Journal Description
Immuno
Immuno
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on immunological research and clinical applications published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, EBSCO, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 28.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Medicine (miscellaneous))
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
2.5 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.0 (2024)
Latest Articles
Balancing Nutrition and Inflammation: The Role of a Healthy Diet in NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation
Immuno 2026, 6(1), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno6010013 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
Research has shown that diet significantly influences the chance of developing chronic inflammatory diseases including inflammatory bowel disease, cardiovascular disease, obesity, type 2 diabetes and several types of cancer. Dietary components modulate the immune system by either promoting or mitigating inflammatory pathways. One
[...] Read more.
Research has shown that diet significantly influences the chance of developing chronic inflammatory diseases including inflammatory bowel disease, cardiovascular disease, obesity, type 2 diabetes and several types of cancer. Dietary components modulate the immune system by either promoting or mitigating inflammatory pathways. One such pathway is the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome—a multiprotein complex that is involved in the innate immune response. The NLRP3 inflammasome is triggered by various stimuli including ionic flux, mitochondrial dysfunction, lysosomal damage and ROS. Upon activation through a two-signal process, an immune response is initiated that protects the body against pathogens and cellular stress. In a healthy body, this pathway is closely regulated to maintain homeostasis and prevent excessive inflammation that can result in tissue damage or chronic inflammatory diseases. Several components present in a human diet can activate or inhibit the NLRP3 inflammasome. To support a balanced diet, organizations like the WHO have developed dietary recommendations. These promote the consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins and healthy fats. These foods contain a variety of nutrients and bioactive compounds, including saturated fatty acids, cholesterol, omega-6 fatty acids and natural sugars, which are pro-inflammatory. At the same time, they also supply anti-inflammatory compounds such as monounsaturated fatty acids, antioxidants and probiotics. While current literature highlights the NLRP3 inflammasome as a critical regulator of inflammation, it lacks detailed insights into how the specific dietary components of a healthy diet influence its modulation. Therefore, this literature review elucidates the various mechanisms through which these dietary compounds modulate the NLRP3 inflammasome. The significance of maintaining a balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory components in the diet is highlighted by its role as a regulator of inflammatory diseases, for example, through mechanisms such as epigenetic pathways.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Extracellular Vesicles in Neuroinflammation: Insights into Pathogenesis, Biomarker Potential, and Therapeutic Strategies
by
Uma Maheswari Deshetty, Seema Singh, Frida L. Martínez-Cuevas, Stuti Jain, Shilpa Buch and Palsamy Periyasamy
Immuno 2026, 6(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno6010012 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) constitute a heterogeneous group of membrane-derived particles generated through distinct biogenesis pathways, each regulated by precise molecular mechanisms. They carry a diverse array of cargo that reflects the physiological or pathological state of their parent cells. Their classification continues to
[...] Read more.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) constitute a heterogeneous group of membrane-derived particles generated through distinct biogenesis pathways, each regulated by precise molecular mechanisms. They carry a diverse array of cargo that reflects the physiological or pathological state of their parent cells. Their classification continues to evolve, as advances in isolation and characterization techniques have revealed novel vesicle subpopulations beyond the traditional categories of microvesicles, and apoptotic bodies, further highlighting the complexity of the EV landscape. Within the central nervous system (CNS), neurons, microglia, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and endothelial cells actively release EVs that contribute to intercellular communication. Growing evidence demonstrates that these vesicles play critical roles in neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration by transporting bioactive molecules that influence disease pathways. Their ability to cross the blood–brain barrier allows CNS-derived EVs to be detected in peripheral fluids, making them promising candidates for noninvasive biomarkers. Moreover, EVs are increasingly being explored as therapeutic tools due to their stability, biocompatibility, and capacity to deliver targeted molecular cargo. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview of EV biogenesis and release mechanisms in CNS cell types, discuss their emerging functions in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disorders, and summarize current advances in EV-based diagnostics and therapeutic approaches, including ongoing clinical trials.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nano-Pharmacology: Nanotechnology Based Therapeutics for Targeting Neuroinflammation)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Molecular Programming of Stem-Cell Differentiation: From Soluble Factors to Agonist Antibodies
by
Hyukmin In and Kyung Ho Han
Immuno 2026, 6(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno6010011 - 31 Jan 2026
Abstract
Stem-cell differentiation technologies have traditionally relied on recombinant growth factors, cytokines, and morphogens to initiate and guide lineage specification toward clinically relevant cell types. These approaches have enabled substantial progress in regenerative medicine, as exemplified by recent advances in cell-replacement therapies for Parkinson’s
[...] Read more.
Stem-cell differentiation technologies have traditionally relied on recombinant growth factors, cytokines, and morphogens to initiate and guide lineage specification toward clinically relevant cell types. These approaches have enabled substantial progress in regenerative medicine, as exemplified by recent advances in cell-replacement therapies for Parkinson’s disease, type 1 diabetes, and retinal degeneration. However, protein-based ligands and soluble factors are often limited by short half-lives, pleiotropic signaling, condition-dependent effects, and challenges in achieving precise spatial and temporal control in scalable systems. In this review, we survey differentiation strategies driven by administered substances, organizing the field into five material-centric modules: recombinant growth factors, cytokines, morphogens, exogenous ligands, and agonist antibodies. For each module, we summarize mechanistic principles, representative studies, controllable variables, and translational considerations. While growth factors, cytokines, morphogens, and exogenous ligands remain central tools for directing lineage commitment and maturation, recent studies indicate that agonist antibodies offer an additional and distinct means of controlling differentiation outcomes. These antibodies can function as receptor agonists while also imparting tissue-selective effects, enabling lineage specification with coordinated spatial targeting. By focusing on differentiation methods driven by administered molecules and excluding direct physical stimulation or complex 3D constructs, this review provides a framework that is particularly relevant to immunology and translational practice. We highlight agonist antibody-based induction as an emerging strategy that complements established ligand-based approaches and may broaden the design space for clinically applicable stem-cell differentiation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Role of Cytokines and Autoantibodies Against Cytokines in Health and Disease)
Open AccessArticle
Association of Treatment Status with Cytokine and sCTLA-4 Profiles in Rheumatoid Arthritis
by
Sonia Elia Ishaq, Taban Kamal Rasheed and Niaz Albarzingi
Immuno 2026, 6(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno6010010 - 28 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is triggered by dysregulated cytokine networks, but the distributional association of conventional synthetic (csDMARDs) and biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs) with circulating mediators has not been fully described. In this study, we aimed to investigate the treatment-associated modulation of TNF-α, IL-17, IL-13,
[...] Read more.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is triggered by dysregulated cytokine networks, but the distributional association of conventional synthetic (csDMARDs) and biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs) with circulating mediators has not been fully described. In this study, we aimed to investigate the treatment-associated modulation of TNF-α, IL-17, IL-13, and soluble CTLA-4 (sCTLA-4) in 64 RA patients (untreated, n = 14; csDMARD, n = 32; bDMARD ± csDMARD, n = 18) and 20 controls. ELISA was used to determine the serum levels, and Kruskal–Wallis tests and false discovery rate correction were used to determine the differences between groups, accompanied by DAS28- and CRP-adjusted quantile regression. Group-level analysis demonstrated that the levels of IL-17 were higher in patients treated with csDMARDs and bDMARDs than in the controls (FDR-adjusted p = 0.0009 and <0.0001, respectively), and the levels of IL-13 were higher in patients treated with bDMARDs than in the controls (p = 0.026). However, quantile regression did not reveal consistent treatment-related associations, suggesting that long-term pathway-specific immune responses and context-dependent regulation may be involved. Smoking independently predicted higher IL-13 at lower quantiles (β = 35.5; p < 0.0001), while TNF-α showed treatment-related increases only at the upper quantile in CRP-adjusted models (β = 323.7; p = 0.049). On the other hand, sCTLA-4 had the largest and most significant treatment-based increase (p < 0.0001), regardless of disease activity, and constant effects across mid-quantiles. Taken together, these findings suggest that sCTLA-4 shows therapy-responsive distributional changes, supporting its potential utility as a biomarker of biological efficacy. In contrast, the observed increases in IL-17 and IL-13 reflect ongoing immune activity and possible environmental influences. Distribution-sensitive biomarker profiling provides a nuanced approach to capturing immune response diversity in RA and may enhance precision in monitoring procedures.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
A Glycan-Based Ligands for Phenotypic Profiling and Selective Immunomodulation of Alveolar Macrophage for Resolution of Inflammation
by
Igor D. Zlotnikov, Alexander A. Ezhov and Elena V. Kudryashova
Immuno 2026, 6(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno6010009 - 20 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The balance of alveolar macrophage (AM) polarization is severely disrupted in chronic inflammatory diseases like bronchiectasis, where a persistent pro-inflammatory (M1) phenotype perpetuates inflammation. To address this, we developed a high-throughput platform using a series of synthetic glycoligands (L1-L5) on a polyethyleneimine (PEI)
[...] Read more.
The balance of alveolar macrophage (AM) polarization is severely disrupted in chronic inflammatory diseases like bronchiectasis, where a persistent pro-inflammatory (M1) phenotype perpetuates inflammation. To address this, we developed a high-throughput platform using a series of synthetic glycoligands (L1-L5) on a polyethyleneimine (PEI) scaffold. These ligands, which have varying affinities for macrophage lectin-like receptors, were used for phenotypic “fingerprinting” of AM subpopulations from pediatric bronchiectasis patients and a healthy control. Analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) revealed a pathogenic, M1-dominant profile (55% M1) in patients, confirming a state of chronic inflammation, which starkly contrasted with the quiescent, M0-dominant profile in the healthy control. We then leveraged this platform for targeted immunomodulation, using a drug-ligand conjugate to steer the dysregulated macrophage population toward a healthy state. The most potent conjugate, Dox-L5, dramatically suppressed the pathogenic M1 population (from 55% to 16%). This M1 suppression was accompanied by a significant shift toward the M2a (tissue-repair) phenotype and the emergence of a quiescent M0-like population, effectively remodeling the AM profile. This work validates a glycan-based platform for both diagnosing and correcting pathological macrophage imbalances. Our targeted approach offers a precise strategy to resolve chronic inflammation in bronchiectasis by suppressing M1 macrophages and promoting a pro-resolving M0/M2 phenotype, thereby restoring lung homeostasis.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Molecular Mimicry Between Trypanosoma cruzi and Human TUBB as a Potential Autoimmune Mechanism in Chagas
by
Ana Valentina Centeno-Iglesias, Celeste Abigail Quille-Juarez, Paul Galvez-Murillo, Anggie Stefany Revilla-Zeballos, Gustavo Alberto Obando-Pereda and Luis Alberto Ponce-Soto
Immuno 2026, 6(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno6010008 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
Chagas disease, caused by Trypanosoma cruzi, affects a significant proportion of patients who develop digestive and cardiac complications, including megaviscera. This pathogenesis has been associated with autoimmune mechanisms mediated by molecular mimicry. In this study, an in silico evaluation of the potential
[...] Read more.
Chagas disease, caused by Trypanosoma cruzi, affects a significant proportion of patients who develop digestive and cardiac complications, including megaviscera. This pathogenesis has been associated with autoimmune mechanisms mediated by molecular mimicry. In this study, an in silico evaluation of the potential structural basis of cross-reactivity of β-tubulin 1.9 of T. cruzi and the human β-4A tubulin isoform 3 was conducted. Using bioinformatics tools, homologous regions were identified and potentially immunogenic epitopes were predicted, considering their structural modeling and molecular docking. The proteins shared 87% sequence identity and 95% similarity, with an almost identical structural overlap, RMSD 0.291 Å. Three epitopes, VPFPRLHFF, NDLVSEYQQYQDATI, and GQSGAGNNWAKGHYTEGAELIDS, exhibited high predicted antigenicity, with the 9-mer and 16-mer peptides displaying structurally compatible docking poses within the binding grooves of MHC class I and class II molecules, respectively, while B-cell epitope potential was inferred from sequence-based property predictions. Normal mode analysis, used as an exploratory approach, suggested comparable flexibility profiles for the parasitic- and human-derived peptide–MHC complexes. These findings provide an exploratory structural framework supporting a potential role of β-tubulin epitopes in molecular mimicry processes implicated in the development of chagasic megaviscera.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Autoimmunity and Immunoregulation)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Conditional Stat2 Knockout Mice as a Platform for Modeling Human Diseases
by
Tess Cremers, Nataliya Miz, Alexandra Afanassiev, Ling Yang, Kevin P. Kotredes and Ana M. Gamero
Immuno 2026, 6(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno6010007 - 12 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 2 (STAT2) is a key component of the type I interferon (IFN-I/III) signaling pathway, which is pivotal in host defense against cancer and viral infections and in shaping immune responses. Building on our previously reported conditional Stat2
[...] Read more.
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 2 (STAT2) is a key component of the type I interferon (IFN-I/III) signaling pathway, which is pivotal in host defense against cancer and viral infections and in shaping immune responses. Building on our previously reported conditional Stat2 knockout (KO) mouse, we expand its utility by validating additional tissue-specific models and exploring novel functional contexts. Mice carrying loxP-flanked Stat2 alleles were crossed with CMV-Cre, Cdx2-Cre or CD11c-Cre mice. Deletion of STAT2 was validated by PCR genotyping and western blotting in the relevant tissues. To confirm defective IFN-I signaling with STAT2 deletion, IFN-β stimulation of splenocytes from CMV-Cre Stat2 KO mice showed a lack of induction of canonical IFN-I target genes, confirming functional disruption of the pathway. In vivo, global Stat2 deletion significantly impaired the antitumor efficacy of IFN-β treatment. Similarly, lung fibroblasts isolated from globally deleted Stat2 KO mice showed defective antiviral responses to IFN-β. Tissue-specific Cre models demonstrated selective ablation of STAT2 in target compartments without affecting its expression in non-target tissues. Together, these studies expand our published conditional Stat2 KO findings and highlight the value of this model as a versatile platform for dissecting STAT2-dependent signaling pathways in a tissue- and disease-specific manner.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dysregulated Efferocytosis in CAD: TNF-α and TGF-β Silencing Reveals Functional Divergence in M1 and M2 Macrophages
by
Fatin Najiah Mohd Idrus, Hayat Asaad Hameed Al-Ali, Zahidah Nasuha Mohd Yasin, Maryam Azlan, Rapeah Suppian, See Too Wei Cun, Hoe Chee Hock, Nurul Shuhadah Ahmad, Zurkurnai Yusof, Wan Yus Haniff Wan Isa, Akbar Ali Mohamed Ali and Yvonne-Tee Get Bee
Immuno 2026, 6(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno6010006 - 26 Dec 2025
Abstract
Efferocytosis, the process by which macrophages clear apoptotic cells, plays a vital role in maintaining immune homeostasis. This study explores the influence of inflammatory cytokines—tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β)—on efferocytosis dysregulation in coronary artery disease (CAD). Peripheral blood samples
[...] Read more.
Efferocytosis, the process by which macrophages clear apoptotic cells, plays a vital role in maintaining immune homeostasis. This study explores the influence of inflammatory cytokines—tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β)—on efferocytosis dysregulation in coronary artery disease (CAD). Peripheral blood samples were collected from 27 non-obstructive and 29 obstructive CAD patients to isolate monocytes, which were then differentiated into M1 and M2 macrophages using specific cytokine stimuli. These macrophages were transfected with TNF-α and TGF-β siRNA to assess cytokine impact on efferocytosis. Expression levels of the efferocytosis receptor MERTK and its regulatory protease ADAM17 were quantified via qPCR. Statistical analysis revealed significantly higher MERTK expression in M2 macrophages compared to M1 (p = 0.002). Notably, TNF-α silencing enhanced efferocytosis in M2 macrophages, with increased clearance of early apoptotic bodies in non-obstructive CAD and late apoptotic bodies in obstructive CAD (both p < 0.001). These findings suggest that macrophage phenotype, apoptotic stage, and cytokine environment influence efferocytosis efficiency and may involve pathways beyond MERTK-ADAM17. They offer preliminary mechanistic insights into cytokine-mediated modulation of efferocytosis in CAD. Further in vivo studies are needed to confirm these observations and evaluate their relevance for future therapeutic strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Innate Immunity and Inflammation)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Nanomodified Nexavar Enhances Efficacy in Caco-2 Cells via Targeting Aspartate β-Hydroxylase-Driven Mitochondrial Cell Death
by
Ahmed M. Tabl, Mohamed E. Ebeid, Yasser B. M. Ali, Khaled A. Elawdan, Mai Alalem, Ahood A. Al-Eidan, Nedaa Alalem, Ahmed S. Mansour, Ahmed M. Awad, Eman A. El-Madawy, Shymaa A. Elbuckley, Rofaida Refaai, Amany M. Elshamy and Hany Khalil
Immuno 2026, 6(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno6010005 - 25 Dec 2025
Abstract
Colorectal tumors consist of diverse cell populations, including cancer cells and immune cells. Sorafenib (Nexavar), an oral multikinase inhibitor, targets tumor growth and angiogenesis while inducing apoptosis. However, its clinical use is hindered by poor solubility, rapid metabolism, and low bioavailability. This study
[...] Read more.
Colorectal tumors consist of diverse cell populations, including cancer cells and immune cells. Sorafenib (Nexavar), an oral multikinase inhibitor, targets tumor growth and angiogenesis while inducing apoptosis. However, its clinical use is hindered by poor solubility, rapid metabolism, and low bioavailability. This study explores a nanotechnology-based approach to enhance Sorafenib’s efficacy against colon cancer. Nexavar was encapsulated into nanoparticles using an oil phase and Span 80 as a stabilizer to produce sub-100 nm droplets. The resulting Nano-Nexavar was evaluated for cytotoxicity on Caco-2 colorectal cancer cells and compared with free Nexavar on both Caco-2 and normal NCM-460 colon cells. Nano-Nexavar significantly reduced cancer cell viability at lower concentrations, with no observed toxicity to normal cells. Both formulations induced lactate dehydrogenase release and cell reduction at 2.5 µM, but Nano-Nexavar triggered nearly 60% apoptosis in Caco-2 cells. It inhibited Raf-1, NFκB, and ERK signaling, and reduced epidermal growth factor (EGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels over time. Notably, unlike Nexavar, the Nano-Nexavar suppressed aspartate β-hydroxylase (ASPH) and enhanced mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis by increasing Bax expression, mitochondrial accumulation, and mtDNA levels indicated by immunofluorescence, immunoblotting, flow cytometry, and qRT-PCR. These data demonstrate that Nano-Nexavar potentiates Sorafenib’s anticancer activity by targeting ASPH, thereby amplifying mitochondrial signaling–induced cell death.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Insights of Anti-cancer Immunity and Cancer Immune Evasion)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Genetic Polymorphisms of IL6-174G/C, TNF-308G/A, and TNF-238G/A and Risk of Pleural Tuberculosis in Venezuelan Patients
by
Zaida Araujo, Jacobus Henri de Waard, Mercedes Fernández-Mestre, Douglas Silva, Carmen Judith Serrano, Luis Adrián De Jesús-González, Juan Ernesto Lopez-Ramos and Bruno Rivas-Santiago
Immuno 2026, 6(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno6010004 - 22 Dec 2025
Abstract
Tuberculosis (TB) has various clinical presentations; pulmonary TB (PTB) affects only the lungs, whereas extrapulmonary TB involves other organs, including pleural TB (PLTB). Immunological studies of patients with extrapulmonary TB primarily focus on the cellular Th1 response, which produces key cytokines, including IFN-γ,
[...] Read more.
Tuberculosis (TB) has various clinical presentations; pulmonary TB (PTB) affects only the lungs, whereas extrapulmonary TB involves other organs, including pleural TB (PLTB). Immunological studies of patients with extrapulmonary TB primarily focus on the cellular Th1 response, which produces key cytokines, including IFN-γ, TNF, IL-12, and IL-6. TNF and IL-6 play functional roles in host resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infection. Findings suggest that TNF facilitates macrophage containment of Mtb, whereas IL-6 increases macrophage apoptosis induced by Mtb. Studies of the human genome have identified single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genes encoding cytokines associated with TB susceptibility. This study aimed to assess the potential of the IL6-174G/C (rs1800795), TNF-308G/A (rs1800629), and TNF-238G/A (rs361525) SNPs as genetic biomarkers of susceptibility to PLTB in the Venezuelan mestizo population. A total of 269 individuals were included: 69 patients with PLTB and 200 healthy individuals. The IL6-174G/C, TNF-308G/A, and TNF-238G/A polymorphisms were determined by sequence-specific primer polymerase chain reaction (SSP-PCR). Results showed significantly higher frequencies of the G/C, G/A, and G/A genotypes in patients with PLTB (94.0%, 94.2%, and 83.3%) than in controls (40.0%, 19.0%, and 13.4%) for the IL6-174G/C, TNF-308G/A, and TNF-238G/A polymorphisms, respectively. Logistic regression analysis showed significant associations between the G/C, G/A, and G/A genotypes and susceptibility to PLTB. The IL6-174G/C, TNF-308G/A, and TNF-238G/A gene polymorphisms may serve as genetic biomarkers of susceptibility to PLTB in the Venezuelan mestizo population.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Role of Cytokines and Autoantibodies Against Cytokines in Health and Disease)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
High Stromal Senescence During the Window of Implantation Is Linked to Plasma Cell Presence and Cluster Formation in the Endometrium
by
Dimitar Parvanov, Dimitar Metodiev, Rumiana Ganeva, Margarita Ruseva, Maria Handzhiyska, Jinahn Safir, Lachezar Jelezarsky, Nina Vidolova, Georgi Stamenov and Savina Hadjidekova
Immuno 2026, 6(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno6010003 - 22 Dec 2025
Abstract
Successful implantation requires a finely regulated endometrial microenvironment during the window of implantation. Chronic endometritis, defined by plasma cell infiltration, and stromal senescence, indicated by p16 expression, represent separate but potentially interacting mechanisms associated with impaired endometrial receptivity. The relationship between these processes
[...] Read more.
Successful implantation requires a finely regulated endometrial microenvironment during the window of implantation. Chronic endometritis, defined by plasma cell infiltration, and stromal senescence, indicated by p16 expression, represent separate but potentially interacting mechanisms associated with impaired endometrial receptivity. The relationship between these processes remains poorly understood. We aim to examine whether stromal senescence is associated with plasma cell density and clustering in the human endometrium during the implantation window. Forty mid-luteal (LH+7) endometrial biopsies were retrospectively analyzed and stratified into low-senescence (<0.5% stromal p16+ cells, n = 20) and high-senescence (>3.5%, n = 20) groups. Plasma cells were identified by immunohistochemistry for MUM1 and CD138 and quantified using HALO® software (version 3.4). Group comparisons were performed using Student’s t-test and chi-squared analysis. CD138+ plasma cells were significantly more abundant in high-senescence endometria than in low-senescence controls (0.065 ± 0.10 vs. 0.014 ± 0.027 cells/mm2, p = 0.02). Only MUM1+ cells formed stromal clusters, which were more frequent in high-senescence samples (67% vs. 31%, p = 0.05). High endometrial stromal senescence during the implantation window is associated with increased plasma cell infiltration and clustering. This interplay may contribute to chronic endometritis and impaired receptivity, providing new insights into potential diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for reproductive failure.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Reproductive Immunology)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Calm Under Challenge: Immune-Balancing and Stress-Quenching Effects of Hericium erinaceus Mycelium in Human Immune Cells
by
Elizabeth Doar, Jessica Kishiyama, Zolton J. Bair and Chase Beathard
Immuno 2026, 6(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno6010002 - 22 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Hericium erinaceus is a medicinal mushroom valued in the wellness industry for its neuroprotective, immunomodulatory, and antioxidant activities. While many extracts and bioactive compounds from both mycelium and fruit bodies have been characterized, the mechanisms driving their effects are not fully understood. Here,
[...] Read more.
Hericium erinaceus is a medicinal mushroom valued in the wellness industry for its neuroprotective, immunomodulatory, and antioxidant activities. While many extracts and bioactive compounds from both mycelium and fruit bodies have been characterized, the mechanisms driving their effects are not fully understood. Here, the transcriptomic and protein-level effects of H. erinaceus mycelium (HDLM) in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were investigated, along with antioxidant and iron chelating activity. A commercially available H. erinaceus fruit body extract (FBE) claiming high β-glucan content was included in a subset of assays to compare immune-related outcomes between mycelial and fruit body constituents. HDLM activated a wide array of immune- and oxidative stress-related transcripts and pathways, exhibited significant antioxidant activity, and consistently reduced IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-8 during LPS challenge while maintaining low basal cytokine expression, indicating targeted immunomodulatory activity. FBE almost doubled production of IL-1β when challenged by LPS, whereas HDLM significantly decreased production of this stress mediator. HDLM also demonstrated augmented iron chelating ability when compared to FBE. Depending on tissue source and preparation methods, different H. erinaceus materials may either potentiate or quench stress responses, highlighting the need for further bioactivity and safety comparisons across H. erinaceus supplements, particularly with respect to cytokine regulation under conditions of immune challenge.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Immune Cell Populations in Idiopathic Recurrent Pregnancy Loss and Unexplained Infertility in Venezuelan Admixed Women
by
Jenny Valentina Garmendia, Isaac Blanca and Juan Bautista De Sanctis
Immuno 2026, 6(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno6010001 - 19 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Unexplained infertility and idiopathic recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) have a prevalence of 1–5% of women of reproductive age in different populations. There are a few reports comparing the circulating immune cell populations and subpopulations in these medical entities in admixed populations. The study
[...] Read more.
Unexplained infertility and idiopathic recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) have a prevalence of 1–5% of women of reproductive age in different populations. There are a few reports comparing the circulating immune cell populations and subpopulations in these medical entities in admixed populations. The study aimed to assess the different leukocyte, mononuclear cell populations, and T lymphocyte subpopulations and HLADR expression, as a marker of activation, in an admixed group of Venezuelan women: 80 controls, 73 women with RPL (53 primary, 20 secondary), and 26 infertile (20 primary, six secondary). Endometriosis was clinically ruled out in all patients and controls. Total leukocytes were 10–12% higher (p < 0.0001) in the infertile group, while neutrophils were 11% in the infertility group (p < 0.0001). In contrast, lymphocytes, CD3CD4 cells, NK cells, and HLADR+ cells were elevated (10–15, 18–22, 50–60, and 700–800% increase, respectively) in all patient groups. Changes in B cell numbers and monocyte counts were also observed. HLADR expression was significantly increased (p < 0.0001) in T cells, CD56+ cells, and monocytes of all patients. In infertile patients, a correlation was recorded between HLADR and T memory cells. Marked differences in peripheral blood leukocytes, NK cells, monocytes, T-cell populations, and HLADR suggest a proinflammatory effect. HLADR can be used as a simple biomarker to monitor pharmacological treatment in these patients.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
B and T Cell Interplay, Germinal Center Dynamics and Role of Regulatory T Cells (Tregs) in B Cell Modulation and Immune Tolerance: A Narrative Review
by
Mohammad Shahid Iqbal, Ahmad F. Arbaeen, M. A. Bendary, Hasan H. Qadi, Aisha Tabassum, Othman M. Fallatah, Sami Melebari, Nadeem Ikram, Mohammed Parvez and Kamal H. Alzabeedi
Immuno 2025, 5(4), 62; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5040062 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
T cells and B cells are central components of the adaptive immune system, orchestrating immune responses through a complex network of interactions. This review explores the dynamic interplay between T and B cells, focusing on their development, activation, and functional coordination in immune
[...] Read more.
T cells and B cells are central components of the adaptive immune system, orchestrating immune responses through a complex network of interactions. This review explores the dynamic interplay between T and B cells, focusing on their development, activation, and functional coordination in immune defense. T cells provide essential help to B cells through cytokine signaling and direct cell–cell interactions, facilitating antibody production and affinity maturation in germinal centers. Conversely, B cells contribute to antigen presentation and cytokine modulation, influencing T cell differentiation and function. The regulation of these interactions is critical for maintaining immune homeostasis, preventing autoimmunity, and enhancing vaccine efficacy. Dysregulation of T-B cell crosstalk is implicated in various immune disorders, including autoimmune diseases and immunodeficiencies. Recent advances in immunotherapy have targeted these pathways to modulate immune responses in conditions such as cancer, infections, and inflammatory diseases. This review synthesizes current knowledge on T and B cell physiology, highlighting emerging research on their cooperative mechanisms.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Oro-Facial Angioedema: An Overview
by
Domenico De Falco, Diego Misceo, Giuseppe Carretta, Gioele Gioco, Carlo Lajolo and Massimo Petruzzi
Immuno 2025, 5(4), 61; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5040061 - 16 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Angioedema (AE) is a heterogeneous condition characterized by acute, localized, non-pitting edema of the skin, mucosa, and submucosal tissues, with potentially life-threatening airway involvement. This comprehensive review aims to provide an updated overview of the different AE subtypes, their pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnostic
[...] Read more.
Angioedema (AE) is a heterogeneous condition characterized by acute, localized, non-pitting edema of the skin, mucosa, and submucosal tissues, with potentially life-threatening airway involvement. This comprehensive review aims to provide an updated overview of the different AE subtypes, their pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnostic criteria, therapeutic strategies, and dental implications. A literature search of PubMed, MEDLINE, and Google Scholar was performed for articles published between 1950 and 2025, focusing on both bradykinin- and histamine-mediated forms. The findings highlight the importance of distinguishing histaminergic AE, which typically responds to antihistamines, corticosteroids, and epinephrine, from bradykinin-mediated AE, which requires targeted therapies such as C1 esterase inhibitor (C1-INH), icatibant, or kallikrein inhibitors. Subtypes including hereditary, acquired, and drug-induced AE are reviewed, with emphasis on diagnostic markers (C4, C1-INH, C1q) and recent genetic insights in HAE-nC1INH. In dental and surgical settings, invasive procedures may act as triggers, making prophylaxis with plasma-derived C1-INH and stress management strategies essential. In conclusion, accurate subtype recognition is crucial to guide therapy and perioperative care, and further research is needed to refine diagnostic algorithms and preventive strategies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Relationship Between Autoimmune Disease and Intermittent Fasting: A Narrative Review
by
Krista Yasuda and Rebecca Jean Ryznar
Immuno 2025, 5(4), 60; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5040060 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Autoimmune disease (AD) is a breakdown of self-tolerance by the immune system and has a variety of clinical manifestations and complications across all organ systems. One of the targets for treatment of AD aims at reducing inflammation and upregulating factors that eliminate autoreactive
[...] Read more.
Autoimmune disease (AD) is a breakdown of self-tolerance by the immune system and has a variety of clinical manifestations and complications across all organ systems. One of the targets for treatment of AD aims at reducing inflammation and upregulating factors that eliminate autoreactive cells. Intermittent fasting (IF) has recently gained popularity as a dietary intervention for weight management, but has also been found to interact and positively interfere with pathways involved in the pathophysiology of AD. Methods include searching in the PubMed and Google Scholar databases for reviews and clinical trials studying any relationships between AD and IF. The search results have identified a variety of anti-inflammatory effects IF has on the immune system that can potentially reduce AD severity and several trials specifically studying IF’s effects on type I diabetes (T1D), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and multiple sclerosis (MS). Based on the findings, IF has potential anti-inflammatory effects that could assist with decreasing AD severity. Future directions include studies to further determine safety and efficacy of IF with AD, broader investigations to include IF’s impact on a wide variety of ADs, an ideal time frame of how long patients should remain on IF, and any potential interactions IF may have on current drug therapies used to treat AD. This review also aims to encourage more human studies of IF and its application to AD given that many of these results are largely from in vitro, cellular and molecular, and animal studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Autoimmunity and Immunoregulation)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigating the Dichotomous Nature of Nitric Oxide During the Enteral Phase of Trichinella spiralis Infection in Mice: An Experimental Study
by
Marwa Omar, Ghada Fathy, Samira Mohammed and Asmaa El-taib
Immuno 2025, 5(4), 59; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5040059 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The exact role of nitric oxide (NO) in the complex interplay between the host and Trichinella spiralis (T. spiralis) parasite remains uncovered. While much has been revealed about the role of the inducible isoenzyme (iNOS) in different parasitic infections, research is
[...] Read more.
The exact role of nitric oxide (NO) in the complex interplay between the host and Trichinella spiralis (T. spiralis) parasite remains uncovered. While much has been revealed about the role of the inducible isoenzyme (iNOS) in different parasitic infections, research is slowly progressing toward understanding the neuronal enzyme (nNOS)-derived impacts on trichinosis. This study aims to clarify the dual nature of (NO) during the enteral phase of experimental trichinosis by examining the participation of both iNOS and nNOS in T. spiralis-infected mice. The experimental design included 48 male Swiss albino mice divided into six groups: (G1) negative control, (G2) infected control, (G3) infected–Albendazole-treated, (G4) infected-infected–L-arginine-treated, (G5) infected–Aminoguanidine-treated, and (G6) infected–7-Nitroindazole-treated. On the seventh day post-infection, the study groups underwent parasitological (adult worm count), histopathological, immunohistochemical, and biochemical assessments. Our results showed that (nNOS) predominance during the enteral phase of trichinosis enhanced parasitic clearance. Conversely, NO produced by iNOS was not essential for worm expulsion but contributed to T. spiralis-mediated enteropathy. Nitric oxide seems to play a puzzling role in T. spiralis infection. While (iNOS) is known for eliminating numerous infections, this is the first example we are aware of where the activity of the neuronal isoform (nNOS) is required in trichinosis.
Full article
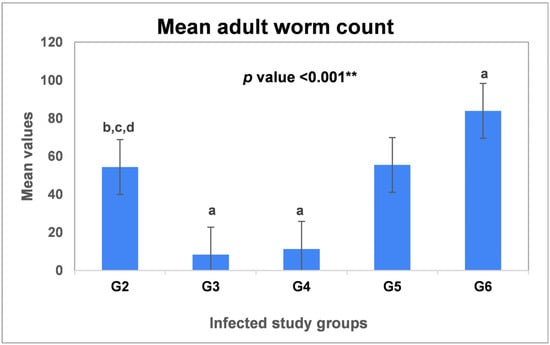
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of Acute Leukemia-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Adults: A Single-Center Experience
by
Wen-Jing Yu, Ying Wu, Wen-Bing Duan, Qi Chen, Xu-Ying Pei, Jin-Song Jia, Jing Wang, Xiao-Lu Zhu, Xiao-Su Zhao, Xiao-Jun Huang and Hao Jiang
Immuno 2025, 5(4), 58; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5040058 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The clinical features and outcomes of adult acute leukemia (AL)-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (AL-HLH) remain insufficiently characterized. We retrospectively analyzed 45 adult patients diagnosed with AL-HLH between December 2019 and June 2023. Among 746 AL patients, 45 developed HLH, with 40 developing acute myeloid
[...] Read more.
The clinical features and outcomes of adult acute leukemia (AL)-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (AL-HLH) remain insufficiently characterized. We retrospectively analyzed 45 adult patients diagnosed with AL-HLH between December 2019 and June 2023. Among 746 AL patients, 45 developed HLH, with 40 developing acute myeloid leukemia (AML), 4 developing acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), and 1 developing mixed-phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL). According to the ELN 2022 criteria, 16 (35.6%) had favorable, 3 (6.7%) had interediate, and 26 (57.7%) had poor risk. At the time of HLH onset, seven (15.6%) patients were in composite complete remission (CCR), and 38 (84.4%) were in non-CCR states; 25 (55.6%) patients were newly diagnosed before induction chemotherapy. The HLH-94/04-based regimens (etoposide and dexamethasone) with or without ruxolitinib achieved an ORR (overall remission rate) of 82.2% and a CR rate of 66.7%. After anti-leukemic therapy, 60% (27/45) of patients achieved CCR for leukemia (including patients in CCR at HLH onset and those achieving CCR after treatment). Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) independently predicted sustained remission. The estimated overall rates at 6 and 12 months after HLH diagnosis were 73.1% and 59.2%, respectively. Multivariate Cox analysis identified failure to achieve CCR for leukemia as the only independent adverse prognostic factor. AL-HLH is an uncommon but severe complication that predominantly occurs in AML patients with poor-risk cytogenetics or active disease. Early recognition, effective HLH control, and achievement of CCR in AL are crucial for improving patient prognosis.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Immune Responses to Filarial Nematodes: A Mechanistic Evaluation of Evasion and Modulation Strategies
by
Tripti Singh, Shivani Sharma, Animesh Tripathi, Sunil Kumar and Anchal Singh
Immuno 2025, 5(4), 57; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5040057 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Filarial parasites are long-lived organisms that cause extreme morbidity due to pathological manifestations, including lymphedema, hydrocele, and elephantiasis. Understanding the hosts’ immune responses to filarial parasites is crucial to developing new and effective anti-filarial treatments. The review thoroughly examines and summarises immunological modulation,
[...] Read more.
Filarial parasites are long-lived organisms that cause extreme morbidity due to pathological manifestations, including lymphedema, hydrocele, and elephantiasis. Understanding the hosts’ immune responses to filarial parasites is crucial to developing new and effective anti-filarial treatments. The review thoroughly examines and summarises immunological modulation, evasion strategies, and filarial–host immune interactions to provide an updated knowledge of the immune evasion manoeuvres used by filarial parasites. An extensive literature search was conducted using databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, ScienceDirect, Web of Science, and Scopus to identify articles published mostly between 2000 and 2025 that focus on the crucial molecular, cellular, and immunomodulatory strategies of filarial parasites. The immune evasion mechanisms include the modulation of effector T cells, induction of apoptosis in immune cells, the release of immunomodulatory proteins, and the induction of regulatory immune cell populations, thereby ensuring the mutual survival of both the parasite and the host. An antigen-specific T helper 2 (Th2) response and an increase in Interleukin-10 (IL-10) producing CD4+ T cells, along with a suppressed T helper 1 (Th1) response, are the key immunological characteristics of filarial pathogenesis. This antigen-specific T-cell hyporesponsiveness seems necessary for keeping the long-term infection going, which often involves large parasite densities. This review summarises filarial parasites’ mechanisms and strategies in regulating host immune responses and will facilitate future studies on the filarial pathogenesis, leading to the development of novel anti-filarial therapeutics.
Full article
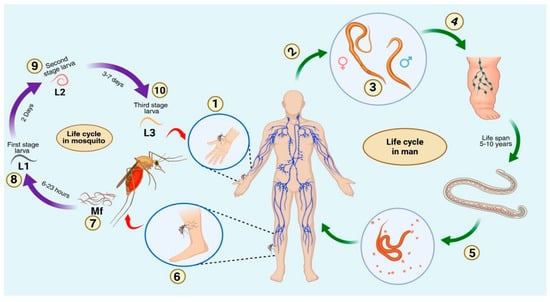
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Immunophenotypic Characterization of LAMP-1 on Cytotoxic T Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients and Its Correlation with Disease Activity
by
Asmaa K. K. AbdelMaogood, Marwa G. Tawfik, Sally Khattab, Heba A. Attea, Hidi A. A. Abdellatif, Nora Hosny and Aya Mohamed Askar
Immuno 2025, 5(4), 56; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5040056 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a multifactorial autoimmune disease in which cytotoxic T cells contribute to tissue damage through dysregulated effector pathways. CD107a (LAMP-1) serves as a functional marker of CD8+ T-cell degranulation and may reflect disease-related alterations in cytotoxicity. Objective:
[...] Read more.
Background: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a multifactorial autoimmune disease in which cytotoxic T cells contribute to tissue damage through dysregulated effector pathways. CD107a (LAMP-1) serves as a functional marker of CD8+ T-cell degranulation and may reflect disease-related alterations in cytotoxicity. Objective: To investigate the expression of CD107a on cytotoxic T cells in SLE patients and evaluate its relationship with disease activity and immunological features. Methods: Demographic, hematological, and immunological profiles of SLE patients and controls were compared. Flow cytometry was used to evaluate CD3+, CD3+CD8+, CD4+, double-negative T cells, and CD107a+CD8+ subsets. Correlations with disease activity and diagnostic performance were assessed. Results: SLE patients showed anemia, thrombocytopenia, and lymphopenia compared with controls. Immunophenotyping revealed significantly elevated CD3+CD8+, CD107a+CD8+ T cells in SLE, and reduced CD4+ counts. While CD107a+CD8+ levels were strongly elevated, they did not correlate with disease activity scores, suggesting persistent upregulation of CD107a expression independent of clinical severity. ROC curve analysis indicated that CD3+ and CD3+CD8+ subsets had diagnostic utility, while double-negative T cells showed additional value. Conclusion: SLE is associated with increased CD107a+CD8+ T cells, reflecting heightened basal expression of this degranulation marker regardless of disease activity level. These findings underscore the role of altered cytotoxic T-cell function in SLE immunopathogenesis and support CD107a as a potential biomarker of immune dysregulation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Autoimmunity and Immunoregulation)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Cells, Immuno, IJMS, JCM, Allergies, Dermato
Skin Barrier Function and Immune Mediators as Key Therapeutic Targets of Main Inflammatory Diseases
Topic Editors: Marco Manfredini, Carlo PincelliDeadline: 31 August 2026
Topic in
IJMS, Cells, Biomolecules, Geriatrics, Immuno
Inflammaging: The Immunology of Aging, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Brianna Cyr, Juan Pablo de Rivero VaccariDeadline: 15 February 2027
Topic in
Biomedicines, Cancers, Immuno, IJMS, Biologics
New Advancements in Innate Immunity and Cancer Immunotherapy
Topic Editors: Jeonghyun Ahn, Zhiwei HuDeadline: 30 June 2027

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Immuno
The Role of Cytokines and Autoantibodies Against Cytokines in Health and Disease
Guest Editor: Juan Bautista De SanctisDeadline: 20 February 2026
Special Issue in
Immuno
Nano-Pharmacology: Nanotechnology Based Therapeutics for Targeting Neuroinflammation
Guest Editor: Supriya MahajanDeadline: 28 February 2026
Special Issue in
Immuno
Young Scholars’ Developments in Immunology
Guest Editors: Toshihiko Torigoe, Bashar SaadDeadline: 28 February 2026
Special Issue in
Immuno
New Insights of Anti-cancer Immunity and Cancer Immune Evasion
Guest Editor: Vadim SumbayevDeadline: 31 May 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Immuno
Recent Advances in Onco-Rheumatology
Collection Editor: Kosaku Murakami







