- Article
Clinical Management of Severe Cupriavidus gilardii Superinfection After Influenza a Virus Pneumonia: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Chenxia Guo,
- Cuihong Sun and
- Ying Liang
- + 2 authors
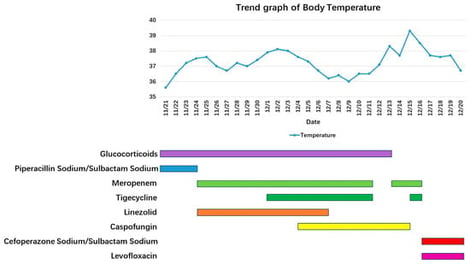
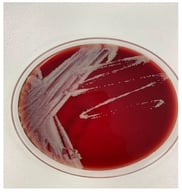
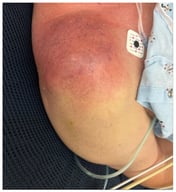
Background: Cupriavidus is an aerobic Gram-negative bacterium and a rare conditional pathogen that mainly infects immunocompromised patients or those undergoing invasive procedures. Methods: We present the case of a 70-year-old male with diabetes mellitus who developed septic shock following influenza A virus (IAV) pneumonia. Cupriavidus gilardii (C. gilardii) was identified in his blood and sputum samples. Through a literature review, we identified 31 reported cases of Cupriavidus infections. Clinical data, including demographic information, clinical characteristics, comorbidities, laboratory results, Cupriavidus species, treatment, and clinical outcomes, were collected. Results: Among these 32 patients (including our patient), 23 were male (71.9%) and 9 were female (28.1%). The median patient age was 32.5 (2.12–70) years. Most patients had relevant risk factors or comorbidities before Cupriavidus infection, including exposure to polluted environments and recent invasive procedures (68.9%). Among these cases, Cupriavidus pauculus was the most common strain, accounting for 56.3% of cases. The mortality rate was the highest for Cupriavidus pauculus infections. Conclusions: Cupriavidus is a rare opportunistic pathogen in patients with compromised immune function. Early identification of pathogen and timely treatment are crucial. When traditional microbiological detection methods encounter difficulties, gene sequencing can be used as an auxiliary diagnostic tool and can further predict drug resistance. Targeted anti-infection treatment is effective in most cases, but some severe infection cases may lead to death due to serious complications.
13 March 2026