Controlling Heterogeneous Multi-Agent Systems Under Uncertainty Using Fuzzy Inference and Evolutionary Search
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
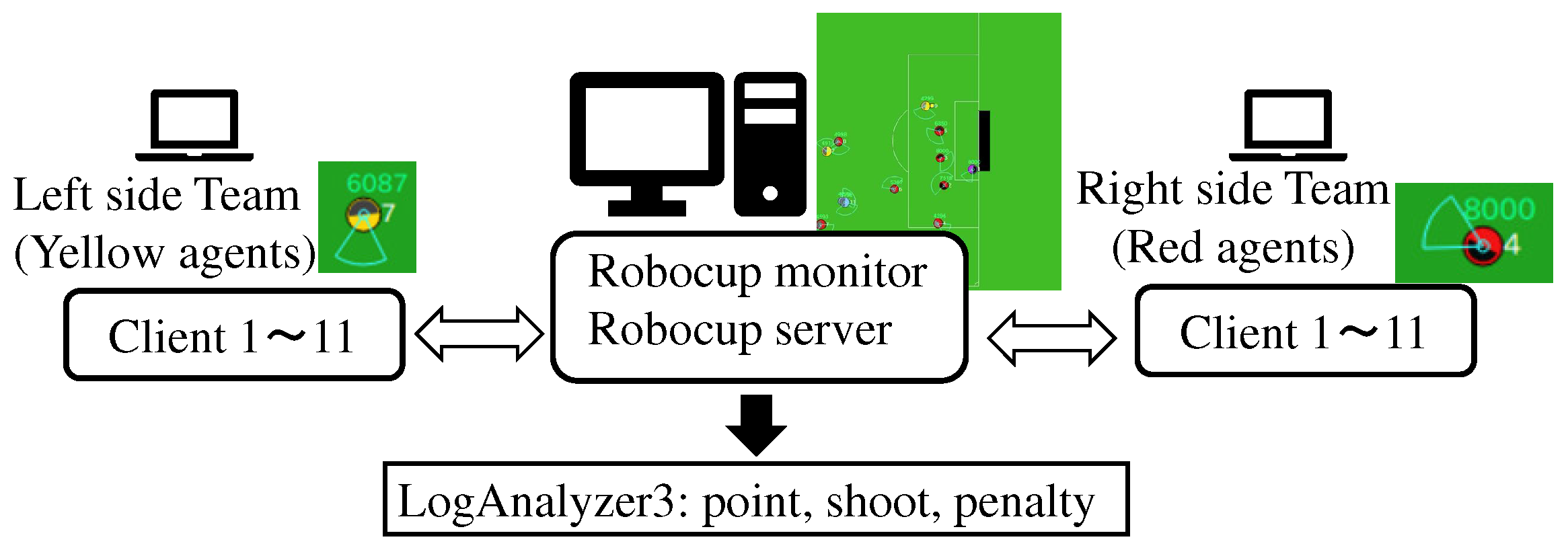
3. RoboCup 2D as an Experimental Platform
4. Agent2D as a Benchmark in Multi-Agent Systems
4.1. Characteristics of Agent2D in Multi-Agent Contexts
4.2. Action Sequence Search Algorithm
4.3. Motivation for Optimization of Evaluation Function
- The evaluation focuses on task-specific indicators, including the following:
- Number of shots taken;
- Frequency of ball penetration into the penalty area;
- Scoring success rate.
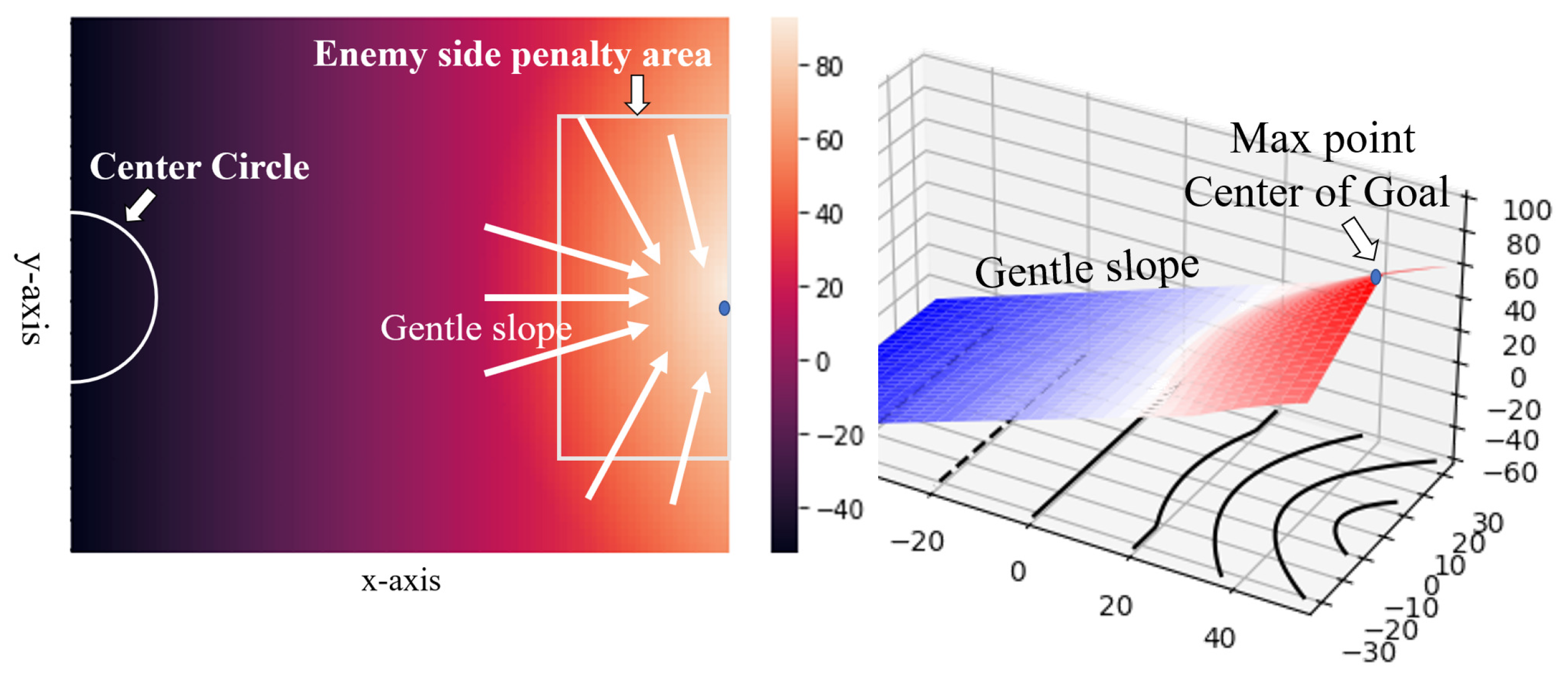
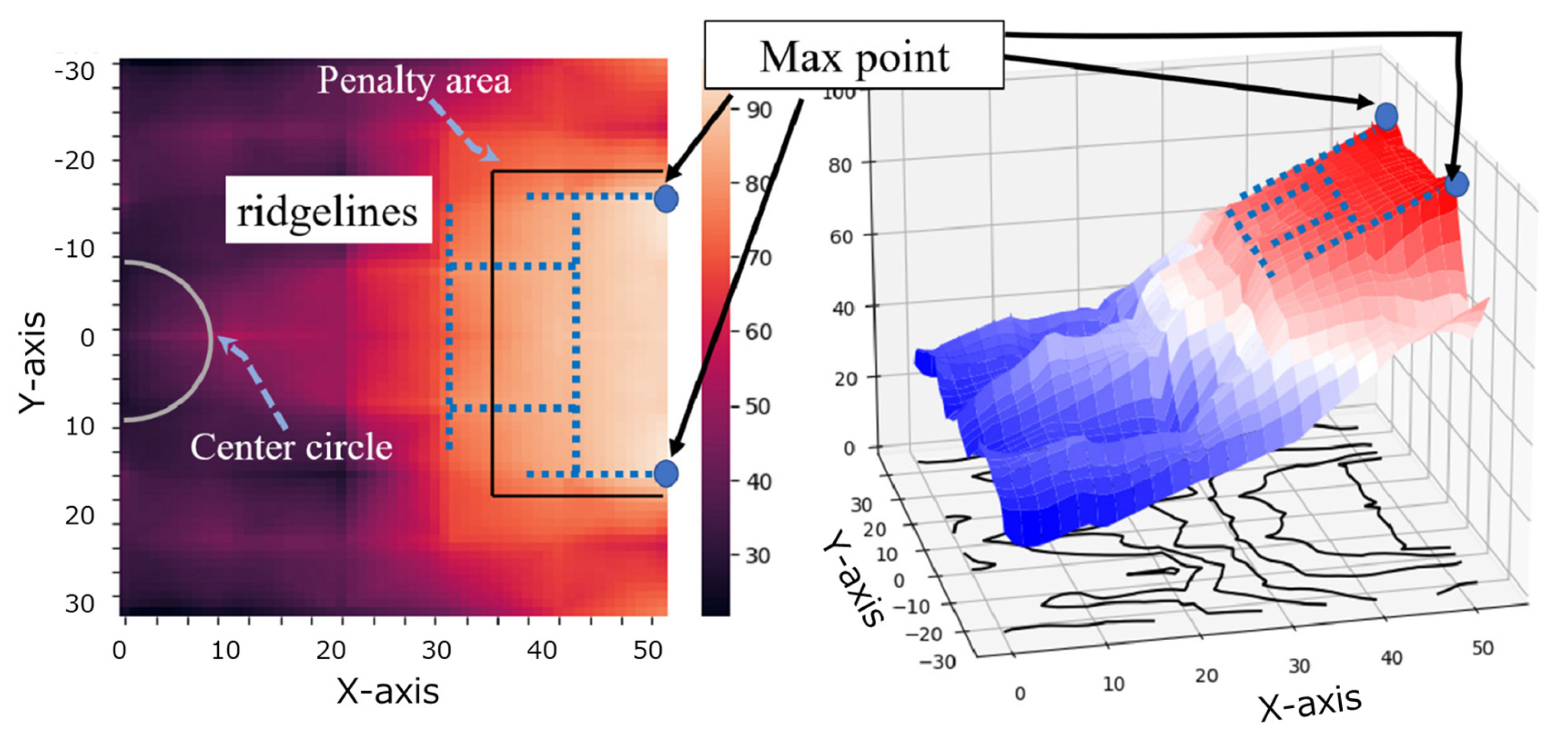
4.4. Illustration of the Default Evaluation Function
5. Methodology
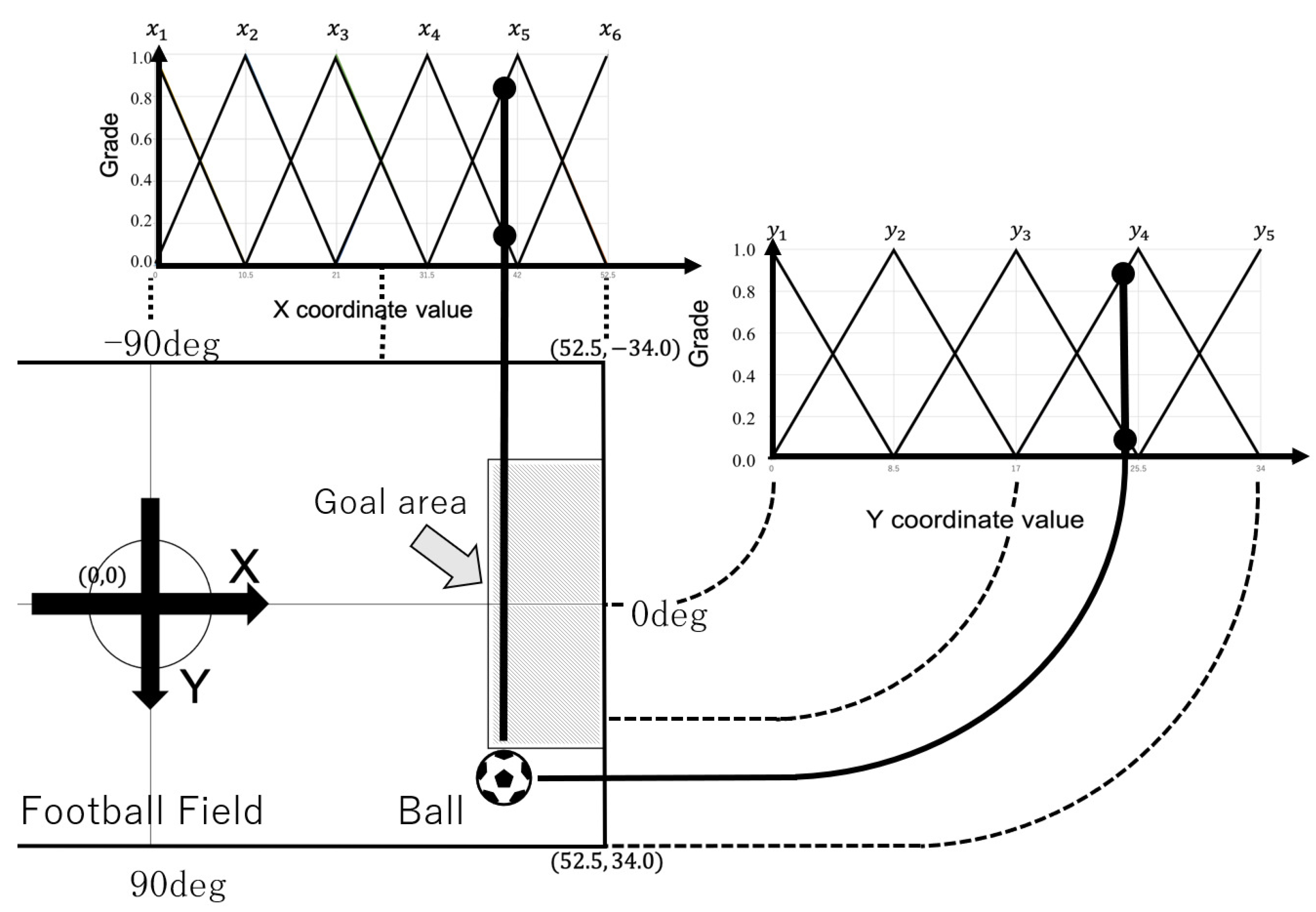
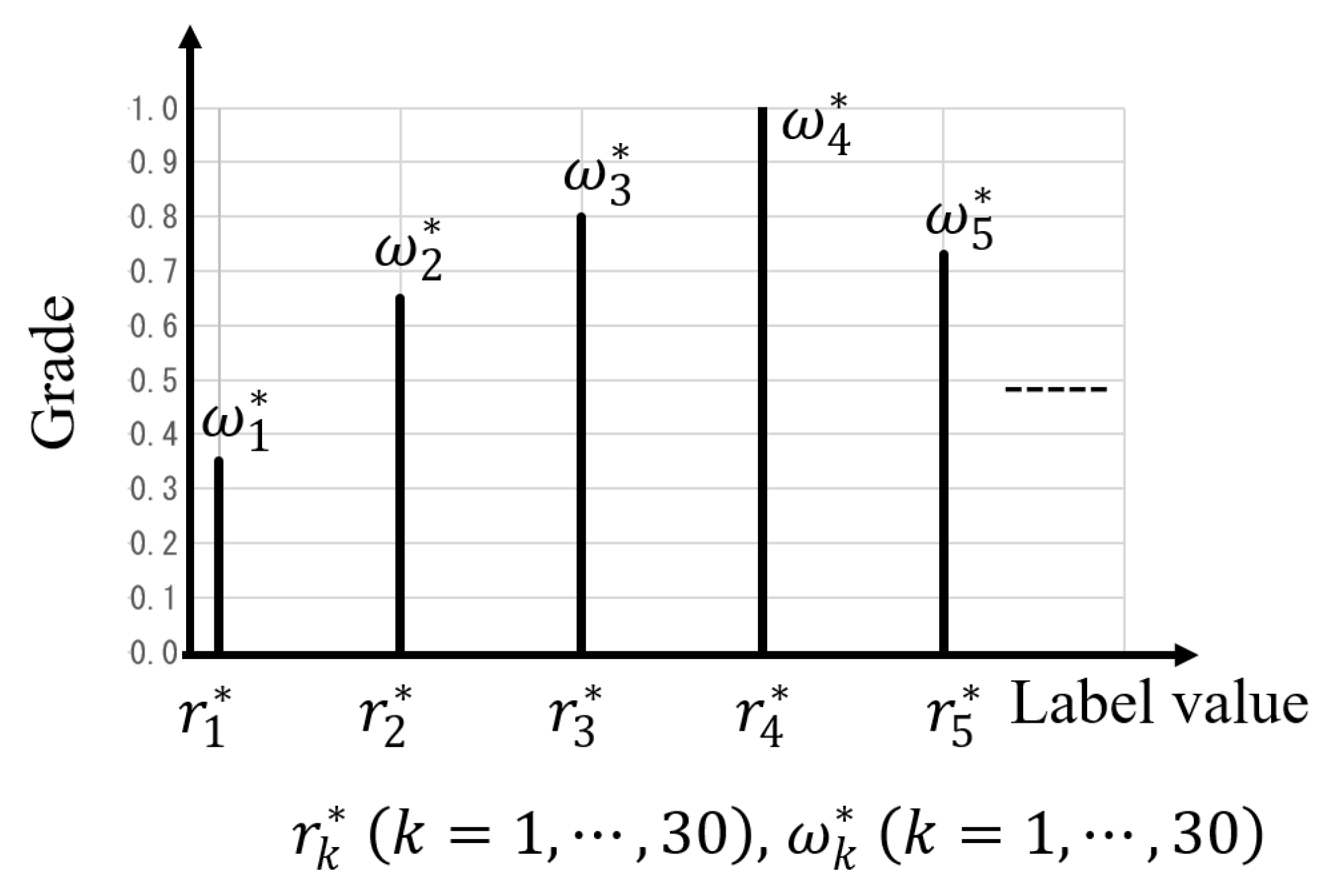
5.1. Fuzzy Inference-Based Evaluation Function
| Algorithm 1 Fuzzy-Evaluated Action Sequence Search | |
| Require:
current state , depth D Ensure: best action sequence | |
|
1: , 2: for all action sequences of length do 3: 4: 5: for a in do | |
| 6: simulate_action() | ▹ predict next ball pos. |
| 7: | ▹ via fuzzy inference (Equation (4)) |
|
8: end for 9: if then 10: end if 11: end for 12: return | |
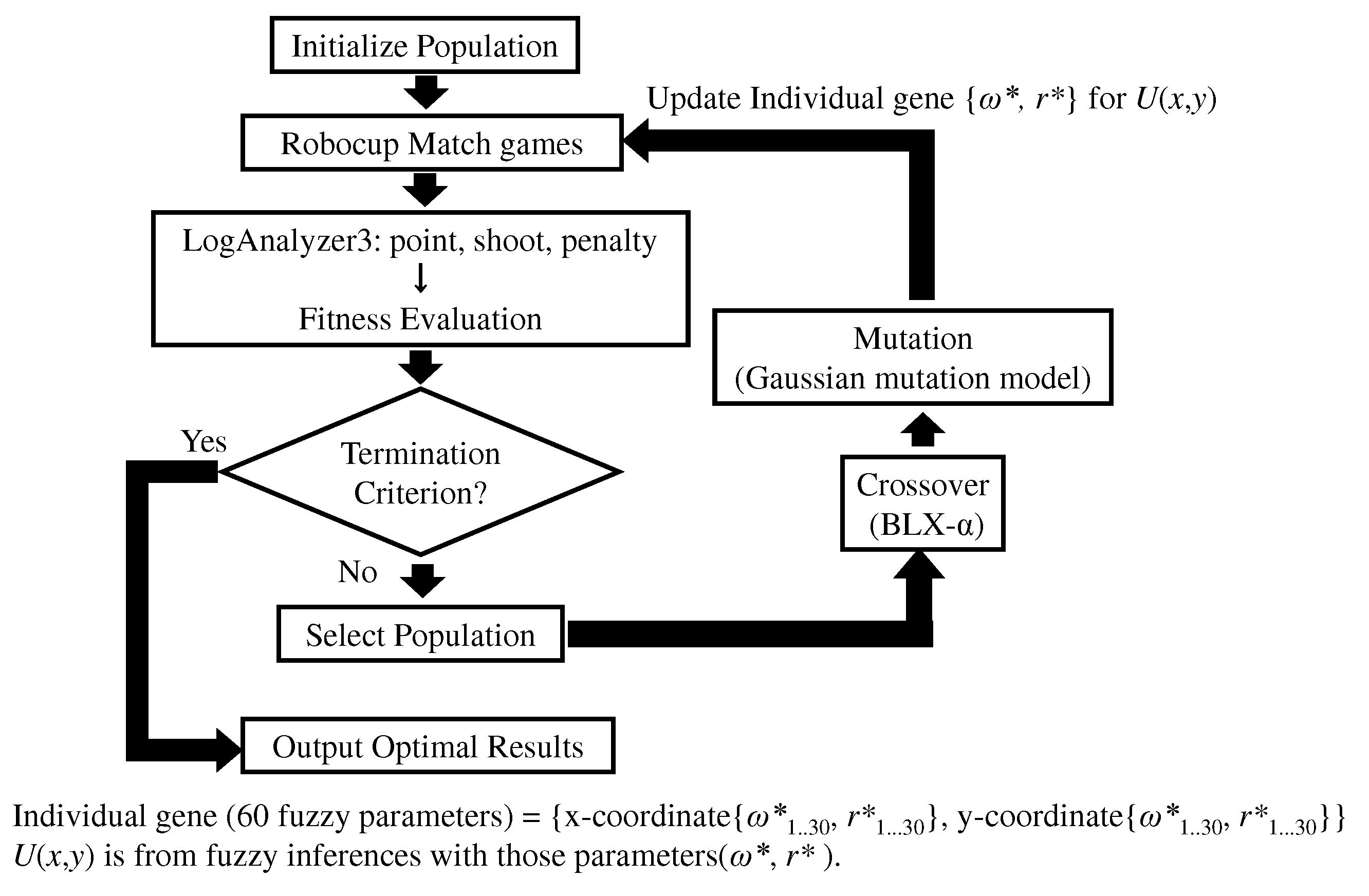
5.2. Genetic Algorithm for Fuzzy Parameter Optimization
- Number of goals scored (point);
- Number of shots taken (shoot);
- Number of penalty area penetrations (penalty).
| Algorithm 2 Genetic Algorithm-Based Fuzzy Parameter Optimization |
|
5.3. Experimental Setup
6. Results and Discussion
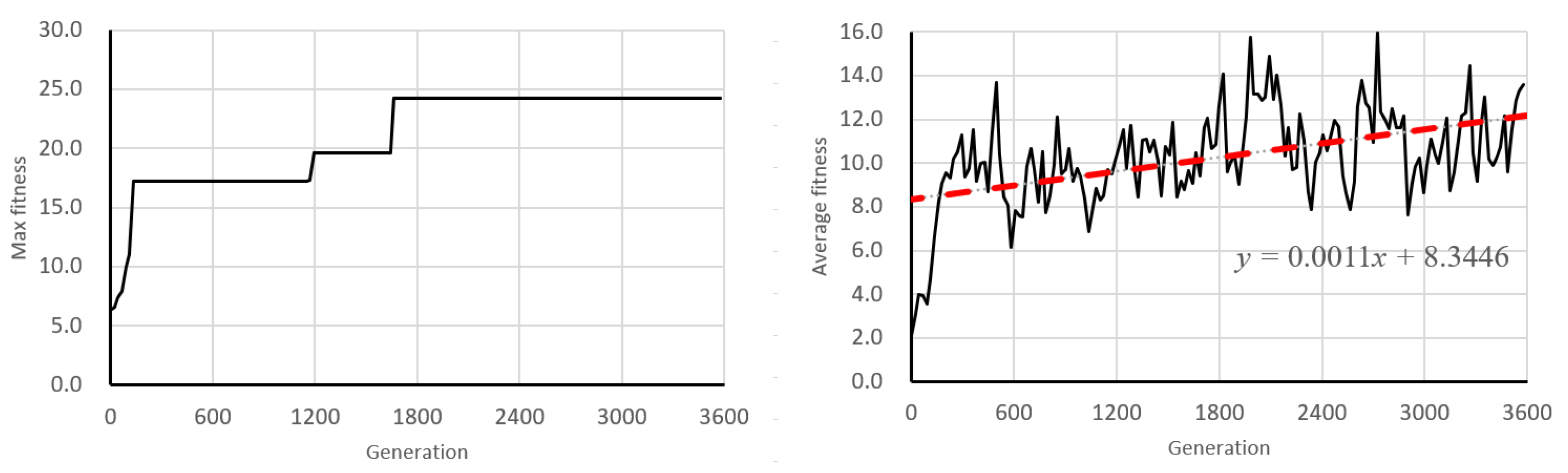
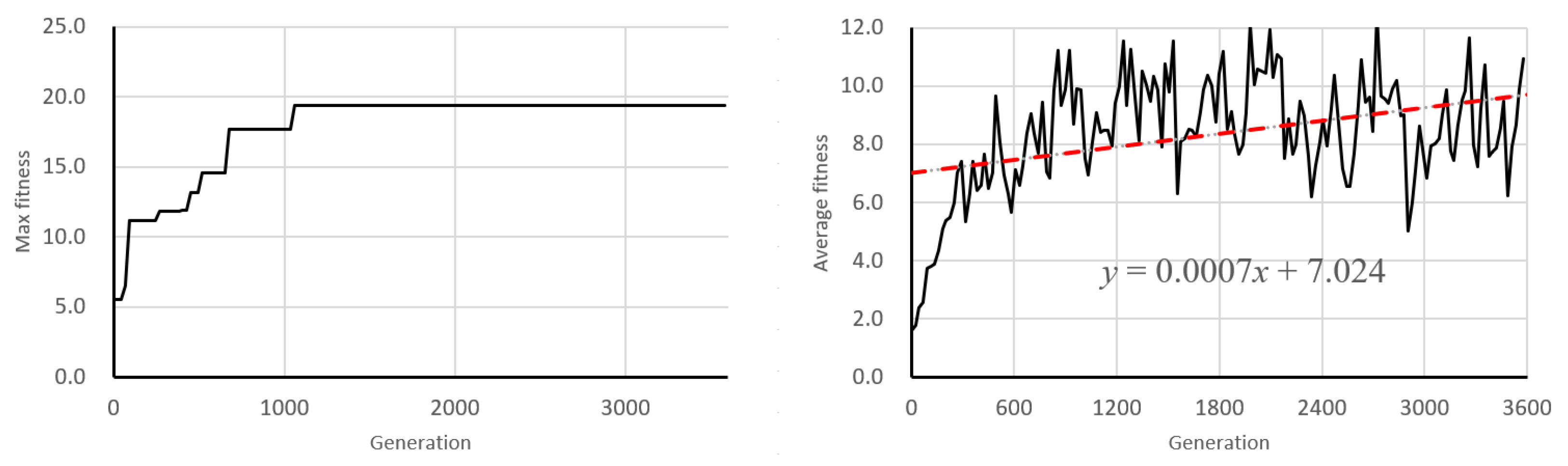
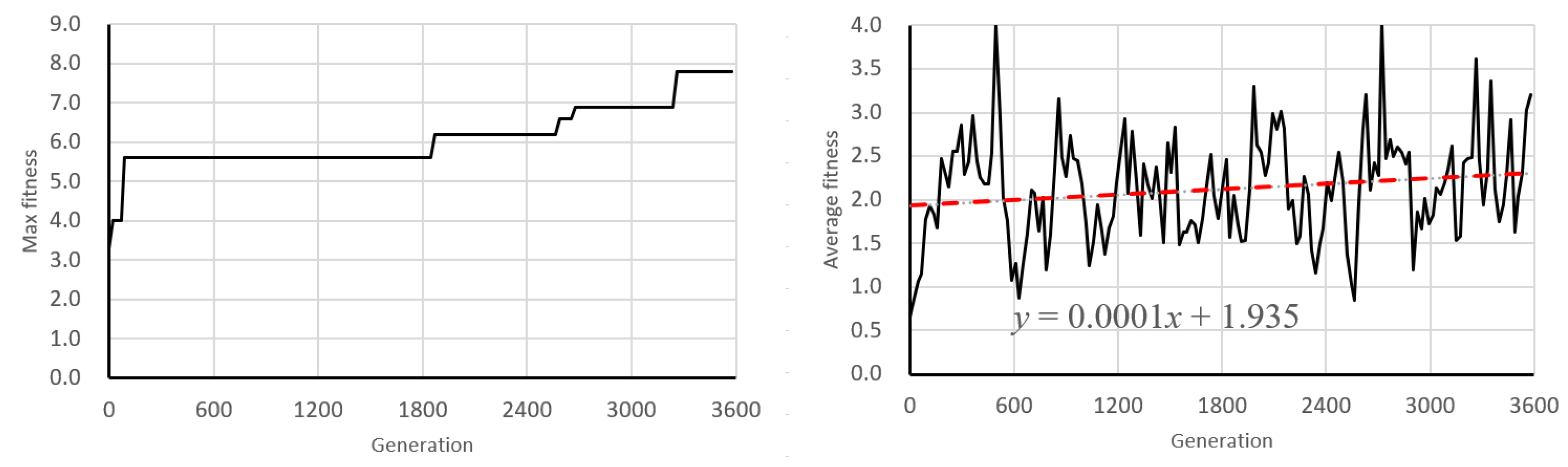
6.1. Learning Behavior of Genetic Algorithm
6.2. Discussion of Learning Dynamics and Convergence Trends
- 100–130 generations (early training phase);
- 2000–2030 generations (middle-to-late phase);
- 3570–3600 generations (final convergence phase).
- Goals Scored (Points)—indicating final task success;
- Shoot Attempts (Time)—reflecting offensive activity and aggressiveness;
- Penalty Area Entries (Time)—representing spatial penetration and strategic advancement.
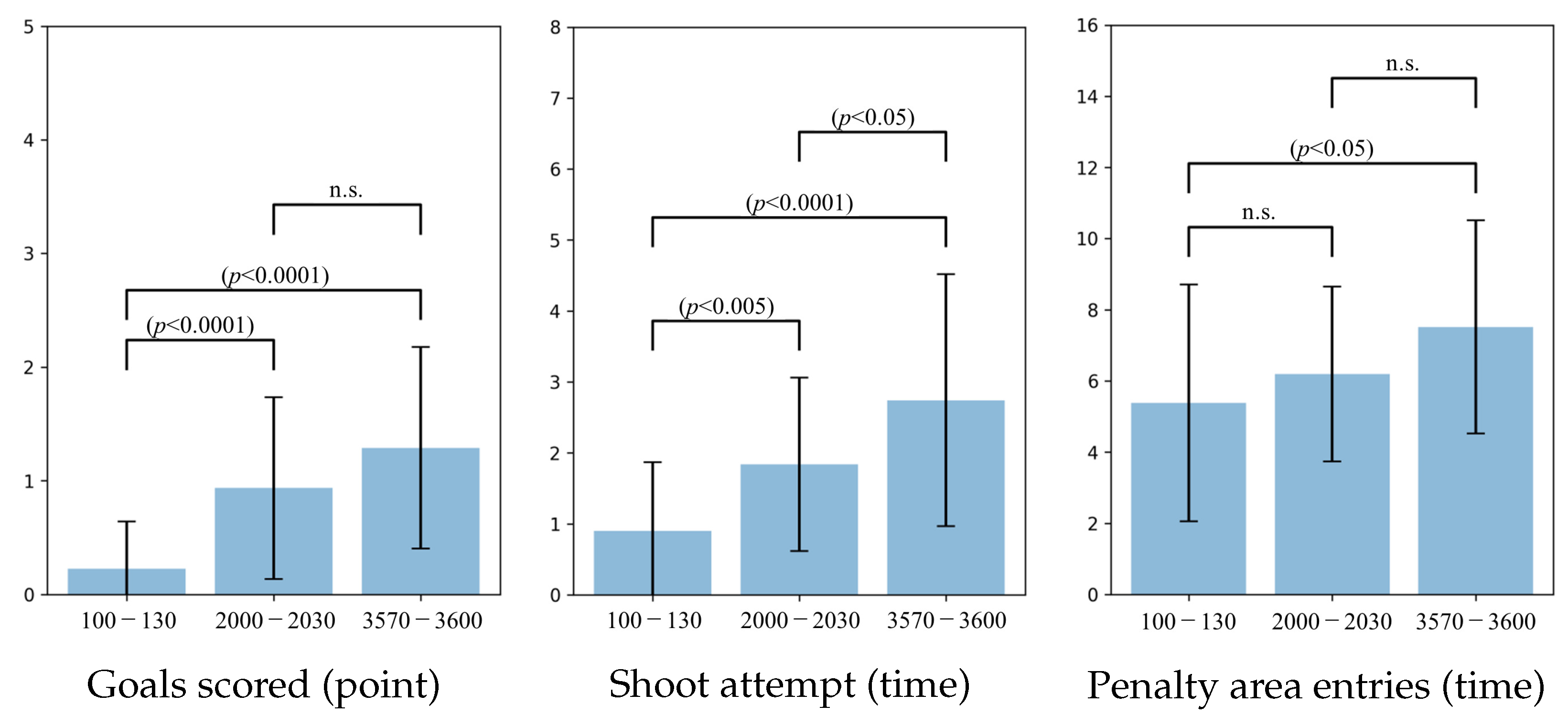
6.3. Agent2D
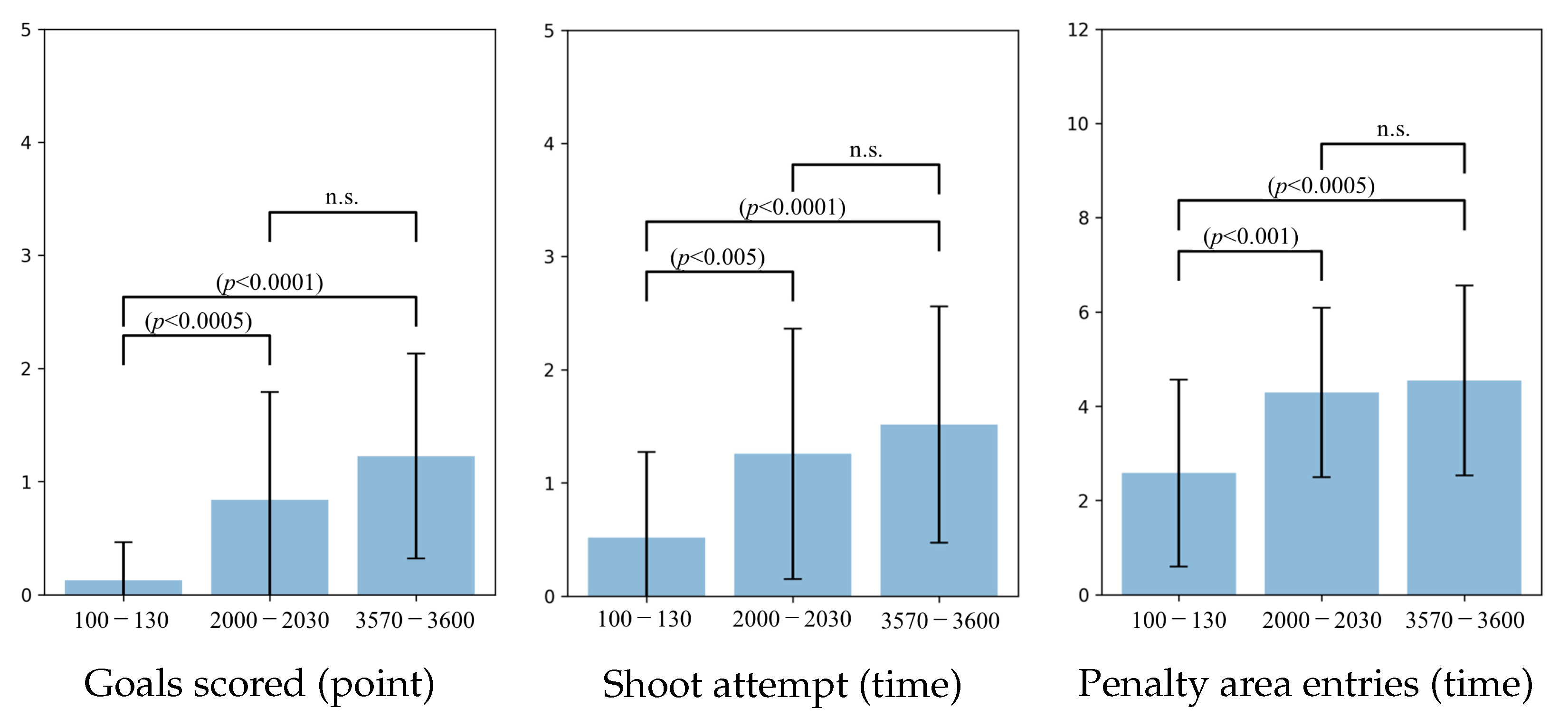
6.4. Persepolis
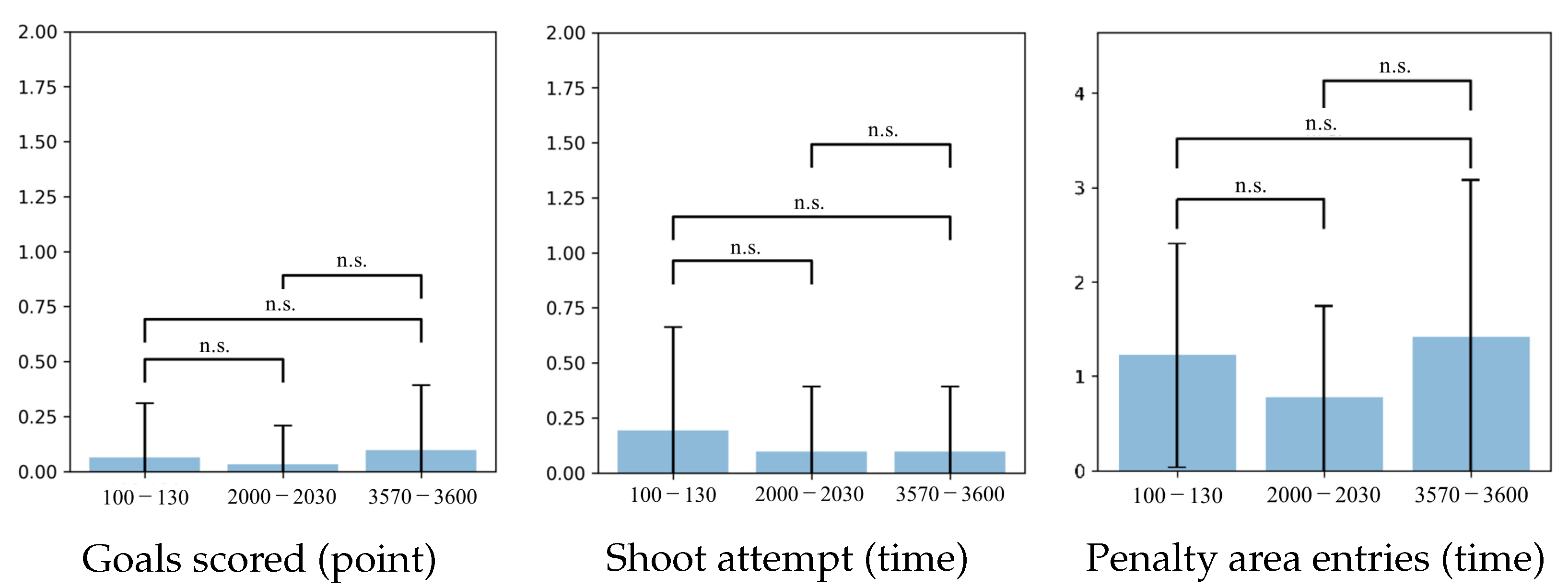
6.5. Jyo_sen
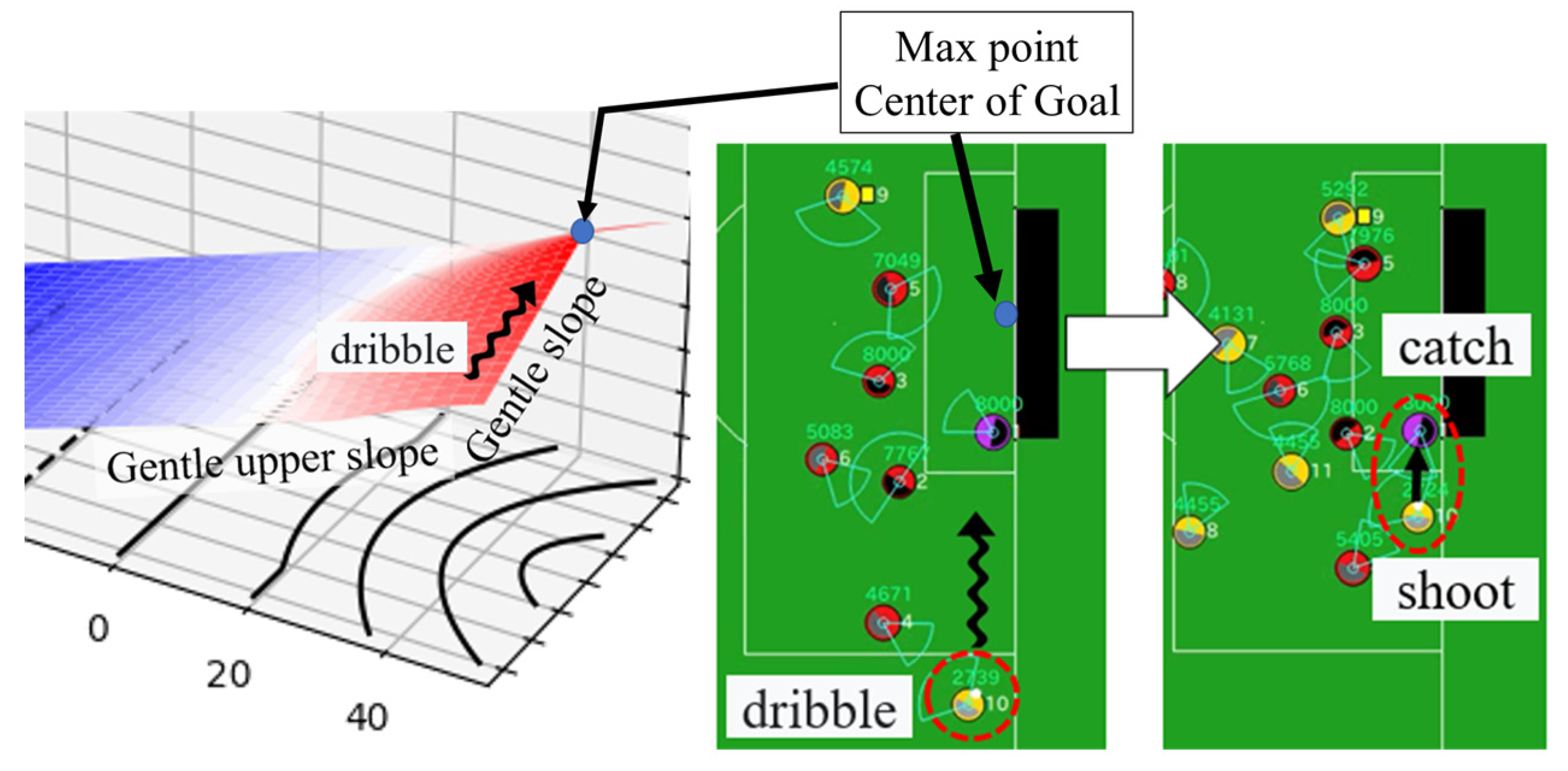
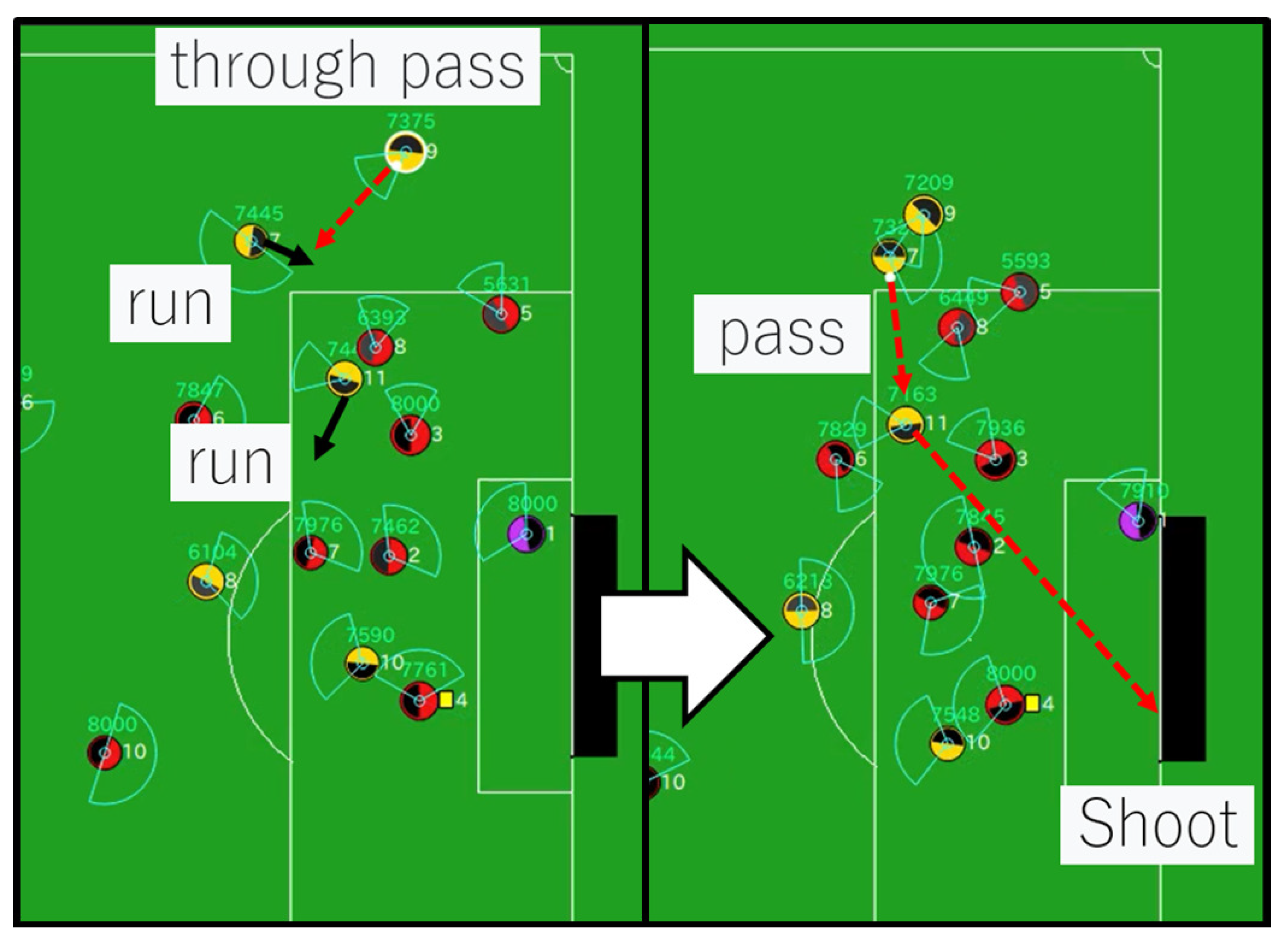
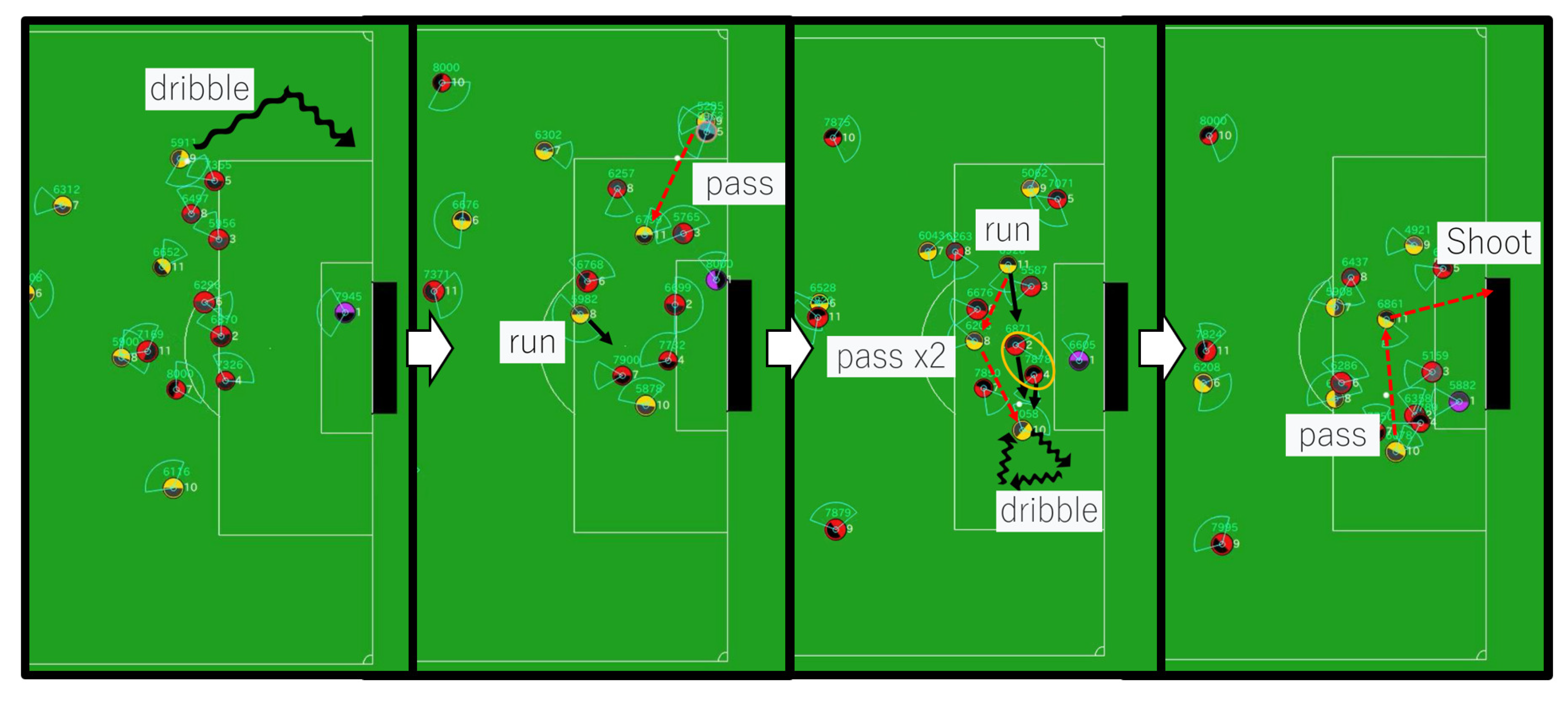
6.6. Behavioral Analysis of Soccer Agent Team
7. Conclusions
8. Highlights and Contributions
8.1. NovelEvaluation Function Based on Fuzzy Inference and Evolutionary Search
8.2. Emergence of Ridgeline Strategies and Adaptive Team Behavior
8.3. Interpretability via Visualization of
8.4. Broader Implications for Real-World Multi-Agent Systems
8.5. Toward Human AI Co-Design and Learning
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence; |
| ANFIS | Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System; |
| BLX- | Blend Crossover with Alpha of Genetic Algorithm; |
| FIS | Fuzzy Inference System; |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm; |
| MAS | Multi-Agent System; |
| n.s. | Not Significant; |
| PA | Penalty Area; |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization; |
| RL | Reinforcement Learning; |
| RoboCup2D | RoboCup Soccer Simulation 2D League; |
| XAI | Explainable Artificial Intelligence. |
References
- Luzolo, P.H.; Elrawashdeh, Z.; Tchappi, I.; Galland, S.; Koukam, A. Combining multi-agent systems and Artificial Intelligence of Things: Technical challenges and gains. Internet Things 2024, 28, 101364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepaniuk, H.; Szczepaniuk, E.K. Applications of Artificial Intelligence Algorithms in the Energy Sector. Energies 2022, 16, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Li, M.; Song, Z.; Xu, K.; Xia, Q.; Sun, N.; Zhou, P.; Xia, M. A Review of Research on Reinforcement Learning Algorithms for Multi-Agents. Neurocomputing 2024, 599, 128068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wu, R. Reinforcement Learning in Dynamic Job Shop Scheduling: A Comprehensive Review of AI-Driven Approaches in Modern Manufacturing. J. Intell. Manuf. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali Khalil Abadi, Z.; Mansouri, N. A Comprehensive Survey on Scheduling Algorithms Using Fuzzy Systems in Distributed Environments. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.H. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems; University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1975; Volume 7, pp. 390–401. [Google Scholar]
- Tynchenko, V.V.; Malashin, I.; Kurashkin, S.O.; Tynchenko, V.; Gantimurov, A.; Nelyub, V.; Borodulin, A. Multi-Criteria Genetic Algorithm for Optimizing Distributed Computing Systems in Neural Network Synthesis. Future Internet 2025, 17, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalusivalingam, A.K.; Sharma, A.; Patel, N.; Singh, V. Optimizing Resource Allocation with Reinforcement Learning and Genetic Algorithms: An AI-Driven Approach. Int. J. AI Cogn. Comput. 2020, 1, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino, Y.; Rathnayake, N.; Dang, T.L.; Rathnayake, U. Cascaded-ANFIS and its successful real-world applications. In Fuzzy Logic—Advancements in Dynamical Systems, Fractional Calculus and Computational Techniques; Balasubramaniam, P., Babu, N.R., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Heydari, B. Dynamic resource allocation in systems-of-systems using a heuristic-based interpretable deep reinforcement learning. J. Mech. Des. 2022, 144, 091711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, J.; Dutta, M.; Marques, G. A novel application of fuzzy inference system optimized with particle swarm optimization and genetic algorithm for PM10 prediction. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 4847–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Networks (ICNN’95), Perth, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- De Santis, E.; Rizzi, A.; Sadeghian, A. Hierarchical genetic optimization of a fuzzy logic system for energy flows management in microgrids. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 58, 669–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Jiao, X.; Li, Y. Adaptive real-time energy management control strategy based on fuzzy inference system for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. Control Eng. Pract. 2021, 108, 104695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, I.; Matsubara, H. Soccer server and researches on multi-agent systems. In Proceedings of the IROS-96 Workshop on RoboCup, Osaka, Japan, 4–8 November 1996; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, H.; Nakashima, T. HELIOS Base: An Open Source Package for the RoboCup Soccer 2D Simulation. In Proceedings of the Robot Soccer World Cup, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 24 June 2013; pp. 528–535. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, H.; Nakashima, T.; Fukushima, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Ohori, A. HELIOS2019, Team Description Paper. In Proceedings of the RoboCup 2019 Symposium and Competitions, Sydney, Australia, 2–8 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Kuga, R.; Omori, H.; Fukushima, T.; Nakashima, T.; Akiyama, H. Helios2021: Team description paper. In Proceedings of the RoboCup 2021 Symposium and Competitions, Worldwide, Online, 28 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Akhondi, F.; Esmaelifar, S.; Esmaelifar, S.; Rokni, S.R.; Rajabi, A.; Hasanpour, G. Hades2D Soccer 2D Simulation Team Description Paper. In Proceedings of the RoboCup 2021 Symposium and Competitions: Team Description Papers, Worldwide, Online, 22–28 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zare, N.; Sayareh, A.; Sarvmaili, M.; Amini, O.; Soares, A.; Matwin, S. CYRUS Soccer Simulation 2D Team Description Paper 2021. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.02310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryo, T.; Shunsaku, T.; Harukazu, I. Adjustment of weight parameters in a state evaluation function used in chain action of Agent2d. FIT2014 2014, 13, 285–288. [Google Scholar]
- Silver, D.; Huang, A.; Maddison, C.J.; Guez, A.; Sifre, L.; Van Den Driessche, G.; Schrittwieser, J.; Antonoglou, I.; Panneershelvam, V.; Lanctot, M.; et al. Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature 2016, 529, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, D.; Schrittwieser, J.; Simonyan, K.; Antonoglou, I.; Huang, A.; Guez, A.; Hubert, T.; Baker, L.; Lai, M.; Bolton, A.; et al. Mastering the game of Go without human knowledge. Nature 2017, 550, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, T.; Igarashi, H.; Yamagishi, J.; Irikura, M. Evaluation Function of Offensive Soccer Agents: Supervised Learning Based on Policy Gradients. In Proceedings of the 34th Fuzzy System Symposium (FSS 2018), Online, 9 January 2018; pp. 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, N.; Sarvmaili, M.; Sayareh, A.; Amini, O.; Matwin, S.; Soares, A. Engineering Features to Improve Pass Prediction in Soccer Simulation 2D Games. In RoboCup 2021: Robot World Cup XXIV; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Alami, R., Biswas, J., Cakmak, M., Obst, O., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 13132, pp. 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadose, K.; Nishino, J. Improvement of the Decision Making of RoboCup Soccer Agents Using Fuzzy Evaluation Function of States. In Proceedings of the 33rd Fuzzy System Symposium (FSS 2017), Online, 9 January 2017; pp. 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, M.; Murakami, S. Self-Tuning Fuzzy Controller. Soc. Instrum. Control Eng. 1998, 24, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, M.; Kataoka, T.; Ueda, R.; Tatenuma, R.; Sugihara, K.; Nakamura, M. Jyo_sen2021 (Japan) 2D Soccer Simulation League Team Description Paper. In Proceedings of the RoboCup 2021 Symposium and Competitions: Team Description Papers, Worldwide, Online, 22–28 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Noohpisheh, M.; Shekarriz, M.; Barzegar, S.; Borzoo, D.; Kariminia, A. Razi Soccer 2D Simulation Team Description Paper 2018. In Proceedings of the RoboCup 2018 Symposium and Competitions: Team Description Papers, Montreal, QC, Canada, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Noohpisheh, M.; Shekarriz, M.; Bordbar, A.; Liaghat, M.; Salimi, A.; Borzoo, D.; Zarei, A. Razi Soccer 2D Simulation Team Description Paper 2019. In Proceedings of the RoboCup 2019 Symposium and Competitions: Team Description Papers, Sydney, Australia, 2–8 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Noohpisheh, M.; Shekarriz, M.; Zaremehrjardi, F.; Khademi Ardekani, F.; Khorsand, S.A. Persepolis Soccer 2D Simulation Team Description Paper 2021. In Proceedings of the RoboCup 2021 Symposium and Competitions: Team Description Papers, Worldwide, Online, 22–28 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fuladipanah, M.; Shahhosseini, A.; Rathnayake, N.; Azamathulla, H.M.; Rathnayake, U.; Meddage, D.P.P.; Tota-Maharaj, K. In-depth simulation of rainfall–runoff relationships using machine learning methods. Water Pract. Technol. 2024, 19, 2442–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Generations | 3600 |
| Population size | 30 |
| Gene structure | 60-dimensional real vector: , for |
| Selection method | Tournament selection (size = 4) |
| Crossover method | BLX- crossover () |
| Crossover probability | 0.5 |
| Mutation method | Gaussian mutation (mean = 0; std. dev = 10) |
| Mutation probability | 0.2 |
| Fitness evaluation | Average over 3 games (3000 cycles each) |
| Agent2D | Goals Scored | Shot Attempts | Penalty Area Entries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agent2D | |||
| Persepolis | |||
| Jyo_sen |
| Proposed Method | Goals Scored | Shot Attempts | Penalty Area Entries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agent2D | |||
| Persepolis | |||
| Jyo_sen |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoshino, Y.; Yoshimi, K.; Dang, T.L.; Rathnayake, N. Controlling Heterogeneous Multi-Agent Systems Under Uncertainty Using Fuzzy Inference and Evolutionary Search. Information 2025, 16, 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090732
Hoshino Y, Yoshimi K, Dang TL, Rathnayake N. Controlling Heterogeneous Multi-Agent Systems Under Uncertainty Using Fuzzy Inference and Evolutionary Search. Information. 2025; 16(9):732. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090732
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoshino, Yukinobu, Keigo Yoshimi, Tuan Linh Dang, and Namal Rathnayake. 2025. "Controlling Heterogeneous Multi-Agent Systems Under Uncertainty Using Fuzzy Inference and Evolutionary Search" Information 16, no. 9: 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090732
APA StyleHoshino, Y., Yoshimi, K., Dang, T. L., & Rathnayake, N. (2025). Controlling Heterogeneous Multi-Agent Systems Under Uncertainty Using Fuzzy Inference and Evolutionary Search. Information, 16(9), 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090732







