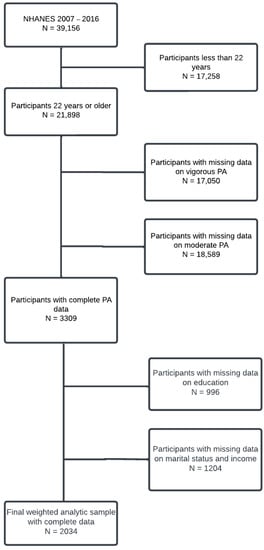
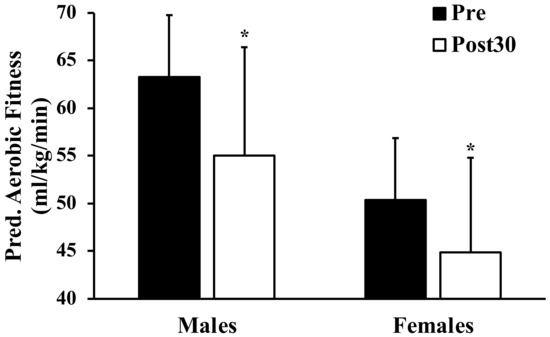
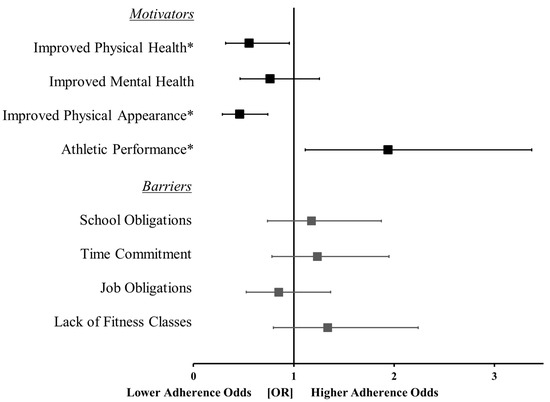
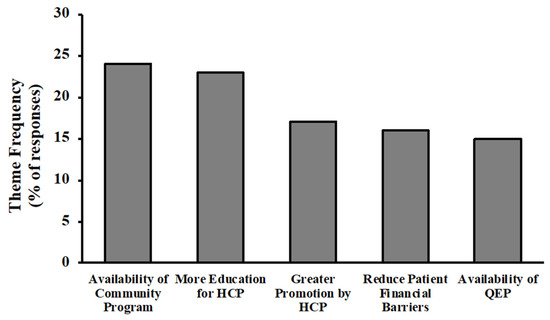
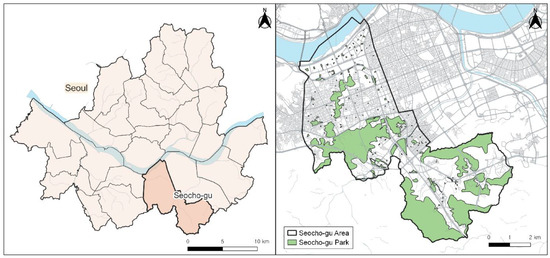
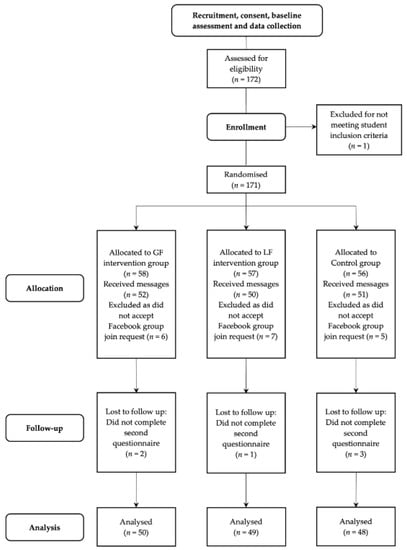
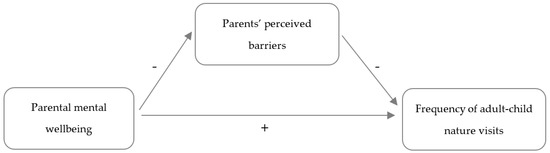
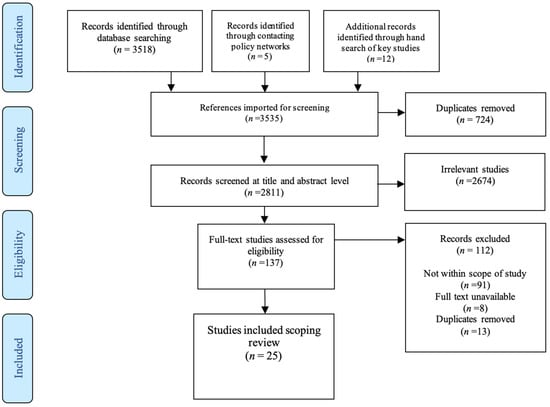
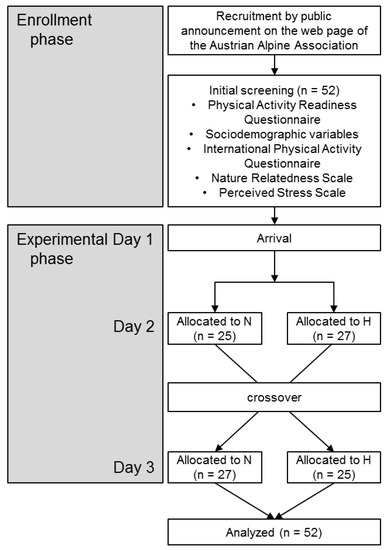
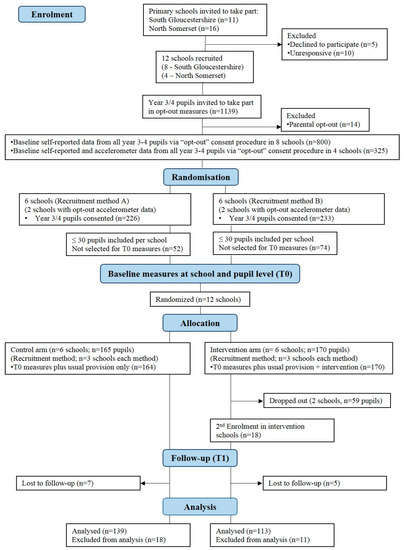
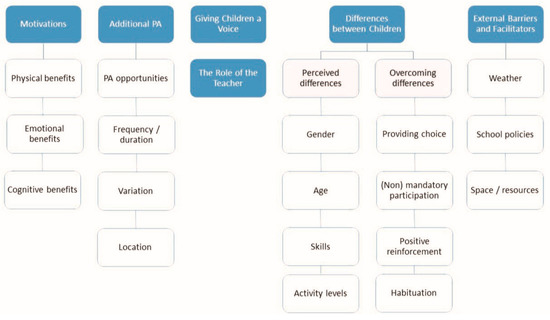
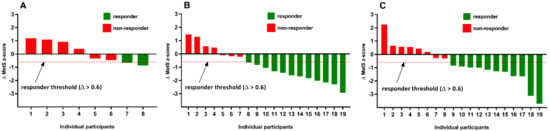
Physical Activity and Public Health
A topical collection in International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health (ISSN 1660-4601).
Submission Status: Closed | Viewed by 430471Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
We are organizing a Topic Collection on Physical Activity and Public Health in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. The venue is a peer-reviewed scientific journal that publishes articles and communications in the interdisciplinary area of environmental health sciences and public health. For detailed information on the journal, we refer you to https://www.mdpi.com/journal/ijerph.
There is compelling evidence for the importance of regular physical activity in attaining and maintaining a wide range of health outcomes across the lifespan. Active lifestyles are important for disease prevention as well as disease management and rehabilitation. Accordingly, understanding the associations of physical activity with health, as well the psychological, social, and environmental factors that shape physical activity behaviours, are urgent public health priorities. To advance our understanding and consequently develop more effective physical activity promotion, researchers in this field are continually seeking to develop improved methods of measuring physical activity and analysing raw data.
This Collection welcomes contributions across the broad field of physical activity and public health, including (but not limited to) the following topics:
- Determinants/correlates of physical activity, as a global measure or in specific contexts such as leisure, occupation, active transport, organized sport.
- Physical activity and disease prevention
- Physical activity outcomes in clinical populations, including, for example, cancer survivorship and cardiac rehabilitation
- Physical activity and mental health
- Physical activity and cognition
- Physical activity in ageing populations
- Physical activity and educational attainment in children
- Physical activity measurement: challenges and recent advances
- Physical activity prescription for health
We will welcome contributions that: focus on children or adults; report quantitative or qualitative studies; and use cross-sectional, experimental, or cohort designs.
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2500 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Physical activity
- Public health
- Adults
- Older adults
- Children
- Mental health
- Cognition
- Correlates
- Determinants
- Leisure
- Active transport
- Sport
- Rehabilitation
- Measurement
- Exercise