- Article
Predictive Value of Preoperative CT Findings for Bowel Ischemia in Patients with Blunt Mesenteric Injury: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- Suyeong Hwang,
- Sung Hoon Cho and
- Gun Woo Kim
- + 2 authors
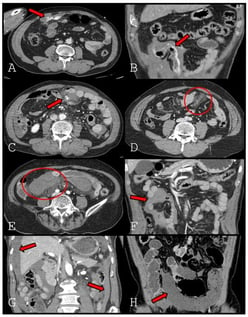
Background: Delayed bowel ischemia is a major cause of failure of nonoperative management in patients with blunt mesenteric injury. Although decreased bowel wall enhancement on computed tomography (CT) is a definitive sign of bowel ischemia, it is uncommon and may be absent on early imaging. This study aimed to identify specific CT findings that predict bowel ischemia to distinguish patients requiring surgery from those suitable for conservative management. Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 174 patients with blunt mesenteric injury treated at a Level 1 trauma center between January 2013 and December 2024. Initial CT findings were classified as mesenteric contrast extravasation freely extending into the peritoneal cavity (extravasation type 1), contrast extravasation tracking along the bowel contour (extravasation type 2), pseudoaneurysm, mesenteric haziness, mesenteric hematoma, interloop fluid, dependent portion fluid, and decreased bowel wall enhancement. Predictors of bowel ischemia were evaluated using univariate analysis and ridge-penalized multivariable logistic regression. Results: Bowel ischemia occurred in 30 patients (17.2%). Decreased bowel wall enhancement was rare (4.6%) but demonstrated perfect specificity and positive predictive value (both 100%), with low sensitivity (26.7%). Extravasation type 2 showed high specificity (97.2%) and remained an independent predictor of bowel ischemia. Dependent portion fluid showed relatively high sensitivity, whereas mesenteric haziness and mesenteric hematoma were inversely associated with ischemia. Conclusions: Contrast extravasation tracking along the bowel contour and decreased bowel wall enhancement on early CT are strong predictors of bowel ischemia in patients with blunt mesenteric injury. These findings should prompt consideration of early surgical exploration, even in patients who initially appear hemodynamically stable.
7 February 2026