Journal Description
Genes
Genes
is a peer-reviewed, open access journal of genetics and genomics published monthly online by MDPI. The Spanish Society for Nitrogen Fixation (SEFIN) is affiliated with Genes and its members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, Embase, PubAg, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Genetics and Heredity) / CiteScore - Q2 (Genetics (clinical))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 14.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: Reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
2.8 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.2 (2024)
Latest Articles
Duplication, Divergence and Cardiac Expression of Tropoelastin in Jawed Fishes, Including Tetraploid Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1492; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121492 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/objectives: Tropoelastin is a highly hydrophobic extracellular matrix protein responsible for the extensibility and elastic recoil of various organs. The Windkessel effect in blood vessels dampens pressure variations during the cardiac cycle to provide continuous perfusion of tissues, such as the fragile gill
[...] Read more.
Background/objectives: Tropoelastin is a highly hydrophobic extracellular matrix protein responsible for the extensibility and elastic recoil of various organs. The Windkessel effect in blood vessels dampens pressure variations during the cardiac cycle to provide continuous perfusion of tissues, such as the fragile gill capillaries in fish. The teleost-specific whole-genome duplication was followed by structural and functional divergence of the duplicated tropoelastins, of which ElnB confers the uniquely low stiffness of the bulbus arteriosus. Methods: We have examined the diversity of tropoelastins in all major fish clades by searching for tropoelastin (eln) genes in the sequenced genomes. Duplication of eln genes in tetraploid salmonids and cyprinids was examined by maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis, and cardiac eln expression in rainbow trout was quantified by qPCR. Results: The tetraploid salmonid genomes harbor two elna genes but a single elnb, except for the tandem duplicated elnb genes in sockeye salmon and lake whitefish, while the tetraploid common carp possesses four elna and elnb genes on separate chromosomes. Rainbow trout showed strong elastin staining in the larval bulbus and ventral aorta, and the bulbar expression of elnb was 15 times higher than the ventricular levels in juvenile fish. The expression of elna1 and elna2 was also significantly higher in the bulbus, and together their transcript levels were almost similar as the elnb levels. The overall hydrophobicity of the fish tropoelastins differed considerably among the species ranging from 28.6% in Emerald rockcod ElnB to 56.3% in lesser devil ray Eln, but showed no significant difference with the tetrapods examined, except for the lower hydrophobicity of teleost ElnB. Conclusions: The inclusion of tetrapods in the analysis revealed a positive relationship between ventral aortic blood pressure and tropoelastin hydrophobicity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Genetics and Genomics)
Open AccessArticle
Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Insights into the Hepatic Response to Dietary Carvacrol in Pengze Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus var. Pengze)
by
Wenshu Liu, Yuzhu Wang, Xiaoze Guo, Jingjing Lu, Lingya Li, Siming Li, Yanqiang Tang and Haihong Xiao
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1491; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121491 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Carvacrol, a major active component of oregano oil and common feed additive, has been widely studied for its effects on fish growth, immunity, and intestinal health. But its transcriptional/metabolic impacts on fish liver remain unclear. This study investigated these effects in Pengze
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Carvacrol, a major active component of oregano oil and common feed additive, has been widely studied for its effects on fish growth, immunity, and intestinal health. But its transcriptional/metabolic impacts on fish liver remain unclear. This study investigated these effects in Pengze crucian carp (Carassius auratus var. Pengze). Methods: Fish were fed a basal diet (control) or basal diet supplemented with 10% microencapsulated carvacrol (600 mg/kg) for 56 days; liver samples were analyzed via transcriptomics and metabolomics. Results: Transcriptomic analysis revealed 482 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the liver of Pengze crucian carp following carvacrol supplementation, with 158 upregulated and 324 downregulated genes. Functional annotation highlighted enrichment in translation, signal transduction, amino acid metabolism, and posttranslational modification pathways. GO analysis further identified key processes, including carboxylic acid transport, tRNA aminoacylation, and mitochondrial nucleoid function, while KEGG pathways were implicated in amino acid biosynthesis, lipid metabolism (e.g., alpha-linolenic acid), and insulin signaling. Metabolomic profiling identified 679 significantly altered metabolites, including 113 upregulated and 566 downregulated ones. Among these, upregulated compounds like L-asparaginyl-L-lysine (Log2FC = 4.36) and 2′-Deoxyadenosine-5′-diphosphate (Log2FC = 4.31) are linked to nucleotide metabolism, and downregulated peptides (e.g., Ala-Phe-Tyr-Arg) suggesting modulated protein turnover. Joint omics analysis revealed convergent pathways in glycerophospholipid metabolism, aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis, and autophagy. Notably, the chaperone gene dnaja3b was correlated strongly with neuroactive metabolites (e.g., normetanephrine), potentially implicating carvacrol in stress response regulation. Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that carvacrol modulates liver gene expression and metabolic profiles, primarily influencing amino acid and lipid metabolism pathways, autophagy, and stress responses. The observed correlations between dnaja3b and specific metabolites offer mechanistic insights into the action of carvacrol in fish liver.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Genetics and Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures
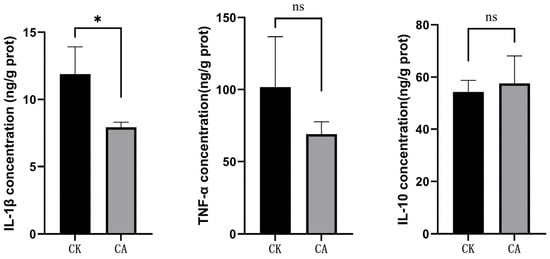
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigation of Prothrombin G20210A and Factor V Leiden G1691A Variants in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome Presenting to the Emergency Department with Chest Pain
by
Fulya Yukcu, Murtaza Kaya, Fatmagul Can and Harun Yildirim
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1490; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121490 (registering DOI) - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is a major cardiovascular emergency influenced by environmental and genetic factors. Thrombophilic variants such as prothrombin G20210A (rs1799963) and factor V Leiden G1691A (rs6025) may influence thrombin generation and has been reported to show associations with coronary events.
[...] Read more.
Background: Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is a major cardiovascular emergency influenced by environmental and genetic factors. Thrombophilic variants such as prothrombin G20210A (rs1799963) and factor V Leiden G1691A (rs6025) may influence thrombin generation and has been reported to show associations with coronary events. Methods: This case–control study included 100 ACS patients and 131 age and sex-matched healthy controls. Genotyping of rs1799963 and rs6025 was performed using polymerase chain reaction followed by restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) analysis. Results: The GG genotype was markedly more common among ACS patients for both variants. For rs1799963, carriers of the A allele (GA + AA) were less common in ACS (2.0%) than controls (9.2%; p = 0.039), corresponding to an 8.6-fold higher odds of ACS in GG carriers (OR = 8.624; 95% CI: 1.757–42.345; p = 0.008). For rs6025, A allele carriers (9.0%) were also reduced in ACS versus controls (18.3%; p = 0.049), and GG homozygotes exhibited a 2.6-fold higher risk (OR = 2.635; 95% CI: 1.104–6.290; p = 0.029). Age was independently associated with higher ACS risk (OR = 1.047; 95% CI: 1.029–1.066; p < 0.001). Conclusions: Our findings indicate that the rs1799963 and rs6025 variants were independently associated with ACS, together with advancing age. Both the GG genotype and older age were associated with higher odds of ACS, whereas A-allele carriers appeared less common among ACS cases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Genomics and Genetic Diseases)
Open AccessArticle
Causal Association Between Psoriasis and Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
by
Young Lee, Soojin Kim and Je Hyun Seo
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1489; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121489 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Psoriasis and age-related macular degeneration (AMD) may share immune-related pathophysiologic characteristics. However, few studies have investigated the relationship between psoriasis and AMD. We assessed the possible causal link between psoriasis and AMD in European populations. Methods: Single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated with psoriasis exposure
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Psoriasis and age-related macular degeneration (AMD) may share immune-related pathophysiologic characteristics. However, few studies have investigated the relationship between psoriasis and AMD. We assessed the possible causal link between psoriasis and AMD in European populations. Methods: Single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated with psoriasis exposure were employed as instrumental variables (IVs) based on genome-wide significance (p < 5.0 × 10−8) in the FinnGen genome-wide association study (GWAS). The GWAS data for AMD were obtained from 11 studies performed by the International AMD Genomics Consortium. We performed a two-sample Mendelian randomisation (MR) study to estimate causal effects using the inverse-variance weighted, weighted median, and MR-Egger methods, as well as the MR-Pleiotropy Residual Sum and Outlier (MR-PRESSO) test. Results: We observed significant causal associations of psoriasis with AMD. Using the weighted median method, the odds ratio (OR) was 1.09 (95% CI = [1.03–1.16] and p = 0.005), and using the MR-PRESSO test, the OR was 1.04 (95% CI = [1.00–1.09] and p = 0.043). Conclusions: A potential causal association between psoriasis and AMD underscores the need to investigate inflammation as a risk factor for AMD.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Genetic Diagnosis and Therapeutics of Eye Diseases)
Open AccessArticle
Three New Mitochondrial Genomes of Semisulcospiridae J. P. E. Morrison, 1952 (Caenogastropoda: Cerithioidea) from China and Insights into Their Phylogenetic Position
by
Yibin Xu, Yuanzheng Meng, Sheng Zeng, Deyuan Yang, Shen Zhong, Zeyang Lin, Xiaohong Chen, Zhao Zhang, Hangjun Wang and Huidong Zheng
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1488; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121488 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Semisulcospiridae is a family of freshwater gastropods with over 100 species, primarily distributed in East Asia and North America. They play crucial ecological roles and are of medical importance as intermediate hosts for parasites. However, their phylogenetic relationship remains unclear. Most previous
[...] Read more.
Background: Semisulcospiridae is a family of freshwater gastropods with over 100 species, primarily distributed in East Asia and North America. They play crucial ecological roles and are of medical importance as intermediate hosts for parasites. However, their phylogenetic relationship remains unclear. Most previous studies, which focused on fewer molecular markers (e.g., COI, 16S, 28S), have shown limitations in resolving relationships with low resolution. Mitochondrial genomes, with their richer phylogenetic information, offer a promising tool to infer the evolutionary relationships within this family. Methods: This study sequenced, assembled, and annotated the complete mitochondrial genomes of three Semisulcospiridae species from China: Koreoleptoxis friniana, Hua textrix, and Hua yangi. Phylogenetic analyses were conducted using Maximum Likelihood (ML) and Bayesian Inference (BI) methods on five distinct datasets derived from the mitochondrial genomes, including nucleotide sequences of protein-coding genes (with and without third codon positions), amino acid sequences, and combinations with two ribosomal RNA genes. Results: The complete (or near-complete) mitochondrial genomes of K. friniana, H. textrix, and H. yangi were 15,474 bp, 15,660 bp, and 15,744 bp in length, respectively, showing typical gene content and an A+T bias. The gene order was highly conserved. Phylogenetic analyses consistently recovered the family Semisulcospiridae as monophyletic and revealed three well-supported, distinct clades corresponding to the genera Semisulcospira, Koreoleptoxis, and Hua. While the overall tree topologies were robust for Semisulcospiridae, some incongruences were observed in the placements of other cerithioidean families depending on the dataset used. Evolutionary rate analysis (Ka/Ks) indicated strong purifying selection across all protein-coding genes, with COX1 being the most conserved. Conclusions: This study provided three new mitochondrial genomes for Semisulcospiridae: K. friniana, H. textrix, and H. yangi. Phylogenetic analysis based on mitochondrial genome datasets offers new evidence that supports the monophyly of the three Asian genera of Semisulcospiridae. Future research should include broader taxonomic sampling, particularly of the North American genus Juga and the atypical Japanese Semisulcospira lineages, to achieve a comprehensive phylogenetic framework.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Genetics and Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Medical Marijuana and Treatment Personalization: The Role of Genetics and Epigenetics in Response to THC and CBD
by
Małgorzata Kalak, Anna Brylak-Błaszków, Łukasz Błaszków and Tomasz Kalak
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1487; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121487 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Personalizing therapy using medical marijuana (MM) is based on understanding the pharmacogenomics (PGx) and drug–drug interactions (DDIs) involved, as well as identifying potential epigenetic risk markers. In this work, the evidence regarding the role of variants in phase I (CYP2C9, CYP2C19
[...] Read more.
Personalizing therapy using medical marijuana (MM) is based on understanding the pharmacogenomics (PGx) and drug–drug interactions (DDIs) involved, as well as identifying potential epigenetic risk markers. In this work, the evidence regarding the role of variants in phase I (CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP3A4/5) and II (UGT1A9/UGT2B7) genes, transporters (ABCB1), and selected neurobiological factors (AKT1/COMT) in differentiating responses to Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) has been reviewed. Data indicating enzyme inhibition by CBD and the possibility of phenoconversion were also considered, which highlights the importance of a dynamic interpretation of PGx in the context of current pharmacotherapy. Simultaneously, the results of epigenetic studies (DNA methylation, histone modifications, and ncRNA) in various tissues and developmental windows were summarized, including the reversibility of some signatures in sperm after a period of abstinence and the persistence of imprints in blood. Based on this, practical frameworks for personalization are proposed: the integration of PGx testing, DDI monitoring, and phenotype correction into clinical decision support systems (CDS), supplemented by cautious dose titration and safety monitoring. The culmination is a proposal of tables and diagrams that organize the most important PGx–DDI–epigenetics relationships and facilitate the elimination of content repetition in the text. The paper identifies areas of implementation maturity (e.g., CYP2C9/THC, CBD-CYP2C19/clobazam, AKT1, and acute psychotomimetic effects) and those requiring replication (e.g., multigenic analgesic signals), indicating directions for future research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Epigenomics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Metabolic and Proteomic Reveals of 7Li (Lithium-7) Ion Beam Radiation in Capsicum annuum L.
by
Yue Huang, Maojingkai Li, Yan Li, Xingliang Wang, Chongyu Gu, Jianzhong Wu and Xue Wang
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1486; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121486 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Chili pepper (Capsicum annuum L.), a globally cultivated and ancient domesticated crop, carries considerable significance in agriculture. While radiation-induced mutagenesis has found application in this crop, the mutagenic efficacy and molecular-level impacts of 7Li ion beam radiation remain poorly elucidated. Methods:
[...] Read more.
Background: Chili pepper (Capsicum annuum L.), a globally cultivated and ancient domesticated crop, carries considerable significance in agriculture. While radiation-induced mutagenesis has found application in this crop, the mutagenic efficacy and molecular-level impacts of 7Li ion beam radiation remain poorly elucidated. Methods: We irradiated pepper with a beam of 7Li ions to create a mutant, which showed good economic traits, and phenotypic and physio-biochemical characterization were combined with proteomic and metabolomic profiling to delineate the mutagenic mechanisms. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was further utilized to assess the biological impact and underlying response pathways. We used this to evaluate the biological impact and the reaction mechanisms behind it. Results: 7Li beam radiation positively influenced morphology and physiological traits, notably chlorophyll and anthocyanin content. Leveraging proteomic profiling detected 6082 proteins, including 355 differential proteins (139 upregulated, 216 downregulated), enriched in 4 KEGG pathways. Based on GO and KEGG network analysis, 250 metabolites were quantified, with 120 being differentially abundant (112 upregulated, 8 downregulated), enriched in 9 metabolic pathways. Furthermore, qRT-PCR results revealed that differentially expressed genes were consistent with the corresponding metabolomic data. Joint analysis revealed the coordinated enrichment of differential metabolites and proteins in pathways related to amino acid and carbohydrate metabolism. These findings suggest that these active pathways in pepper are related to its response to ion beam radiation. Overall, this study is a valuable resource for subsequent genomic research on peppers and 7Li ion beam radiation research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Plant Genetics and Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Study on the Developmental Differences Between Female and Male Early Embryos in Cattle In Vivo
by
Jie Wang, Fei Huang, Di Fang, Peng Niu, Jie-Ru Wang and Qing-Hua Gao
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1485; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121485 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: The developmental differences between female and male early embryos regarding sex development remain a topic of controversy. Objectives: This study aims to investigate whether there are significant developmental differences between female and male bovine embryos during in vivo development. Methods: The CIDR
[...] Read more.
Background: The developmental differences between female and male early embryos regarding sex development remain a topic of controversy. Objectives: This study aims to investigate whether there are significant developmental differences between female and male bovine embryos during in vivo development. Methods: The CIDR + FSH + PGF2α + GnRH method was employed to induce superovulation in 20 donor cows. Subsequently, artificial insemination was performed on the donor cows using high-purity X and Y frozen semen, with 10 cows receiving each type of semen. Seven days later, the embryos were flushed from the donor cows. The flushed embryos underwent embryonic sex determination, followed by immunofluorescence analysis to observe proliferation and apoptosis, and finally, RT-PCR was conducted to detect genes associated with proliferation and apoptosis. Results: The results indicated that the sex ratio of embryos obtained through artificial insemination using X/Y semen did not significantly differ based on semen purity (p ≥ 0.05). However, the fluorescence intensity of apoptotic cells in the X-BL group was significantly higher than that in the Y-BL group (p < 0.05). Conversely, the fluorescence intensity of proliferating cells in the X-BL group was significantly lower than that in the Y-BL group (p < 0.05). Furthermore, the expression levels of apoptosis-related genes in the X-BL group were significantly higher compared to the Y-BL group (p < 0.05), while the expression levels of proliferation-related genes in the X-BL group were significantly lower than those in the Y-BL group (p < 0.01). Conclusions: The above results indicate that during in vivo development of bovine early embryos, male embryos develop at a faster rate than female embryos.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Cattle Genetics, Genomics and Breeding: From Molecular Insights to Sustainable Production)
►▼
Show Figures
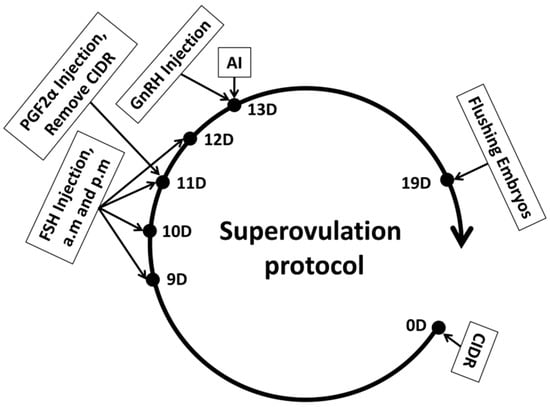
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Prenatal Identification of an EDA Variant in Dichorionic Male Twins: CfDNA Signal with Invasive Confirmation
by
Simone Marcella, Roberto Sirica, Nadia Petrillo, Monica Ianniello, Alessio Mori, Rosa Castiello, Sossio Federico Capone, Eloisa Evangelista, Teresa Suero, Raffaella Ruggiero, Alfredo Columbro, Antonio Barone, Ioannis Malandrenis, Antonio Fico and Giovanni Savarese
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1484; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121484 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (XLHED) is a rare monogenic disorder characterized by hypohidrosis, hypotrichosis, and hypodontia, caused primarily by pathogenic variants in the EDA gene. XLHED predominantly affects males due to its X-linked recessive inheritance, while female carriers may exhibit variable phenotypes
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (XLHED) is a rare monogenic disorder characterized by hypohidrosis, hypotrichosis, and hypodontia, caused primarily by pathogenic variants in the EDA gene. XLHED predominantly affects males due to its X-linked recessive inheritance, while female carriers may exhibit variable phenotypes due to random X-inactivation. Early diagnosis is critical for timely counseling and emerging therapeutic interventions. We report a rare prenatal diagnosis of XLHED in dizygotic dichorionic male twins during a dichorionic diamniotic pregnancy. At 24 weeks’ gestation, ultrasonographic anomalies—facial dysmorphisms, oligodontia, and hypoechogenic skin—raised suspicion for ectodermal dysplasia. Methods: Non-invasive prenatal test and targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) of Cell-free DNA identified an hemizygous EDA deletion (c.612_629del; p.Ile205_Gly210del) with 52% variant allele frequency. Results: This in-frame deletion affects a highly conserved region in the TNF homology domain of ectodysplasin-A1, likely compromising protein function. The variant was confirmed in both fetuses via genetic analysis on amniotic fluid and in the heterozygous state in the mother, consistent with X-linked recessive inheritance. Family history revealed a maternal uncle with XLHED. Additional heterozygous variants were also identified in CPT2, GBA1, GJB2, and SMN1 genes. Following comprehensive genetic counseling, the mother opted for abortion. Conclusions: This case underscores the value of applying advanced genomic technologies—cfDNA-based NGS—for prenatal diagnosis of rare genetic disorders. The identification of apathogenic EDA variant expands the mutational spectrum of XLHED and supports early diagnosis for informed reproductive decisions and potential access to emerging prenatal therapies. Broader application of such technologies may improve outcomes in future pregnancies at risk for monogenic disorders.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Genomics and Genetic Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
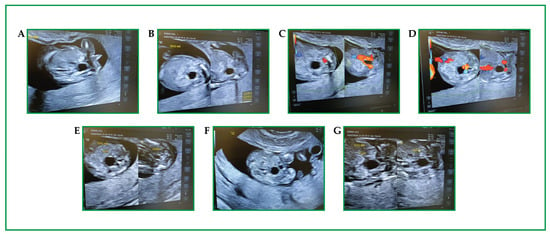
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Integrated Transcriptomic Analysis Identifies Core Hub Genes Regulating Mammary Gland Traits (Milk Quality/Lactation) in Dairy Livestock: Bos taurus and Ovis aries
by
Qiang Zhang, Lulu Yang, Yunhan Li, Pengbo Gu, Riguleng Si, Shuai Li, Lin Zhu and Wenguang Zhang
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1483; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121483 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Mammary gland traits (milk quality and lactation performance) are economically critical for B. taurus and O. aries, but core regulatory hub genes remain unclear due to high false positives in single-method transcriptomic analyses. This study aimed to identify robust hub genes
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Mammary gland traits (milk quality and lactation performance) are economically critical for B. taurus and O. aries, but core regulatory hub genes remain unclear due to high false positives in single-method transcriptomic analyses. This study aimed to identify robust hub genes linked to species-specific differences in mammary gland tissue via an integrated bioinformatics strategy. Methods: Raw transcriptomic data (77 B. taurus and 77 O. aries mammary gland samples) were retrieved from the European Nucleotide Archive (ENA); after quality control, differential expression gene (DEG) screening, weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA), and SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP)-assisted machine learning were performed, with core genes defined as the intersection of the three gene sets, and functional enrichment and protein–protein interaction (PPI) network analyses were used to prioritize hub genes. Results: A total of 13,138 high-quality genes were retained, including 6148 DEGs, 4698 WGCNA core module genes, and 500 SHAP-high-contribution genes, yielding 178 core genes that were significantly enriched in the “translation” (p < 0.001) pathways; hub genes were identified via PPI network analysis. Conclusions: These findings indicate that RPS15 and RPL7A are core species-difference signals in mammary gland tissue of B. taurus and O. aries, providing insights into inter-species molecular differences, and this integrated strategy enhances the robustness of hub gene identification in pure bioinformatics studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advances in Molecular Genetics and Breeding of Cattle, Sheep, and Goats)
►▼
Show Figures
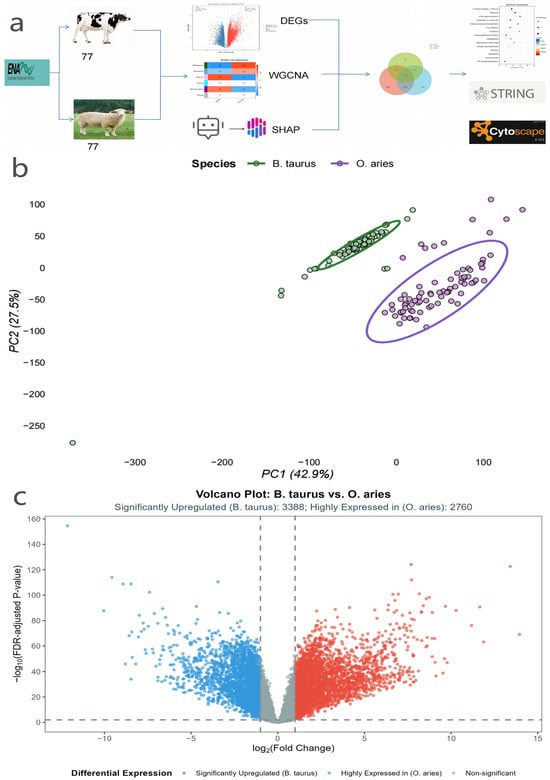
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
WES-Based Screening of a Swedish Patient Series with Parkinson’s Disease
by
Efthymia Kafantari, Kajsa Atterling Brolin, Joel Wallenius, Maria Swanberg and Andreas Puschmann
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1482; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121482 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objective: Genetic factors contribute significantly to Parkinson’s disease (PD), especially in cases with early onset or positive family history. However, previous investigations of the genetic landscape in PD populations were mainly based on targeted genotyping. The aim of this study was to investigate
[...] Read more.
Background/Objective: Genetic factors contribute significantly to Parkinson’s disease (PD), especially in cases with early onset or positive family history. However, previous investigations of the genetic landscape in PD populations were mainly based on targeted genotyping. The aim of this study was to investigate the prevalence of pathogenic variants in known PD-associated genes in a series of Swedish PD patients. Methods: We performed whole-exome sequencing on 285 PD probands from southern Sweden. Our series was enriched for patients with early disease onset or positive family history. We focused on 44 genes previously linked to PD. Results: We identified a CHCHD2 p.(Phe84LeufsTer6) frameshift variant in two unrelated patients and report the first PD case of Swedish ancestry carrying the VPS35 p.(Asp620Asn) variant. Additionally, in one patient each, we found an SNCA duplication, an SNCA p.(Ala53Thr) variant, and a LRRK2 p.(Gly2019Ser) variant. Thus, only 2.1% (n = 6) of patients in this series had Mendelian monogenic PD forms. In addition, forty-three patients carried variants in GBA1, including T369M, which may lack disease-association in our population (n = 12); E326K (n = 22), which is classified as a PD risk variant; as well as N370S (n = 3), R329H (n = 3), S107L (n = 1), and L444P (n = 1), with one patient harboring both T369M and E326K. Pathogenic variants in ARSA, ATP7B, and PRKN genes were also detected in heterozygote form, but their role in PD remains uncertain. Conclusions: Monogenic forms of PD are rare in southern Sweden, even among the familial and early-onset PD patients that were overrepresented in our study. Our findings highlight the genetic diversity in Swedish PD patients and identify key variants for further functional and clinical studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Neurogenomics)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Analysis and Characterization of Plastid Genomes of Mycetia (Rubiaceae)
by
Dongxian Xu, Lingyu Zhang, Chi Zhang, Lei Song, Wanhui Qian, Hao Luo and Qing Zhao
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1481; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121481 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Mycetia, a subshrub genus within the subfamily Rubioideae (Rubiaceae), is predominantly distributed in tropical Asia, lacking comprehensive plastid genomic resources. This study aimed to characterize the complete plastid genomes of two Mycetia species and explore their structural features and evolutionary relationships.
[...] Read more.
Background: Mycetia, a subshrub genus within the subfamily Rubioideae (Rubiaceae), is predominantly distributed in tropical Asia, lacking comprehensive plastid genomic resources. This study aimed to characterize the complete plastid genomes of two Mycetia species and explore their structural features and evolutionary relationships. Methods: The plastid genomes of Mycetia hirta and Mycetia sinensis were sequenced and assembled. We analyzed genome structure, simple sequence repeats (SSRs), long repeats, codon usage, nucleotide diversity (π), and Ka/Ks and conducted phylogenetic analysis. Results: Both genomes exhibited a typical quadripartite structure (153,989–154,588 bp; GC content 37.7–37.8%), encoding 127 genes (86 protein-coding, 8 rRNA, and 32 tRNA). Both chloroplast genomes contained 52–60 SSRs and three repeat types with minor interspecific differences. Junction regions and codon usage were highly conserved, with slight variations in RSCU values. The average π was 0.0096, and the non-coding trnE-trnT (π = 0.0817) emerged as a potential DNA barcode. The average Ka/Ks was 0.2900, indicating purifying selection. Phylogenetic analysis confirmed the monophyly of Mycetia within Argostemmateae. Conclusions: This study provides the first comparative plastid genomic analysis for Mycetia, enhancing our understanding of its genetic diversity and supporting future phylogenetic and taxonomic research on the genus.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Plant Genetics and Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
G2H: A Precise Block-Scanning Strategy for Genetic Background Assessment in Maize Backcross Breeding
by
Xiangyu Qing, Weiwei Wang, Liwen Xu, Yunlong Zhang, Yikun Zhao, Jianrong Ge, Xuelei Shen, Rui Wang, Yingjie Xue and Fengge Wang
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1480; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121480 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
(1) Background: Backcross (BC) breeding is a key technology of crop improvement, yet its efficiency largely depends on the precise assessment of the genetic background recovery. Conventional molecular marker-assisted techniques suffer from inadequate genomic coverage or an inability to resolve true chromosomal structure.
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: Backcross (BC) breeding is a key technology of crop improvement, yet its efficiency largely depends on the precise assessment of the genetic background recovery. Conventional molecular marker-assisted techniques suffer from inadequate genomic coverage or an inability to resolve true chromosomal structure. (2) Methods: To address major issues in maize BC breeding, we devised a G2H block-scanning strategy. This approach converts high-density point markers into haplotype blocks, enabling precise evaluation of the genetic background in backcross progenies. A key innovation is the CFDI, which quantifies the distribution of unrecovered fragments, allowing for visual tracking of chromosomal recombination and identification of ideal individuals with both a high genetic background recovery rate and few small fragments retention. (3) Results: We validated the accuracy and effectiveness of the G2H strategy across multiple backcross generations. Through enabling a precise “point-to-line-to-area” panoramic assessment of genetic background, G2H provides a powerful tool for developing ideal breeding materials with pure genetic background and minimized linkage drag. (4) Conclusions: Notably, this strategy significantly shortens the breeding cycle by 2–3 generations compared to conventional background assessment methods, thereby accelerating precision molecular design breeding in crops.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Plant Genetics and Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures
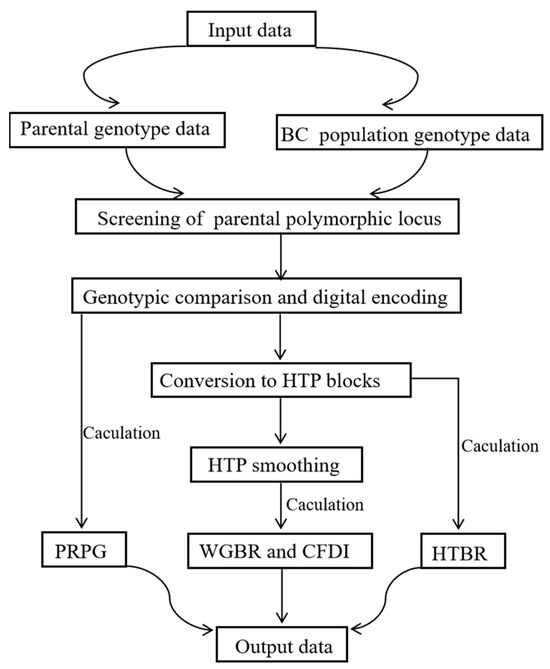
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Exploratory, Retrospective Study of the CYPRI Score for Pharmacogenetic Testing Among Mental Health Patients
by
Samira Marie Comtesse, Ivana Tašková, Nicole Safářová and Martina Hahn
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1479; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121479 - 9 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Pharmacogenetic (PGx) testing is gaining importance in optimizing psychiatric pharmacotherapy, yet routine use remains limited due to cost and unclear patient selection criteria. The CYP Pharmacogenetic Risk Score (CYPRI) is a clinical tool designed to identify psychiatric patients most likely to
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Pharmacogenetic (PGx) testing is gaining importance in optimizing psychiatric pharmacotherapy, yet routine use remains limited due to cost and unclear patient selection criteria. The CYP Pharmacogenetic Risk Score (CYPRI) is a clinical tool designed to identify psychiatric patients most likely to benefit from PGx testing, based on medication profile, adverse drug reactions (ADRs), and therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) results. This study aimed to evaluate the clinical relevance of the CYPRI by identifying its weaknesses and gaps in a clinical setting, propose targeted modifications to address those limitations, and assess the applicability of the improved version in a routine clinical setting. Methods: In a retrospective analysis, data from 92 patients with depression at Frankfurt University Hospital were evaluated using the CYPRI score. Its association with the clinical impact of PGx testing, measured by the IMPACT score, was analyzed using ordinal regression and Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis. Based on the findings, a revised version of CYPRI was developed and applied to the retrospective cohorts of Frankfurt and Prague. Results: The original CYPRI score was significantly associated with increased IMPACT score, suggesting its clinical value in detecting non-normal CYP2D6 and/or CYP2C19 metabolizers. However, the corrected version (hereafter referred to as CYPRI_cor), which emphasized clinically relevant pharmacokinetic factors, showed improved clinical specificity while maintaining similar discriminative performance. In the Frankfurt cohort, the area under the curve (AUC) for CYPRI_cor was 0.68 (95% CI 0.56–0.79), and in the Prague cohort, the AUC for CYPRI_cor was 0.71 (95% CI 0.60–0.81). While the overall discriminative ability in Frankfurt was slightly lower, CYPRI_cor achieved a specificity of 0.69, enabling more precise identification of patients most likely to benefit from PGx testing. A CYPRI Cut-off of ≥4 was determined to indicate clinical impact. Conclusions: The CYPRI_cor score was designed to optimize and to rule out potential limitations of the original score, particularly regarding the attribution of ADRs and the weighting of TDM results. Although the modifications did not improve discriminative performance in the Frankfurt dataset, the proposed changes remain meaningful. Prospective clinical studies need to verify the clinical utility of the CYPRI_cor.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Psychiatric Pharmacogenomics)
►▼
Show Figures
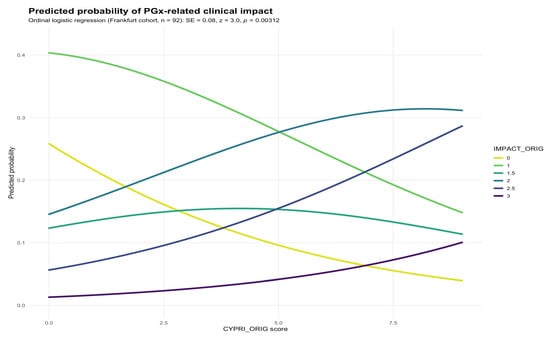
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
From Digenic to Monogenic Sex Determination in Insects: A Genetic Model Based on Imprinting and X Chromosome Elimination
by
Lucas Sánchez
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1478; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121478 - 9 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: In digenic populations, all females produce males and females in their offspring. Monogenic populations are composed of gynogenic (female-producing) and androgenic (male-producing) females. A theoretical population genetic model for evolution of digenic to monogenic populations is presented here. Methods: A controlling gene
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: In digenic populations, all females produce males and females in their offspring. Monogenic populations are composed of gynogenic (female-producing) and androgenic (male-producing) females. A theoretical population genetic model for evolution of digenic to monogenic populations is presented here. Methods: A controlling gene was associated with each of the four processes that characterise monogenic populations: (1) oogenesis is conventional, whereas spermatogenesis is unusual and it is characterised by the exclusive formation of X-bearing sperm (gene (s)), i.e., the paternal chromosomes are eliminated so that only the maternal ones are transmitted to the next generation; (2) the X chromosome that is eliminated in the zygote is the one inherited from the father (gene r); (3) an imprinting process occurs in the mother (gene g), which protects the maternally inherited X chromosome from elimination in the zygote and the whole maternal chromosome complement in spermatogenesis; (4) a maternal factor is produced during oogenesis (gene e), which inactivates the elimination factor [r] in the zygote, thus controlling the elimination of the paternal X chromosome. The sequences of emergence of the genes (e s r g) that transform a digenic population into a monogenic one were analysed. Results: The following evolutionary sequences were found: (1) the sequence (r s e) under dominant conditions of gene (s) and recessive conditions of gene (r); and (2) the sequences (s r e), (r s e), and (e s r) under recessive conditions of gene (s) and gene (r). It was also found that the process of genomic imprinting is a necessary condition for the generation of a monogenic population. Furthermore, a quantitative change in the interaction between the elimination factor and its maternal inhibitor modifies the genotypic formula of the monogenic state. Conclusions: The number and types of evolutionary transitions of a digenic to a monogenic population depends on the dominant or recessive characteristic of the newly emerging genes. The imprinting process must already be present in the digenic population from which the monogenic one evolves; otherwise, the population cannot reach the monogenic state.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Genetics and Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures
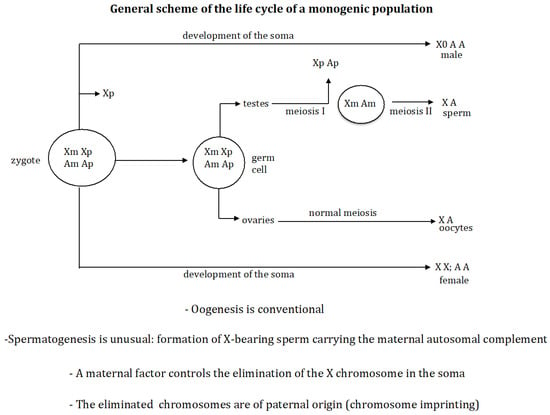
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Revealing Ancient Wheat Phylogenetic Diversity: Machine Learning and Logistic Regression Identify Triticum sphaerococcum in Bronze Age Iberia
by
Diego Rivera, Milagros Ros-Sala, Diego-José Rivera-Obón, Francisco Alcaraz, P. Pablo Ferrer-Gallego, Emilio Laguna, Nikolay P. Goncharov, Yulia V. Kruchinina and Concepción Obón
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1477; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121477 - 9 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Identifying archaeobotanical wheat remains is central to reconstructing the evolutionary history of cereal crops. Beyond documenting agricultural practices, such analyses provide critical evidence of phylogenetic diversity, lineage persistence, and local extinction events within the genus Triticum L. This study applies advanced computational
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Identifying archaeobotanical wheat remains is central to reconstructing the evolutionary history of cereal crops. Beyond documenting agricultural practices, such analyses provide critical evidence of phylogenetic diversity, lineage persistence, and local extinction events within the genus Triticum L. This study applies advanced computational morphometrics to reveal deep-time changes in wheat species distribution, including the disappearance of taxa now phylogeographically confined to central Asia. Methods: We developed a machine learning framework integrating Random Forest compared with logistic regression to classify morphometric data from 848 dry and 340 experimentally carbonized modern grains representing multiple wheat taxa (genus Triticum), alongside 15 archaeobotanical T. turgidum subsp. parvicoccum and 38 T. aestivum var. antiquorum. This probabilistic classifier was then applied to 2463 archeological wheat grains, including 48 from Punta de los Gavilanes and 517 from Almizaraque (southeastern Spain, 3rd–2nd millennium BC). Results: The analysis identified Triticum sphaerococcum and other phylogenetically distinct wheat taxa—today restricted to central and south Asia—among western European Bronze Age assemblages. These findings indicate that lineages now regionally extinct once formed part of a broader cultivated gene pool spanning into the western Mediterranean. Morphometric evidence highlights that past wheat diversity encompassed multiple clades and morphotypes absent from modern European germplasm. Conclusions: Our results demonstrate substantial phylogenetic turnover in wheat over the past 4000 years, marked by regional extirpations and contraction of once-widespread lineages to central Asia. This provides rare archeological evidence for the tempo and mode of cereal phylogeography, illustrating how domesticated lineages underwent extinction and range restriction akin to wild taxa. By integrating computational morphometrics with archaeobotanical evidence, this study establishes a scalable framework for tracing cryptic phylogenetic diversity, refining models of wheat domestication and assessing long-term genetic erosion in cultivated plants.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Plant Genetics and Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures
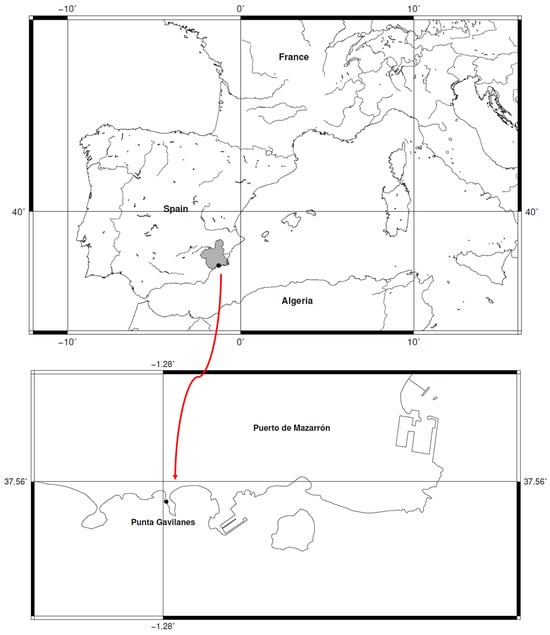
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Concordance of Secondary Pathogenic Germline Variants Identified by Tumor Genomic Profiling in Adult Solid Tumor Patients at Two US Community Cancer Centers
by
Sarah Moncado, Sourat Darabi, Diana Ivankovic and Luigi Boccuto
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1476; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121476 - 9 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Secondary pathogenic/likely pathogenic germline variants (P/LPGVs) identified on solid tumor genomic profiling (TGP) are a commonly encountered clinical issue. A proportion of oncology patients that undergo TGP will have a secondary P/LPGV identified that may not have been otherwise discovered based on
[...] Read more.
Background: Secondary pathogenic/likely pathogenic germline variants (P/LPGVs) identified on solid tumor genomic profiling (TGP) are a commonly encountered clinical issue. A proportion of oncology patients that undergo TGP will have a secondary P/LPGV identified that may not have been otherwise discovered based on clinical and family history criteria for hereditary cancer syndrome screening. The confirmation of P/LPGVs on germline sequencing has potential treatment implications for patients. Methods: The study design was a retrospective review for secondary data analysis. The inclusion criteria for this study were adult patients with solid tumor malignancy who underwent TGP and germline sequencing. The objective of this study is to evaluate the concordance rate of secondary P/LPGVs on TGP of adult patients with solid tumor malignancy at Hoag Presbyterian Hospital and Tower Health-Reading Hospital. The second and third aims are to analyze if the confirmed P/LPGVs are concordant with the patient’s tumor type and to analyze the variant allele frequencies (VAFs) of the identified secondary P/LPGVs on the tumor genomic profiling. Results: The data included 75 patients who underwent both TGP and germline sequencing, with a median age of 62.5 years. The most represented genes with P/LPGVs in the combined data included BRCA1 and BRCA2, both with 14, and MSH2, with 9. The overall germline concordance rate for the combined population was 64.1%, with 59 out of 92 P/LPGVs identified on both germline and somatic tumor testing. Conclusions: The overall germline concordance rate of 64% for the combined population is in accordance with the reported literature. Possible reasons for the variability in rates could be related to reporting guidelines for secondary germline variants, which can vary by company, and differences between somatic and germline variant curation. The study of P/LPGVs in populations from community cancer centers has the potential to increase the data of underrepresented minority groups regarding this important clinical issue and help expand understanding of hereditary cancer syndrome phenotypes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Bioinformatics)
►▼
Show Figures
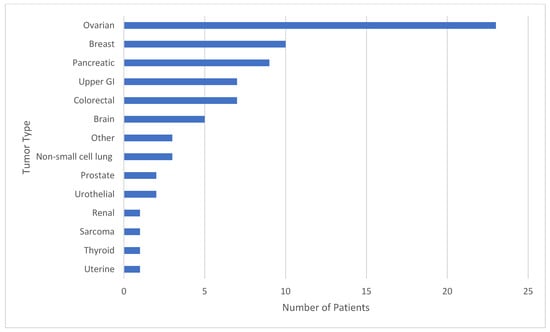
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Hypophosphatasia: 90 Years from a Canadian Discovery—A Comprehensive Review of the APLP Gene Underlying Rathbun’s Syndrome
by
Consolato M. Sergi
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1475; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121475 - 9 Dec 2025
Abstract
Hypophosphatasia (HPP) is an exceptional genetic bone disorder of metabolic character caused by a deficit of the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase isoenzyme (TNSALP). This protein is encoded by the ALPL (alkaline phosphatase liver/bone/kidney) gene. In the medical literature, HPP is also known as Rathbun’s
[...] Read more.
Hypophosphatasia (HPP) is an exceptional genetic bone disorder of metabolic character caused by a deficit of the tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase isoenzyme (TNSALP). This protein is encoded by the ALPL (alkaline phosphatase liver/bone/kidney) gene. In the medical literature, HPP is also known as Rathbun’s syndrome, named after the Canadian physician who first identified this disorder. Patients exhibit persistently low serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels. In fact, ALP renders this measure a reliable indicator of the condition. Adult HPP is varied, with some patients exhibiting only moderate, non-pathognomonic symptoms. They include arthropathy, arthrodynia, chondrocalcinosis, osteopenia, osteomalacia, and generic musculoskeletal discomfort. Healthcare may require coordinating several services to manage a patient with HPP. This comprehensive review will highlight the genetic knowledge, pathology data, and patient management approaches, including Medicare’s coverage. In addition, this paper aims to address specific themes related to HPP, including its significance, current challenges, and controversies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Genomics and Genetic Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Expanding the Genetic Spectrum in IMPG1 and IMPG2 Retinopathy
by
Saoud Al-Khuzaei, Ahmed K. Shalaby, Jing Yu, Morag Shanks, Penny Clouston, Robert E. MacLaren, Stephanie Halford, Samantha R. De Silva and Susan M. Downes
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1474; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121474 - 9 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Pathogenic variants in interphotoreceptor matrix proteoglycan 1 (IMPG1) have been associated with autosomal dominant and recessive retinitis pigmentosa (RP) and autosomal dominant adult vitelliform macular dystrophy (AVMD). Monoallelic pathogenic variants in IMPG2 have been linked to maculopathy and biallelic variants
[...] Read more.
Background: Pathogenic variants in interphotoreceptor matrix proteoglycan 1 (IMPG1) have been associated with autosomal dominant and recessive retinitis pigmentosa (RP) and autosomal dominant adult vitelliform macular dystrophy (AVMD). Monoallelic pathogenic variants in IMPG2 have been linked to maculopathy and biallelic variants to RP with early onset macular atrophy. Herein we characterise the phenotypic and genotypic features of patients with IMPG1/IMPG2 retinopathy and report novel variants. Methods: Patients with IMPG1 and IMPG2 variants and compatible phenotypes were retrospectively identified. Clinical data were obtained from reviewing the medical records. Phenotypic data included visual acuity, imaging included ultra-widefield pseudo-colour, fundus autofluorescence, and optical coherence tomography (OCT). Genetic testing was performed using next generation sequencing (NGS). Variant pathogenicity was investigated using in silico analysis (SIFT, PolyPhen-2, mutation taster, SpliceAI). The evolutionary conservation of novel missense variants was also investigated. Results: A total of 13 unrelated patients were identified: 2 (1 male; 1 female) with IMPG1 retinopathy and 11 (7 male; 4 female) with IMPG2 retinopathy. Both IMPG1 retinopathy patients were monoallelic: one patient had adult vitelliform macular dystrophy (AVMD) with drusenoid changes while the other had pattern dystrophy (PD), and they presented to clinic at age 81 and 72 years, respectively. There were 5 monoallelic IMPG2 retinopathy patients with a maculopathy phenotype, of whom 1 had PD and 4 had AVMD. The mean age of symptom onset of this group was 54.2 ± 11.8 years, mean age at presentation was 54.8 ± 11.5 years, and mean BCVAs were 0.15 ± 0.12 logMAR OD and −0.01 ± 0.12 logMAR OS. Six biallelic IMPG2 patients had RP with maculopathy, where the mean age of onset symptom onset was 18.4 years, mean age at examination was 68.7 years, and mean BCVAs were 1.90 logMAR OD and 1.82 logMAR OS. Variants in IMPG1 included one missense and one exon deletion. A total of 11 different IMPG2 variants were identified (4 missense, 7 truncating). A splicing defect was predicted for the c.871C>A p.(Arg291Ser) missense IMPG2 variant. One IMPG1 and five IMPG2 variants were novel. Conclusions: This study describes the phenotypic spectrum of IMPG1/IMPG2 retinopathy and six novel variants are reported. The phenotypes of PD and AVMD in monoallelic IMPG2 patients may result from haploinsufficiency, supported by the presence of truncating variants in both monoallelic and biallelic cases. The identification of novel variants expands the known genetic landscape of IMPG1 and IMPG2 retinopathies. These findings contribute to diagnostic accuracy, informed patient counselling regarding inheritance pattern, and may help guide recruitment for future therapeutic interventions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Genomics and Genetic Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Preliminary Assessment of Arnica montana L. Extract: Antimicrobial Activity Against Acinetobacter baumannii and Biofilm-Related Gene Expression Profiling
by
Sylwia Andrzejczuk, Magdalena Sozoniuk and Danuta Sugier
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1473; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121473 - 9 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Arnica montana L. is widely recognized for its diverse biological activities, including antimicrobial effects. This study aimed to evaluate the antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of A. montana L. extracts against Acinetobacter baumannii, a pathogen of urgent public health concern due
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Arnica montana L. is widely recognized for its diverse biological activities, including antimicrobial effects. This study aimed to evaluate the antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of A. montana L. extracts against Acinetobacter baumannii, a pathogen of urgent public health concern due to its increasing antibiotic resistance and capacity for biofilm formation. Methods: The antimicrobial activity of ethanolic (EtE) and aqueous (AqE) extracts of A. montana flowers was evaluated via the broth microdilution method. The minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC), and the MBC/MIC ratio were used. The effects of EtE on A. baumannii biofilm formation were assessed via a crystal violet assay. Additionally, transcriptional profiling of biofilm-associated genes following exposure to sub-MIC levels of the extract was conducted via RT-qPCR. Results: The anti-Acinetobacter activity of EtE was demonstrated (MIC = 234.4 and 468.75 µg/mL for A. baumannii ATCC BAA-3252 and ATCC 19606, respectively). The EtE exhibited bactericidal activity against both strains, whereas the AqE showed no activity. Additionally, EtE inhibited biofilm formation and significantly downregulated the expression of key biofilm-associated genes, including those of the csu operon and ompA. Conclusions: Arnica montana EtE demonstrated antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities against A. baumannii and inhibited biofilm development by suppressing the transcription of genes involved in pilus assembly and surface adherence, highlighting their essential role in biofilm formation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Molecular Microbiology, Genetics, and Bioinformatics of Multiple-Drug-Resistant Bacteria in Public Health)
►▼
Show Figures
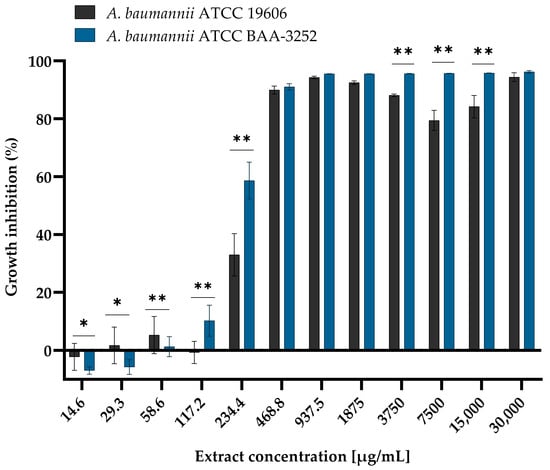
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Genes Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
BioTech, DNA, Genes, IJMS, CIMB
Single-Cell Technologies: From Research to Application
Topic Editors: Ken-Hong Lim, Chung-Der Hsiao, Pei-Ming YangDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Animals, Dairy, Genes, Agriculture, Poultry, Ruminants, Veterinary Sciences
Application of Reproductive and Genomic Biotechnologies for Livestock Breeding and Selection: 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Manuel García-Herreros, Pedro Manuel AponteDeadline: 30 April 2026
Topic in
Biomedicines, Future Pharmacology, Pharmacy, IJMS, Biomolecules, Genes
Prospects of Multi-Target Agonists in Metabolic and Epigenetic Medicine
Topic Editors: Riham Abouleisa, Yanming LiDeadline: 30 November 2026
Topic in
Applied Biosciences, Forests, Genes, Horticulturae, IJMS, Plants
Genetic Breeding and Biotechnology of Garden Plants
Topic Editors: Bin Dong, Guirong Qiao, Shiwei ZhongDeadline: 31 December 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Genes
Plant Genetics, Evolution, Cytogenetics and Cytogenomics for Biodiversity Conservation
Guest Editors: Eric Javier Martínez, Ana Isabel Honfi, Anna ReutemannDeadline: 15 December 2025
Special Issue in
Genes
Genetic and Molecular Insights into Cardiovascular Disease: From Mechanisms to Precision Medicine
Guest Editors: Lingfeng Luo, Laurent MetzingerDeadline: 15 December 2025
Special Issue in
Genes
Research on Molecular Mechanisms of DNA Damage
Guest Editor: Judith Miné-HattabDeadline: 15 December 2025
Special Issue in
Genes
Molecular Genetics of Stress Response in Crops
Guest Editor: Jie ZhanDeadline: 15 December 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Genes
Tools for Population and Evolutionary Genetics
Collection Editors: David Alvarez-Ponce, Julie M. Allen, Won C. Yim, Marco Fondi
Topical Collection in
Genes
Eukaryotic Non-coding RNAs: Diversity, Structure/Function, Implication in Cardiovascular Disease
Collection Editors: Morten Andre Høydal, Christiane Branlant
Topical Collection in
Genes
Study on Genotypes and Phenotypes of Pediatric Clinical Rare Diseases
Collection Editors: Livia Garavelli, Stefano Giuseppe Caraffi








