- Case Report
Digenic Contribution of Heterozygous ALPK3 and TRIM63 Variants to End-Stage Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in a Young Adult
- Olga S. Chumakova,
- Natalia V. Milovanova and
- Ekaterina Y. Zakharova
- + 2 authors
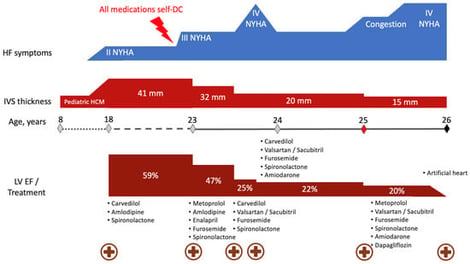
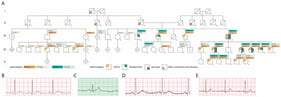
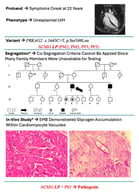
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), the most common inherited cardiac disorder, is usually caused by pathogenic variants in sarcomeric genes and is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Around 5% of cases are caused by variants in non-sarcomeric genes, which may involve alternative modes of inheritance. This study presents the first reported case of HCM associated with digenic contribution of heterozygous variants in two non-sarcomeric genes: ALPK3 and TRIM63. The patient was incidentally diagnosed with non-obstructive HCM in childhood and developed extreme myocardial hypertrophy with moderate heart failure at the age of 18. Rapid progressive left ventricular dysfunction promptly resulted in death at the age of 26. Genetic testing with an extended HCM panel identified no sarcomeric variants but revealed two truncating variants in the ALPK3 and TRIM63 genes. Whole-genome sequencing excluded any other causes of the disease. Heterozygous ALPK3 variants are typically associated with late-onset HCM, whereas TRIM63 variants are only considered pathogenic in a recessive state. This case, therefore, suggests a synergistic contribution of both variants to the development of a severe phenotype. The potential mechanisms of interaction between the protein products of ALPK3 and TRIM63 within the M-band of the sarcomere are discussed.
1 January 2026