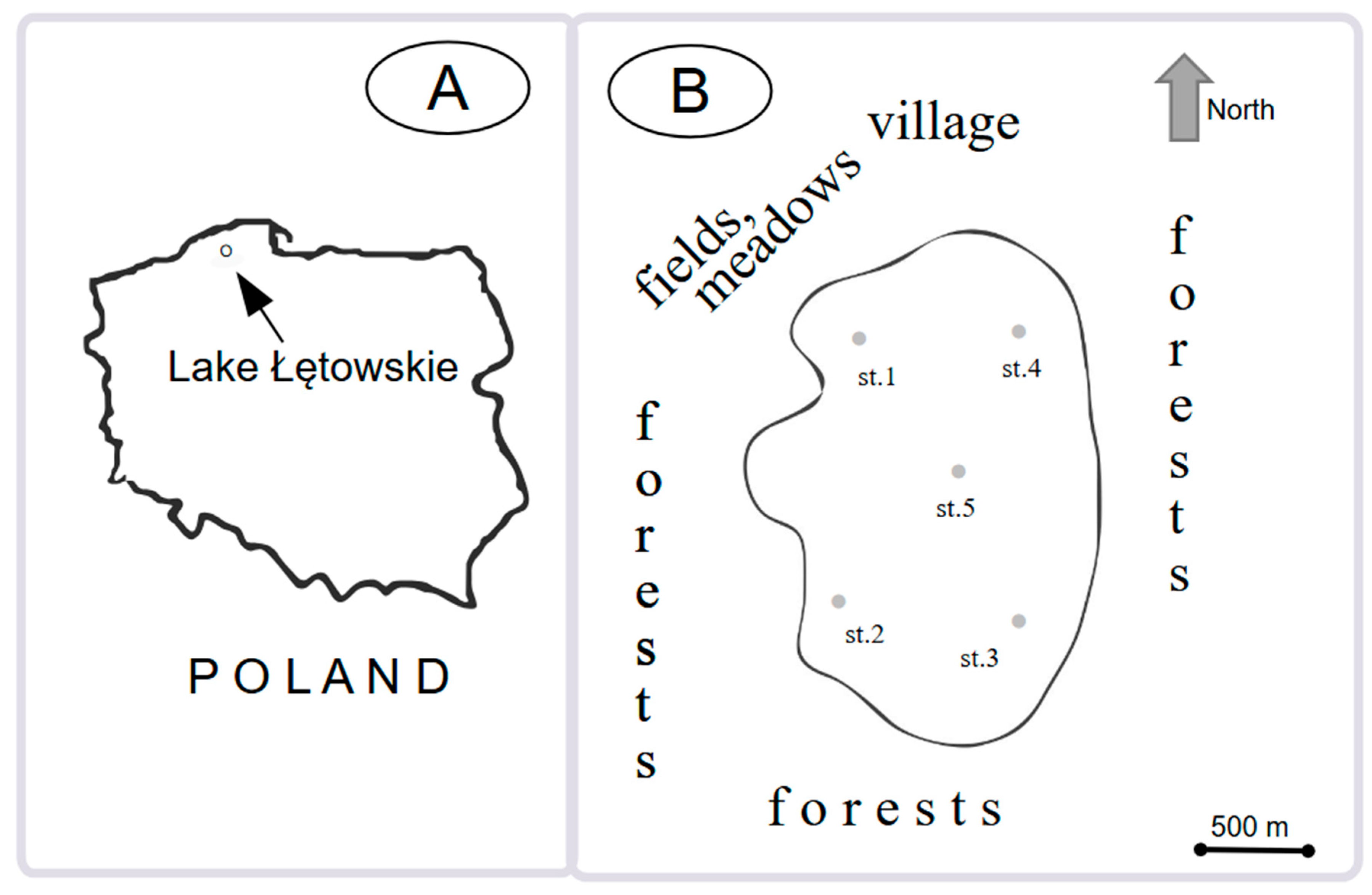
| Parameter and Unit | Value |
|---|---|
| Latitude and longitude | 54°16.2′–16°49.7′ |
| Surface area [ha] | 402.0 |
| Volume [103 m3] | 33,128.5 |
| Maximum depth [m] | 18.7 |
| Average depth [m] | 8.2 |
| Maximum length [m] | 2800 |
| Maximum width [m] | 1900 |
| m/z | Mean | Median | Min. | Max. | Lower Quartile | Upper Quartile | SD | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| u | ppb | ppb | ppb | ppb | ppb | ppb | ppb | % |
| 57 | 9.84 | 9.45 | 7.29 | 15.63 | 8.15 | 11.03 | 2.27 | 23.10 |
| 61 | 12.91 | 11.62 | 9.08 | 22.28 | 9.76 | 14.91 | 3.98 | 30.79 |
| 63 | 1.14 | 1.16 | 0.41 | 2.06 | 0.75 | 1.43 | 0.43 | 37.88 |
| 69 | 4.39 | 4.06 | 3.30 | 6.94 | 3.66 | 4.54 | 1.04 | 23.79 |
| 75 | 2.44 | 1.98 | 1.18 | 6.11 | 1.46 | 3.43 | 1.36 | 55.52 |
| 81 | 1.12 | 1.00 | 0.49 | 3.13 | 0.67 | 1.32 | 0.66 | 58.45 |
| 83 | 3.66 | 3.45 | 1.83 | 5.71 | 3.22 | 3.90 | 1.01 | 27.59 |
| 85 | 2.52 | 2.49 | 1.42 | 4.33 | 1.95 | 3.26 | 0.81 | 32.02 |
| 87 | 2.16 | 2.06 | 1.13 | 4.11 | 1.51 | 2.75 | 0.82 | 37.99 |
| 95 | 1.38 | 1.37 | 0.83 | 2.10 | 0.99 | 1.75 | 0.41 | 29.37 |
| 97 | 3.31 | 2.52 | 1.70 | 6.70 | 2.36 | 4.34 | 1.46 | 44.25 |
| 99 | 2.12 | 1.93 | 1.08 | 5.04 | 1.67 | 2.26 | 0.91 | 42.88 |
| 101 | 3.63 | 3.24 | 2.01 | 7.01 | 3.07 | 3.80 | 1.29 | 35.47 |
| 109 | 5.45 | 4.92 | 3.10 | 8.58 | 3.91 | 7.10 | 1.74 | 32.03 |
| 111 | 2.03 | 1.79 | 0.89 | 4.27 | 1.25 | 2.96 | 0.95 | 46.68 |
| 127 | 3.55 | 3.27 | 2.06 | 6.19 | 2.65 | 4.50 | 1.11 | 31.37 |
| 129 | 1.32 | 1.19 | 0.66 | 2.62 | 0.98 | 1.60 | 0.47 | 35.46 |
| 137 | 1.05 | 1.06 | 0.11 | 2.53 | 0.47 | 1.59 | 0.64 | 61.26 |
| 149 | 0.65 | 0.67 | 0.14 | 1.34 | 0.26 | 0.90 | 0.39 | 59.98 |
| 157 | 3.17 | 2.90 | 1.67 | 5.40 | 2.28 | 4.10 | 1.13 | 35.60 |
| m/z | F | p | Tukey Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| 63 | 3.94 | * | st. 4–st. 2 |
| 75 | 7.93 | ** | st. 1–st. 3, st. 1–st. 4, st. 1–st. 5 |
| 83 | 3.54 | * | ns |
| 85 | 3.65 | * | st. 1–st. 5 |
| 97 | 3.90 | * | ns |
| 109 | 5.81 | * | st. 1–st. 4, st. 1–st. 5 |
| 111 | 3.63 | * | ns |
| 157 | 3.76 | * | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antonowicz, J.; Wróblewski, T. Studies of Volatile Organic Compounds Emission from Bottom Sediments of Mid–Forest Eutrophic Lake with the Use of Proton Transfer Reaction Mass Spectrometry. Limnol. Rev. 2025, 25, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25040049
Antonowicz J, Wróblewski T. Studies of Volatile Organic Compounds Emission from Bottom Sediments of Mid–Forest Eutrophic Lake with the Use of Proton Transfer Reaction Mass Spectrometry. Limnological Review. 2025; 25(4):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25040049
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntonowicz, Józef, and Tomasz Wróblewski. 2025. "Studies of Volatile Organic Compounds Emission from Bottom Sediments of Mid–Forest Eutrophic Lake with the Use of Proton Transfer Reaction Mass Spectrometry" Limnological Review 25, no. 4: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25040049
APA StyleAntonowicz, J., & Wróblewski, T. (2025). Studies of Volatile Organic Compounds Emission from Bottom Sediments of Mid–Forest Eutrophic Lake with the Use of Proton Transfer Reaction Mass Spectrometry. Limnological Review, 25(4), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25040049





