- Review
Biogenic Copper-Based Nanoparticles: Emerging Antimicrobial Agents Against Pathogenic Microorganisms
- Edith Dube and
- Grace Emily Okuthe
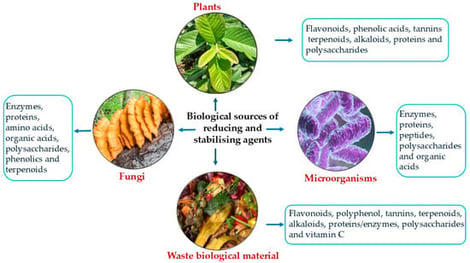
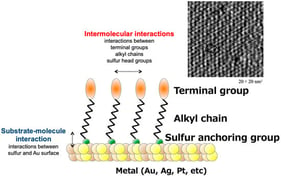
Biogenic copper-based nanoparticles have attracted attention as potent antimicrobial agents synthesised via environmentally sustainable routes using plants, microorganisms, and biological waste. Green synthesis leverages phytochemicals, enzymes, and proteins as natural reducing and stabilising agents, enabling nanoparticle formation under mild, non-toxic conditions without hazardous reagents. The resulting nanoparticles are typically spherical, <100 nm in size, and enriched with bioactive surface functionalities that contribute to broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against bacteria, fungi, and biofilms. Their antimicrobial effects arise from interconnected mechanisms, including the generation of reactive oxygen species, the release of Cu2 ions, membrane disruption, and interference with vital metabolic and genetic processes. Hybrid systems such as Ag–Cu, Zn–CuO, and CuS nanoparticles further enhance efficacy through synergistic redox and photothermal effects. These properties support applications in medical coatings, wound dressings, food packaging, aquaculture disease management, and sustainable crop protection. However, toxicity is highly context-dependent, influenced by factors such as nanoparticle size, shape, surface chemistry, capping agent, concentration, exposure medium, and the biological system. Small or weakly capped NPs can induce cytotoxicity, hemolysis, developmental defects, or growth inhibition, whereas functionalization or capping can improve selectivity and biocompatibility. Standardised physicochemical characterisation, harmonised toxicity testing, and mechanistic understanding are critical for the safe translation of biogenic CuNPs into regulatory-approved applications. This review summarises recent advances (2015–2025) in the biogenic synthesis of copper-based nanoparticles, highlighting how biological systems govern nanoparticle morphology, stability, and antimicrobial efficiency. It integrates mechanistic insights, compares monometallic and hybrid systems, and evaluates emerging applications in medicine, agriculture, aquaculture, and food safety. The review also identifies current limitations and future directions for standardisation, toxicity evaluation, and regulatory approval.
10 February 2026



![The optical transmission spectrum of a thin film highlights the elements to consider when determining thickness [47].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/applnano/applnano-07-00002/article_deploy/html/images/applnano-07-00002-g001-550.jpg)

