- Article
FFM-Net: Fusing Frequency Selection Information with Mamba for Skin Lesion Segmentation
- Lifang Chen,
- Entao Yu and
- Qihang Cao
- + 1 author
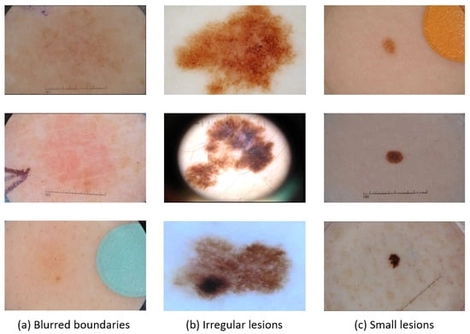
Accurate segmentation of lesion regions is essential for skin cancer diagnosis. As dermoscopic images of skin lesions demonstrate different sizes, diverse shapes, fuzzy boundaries, and so on, accurate segmentation still faces great challenges. To address these issues, we propose a new dermatologic image segmentation network, FFM-Net. In FFM-Net, we design a new FM block encoder based on state space models (SSMs), which integrates a low-frequency information extraction module (LEM) and an edge detail extraction module (EEM) to extract broader overall structural information and more accurate edge detail information, respectively. At the same time, we dynamically adjust the input channel ratios of the two module branches at different stages of our network, so that the model can learn the correlation relationship between the overall structure and edge detail features more effectively. Furthermore, we designed the cross-channel spatial attention (CCSA) module to improve the model’s sensitivity to channel and spatial dimensions. We deploy a multi-level feature fusion module (MFFM) at the bottleneck layer to aggregate rich multi-scale contextual representations. Finally, we conducted extensive experiments on three publicly available skin lesion segmentation datasets, ISIC2017, ISIC2018, and PH2, and the experimental results show that the FFM-Net model outperforms most existing skin lesion segmentation methods.
13 December 2025