- Article
Ergonomics in Sleep Medicine: Interfacing Myofunctional Therapy with Orofacial Muscular Balance and Sleep Posture
- Siddharth Sonwane and
- Shweta Sonwane
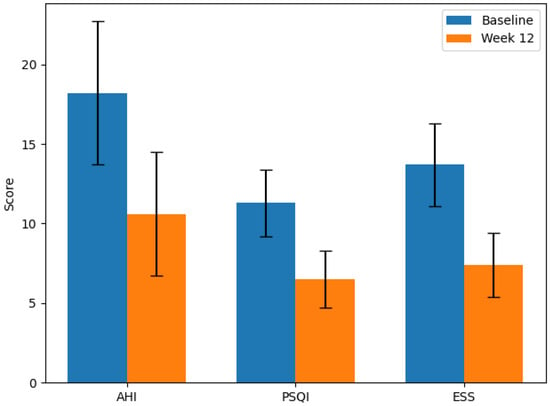
Background/Objectives: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a prevalent sleep-related breathing disorder characterized by repeated episodes of upper airway obstruction during sleep, leading to intermittent hypoxia and fragmented sleep architecture. Orofacial myofunctional therapy (OMT) has emerged as a promising non-invasive approach to improving airway patency in individuals with mild-to-moderate OSA. However, the role of sleep ergonomics—including sleep posture and pillow support—in enhancing OMT outcomes remains underexplored. This study aimed to evaluate whether ergonomic interventions could augment the therapeutic effects of OMT in adult patients with mild-to-moderate OSA. Methods: A 12-week prospective cohort study was conducted involving 60 adult participants diagnosed with mild-to-moderate OSA. All participants underwent a structured orofacial myofunctional therapy (OMT) program comprising exercises for tongue elevation, lip seal enhancement, and soft palate strengthening. In addition, ergonomic instructions were provided regarding optimal sleeping posture and pillow adjustment. Compliance with ergonomic practices was monitored weekly using infrared night-vision cameras and reviewed by a blinded sleep technician. Pre- and post-intervention assessments included apnea–hypopnea index (AHI), Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), and Ep-worth Sleepiness Scale (ESS). Results: Statistically significant improvements were observed in all measured parameters following the intervention. AHI scores reduced from 18.2 ± 4.5 to 10.6 ± 3.9 events/hour (p < 0.001), PSQI scores improved from 11.3 ± 2.1 to 6.5 ± 1.8 (p < 0.001), and ESS scores declined from 13.7 ± 2.6 to 7.4 ± 2.0 (p < 0.001). Participants with high adherence to ergonomic recommendations demonstrated significantly greater clinical improvements compared to less adherent individuals. Conclusions: The combination of ergonomic sleep posture interventions with OMT was associated with positive improvements in sleep-related outcomes, comparable to or in some cases better than those reported in previous studies evaluating these interventions independently. As an observational cohort without a control arm, this study cannot establish causality but provides preliminary evidence to guide the design of future randomized clinical trials.
30 December 2025