- Article
Development and Characterization of Gellan Gum Microspheres for the Controlled Release of Antioxidants from Vaccinium myrtillus Extract
- Norma Mallegni,
- Niccoletta Barbani and
- Caterina Cristallini
- + 5 authors
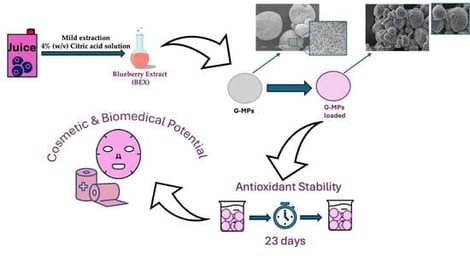
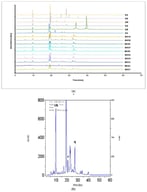
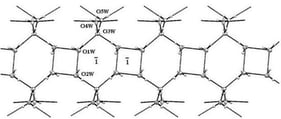
In this work, gellan gum microspheres (G–MPs) were developed as delivery systems for blueberry extract (Vaccinium myrtillus) (BEX), a source of natural antioxidants rich in anthocyanins (ATCs) and phenolic compounds (PHCs). Gellan gum, an anionic polysaccharide produced via fermentation by Sphingomonas elodea, was selected for its biocompatibility and gelling properties. BEX was obtained using a mild citric acid–based extraction method to preserve antioxidant capacity and was characterized for its total polyphenol, flavonoid, and anthocyanin content before loading. The extract was loaded into gellan gum microspheres via absorption (G–MPs–BEX). The resulting microspheres exhibited a spherical and porous morphology that favoured both encapsulation and controlled release. FT–IR analysis confirmed the absorption of the extract within the polymer network and revealed hydrogen bonding interactions between the matrix and active compounds. Despite these interactions, microspheres retained a high swelling capacity and enabled rapid release, with maximum release of polyphenols and anthocyanins within 30 min at pH 5.5. The antioxidant activity of BEX, assessed via DPPH assay, remained stable during storage (up to 60 days) and after incorporation into the microspheres. Overall, this study demonstrates that G–MPs can efficiently absorb, stabilize, and release natural antioxidant compounds, supporting their potential use in biomedical, nutraceutical, and cosmetic applications.
5 February 2026