- Review
Biosynthesis of Nanoparticles Using Commelina benghalensis: Photocatalytic Dye and Pharmaceutical Degradation and Antimicrobial Activity
- Dineo A. Bopape and
- Mmbulaheni Ramulondi
The trend toward developing sustainable nanotechnology has driven researchers to explore environmentally friendly techniques for nanomaterial fabrication. This review examines the utilisation of Commelina benghalensis plant extracts as an effective biological tool for the green synthesis of various nanomaterials. The procedures involve reducing metal salt precursors with aqueous or polar solvent extracts rich in phytochemicals such as flavonoids and polyphenols, followed by a calcination step that yields crystalline products. The findings show that the properties of ZnO, TiO2, Ag, NiO, and their composites are directly influenced by synthesis factors, including solvent, plant component, and extract concentration. This directly influenced their specific sizes, morphologies, and phases. Furthermore, these C. benghalensis-mediated nanomaterials showed high efficiency in the photocatalytic degradation of textile dyes and pharmaceuticals, as well as potential antibacterial and antioxidant properties. The Commelina benghalensis plant is flexible and renewable for efficient nanomaterial synthesis; nevertheless, issues with standardisation and scalability must be overcome to fully realise its promise for commercial and industrial uses.
2 February 2026



![Shows panorama (A), detail (B), and the flowers (C) of the Commelina benghalensis plant. Reproduced under the terms and conditions of Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY) license [32]. Copyright 2024.](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=470,h=317/https://mdpi-res.com/colorants/colorants-05-00005/article_deploy/html/images/colorants-05-00005-ag-550.jpg)
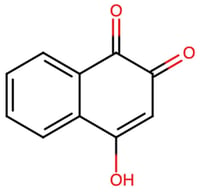
![Classification of natural and synthetic dyes (OA) Revised and Reprinted from [14].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/colorants/colorants-05-00003/article_deploy/html/images/colorants-05-00003-g001-550.jpg)
![Map with the location of iron (red lozenges) and manganese (blue lozenges) oxide ores in ancient Mesopotamia and adjacent regions, including those that were potentially accessible to the Sumerians and Assyrians. Red zones represent areas with diffuse occurrence of iron oxides. Data from: [38,39].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/colorants/colorants-05-00002/article_deploy/html/images/colorants-05-00002-g001-550.jpg)