Abstract
This study explores the photocatalytic efficiency of Zn/Fe/TiO2 catalysts, synthesized via the wet impregnation method, for degrading the food colorings Allura Red and Tartrazine Yellow. A 22 factorial design with a central point replication guided the catalyst synthesis. Characterization involved BET surface area analysis, SEM-EDX, XRD, and PZC determination. Photocatalytic tests were conducted in batch mode under natural sunlight with 10 mg L−1 food coloring solutions. Kinetic modeling and statistical analysis were performed, and catalyst reuse was evaluated under artificial light. Results showed that low calcination temperatures (200–273 °C) and Zn loadings of 2–10% led to nearly 99% discoloration and degradation efficiency. The Behnajady–Modirshahla–Ghanbery kinetic model best described the discoloration data, confirming the significant impact of both variables. The optimal catalyst for Allura Red degradation was 2%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 calcined at 200 °C, while for Tartrazine Yellow, 6%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 calcined at 300 °C was most effective. Both catalysts exhibited excellent stability, maintaining efficiency over four reuse cycles. These findings demonstrate the potential of Zn/Fe/TiO2 catalysts for sustainable wastewater treatment.
1. Introduction
Colorants play a key role in the food industry, where they are used extensively to enhance the visual appeal of products, influence consumer perception, and ensure consistency in food appearance [1]. Among synthetic colorants, Allura Red (AR) and Tartrazine Yellow (TY) are two of the most widely used azo dyes due to their vibrant hues, stability, and cost-effectiveness [2,3]. These dyes are commonly found in beverages, candies, ice creams, baked goods, and processed snacks, particularly in Brazil, where they are integral to the food industry due to their widespread use and low cost [4]. In Brazil, these dyes are added to a variety of food products to meet consumer demands for attractive colors and consistent appearance. However, during production, large amounts of dye-laden wastewater are discharged into the environment, contributing to effluent pollution. The widespread use of synthetic colorants has led to significant environmental challenges, as large volumes of dye-laden effluents are discharged into water bodies during production and processing [5]. The persistence of these colorants in the environment poses risks to aquatic ecosystems and human health, as they are resistant to conventional wastewater treatment methods [6].
Synthetic colorants, particularly azo dyes like AR and TY, are characterized by complex aromatic structures that make them highly stable and difficult to degrade [7]. When released into water bodies, they can interfere with sunlight penetration, disrupting photosynthetic processes and harming aquatic life [8]. Moreover, some colorants and their degradation byproducts have been linked to carcinogenic and mutagenic effects, raising concerns about their impact on human health [9]. Despite these risks, the treatment of wastewater containing synthetic colorants remains a challenge, as conventional methods such as biological degradation, coagulation, and adsorption often prove ineffective in completely removing these persistent pollutants [10,11].
In recent years, advanced oxidation processes (AOP) have emerged as a promising solution for the degradation of synthetic colorants [12]. AOP generate highly reactive oxygen species, such as hydroxyl radicals (•OH), which can oxidize and mineralize complex organic pollutants into harmless byproducts like CO2 and H2O [13]. Among AOP, photocatalysis has gained significant attention due to its ability to harness solar energy for environmental remediation [14]. Photocatalysis involves the activation of a semiconductor material, such as titanium dioxide (TiO2), by light irradiation, leading to the production of electron–hole pairs that drive redox reactions for pollutant degradation [15]. This approach is particularly relevant for synthetic colorants, as their complex structures require advanced treatment methods for effective breakdown [16].
The use of solar light in photocatalysis offers several advantages over conventional treatment methods [17]. Solar-driven photocatalysis is a sustainable and cost-effective approach, as it utilizes renewable energy and reduces reliance on external power sources [18]. Additionally, it can achieve higher degradation efficiencies for persistent pollutants like synthetic colorants, making it an attractive option for wastewater treatment [19]. However, the widespread application of TiO2-based photocatalysts is limited by their relatively wide bandgap, which restricts their activity to ultraviolet (UV) light [20]. To overcome this limitation, doping TiO2 with transition metals such as zinc (Zn) and iron (Fe) has been explored as a strategy to enhance light absorption in the visible spectrum and improve photocatalytic performance [21,22].
Zinc and iron are particularly attractive dopants due to their ability to modify the electronic structure of TiO2, reduce electron–hole recombination, and enhance photocatalytic activity under visible light [23]. The wet impregnation method is a widely used technique for preparing such catalysts, as it allows for uniform dispersion of dopants on the TiO2 support and is relatively simple to implement. This method involves impregnating a surface area of TiO2 with a metal precursor solution, followed by evaporation at a high temperature, which leads to the reduction of the metal precursor into metal particles on the support. The advantages of the wet impregnation method over other synthesis techniques include its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and ability to achieve uniform metal dispersion. Unlike more complex methods such as sol–gel or hydrothermal processes, wet impregnation allows for precise control of the metal loading, is less resource-intensive, and is easier to scale up for practical applications [24]. However, one potential drawback is the weak interaction between the metal particles and the support, which can result in larger particle sizes and the formation of impurities if not optimized. Despite these challenges, the wet impregnation method remains a viable option for synthesizing TiO2-based photocatalysts for the degradation of synthetic colorants. The synergistic effects of Zn and Fe doping on TiO2 supports and their influence on the photodegradation of complex colorants like AR and TY, however, remain underexplored [25]. Understanding these effects is crucial for optimizing catalyst design and improving the efficiency of solar-driven photocatalysis for the treatment of colorant-laden wastewater [26].
This study aims to assess the effect of Zn doping on Fe/TiO2 support in the preparation of catalysts via the wet impregnation method for the photodegradation of AR and TY, two of the most widely used synthetic colorants in the food industry. The catalysts will be characterized using advanced techniques. Photocatalytic tests will be conducted under sunlight exposure, and the degradation efficiency will be evaluated through kinetic data modeling, chemical oxygen demand (COD) reduction, and statistical analysis. By optimizing the synthesis parameters, this work seeks to contribute to the development of efficient and sustainable photocatalytic systems for the treatment of wastewater containing synthetic colorants, addressing environmental challenges.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Titanium dioxide (TiO2, ≥91%), zinc chloride (ZnCl2, ≥97%), iron chloride (FeCl3·6H2O, ≥99%), sodium hydroxide (NaOH, ≥97%), hydrochloric acid (HCl, ≥37%), Allura Red dye (AR, ≥85%), and Tartrazine Yellow dye (TY, ≥85%) were purchased from Merck Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, United States). All chemicals used in this study were of analytical grade and were used as received, without further purification. The main solvent used in the synthesis process was ultrapure Milli-Q® water (resistivity of 18 MΩcm).
2.2. Synthesis and Preparation of Zn/Fe/TiO2 Catalysts
The Fe/TiO2 catalyst support was synthesized using the wet impregnation method, targeting an iron loading of 2% (m m−1), following the procedure described by Castro et al. [6]. For this, approximately 30 g of TiO2 was used as the base material. The iron precursor, FeCl3·6H2O, was weighed to achieve the desired 2% (m m−1) loading, corresponding to approximately 2.96 g of FeCl3·6H2O. The precursor was dissolved in 30 mL of ultrapure Milli-Q® water (resistivity of 18 MΩcm) to form a homogeneous solution. The resulting mixture was stirred at room temperature (~25 °C) in a rotary evaporator for 17 h to ensure complete impregnation of the support. After impregnation, the solvent was evaporated by maintaining the rotary evaporator at 70 °C for 1 h. The partially dried material was then transferred to a vacuum oven and dried at 120 °C under vacuum for 21 h. Subsequently, the dried material was calcined in a muffle furnace at three different temperatures—200 °C, 300 °C, or 400 °C—for 5 h, at a heating rate of 5 °C min−1. This Fe/TiO2 material served as the support for the subsequent Zn co-doping step.
For the Zn co-doping, the same wet impregnation procedure was employed. ZnCl2 was used as the zinc precursor, with Zn loadings adjusted to 2%, 6%, and 10% (m m−1) relative to the mass of the Fe/TiO2 support. Specifically, for each synthesis batch, approximately 30 g of Fe/TiO2 was impregnated with approximately 1.27 g, 3.99 g, or 6.94 g of ZnCl2, corresponding to 2%, 6%, and 10% Zn, respectively. The ZnCl2 was first dissolved in 30 mL of ultrapure Milli-Q® water, and the Fe/TiO2 support was then added to the solution. The suspension was stirred at room temperature in a rotary evaporator for 17 h, followed by solvent evaporation at 70 °C for 1 h. The resulting material was dried at 120 °C under vacuum for 21 h.
Finally, the Zn/Fe/TiO2 catalysts were calcined at three selected temperatures—200 °C, 300 °C, or 400 °C—for 5 h, following the same heating protocol as for the support preparation. A 22 central factorial experiment (CFE) was designed to evaluate the effects of calcination temperature and Zn loading on the photodegradation efficiency of AR and TY. The central points were prepared in triplicate to ensure statistical reliability. The levels of each variable are presented in Table 1. Tests with the Fe/TiO2 catalyst support were conducted at calcination temperatures of 200, 300, and 400 °C to serve as controls for evaluating the effect of Zn co-doping.

Table 1.
Control variables considered in the 22 factorial design and experiments for Zn/Fe/TiO2 catalyst synthesis.
2.3. Characterization of Zn/Fe/TiO2 Catalysts
The catalysts were characterized by their morphological, structural, surface, and compositional properties.
N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms at 77 K were measured using a sorption analyzer (Quantachrome Instruments, model NOVA 2000e, Boynton Beach, USA). Specific surface area (So), average pore volume (Vp), and average pore diameter (dp) were calculated using the Brunauer–Emmertt–Teller (BET) method, and pore size distribution using the Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) method.
Scanning electron microscopy with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM/EDS, TESCAN, microscope model VEGA3, Brno, Czech Republic) was used to obtain micrographs and determine elemental composition of the adsorbents.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) was performed using a diffractometer with a copper emission line (Cu Kα, λ = 1.54056 Å), operated at 30 kV acceleration voltage, 20 mA current, and a scanning velocity of 2° 2θ min−1.
Surface charge distribution was determined by the point of zero charge (PZC), where 50 mg of the adsorbent was added to 50 mL aqueous solutions at pH ranging from 2 to 12, and pHPZC was measured after 24 h [10,11].
2.4. Photocatalytic Assay
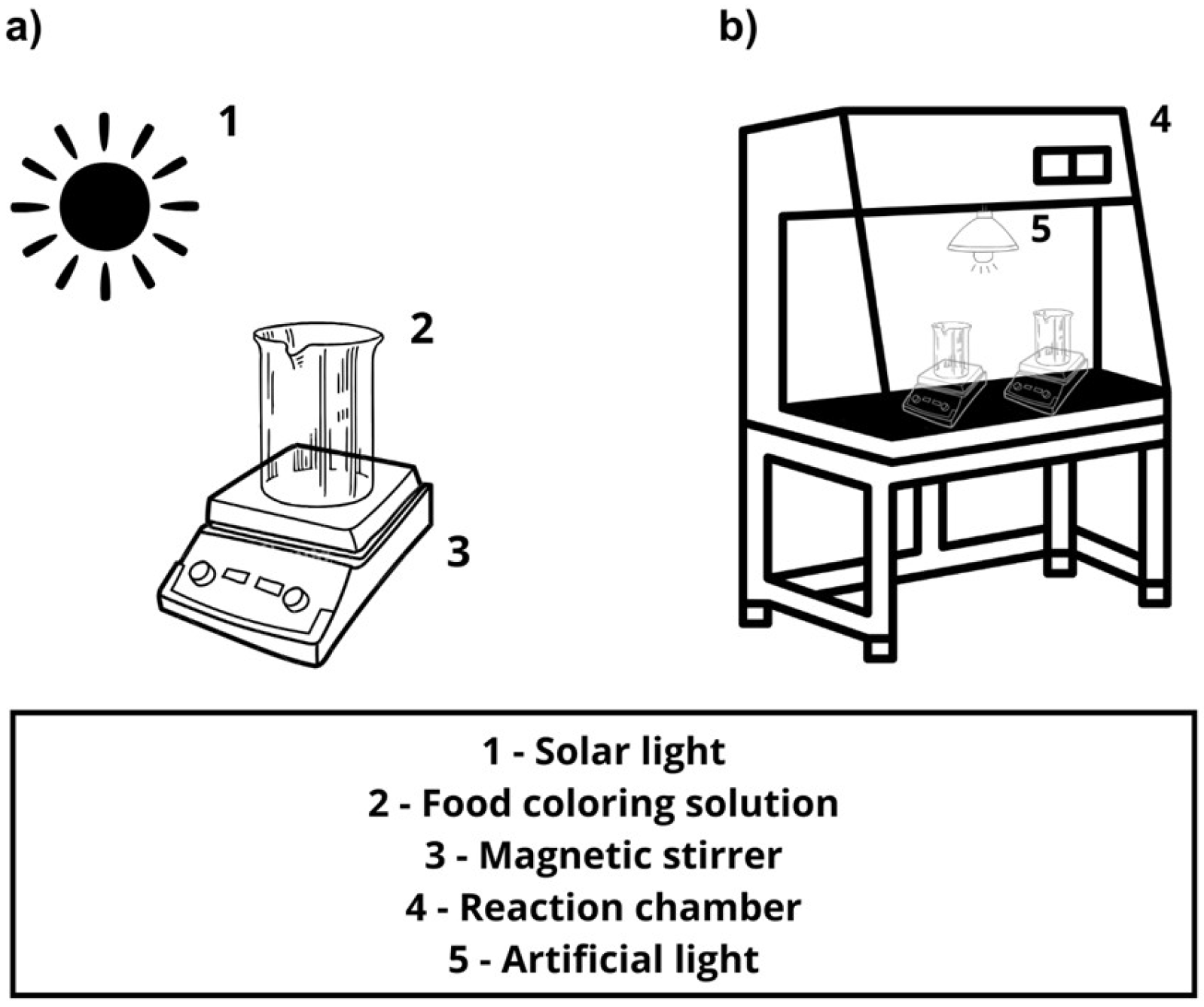
The photocatalytic assays were conducted under sunlight, as illustrated in Figure 1a. The experimental system consisted of a tank-type reactor (a 250 mL beaker) operating in batch mode, with a magnetic stirrer to ensure sample homogenization throughout the 2 h experiment. In the AR and TY discoloration tests (Table 2), reactions were carried out with each catalyst suspension, consisting of 150 mL of a 10 mg L−1 aqueous food coloring solution and 50 mg of catalyst, irradiated under sunlight. To evaluate the photocatalytic activity, experiments were performed at two different food coloring solution pH levels, 7 and 4. At reaction times of 0, 30, 60, 90, and 120 min, aliquots were collected for further discoloration analysis. These aliquots were vacuum-filtered using cellulose ester membranes (47 mm in diameter, 0.45 μm porosity) and stored in a refrigerator. The photocatalytic tests were performed from 5 January to 7 January 2025, between 11:00 a.m. and 1:00 p.m. During this period, the average solar radiation was measured using a UV radiation meter (model LI-200, SIMEPAR, Curitiba, Brazil) in the 390–1100 nm range, with values ranging from 1038.0 to 1087.5 W m−2.
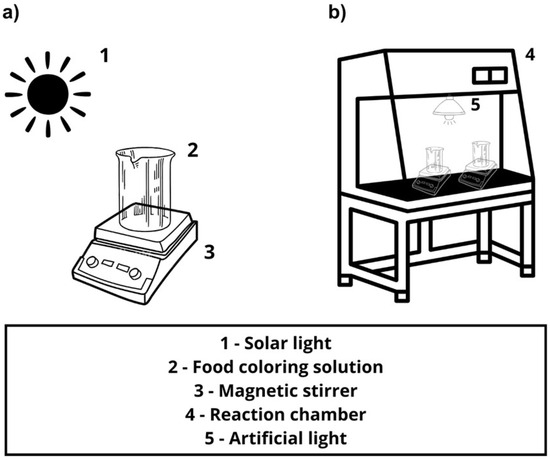
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the photocatalytic apparatus for food coloring degradation: (a) Under solar light. (b) Under artificial light.

Table 2.
Physical–chemical properties of the food coloring.
To better understand the photocatalytic behavior, preliminary adsorption tests were conducted to evaluate the capacity of the catalysts to discolor AR and TY in the absence of light for 30 min, under the same conditions as the photocatalytic assays. Additionally, a photolysis test was performed in the absence of the catalysts to assess the photosensitivity of the food coloring under solar light during a 120 min process.
The discoloration of the solutions over time was determined using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Drawell, Model EEQ9011I. UV-B, Chongqing, China), with the measured wavelengths listed in Table 2. Absorbance values were recorded, and concentrations were determined using the calibration curve method. The discoloration percentage was calculated using Equation (1).
where D represents the percentage of discoloration of the food coloring solutions (AR and TY) (%), C0 the food coloring concentration before the photocatalytic tests (10 mg L−1) and Ct the food coloring concentration after the photocatalytic test at t time (mg L−1).
2.5. Photodiscoloration Kinetics
To evaluate the discoloration kinetics of the solar photocatalytic process of AR and TY, three models were used: pseudo-first-order (PFO) (Equation (2)), pseudo-second-order (PSO) (Equation (3)), and the Behnajady–Modirshahla–Ghanbery (BMG) (Equation (4)) kinetic model (Table 3).

Table 3.
Kinetics models used in the experiment.
2.6. Photodegradation Assessment
The photodegradation of the AR and TY food colorings was evaluated through the reduction in the chemical oxygen demand (COD) percentage at the end of the photocatalytic process (120 min), according to the Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater [30].
2.7. Catalyst Reusability Test
To assess catalyst reusability, the tests were conducted following the same procedure as the previous batch experiments (Section 2.4). However, in this evaluation, the photocatalytic activity was tested under artificial irradiation using a 250 W mercury vapor lamp, as illustrated in Figure 1b. The reuse tests were repeated four times using the best catalyst and the best conditions from the batch assays.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
The results were analyzed using analysis of variance (ANOVA) to assess statistically significant factors and interaction effects between variables. Significant differences were tested using Tukey’s method (p ≤ 0.05). The experimental results for COD and discoloration percentage were evaluated using response surface methodology (RSM), described by second-order equations (Equation (5)). The regression coefficients for the response variables were determined through RSM, and their significance was confirmed by ANOVA (p ≤ 0.05). Additionally, the response variables were optimized using the Simplex method. All statistical analyses were conducted in MiniTab® software (version 19, Minitab, LLC., State College, PA, USA).
where Y1 is the studied response variable; β0 is a constant; βi are coefficients related to linear effects; βii are coefficients associated with quadratic effects; and βij are coefficients for second-order cross terms.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Catalyst Characterization
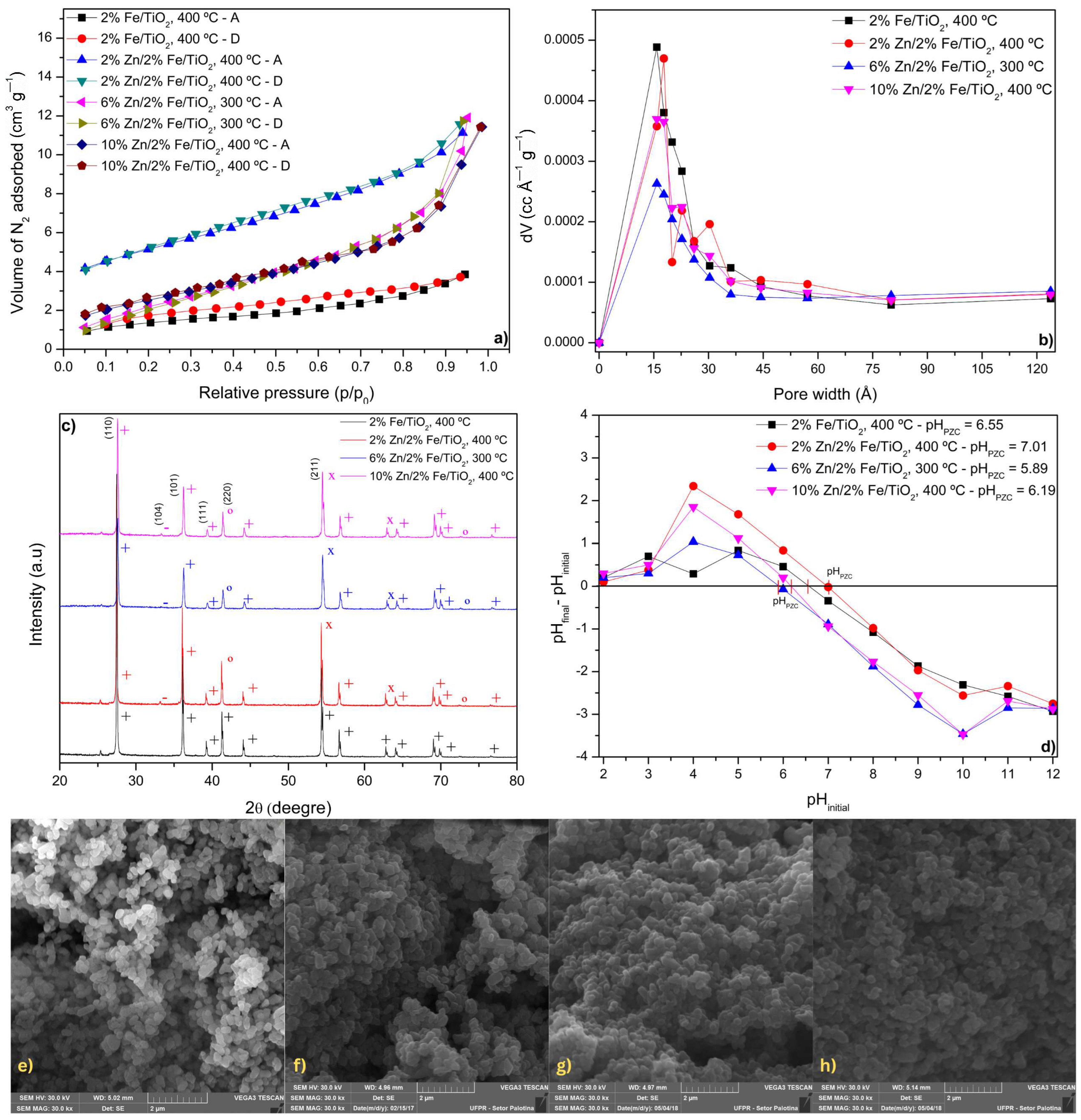
The isotherm measurements shown in Figure 2a provide valuable insights into the porous structure and adsorption behavior of the different catalysts, all calcined at the highest temperature of the CFE (2%Fe/TiO2, 2%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2, 6%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2, and 10%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2). The N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms at 77 K can be classified according to IUPAC, and for all the catalysts, the isotherm resembles a Type II isotherm, which is characteristic of non-porous or macroporous materials, where adsorption occurs primarily on the external surface rather than within a well-defined porous network [31]. This characteristic can significantly influence the photocatalytic degradation of food coloring, as the efficiency of the process depends on the interaction between the food coloring molecules and the active sites of the photocatalyst [7]. The large external surface area allows for better light exposure and increased accessibility of reactive sites, facilitating the generation of reactive oxygen species, such as hydroxyl radicals, and superoxide anions. These species play a crucial role in breaking down complex food coloring molecules into smaller, less toxic compounds [6]. Additionally, the presence of Zn and Fe dopants in TiO2 can enhance charge carrier separation and reduce recombination rates, further improving photocatalytic efficiency. The predominance of external surface adsorption in Type II materials ensures that food coloring molecules are readily available for photocatalytic reactions without diffusion limitations, making them highly effective for food coloring degradation under light irradiation [32].
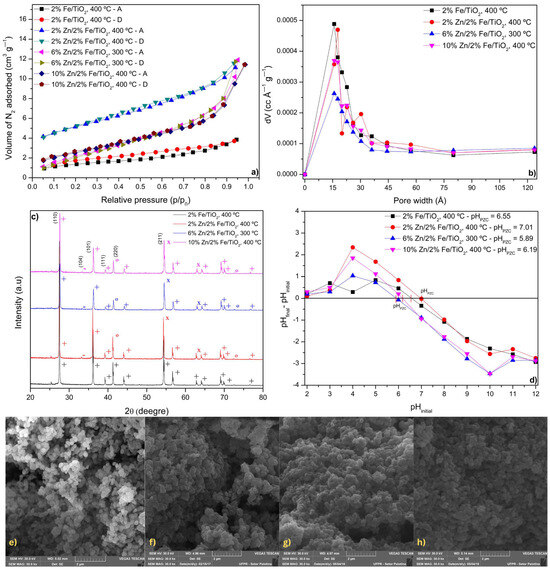
Figure 2.
Catalyst characterization results: (a) N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms; (b) BJH pore size distribution; (c) XRD pattern; (d) Surface charge distribution; SEM micrographs at 30,000× for: (e) 2% Fe/TiO2; (f) 2% Zn/2% Fe/TiO2; (g) 6% Zn/2% Fe/TiO2; and (h) 10% Zn/2% Fe/TiO2. Legend—XRD peak phases: + TiO2 (Rutile), × TiO2 (Anatase), − Fe2O3 (Hematite), ° Fe3O4 (Magnetite).
Finally, the BJH pore size distribution (Figure 2b) further supports these observations. The pore size distributions of the catalysts are concentrated between 15.8 to 17.7 Å, falling within the mesoporous range [31]. This range is commonly observed in studies involving co-doped catalysts and composite materials, highlighting their potential for enhanced adsorption and catalytic activity due to their intermediate pore sizes that facilitate better accessibility and interaction with food coloring [6,7,33].
Table 4 presents the textural properties and elemental composition of the synthesized catalysts, highlighting the effects of calcination temperature and metal doping on surface area, pore volume, and pore diameter. Across all catalysts, calcination generally leads to a reduction in surface area, which is expected due to particle sintering and pore collapse at higher temperatures [34,35,36]. For instance, the 2%Fe/TiO2 catalyst shows a gradual decrease in So from 15.56 m2 g−1 in the non-calcined sample to 10.98 m2 g−1 at 400 °C. A similar trend is observed for the 10%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 catalyst, where So drops from 7.56 m2 g−1 to 6.37 m2 g−1 after calcination at 400 °C.

Table 4.
Textural properties and elemental analysis of the catalysts.
While surface area decreases with calcination, pore volume tends to increase slightly, especially at higher temperatures. In the case of 2%Fe/TiO2, Vp rises from 0.0152 cm3 g−1 in the non-calcined sample to 0.0217 cm3 g−1 at 400 °C, likely due to structural rearrangements and the formation of larger interparticle voids [7].
The pore diameter remains in the mesoporous range (20–50 Å) for 2%Fe/TiO2 and 2%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2, with a slight increase upon calcination. However, for 6%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 and 10%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2, significantly larger pores are observed, with the non-calcined samples already exhibiting pore sizes above 70 Å, reaching 89.62 Å at 400 °C in the case of 10%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2.
This suggests that higher Zn loading promotes pore expansion, possibly due to the agglomeration of Zn species and changes in structural morphology [6]. Increasing Zn content leads to a progressive decrease in surface area while significantly increasing pore diameter. The 10%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 catalyst exhibits the lowest So (6.37 m2 g−1) and the largest pores (89.62 Å at 400 °C), indicating that high Zn loading may induce sintering effects, reducing overall surface area but creating larger pores. Fe doping alone in 2%Fe/TiO2 results in moderate surface area reduction and maintains mesoporosity, whereas co-doping with Zn in 2%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 leads to a more pronounced increase in pore diameter, suggesting that Zn contributes more significantly to structural modifications [6,37].
Elemental analysis confirms the successful incorporation of Fe and Zn, with Fe content remaining relatively stable between 1.74% and 1.91%, while Zn content increases proportionally with nominal doping, reaching 9.21% in 10%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2.
XRD patterns presented in Figure 2c provide insights into the crystalline phases of the synthesized catalysts. The main diffraction peaks correspond to TiO2 in both its rutile (+) and anatase (×) phases, with additional peaks assigned to iron oxides, specifically Fe2O3 (hematite, −) and Fe3O4 (magnetite, °). The XRD pattern of 2%Fe/TiO2 exhibits characteristic peaks for anatase TiO2 at 25.3° (101), 37.8° (004), 48.0° (200), and 55.1° (211), as well as peaks for rutile TiO2 at 27.4° (110), 36.0° (101), 41.2° (111), and 54.3° (211). The dominance of rutile suggests that the wet impregnation synthesis method inherently favors the formation of rutile over anatase [6]. The presence of hematite Fe2O3 is indicated by peaks at 33.2° (104) and 49.5° (024), suggesting oxidation of Fe species within the TiO2 matrix [2].
For the 2%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 catalyst, the diffraction peaks remain similar to those of 2%Fe/TiO2, but with additional peaks attributed to zinc incorporation. Zn doping appears to slightly influence the anatase-to-rutile transformation, potentially stabilizing the anatase phase, as indicated by the persistence of its peaks [6,38]. Hematite and magnetite Fe3O4 phases are also detected, with Fe3O4 peaks at 30.1° (220), 35.4° (311), and 57.2° (511).
The 6%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 catalyst shows a more prominent anatase phase, with reduced intensity for rutile peaks compared to the previous samples. The main anatase peaks remain at 25.3° (101), 37.8° (004), and 48.0° (200). The presence of hematite and magnetite are still evident, particularly at 33.2° (104) and 35.4° (311). In the case of the 10%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 catalyst, the XRD pattern shows a more pronounced rutile phase, with peaks at 27.4° (110), 36.0° (101), 41.2° (111), and 54.3° (211). Zn incorporation might contribute to structural modifications, as reflected in slight shifts in peak positions and intensities [39,40]. Hematite and magnetite phases remain present, reinforcing the role of Fe species in the overall phase composition.
No peaks related to Zn were detected in the catalysts, likely because Zn ions are not incorporated into the TiO2 crystal lattice. Instead, they are probably highly dispersed within the material [7]. Overall, the XRD results indicate that Zn and Fe doping introduce additional phases, particularly iron oxide phases. The retention of anatase suggests that Zn might contribute to phase stabilization, while Fe species undergo oxidation, forming hematite and magnetite. These structural changes could significantly impact the catalytic properties of the materials, influencing their photocatalytic and adsorption performance.
Figure 2d presents the results of the point of zero charge analysis performed on the materials. The PZC evaluates the surface characteristics of catalysts, providing information on whether their surfaces exhibit acidic or basic tendencies. A pHPZC value higher than the solution’s pH indicates a negatively charged surface, while a pHPZC lower than the solution’s pH suggests a positively charged surface. AR solution at 10 mg L−1 had a pH of 6.91, while TY solution had a pH of 6.88. The analysis revealed varying pHPZC values among the catalysts. All the catalysts, except for 2%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2, exhibited pHPZC values lower than the pH of the food coloring solution, indicating positively charged surfaces. In contrast, 2%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 displayed a pHPZC higher than the pH of the AR and TY solutions, signifying a negatively charged surface [10,41].
3.2. Photocatalytic Tests
3.2.1. Adsorption and Photolysis Tests
To evaluate the effect of a non-photocatalytic process in the discoloration of the AR and TY aqueous solution, adsorption and photolysis tests were carried out, and the results are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Adsorption and photolysis tests for the discoloration of food coloring solutions.
Observing the data presented in Table 5, neither adsorption nor photolysis contributed significantly to the overall discoloration process, as the reported percentages remain strikingly low across all tested conditions. For Allura Red at pH 7, adsorption discoloration ranged from 4.44% to 10.03%, suggesting that the adsorption mechanism alone is insufficient for effective food coloring removal. Meanwhile, photolysis was nearly negligible, with discoloration values as low as 0.10–0.15%, reinforcing its minimal role in the process. Similarly, for Tartrazine Yellow at pH 4, adsorption discoloration varied between 1.08% and 8.33%. However, these results still indicate a weak adsorption capacity. Photolysis, though slightly more effective than for Allura Red, remained ineffective, with discoloration values only reaching 1.05–3.50%. The results suggest that Zn doping can moderately enhance adsorption, particularly for Tartrazine Yellow, but the overall discoloration percentages are too low to be practically meaningful. The photolysis results are particularly striking in their inefficacy, as they consistently failed to exceed 3.5% discoloration under any condition. This implies that photocatalysis under sunlight may be necessary to achieve substantial food coloring removal.
3.2.2. Food Coloring Photodiscoloration Under Sunlight
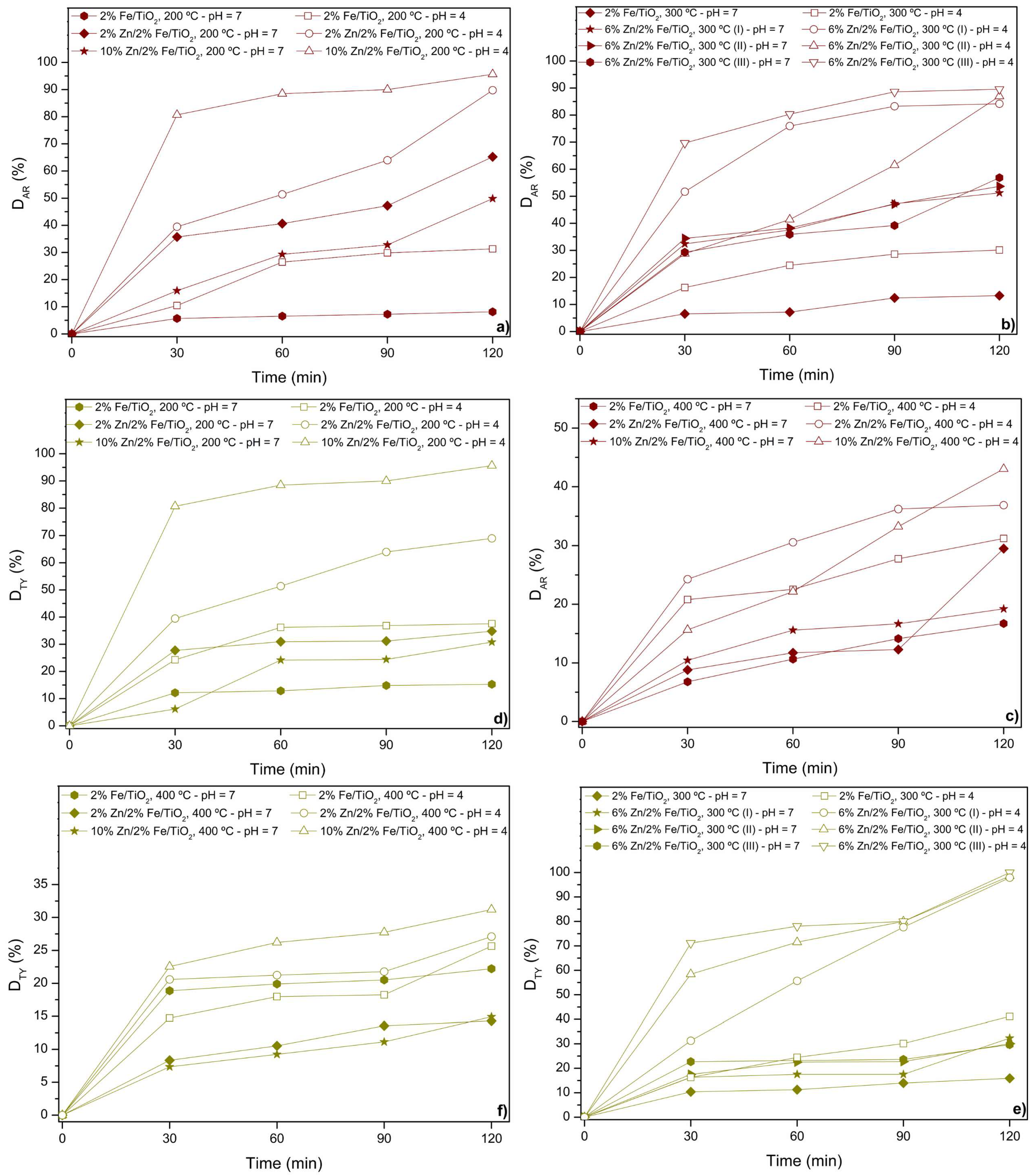
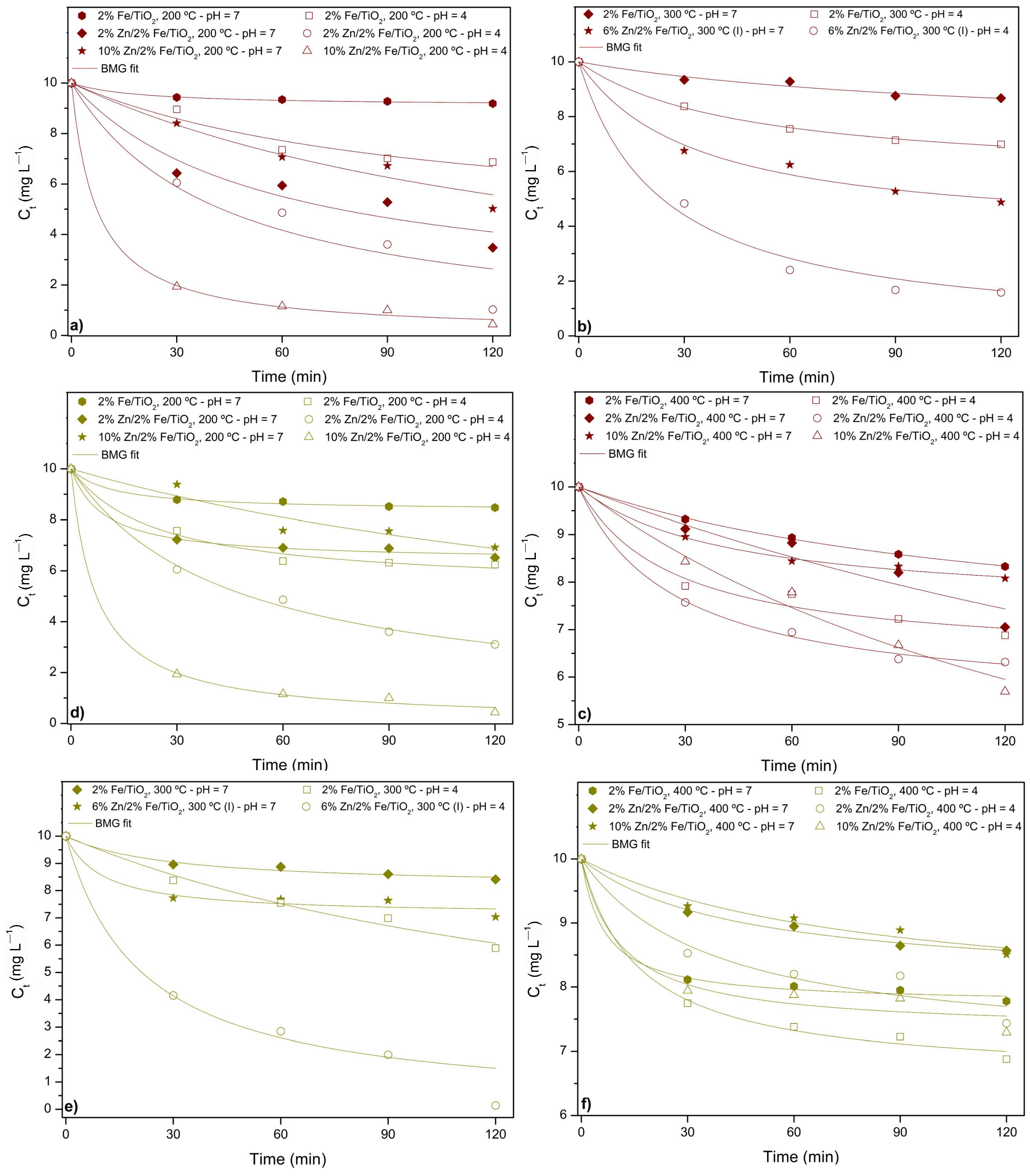
Figure 3 shows the discoloration of the food coloring during sunlight-driven photocatalytic assays. For all the assays, both for AR and TY, and for the two pH values (7 and 4), the Zn loading positively affects the discoloration of the food coloring, as the lowest values for discoloration were obtained from the 2%Fe/TiO2 supports.
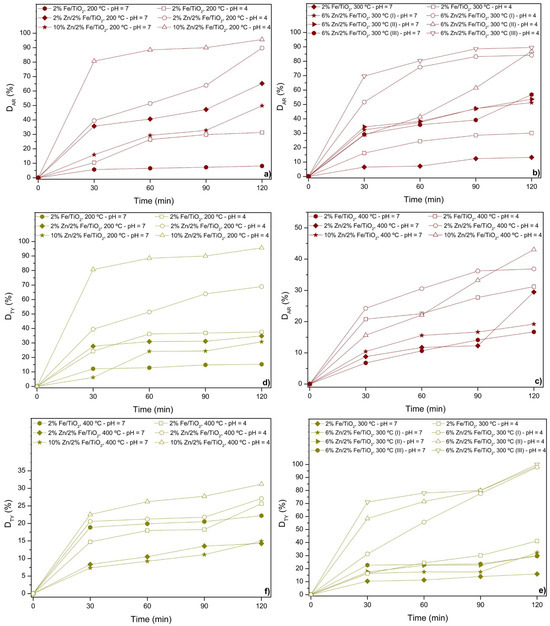
Figure 3.
Photocatalytic discoloration under sunlight: assays for catalysts calcined at (a) 200 °C, (b) 300 °C, (c) 400 °C for Allura Red solution, and (d) 200 °C, (e) 300 °C, (f) 400 °C for Tartrazine Yellow solution. Legend: open symbols (pH 4), closed symbols (pH 7).
Zn co-doping onto Fe/TiO2 can enhance photocatalytic performance in photodiscoloration assays by improving charge carrier separation, increasing surface area, and promoting better food coloring adsorption [6]. The combination of Zn and Fe can create synergistic effects, boosting the generation of reactive oxygen species for more efficient food coloring degradation [42]. When observing the assays for both AR and TY, the effect of calcination temperature on the doped catalysts is also evident. The lowest calcination temperatures (200 and 300 °C) promoted the highest discoloration of the solutions, reaching values higher than 90%; this is probably due to better retention of active sites, optimized crystallinity, and improved surface reactivity [6,7]. Lower temperatures prevent sintering and phase transitions, which can reduce the catalyst’s effectiveness [43,44].
And finally, the pH level also clearly affects the photodiscoloration of food coloring, where pH 4 (open symbols) have higher discoloration percentages than pH 7 (close symbols) for both of the solutions, due to the pH-dependent ionization of the food colorings and the electrostatic interactions between the catalyst and the food colorings [45,46]. At pH 4, the catalyst surface is positively charged (due to its pHPZC being between 5.89 and 7.01—Figure 2d), which favors the adsorption of the neutral or weakly negatively charged forms of both AR (pKa 10.5) and TY (pKa 4) [27]. These electrostatic attractions enhance the photocatalytic degradation process [6]. At pH 7, the catalyst surface is near neutral or slightly negative, while both food colorings are anionic, leading to repulsive interactions that reduce adsorption and thus lower the photodegradation efficiency [7,41]. Therefore, the stronger electrostatic interactions at pH 4 improve the catalyst’s performance in photodegradation assays [8].
In summary, the best catalyst for AR photodiscoloration was 10%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 calcined at 200 °C, achieving values close to 95.6% at pH 4. For TY photodiscoloration, the best catalysts were 6%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 calcined at 300 °C and 10%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 calcined at 200 °C, achieving values close to 99.9% and 95.6%, respectively. These results highlight the influence of both catalyst composition and calcination temperature on the efficiency of photodiscoloration, with optimal performance observed at specific pH conditions for each food coloring.
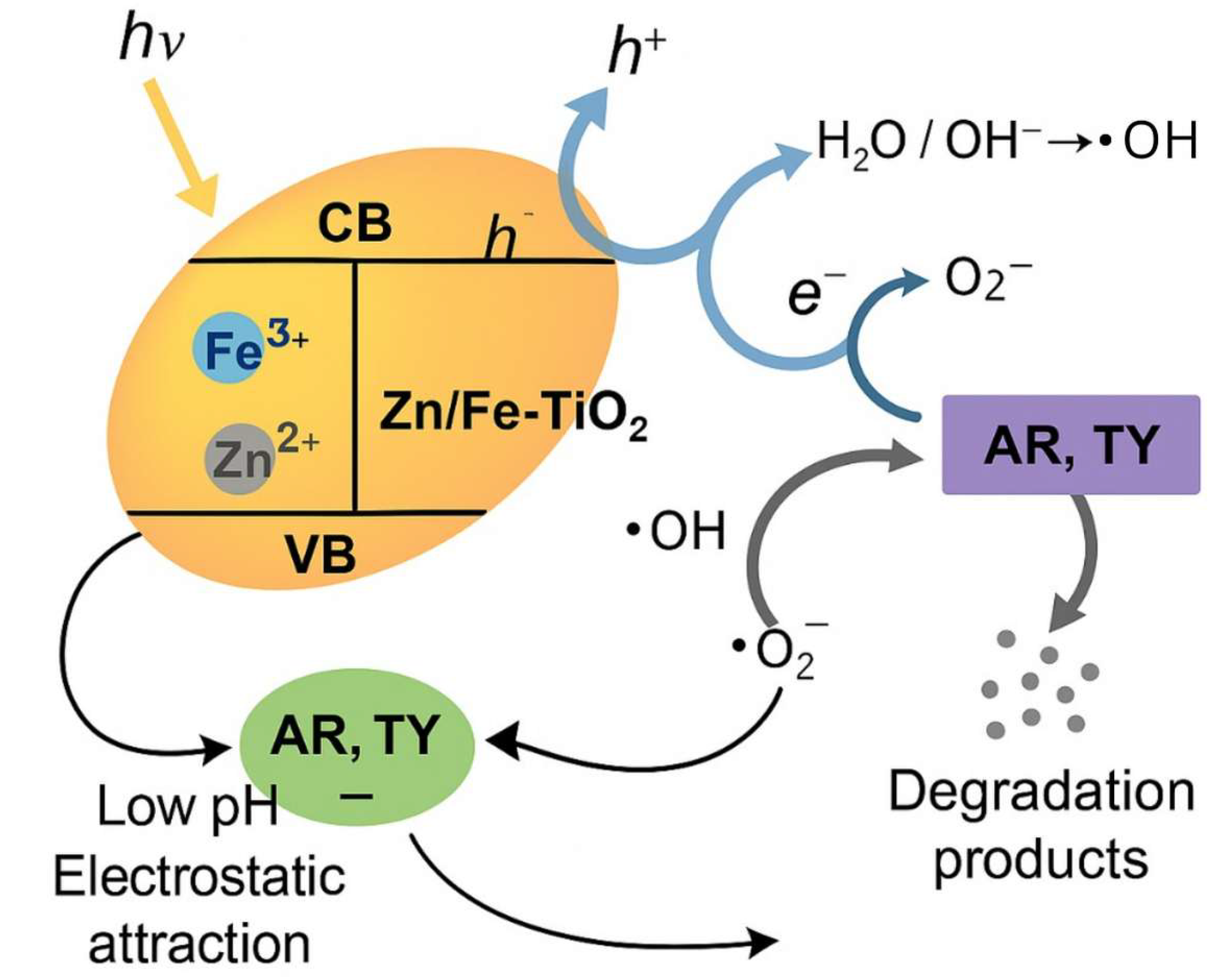
The photodegradation mechanism of dyes Allura Red (AR) and Tartrazine Yellow (TY) by TiO2 catalysts co-doped with Zn and Fe involves a series of photo-induced processes that promote the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Under conditions of irradiation, the photocatalyst absorbs photons and generates electron–lacuna pairs (e−/h+). The doping of Zn2+ has been shown to modify the band structure and enhance light absorption, while Fe3+ functions as an electron trap through the Fe3+/Fe2+ redox cycle, thereby promoting charge separation and reducing recombination. The excited electrons react with molecular oxygen, thereby generating superoxide anions (-O2). Concurrently, the gaps participate in the oxidation of water or hydroxyl ions, which results in the formation of hydroxyl radicals (-OH). These ROS promote the oxidative degradation of the dyes adsorbed on the catalyst surface.
Furthermore, the pH of the solution is a pivotal factor in the efficacy of the process, as the surface charge of the catalysts becomes positive in an acidic environment (pH 4), thereby promoting electrostatic attraction and the adsorption of the anionic dyes AR and TY. The porous nature of the materials under scrutiny exerts a direct influence on the photocatalytic activity. Textural analyses indicate the presence of mesopores with diameters that are suitable for the diffusion and interaction of the dyes with the active sites. This phenomenon is particularly evident in catalysts with a higher Zn content, which possess larger pores and facilitate enhanced mass transport. The high decolorization efficiency observed under optimized conditions is attributable to a synergistic set of structural, electronic, and surface effects. Figure 4 presents a schematic representation of the adsorption and photocatalytic degradation mechanism, as outlined in the text.
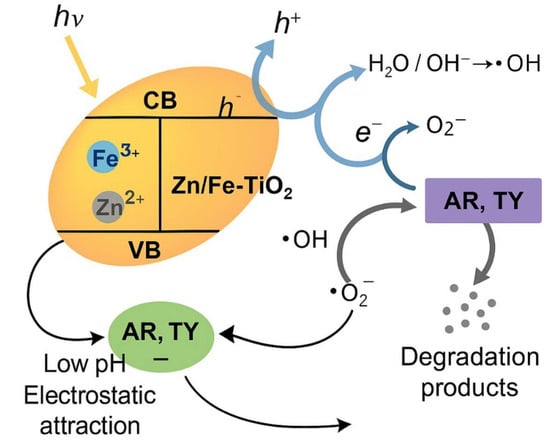
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of the adsorption and photocatalytic degradation mechanism.
3.2.3. Kinetic Modeling of Photodiscoloration Process Under Sunlight
The kinetics of the photocatalysis process can be quite complex due to the numerous steps occurring simultaneously [6]. Three kinetic models—the first-order, second-order, and Behnajady–Modirshahla–Ghanbery models—have been used to assess the fit of experimental data obtained from the discoloration processes. The kinetic parameters for the discoloration of AR and TY, using different catalysts and pH conditions, were calculated based on the models shown in Table 3. The results are presented in Table 6.

Table 6.
Kinetic parameters determined for the Zn/Fe/TiO2 photocatalysis assays.
As the correlation coefficient (R2) approaches 1, the experimental kinetic data align more closely with the kinetic model. As seen in Table 5, the first-order and second-order models do not fit the experimental data well due to their low correlation coefficients. However, the correlation coefficients for the BMG model are generally higher than those of the first-order and second-order models. Therefore, the BMG kinetic model is the most suitable for describing the discoloration of food coloring under various reaction conditions via photocatalysis under sunlight. The BMG model has been successfully applied to describe the discoloration kinetics of AR and TY, and its plot is shown in Figure 5.
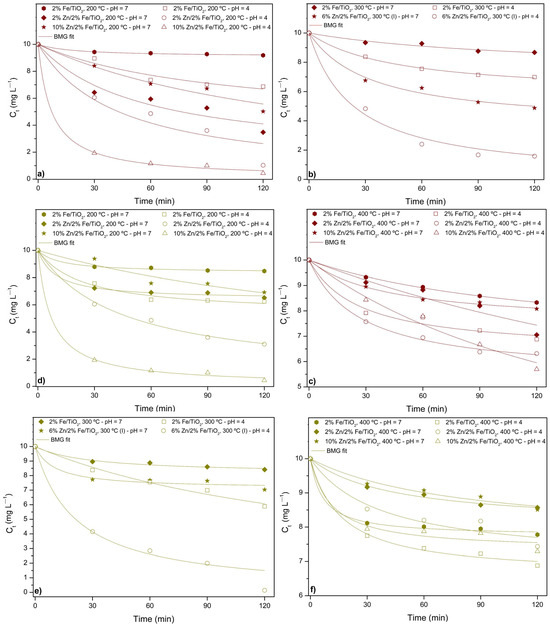
Figure 5.
BMG kinetic curves for photocatalytic assays with catalysts calcined at (a) 200 °C, (b) 300 °C, (c) 400 °C for Allura Red solution, and (d) 200 °C, (e) 300 °C, (f) 400 °C for Tartrazine Yellow solution. Legend: open symbols (pH 4), closed symbols (pH 7).
3.2.4. Food Coloring Photodegradation Assessment
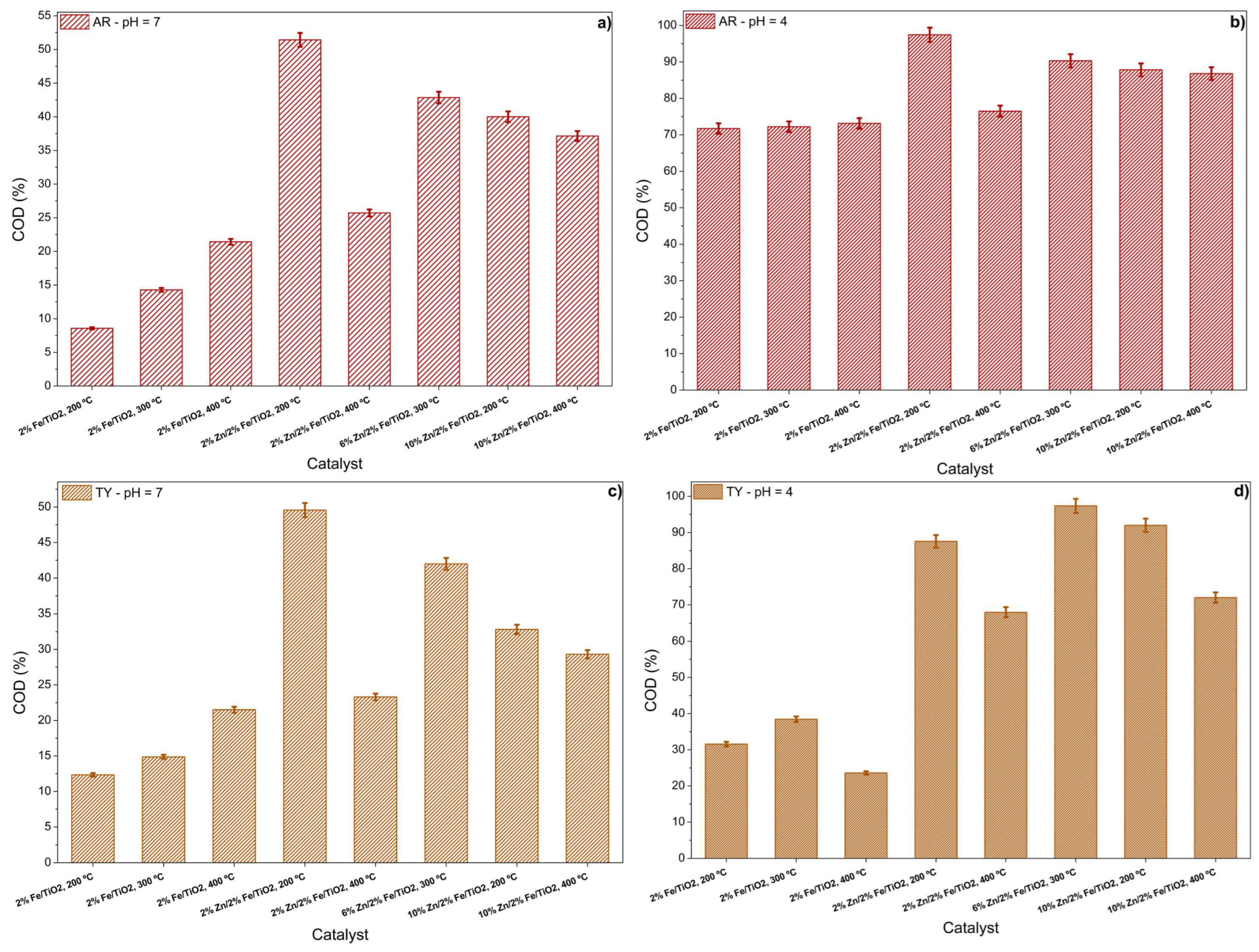
The degradation of the complex structure of the food coloring into less polluting compounds was assessed by measuring the reduction in the chemical oxygen demand of the solutions after the photocatalytic reaction. The results are presented in Figure 6.
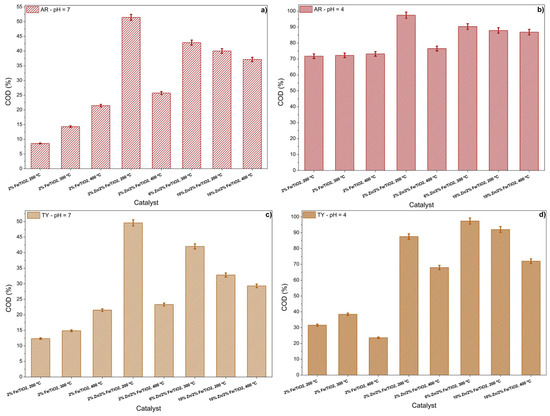
Figure 6.
COD removal by different catalysts for food coloring solution degradation: (a) Allura Red at pH 7, (b) Allura Red at pH 4, (c) Tartrazine Yellow at pH 7, and (d) Tartrazine Yellow at pH 4.
It was observed that in the tests conducted at pH 7 for both AR and TY (Figure 6a and c), the maximum COD reduction was approximately 50%, achieved using the 2%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 catalyst calcined at 200 °C for both food colorings. This reinforces the fact that neutral pH conditions hinder the catalysts’ ability to break down food coloring molecules into compounds with a lower organic load. However, under more acidic conditions (pH 4), both food colorings exhibited COD reductions exceeding 95% (Figure 6b and d). For AR, the most effective catalyst was again the 2%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 calcined at 200 °C, while for TY, the best performance was observed with the 6%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 catalyst calcined at 300 °C. These results demonstrate that the synthesized materials can effectively degrade a wide range of food colorings, breaking them down into compounds with lower organic loads and potentially harmless byproducts.
Studies in the literature have reported similar behavior in dye degradation using different catalysts. Modirshahla et al. (2013) [47] achieved a COD reduction of approximately 92% when degrading Tartrazine Yellow using ZnO catalysts. Similarly, Gupta et al. (2011) [48] reported a COD reduction of around 94% when degrading Tartrazine Yellow with TiO2 catalysts.
3.2.5. Catalyst Reusability Assessment
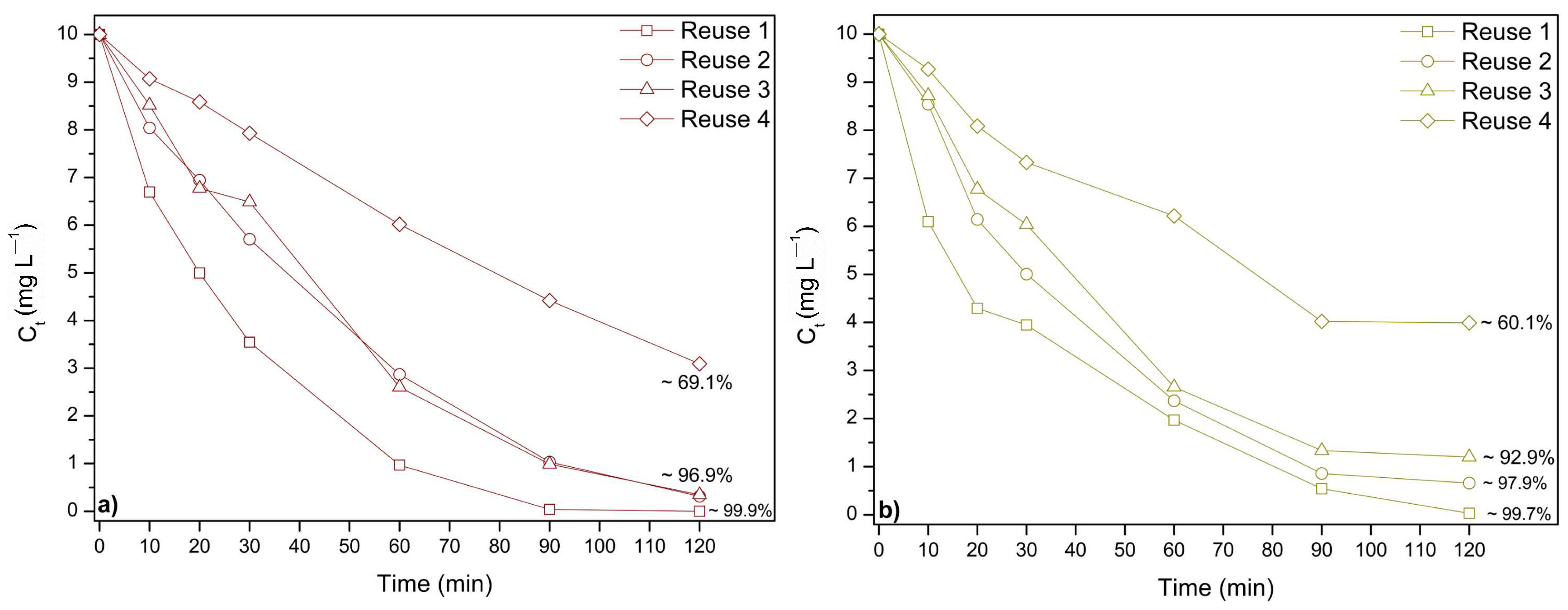
Figure 7 illustrates the reusability of the studied catalysts for the photodegradation of AR and TY over four cycles under UV irradiation. In this study, the most effective catalyst for AR degradation was 2%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 calcined at 200 °C, while for TY, it was 6%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 calcined at 300 °C, as previously observed in Section 3.2.3.
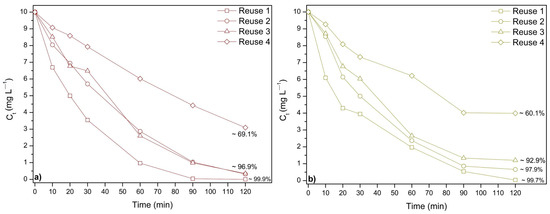
Figure 7.
Reuse performance of the optimal catalyst in the photodegradation of food coloring: (a) Allura Red, and (b) Tartrazine Yellow.
The food coloring concentration was readjusted to its initial value before each cycle. All catalysts exhibited a significant decline in performance from the first to the last cycle. For AR (Figure 7a), the first reuse achieved approximately 99.9% degradation, while by the fourth cycle, this value dropped to around 69%. Similarly, for TY (Figure 7b), the first reuse resulted in approximately 99.7% degradation, decreasing to about 60% in the fourth cycle.
These results indicate that although the catalysts maintain a considerable degradation capacity over multiple cycles, their efficiency decreases over time, likely due to catalyst deactivation caused by surface fouling, structural modifications, or active site depletion [6,7]. Further studies on catalyst regeneration strategies could help improve their long-term stability and reusability.
3.3. Statistical Analysis and Optimization
The effects of different temperatures and pH levels were investigated using a 22 response surface methodology design with replication at the central point. A statistical model incorporating second-order functions was evaluated for all response variables obtained from the photocatalytic assays and analyzed using ANOVA. Table 7 presents the ANOVA results for the response variables.

Table 7.
Analysis of variance.
For AR discoloration and TY COD, factor x (calcination temperature), factor y (Zn %), and factor x2 had a statistically significant effect at a 5% significance level (p-value < 0.05). Additionally, for AR COD, the factors x, x2, and the interaction between x × y (calcination temperature × Zn %) also exhibited a significant statistical effect at the same significance level. Finally, for TY discoloration, all factors and interactions had a statistically significant effect at a 5% significance level (p-value < 0.05).
The residual error for AR discoloration, AR COD, TY discoloration, and TY COD was found to be 1.63, 0.64, 1.02, and 1.14, respectively. The low residual error values indicate that the model effectively predicts the behavior of the variables used in the experiment.
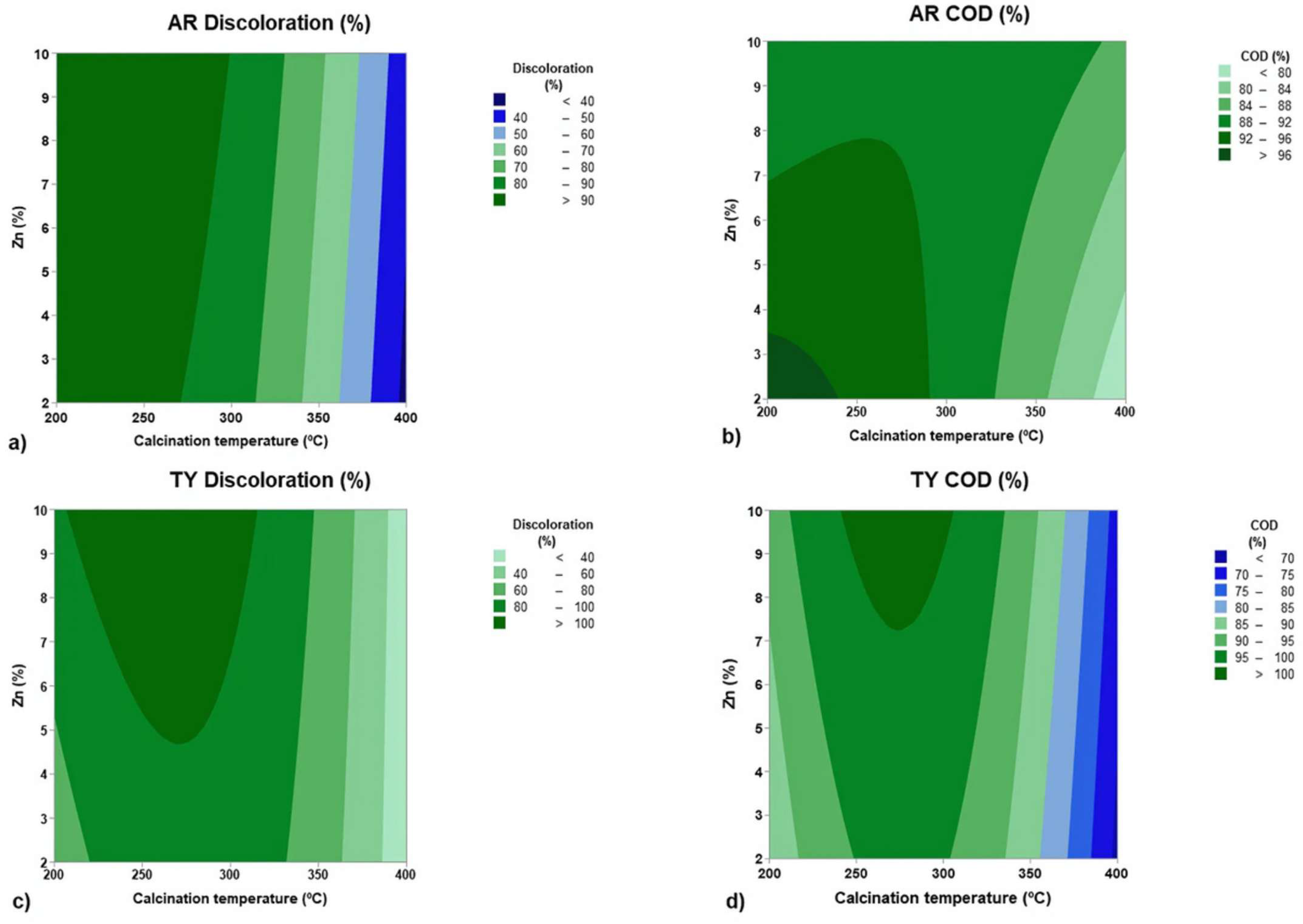
Level curves were generated for the statistically valid variables (Figure 8). The AR discoloration percentage was maximized at a lower temperature range, in the dark greenish region between 200 and 270 °C (Figure 8a), independent of Zn % variation. This result suggests that calcination temperature is the dominant factor influencing the discoloration of Allura Red solutions. However, for AR COD reduction (Figure 8b), the highest values were achieved at the lowest calcination temperatures (between 200 and 240 °C) and the lowest Zn % (between 2 and 3.5%).
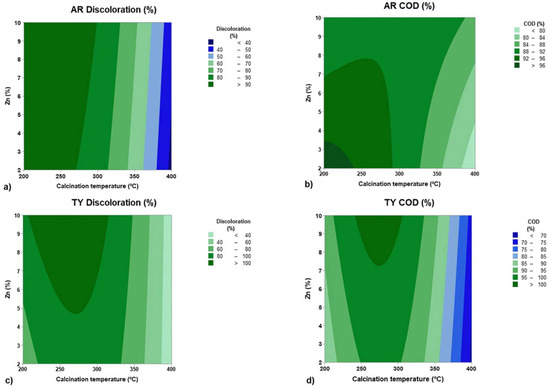
Figure 8.
Response surface plots of the statistical analysis: (a) 2D—level curve for AR discoloration; (b) 2D—level curve for AR COD; (c) 2D—level curve for TY discoloration; and (d) 2D—level curve for TY COD.
For TY discoloration and TY COD reduction (Figure 8c,d), the highest removal efficiencies were observed at intermediate temperatures (between 250–300 °C) and Zn % values in the middle-to-high range (~5–10%). These findings suggest that different operational parameters can be adjusted to optimize calcination temperature and Zn %, depending on the desired outcome for each response variable.
The equations for AR discoloration (Equation (6)), AR COD (Equation (7)), TY discoloration (Equation (8)), and TY COD (Equation (9)), were derived, along with the determination coefficients for the adjusted regression models based on second-order functions.
The determination coefficient was found to be greater than 0.984 for all models, indicating that the models accurately fit the experimental data. To optimize the factorial design and maximize the response variables, the obtained models were subjected to Simplex method analysis to determine the optimal values of the factors that yield the highest discoloration and/or COD reduction.
The calculations were performed using the Solver tool in Microsoft Office Excel®. The constraints applied in the software were based on the factorial design limits: 200 ≤ x ≤ 400 °C and 2 ≤ y ≤ 10, with the objective function being the response variable itself. The optimization results were as follows:
- AR discoloration: T = 236 °C, Zn % = 10, with 97.9% discoloration;
- AR COD reduction: T = 200 °C, Zn % = 2, with 97.8% COD reduction;
- TY discoloration: T = 261 °C, Zn % = 10, with 100% discoloration;
- TY COD reduction: T = 273 °C, Zn % = 10, with 100% COD reduction.
These different optimization conditions demonstrate the flexibility of the photocatalytic process, allowing adjustments in operational parameters depending on the desired outcome. The ability to fine-tune calcination temperature and Zn % offers a valuable advantage in tailoring the process for specific food coloring degradation needs, improving both efficiency and adaptability in practical applications.
where x represents the calcination temperature (°C) and y represents the Zn content (%) used in the photocatalytic process.
4. Conclusions
In this work, Zn/Fe/TiO2 catalysts were successfully synthesized using the wet impregnation method. The variation in Zn content and calcination temperature had a significant influence on both the discoloration and degradation efficiency of aqueous solutions containing the food colorings Allura Red and Tartrazine Yellow.
Statistical analysis confirmed that both calcination temperature and Zn loading played a crucial role in discoloration efficiency and COD removal. The optimal conditions were achieved at low calcination temperatures ranging from 200 °C to 273 °C, with Zn loadings varying between 2% and 10%, resulting in up to 98% discoloration and COD removal for both food colorings.
Among the catalysts tested, the best performance for Allura Red was observed with 2%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 calcined at 200 °C, while for Tartrazine Yellow, the most effective catalyst was 6%Zn/2%Fe/TiO2 calcined at 300 °C. Additionally, both catalysts demonstrated stability, maintaining effectiveness over four reuse cycles.
These findings provide valuable insights for future studies exploring a wider range of calcination temperatures and metal loadings. Furthermore, while optimizing catalytic performance is crucial, it is equally important to consider the economic and environmental implications, as higher synthesis temperatures and increased metal content can elevate production costs. The results of this study contribute to the development of cost-effective and efficient photocatalysts for the degradation of organic pollutants in wastewater treatment applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: L.E.N.C.; Methodology: L.E.N.C., G.G.L., M.K.A., L.N.B.A. and R.B., and L.M.S.C.; Investigation: L.E.N.C., G.G.L., M.K.A., L.N.B.A. and R.B.; Validation: L.E.N.C. and L.M.S.C.; Writing—original draft preparation: L.E.N.C., L.R.M. and L.M.S.C.; Writing—review and editing: L.E.N.C., L.R.M. and L.M.S.C.; Funding acquisition: L.M.S.C.; Resources: L.M.S.C.; Supervision: L.M.S.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study received support from Brazilian funding agencies, including CNPq, and CAPES (001).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are reported in the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors assert that they do not have any identifiable conflicting financial interests or personal associations that might have seemed to exert an impact on the research reported in this manuscript.
References
- Amchova, P.; Siska, F.; Ruda-Kucerova, J. Food Safety and Health Concerns of Synthetic Food Colors: An Update. Toxics 2024, 12, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nippes, R.P.; Macruz, P.D.; Molina, L.C.A.; Scaliante, M.H.N.O. Solar-Fenton Heterogeneous for Removal of Tartrazine Yellow Dye Using Zeolite Y-Fe as Catalyst. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 3675–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Messaoudi, N.; Miyah, Y.; Singh, N.; Gubernat, S.; Fatima, R.; Georgin, J.; El Mouden, A.; Saghir, S.; Knani, S.; Hwang, Y. A Critical Review of Allura Red Removal from Water: Advancements in Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation Technologies, and Future Perspectives. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegbe, E.O.; Uthman, T.O. A Review of History, Properties, Classification, Applications and Challenges of Natural and Synthetic Dyes. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, T.A.; Leite, B.S.; Assunção, L.S.; de Jesus Freitas, T.; Colauto, N.B.; Linde, G.A.; Otero, D.M.; Machado, B.A.S.; Ferreira Ribeiro, C.D. Red Tomato Products as an Alternative to Reduce Synthetic Dyes in the Food Industry: A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.E.N.; Meira, A.H.; Almeida, L.N.B.; Lenzi, G.G.; Colpini, L.M.S. Experimental Design and Optimization of Textile Dye Photodiscoloration Using Zn/TiO2 Catalysts. Desalination Water Treat. 2022, 266, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, L.E.N.; Meurer, E.C.; Alves, H.J.; dos Santos, M.A.R.; de Castro Vasques, E.; Colpini, L.M.S. Photocatalytic Degradation of Textile Dye Orange-122 Via Electrospray Mass Spectrometry. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2020, 63, e20180573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.E.N.; Matheus, L.R.; Albuquerque, L.J.C.; Gasparini, L.J.; Fagnani, K.C.; Alves, H.J.; Colpini, L.M.S. Production of Nanostructured Crystalline Composite Using Residual Ashes from Flocculated Sludge Burning Process in a Poultry Slaughterhouse Wastewater Treatment System. Cerâmica 2022, 68, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagnani, K.C.; Alves, H.J.; de Castro, L.E.N.; Kunh, S.S.; Colpini, L.M.S. An Alternative for the Energetic Exploitation of Sludge Generated in the Physico-Chemical Effluent Treatment from Poultry Slaughter and Processing in Brazilian Industries. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, L.E.N.; Battocchio, D.A.J.; Ribeiro, L.F.; Colpini, L.M.S. Development of Adsorbent Materials Using Residue from Coffee Industry and Application in Food Dye Adsorption Processes. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2023, 66, e23210125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.E.N.; Mançano, R.R.; Battocchio, D.A.J.; Colpini, L.M.S. Adsorption of Food Dye Using Activated Carbon from Brewers’ Spent Grains. Acta Scientiarum. Technol. 2022, 45, e60443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, B.; Li, Q. Progress on Mechanism and Efficacy of Heterogeneous Photocatalysis Coupled Oxidant Activation as an Advanced Oxidation Process for Water Decontamination. Water Res. 2024, 251, 121119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyyappan, J.; Gaddala, B.; Gnanasekaran, R.; Gopinath, M.; Yuvaraj, D.; Kumar, V. Critical Review on Wastewater Treatment Using Photo Catalytic Advanced Oxidation Process: Role of Photocatalytic Materials, Reactor Design and Kinetics. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 9, 100599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbali, P.; Hassani, A.; Wacławek, S.; Andrew Lin, K.-Y.; Sayyar, Z.; Ghanbari, F. Recent Advances in Design and Engineering of MXene-Based Catalysts for Photocatalysis and Persulfate-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes: A State-of-the-Art Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 147920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanos, F.; Razzouk, A.; Lesage, G.; Cretin, M.; Bechelany, M. A Comprehensive Review on Modification of Titanium Dioxide-Based Catalysts in Advanced Oxidation Processes for Water Treatment. ChemSusChem 2024, 17, e202301139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khader, E.H.; Muslim, S.A.; Saady, N.M.C.; Ali, N.S.; Salih, I.K.; Mohammed, T.J.; Albayati, T.M.; Zendehboudi, S. Recent Advances in Photocatalytic Advanced Oxidation Processes for Organic Compound Degradation: A Review. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 318, 100384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaha, S.K.S.M.; Pugazhenthiran, N.; Sathishkumar, P.; Govinda raj, M.; Perarasu, V.T.; Kumaresan, R.; Assiri, M.A.; Selvaraj, M. Peroxymonosulphate Activation by Ultra-Small Ni@NiFe2O4/ZnO Magnetic Nanocomposites for Solar Photocatalytic Degradation of β-Lactam Antibiotic-Cefadroxil. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 36050–36061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Priyadarshini, U.; Remya, N. Solar Photocatalytic Degradation of Ciprofloxacin Using Biochar Supported Zinc Oxide- Tungsten Oxide Photocatalyst. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 32, 9412–9428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanjwani, M.F.; Tuzen, M.; Khuhawar, M.Y.; Saleh, T.A. Trends in Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Dye Pollutants Using Nanoparticles: A Review. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 159, 111613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruva, H.; Khavala, V.B.; Mishra, B.R.; Murugan, K.; Thomas, T.; Murty, B.S. Solar-Photocatalytic Treatment of Industrial Wastewater Using Mechanically Doped CNS-TiO2 and Synergistic TiO2 Incorporation: A Promising Cost-Effective Approach for Industrial Wastewater Treatment. Mater. Res. Bull. 2024, 177, 112825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Dong, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, L.; Cao, X.; et al. Tuning the Heterostructure of Zn–Fe–O Nanoparticles for Highly Efficient Photocatalytic Removal of U(vi) under Different Light Intensities. Environ. Sci. Nano 2024, 11, 3346–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemanathan, G.; Karthikeyan, S.; Kathirvel, R. Comparative Study on Solar Photocatalytic Degradation of Naproxen Using Nitrogen Doped ZnO and Nitrogen Doped TiO2: Kinetics and Intermediates Analysis. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhadeve, G.K.; Gedam, R.S. Visible Light Assisted Photocatalytic Degradation of Mixture of Reactive Ternary Dye Solution by Zn–Fe Co-Doped TiO2 Nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2023, 341, 139990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Rojas, J.; Rao, M.A.; Berruti, I.; Mora, M.L.; Garrido-Ramírez, E.; Polo-López, M.I. Assessment of Solar Photocatalytic Wastewater Disinfection and Microcontaminants Removal by Modified-Allophane Nanoclays Based on TiO2, Fe and ZnO at Laboratory and Pilot Scale. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 503, 157894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliasari, N.; Wijaya, A.; Mohadi, R.; Elfita, E.; Lesbani, A. Photocatalytic Degradation of Malachite Green by Layered Double Hydroxide Based Composites. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal. 2022, 17, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Moin-ud-Din, G.; Iqbal, M.; Nazir, A.; Altaf, I.; Alwadai, N.; Siddiqua, U.H.; Younas, U.; Ali, A.; Kausar, A.; et al. Ag and Zn Doped TiO2 Nano-Catalyst Synthesis via a Facile Green Route and Their Catalytic Activity for the Remediation of Dyes. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 3626–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, R.E.; Othmer, D.F. Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; ISBN 9780471485087. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, W.; Khan, A.; Hussain, S.; Khan, H.; Abumousa, R.A.; Bououdina, M.; Khan, I.; Iqbal, S.; Humayun, M. Enhanced Light Absorption and Charge Carrier’s Separation in g-C3N4-Based Double Z-Scheme Heterostructure Photocatalyst for Efficient Degradation of Navy-Blue Dye. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2024, 17, 2381591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, H. Chemical Kinetic Modeling of Organic Pollutant Degradation in Fenton and Solar Photo-Fenton Processes. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 123, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, E.W.; Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D.; Clesceri, L.S.; Association, A.P.H.; Association, A.W.W.; Federation, W.E. Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater 2012; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780875530130. [Google Scholar]
- ALOthman, Z. A Review: Fundamental Aspects of Silicate Mesoporous Materials. Materials 2012, 5, 2874–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingel, L.W.; Walton, K.S. Surprising Use of the Business Innovation Bass Diffusion Model to Accurately Describe Adsorption Isotherm Types I, III, and V. Langmuir 2023, 39, 4475–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.E.N.; Santos, J.V.F.; Fagnani, K.C.; Alves, H.J.; Colpini, L.M.S. Evaluation of the Effect of Different Treatment Methods on Sugarcane Vinasse Remediation. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2019, 54, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colpini, L.M.S.; Lenzi, G.G.; Urio, M.B.; Kochepka, D.M.; Alves, H.J. Photodiscoloration of Textile Reactive Dyes on Ni/TiO2 Prepared by the Impregnation Method: Effect of Calcination Temperature. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2365–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colpini, L.M.S.; Lenzi, G.G.; de Souza, R.C.T.; Urio, M.B.; Kochepka, D.M.; Santos, M.A.R.; Vasques, E.C.; Alves, H.J. Photodiscoloration Processes of Dyes Reactive Using Radiation and Fe/TiO2. Int. J. Mater. Eng. Technol. 2017, 15, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzi, G.G.; Evangelista, R.F.; Duarte, E.R.; Colpini, L.M.S.; Fornari, A.C.; Menechini Neto, R.; Jorge, L.M.M.; Santos, O.A.A. Photocatalytic Degradation of Textile Reactive Dye Using Artificial Neural Network Modeling Approach. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 57, 14132–14144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmane, V.G.; Owen, S.L.; Abrokwah, R.Y.; Kuila, D. Mesoporous Nanocrystalline TiO2 Supported Metal (Cu, Co, Ni, Pd, Zn, and Sn) Catalysts: Effect of Metal-Support Interactions on Steam Reforming of Methanol. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 408, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, M.; Fang, J.; Song, X.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, Z. Synthesis of Zn-Doped TiO2 Nano-Particles Using Metal Ti and Zn as Raw Materials and Application in Quantum Dot Sensitized Solar Cells. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 791, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.G.; Mazumdar, S.; Modak, B.; Bapat, R.; Ayyub, P.; Bhattacharyya, K. The Role of Surface O-Vacancies in the Photocatalytic Oxidation of Methylene Blue by Zn-Doped TiO2: A Mechanistic Approach. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2017, 345, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Chan, C.K.; Porter, J.F.; Guo, W. Micro-Raman Spectroscopic Characterization of Nanosized TiO2 Powders Prepared by Vapor Hydrolysis. J. Mater. Res. 1998, 13, 2602–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.E.N.; Matheus, L.R.; Sganzerla, W.G.; Colpini, L.M.S. Valorization of Residual Ashes from Boiler Combustion Process into Activated Carbon for Adsorption of Food Industry Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 22, 5341–5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cui, K.; Liu, T.; Cui, M.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, W.-W.; Li, C.-X. Enhanced Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole by Non-Radical-Dominated Peroxymonosulfate Activation with Co/Zn Co-Doped Carbonaceous Catalyst: Synergy between Co and Zn. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 158055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, A.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Iglesia, E. Effects of Zn, Cu, and K Promoters on the Structure and on the Reduction, Carburization, and Catalytic Behavior of Iron-Based Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis Catalysts. Catal Lett. 2001, 77, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Tseng, S.-L. Heterogeneous Catalyst Characteristics of TiO2 Nanoparticles Impregnated with Alkaline CH3ONa for Use in Transesterification Process. Processes 2024, 12, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valarmathy, C.; Sudhaparimala, S. Photodiscoloration of Malachite Green Dye Using Nitrogen Self-Doped Graphene Oxide from Moringa Oleifera Leaves. J. Water Environ. Nanotechnol. 2025, 10, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imessaoudene, A.; Mechraoui, O.; Aberkane, B.; Benabbas, A.; Manseri, A.; Moussaoui, Y.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Amrane, A.; Zoukel, A.; Mouni, L. Synthesis of a TiO2/Zeolite Composite: Evaluation of Adsorption-Photodegradation Synergy for the Removal of Malachite Green. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2024, 38, 101191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modirshahla, N.; Abdoli, M.; Behnajady, M.; Vahid, B. Decolourization of Tartrazine from Aqueous Solutions by Coupling Electrocoagulation with ZnO Photocatalyst. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2013, 39, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Jain, R.; Nayak, A.; Agarwal, S.; Shrivastava, M. Removal of the Hazardous Dye—Tartrazine by Photodegradation on Titanium Dioxide Surface. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).