- Article
Electrocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue Using rGO, Sb2O3, and rGO-Sb2O3 Composite Ink-Based Electrodes
- Maria I. Myers Armas,
- Andrea M. Fletes and
- Helia M. Morales
- + 3 authors
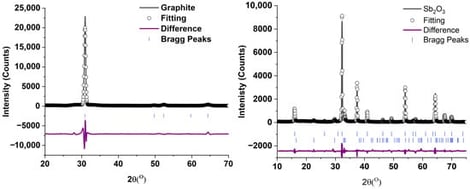
Water pollution from industrial dyes is a critical challenge due to the resistance of these types of compounds to degradation and potentially harmful effects on living organisms and human health. In this study, the electrochemical degradation of methylene blue (MB) was investigated using ink-based copper foam electrodes with reduced graphene oxide (rGO), antimony trioxide (Sb2O3), and rGO/Sb2O3 composites. The materials used to synthesize the electrodes were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), which showed the successful synthesis of GO, rGO, and the Sb2O3-rGO composite. Additionally, the synthesized electrodes were examined using SEM. The MB degradation was studied using kinetic behavior and removal efficiency at pH levels from 3 through 6, monitored using UV-Vis spectroscopy. The electrocatalytic degradation was studied using sodium sulfate as the electrolyte across a pH range of 3 to 8. All electrodes investigated were determined to follow first-order kinetics. The Sb2O3-rGO composite showed the highest rate constants of MB degradation at pH 7 and 8, with rate constants of 0.0160 and 0.0159 min−1, respectively. At the same time, the rGO ink-based electrode worked fastest at pH 3 and pH 4 with rate constants of 0.0178 and 0.0158 min−1, respectively. The Sb2O3 also works best at pH 3 and 4 with rate constants of 0.0151 and 0.0152 min−1. SEM analysis shows the composite electrode was more resilient to degradation than other materials.
17 February 2026




![Shows panorama (A), detail (B), and the flowers (C) of the Commelina benghalensis plant. Reproduced under the terms and conditions of Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY) license [32]. Copyright 2024.](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/colorants/colorants-05-00005/article_deploy/html/images/colorants-05-00005-ag-550.jpg)