- Article
Serum Oxidized LDL and Interleukin-10 as Biomarkers for Peripheral Artery Disease in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients Receiving Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy
- Hernycane Sosilya,
- Muhammad Noor Diansyah and
- Merlyna Savitri
- + 6 authors
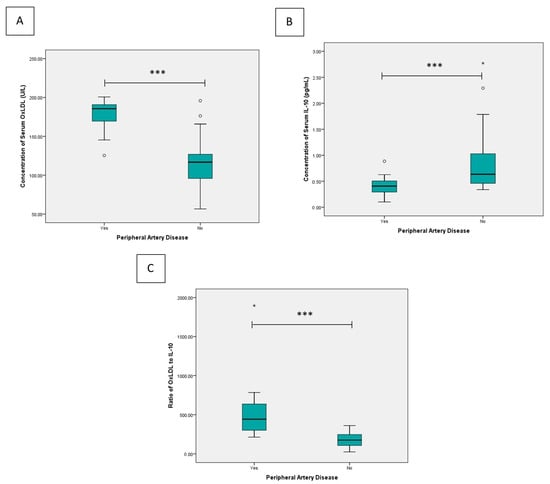
Background/Objectives: Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have transformed the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), yet emerging evidence indicates an increased risk of vascular adverse events, particularly peripheral artery disease (PAD). Reliable biomarkers for early detection of TKI-related vascular toxicity are still lacking. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted on 78 patients with chronic-phase CML treated at Dr. Soetomo General Hospital, Surabaya. PAD was confirmed using ankle–brachial index. Serum oxidized low-density lipoprotein (OxLDL) and interleukin-10 (IL-10) levels were measured using ELISA. Results: PAD was detected in 20% of subjects. The PAD group showed significantly higher OxLDL, lower IL-10, and a markedly elevated OxLDL/IL-10 ratio (all p < 0.001). OxLDL remained independently associated with PAD after adjustment (adjusted OR = 1.132, 95% CI 1.020–1.255, p = 0.019). OxLDL/IL-10 ratio yielded a good diagnostic value (sensitivity 87.5% and specificity of 88.7%). Conclusions: Elevated OxLDL and an increased OxLDL/IL-10 ratio are associated with PAD in CML patients receiving TKI therapy and demonstrated a good diagnostic performance for early detection of TKI-induced vascular toxicity.
4 January 2026