Somatic Embryogenesis: A Biotechnological Route in the Production of Recombinant Proteins
Abstract
1. Introduction
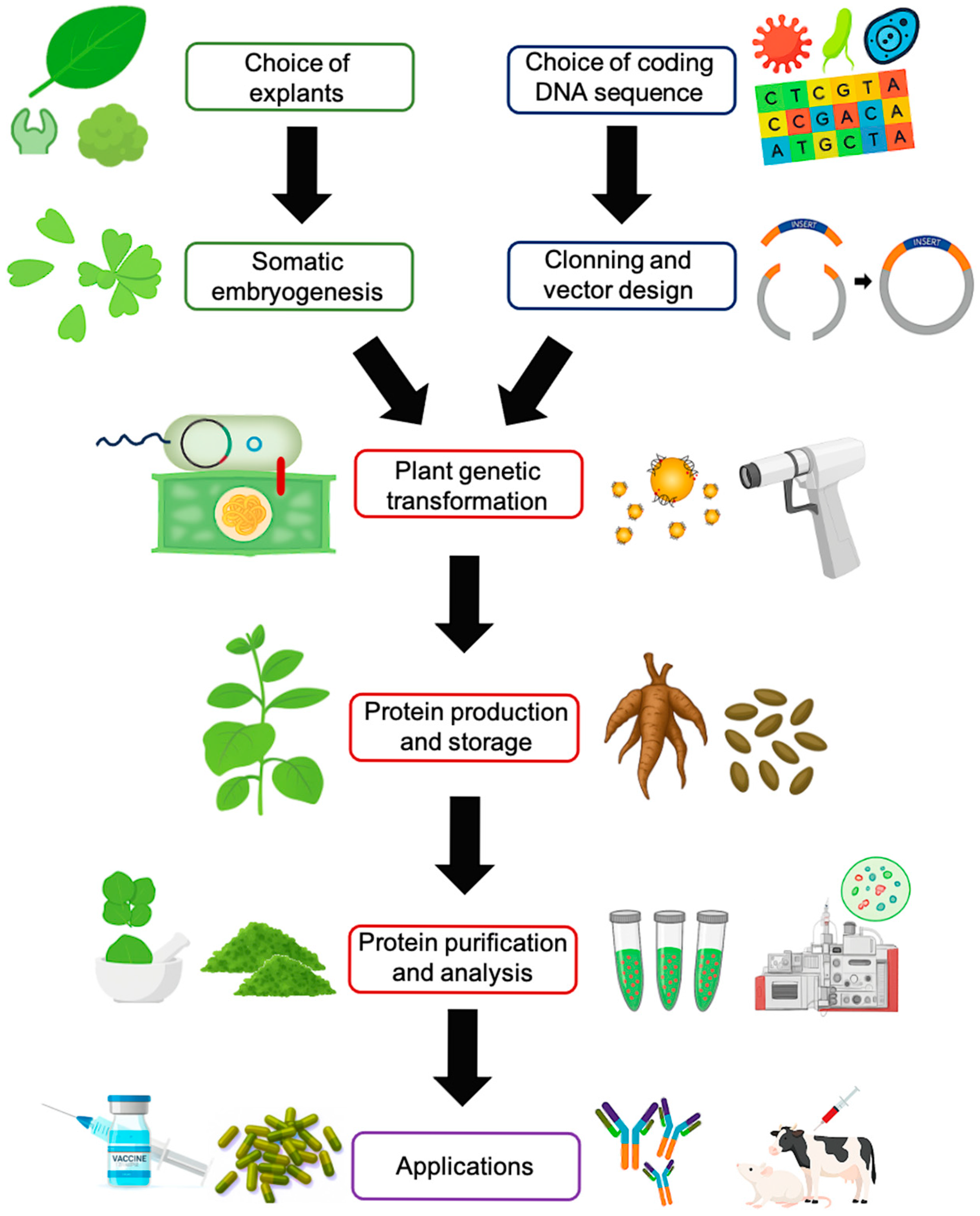
2. Somatic Embryogenesis: A Route for Optimization
2.1. Direct Somatic Embryogenesis
2.2. Indirect Somatic Embryogenesis
3. Plant Genetic Engineering Tools and Heterologous Protein Production
3.1. Designing Transgenic DNA Constructs
3.2. Methods of Plant Genetic Transformation
3.3. Purification and Analysis of Recombinant Proteins
4. Somatic Embryogenesis for Producing Recombinant Proteins with Biomedical Applications
5. Biomedical Potential of Somatic Embryogenesis Systems
5.1. Biomedical Applications of Recombinant Proteins Derived from Somatic Embryogenesis
5.2. Bioactive Metabolites and Integrated Biomanufacturing Potential
5.3. Antibodies and Immunomodulatory Proteins
5.4. Recombinant Proteins for Biopharmaceutical and Veterinary Use
6. Challenges of Somatic Embryogenesis for Recombinant Protein Production
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Radoeva, T.; Vaddepalli, P.; Zhang, Z.; Weijers, D. Evolution, initiation, and diversity in early plant embryogenesis. Dev. Cell 2019, 50, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehér, A. Somatic embryogenesis—Stress-induced remodeling of plant cell fate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2015, 1849, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aflaki, F.; Gutzat, R.; Mozgová, I. Chromatin during plant regeneration: Opening towards root identity? Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2022, 69, 102265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.X.; Shang, G.D.; Wang, J.W. Towards a hierarchical gene regulatory network underlying somatic embryogenesis. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, E.Y.; Biddle, J.; Foale, M.; Adkins, S.W. Cell suspension culture: A potential in vitro culture method for clonal propagation of coconut plantlets via somatic embryogenesis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 147, 112125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Wu, Y.F.; Zhi, L.I.; Song, C.B.; Wang, X.P. Advancements in plant regeneration and genetic transformation of grapevine (Vitis spp.). J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 1407–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, A.; Daniell, H. Chloroplast genetic engineering via organogenesis or somatic embryogenesis. In Arabidopsis Protocols; Springer: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 245–262. [Google Scholar]
- Athmaram, T.N.; Bali, G.; Devaiah, K.M. Integration and expression of Bluetongue VP2 gene in somatic embryos of peanut through particle bombardment method. Vaccine 2006, 24, 2994–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, T.J.; Lee, W.S.; Choi, E.G.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, B.G.; Yang, M.S. Mass production of somatic embryos expressing Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit in Siberian ginseng. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 121, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; van Eerde, A.; Rimstad, E.; Bock, R.; Branza-Nichita, N.; Yakovlev, I.A.; Clarke, J.L. Plant-made vaccines against viral diseases in humans and farm animals. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1170815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.F.; Hall, M.A.; Klerk, G.J.D. Developmental biology. In Plant Propagation by Tissue Culture; George, E.F., Hall, M.A., Klerk, G.J.D., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 283–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, M.; Correia, S.; Cavaleiro, C.; Canhoto, J. Modulation of organogenesis and somatic embryogenesis by ethylene: An overview. Plants 2021, 10, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Mosqueda, M.A. Overview of somatic embryogenesis. In Somatic Embryogenesis: Methods and Protocols; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.; Bae, S.; Seo, P.J. De novo shoot organogenesis during plant regeneration. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo Silva-Cardoso, I.M.; Meira, F.S.; Gomes, A.C.; Scherwinski-Pereira, J.E. Histology, histochemistry and ultrastructure of pre-embryogenic cells determined for direct somatic embryogenesis in the palm tree Syagrus oleracea. Physiol. Plant. 2020, 168, 845–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstman, A.; Bemer, M.; Boutilier, K. A transcriptional view on somatic embryogenesis. Regeneration 2017, 4, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, G.C.; Garda, M. Plant tissue culture media and practices: An overview. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2019, 55, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syeed, R.; Mujib, A.; Malik, M.Q.; Gulzar, B.; Zafar, N.; Mamgain, J.; Ejaz, B. Direct somatic embryogenesis and flow cytometric assessment of ploidy stability in regenerants of Caladium × hortulanum ‘Fancy’. J. Appl. Genet. 2022, 63, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, G.; Singh, M.B.; Bhalla, P.L. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from commercial soybean cultivars. Plants 2020, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Hernández, H.A.; Ledezma-Rodríguez, M.; Avilez-Montalvo, R.N.; Juárez-Gómez, Y.L.; Skeete, A.; Avilez-Montalvo, J.; Loyola-Vargas, V.M. Signaling overview of plant somatic embryogenesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Cheng, F.; Zhong, Y. Induction of direct somatic embryogenesis and shoot organogenesis and histological study in tree peony (Paeonia sect. Moutan). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2020, 141, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mose, W.; Daryono, B.S.; Indrianto, A.; Purwantoro, A.; Semiarti, E. Direct somatic embryogenesis and regeneration of an Indonesian orchid Phalaenopsis amabilis (L.) Blume under a variety of plant growth regulators, light regime, and organic substances. Jordan J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 13, 509–518. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, A.; Qin, M.; Qin, X.; Yang, S.; Su, S.; Zhang, L. Direct and indirect somatic embryogenesis induction in Camellia oleifera Abel. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 644389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, B.; Kosky, R.G.; Reyes, M.; Bermúdez-Carballoso, I.; Gallardo-Colina, J.; Freire-Seijo, M.; Herrera, I. Comparison between two methods of establishment of embryogenic cell suspensions in banana cv. ‘Grande naine’ (Musa AAA). Biotecnol. Veg. 2007, 7, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Fehér, A. Callus, dedifferentiation, totipotency, somatic embryogenesis: What these terms mean in the era of molecular plant biology. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, P.J.; Scowcroft, W.R. Somaclonal variation—A novel source of variability from cell culture for plant improvement. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1981, 60, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duta-Cornescu, G.; Constantin, N.; Pojoga, D.M.; Nicuta, D.; Simon-Gruita, A. Somaclonal variation—Advantage or disadvantage in micropropagation of medicinal plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Mosqueda, M.A.; Iglesias-Andreu, L.G. Indirect organogenesis and assessment of somaclonal variation in plantlets of Vanilla planifolia Jacks. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2015, 123, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Mosqueda, M.A.; Iglesias-Andreu, L.G.; Teixeira da Silva, J.A.; Luna-Rodríguez, M.; Noa-Carrazana, J.C.; Bautista-Aguilar, J.R.; Murguía-González, J. In vitro selection of vanilla plants resistant to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vanillae. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2019, 41, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannachi, S.; Werbrouck, S.; Bahrini, I.; Abdelgadir, A.; Siddiqui, H.A.; Van Labeke, M.C. Obtaining salt stress-tolerant eggplant somaclonal variants from in vitro selection. Plants 2021, 10, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, C.; Furtado de Almeida, A.A.; Costa, M.; Britto, D.; Valle, R.; Royaert, S.; Marelli, J.P. Abnormalities in somatic embryogenesis caused by 2,4-D: An overview. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2019, 137, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, O.; Philipsen, C.; Rahimi, A.; Nurillah, A.R.; Boutilier, K.; Offringa, R. Endogenous auxin maintains embryonic cell identity and promotes somatic embryo development in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2023, 113, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kereša, S.; Kurtović, K.; Ban, S.G.; Vončina, D.; Jerčić, I.H.; Bolarić, S.; Mihovilović, A.B. Production of virus-free garlic plants through somatic embryogenesis. Agronomy 2021, 11, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Xiong, Y.; Guo, B.; Yan, H.; Jian, S.; Ren, H.; Ma, G. Shoot organogenesis and somatic embryogenesis from leaf and root explants of Scaevola sericea. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazri, M.A.; Naciri, R.; Belkoura, I. Maturation and conversion of somatic embryos derived from seeds of olive (Olea europaea L.) cv. Dahbia: Occurrence of secondary embryogenesis and adventitious bud formation. Plants 2020, 9, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Peng, C.; Wang, H.; Shen, H.; Yang, L. Selection of culture conditions for callus induction and proliferation by somatic embryogenesis of Pinus koraiensis. J. For. Res. 2021, 32, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indu, B.K.; Balasubramanya, S.; Anuradha, M.; Shilpa, P. Callus and Cell Suspension Cultures for Secondary Metabolite Production. In In Vitro Production of Plant Secondary Metabolites: Theory and Practice; Anuradha, M., Balasubramanya, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2025; pp. 71–88. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, S.; Chatterjee, V.; Kulkarni, V.M.; Bhat, V. Plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis in cell suspensions of Cenchrus ciliaris L. Plant Methods 2023, 19, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, M.L.; Roy, A.; Bharadvaja, N. Elicitation effect on the production of asiaticoside and asiatic acid in shoot, callus, and cell suspension culture of Centella asiatica. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 9, 067–074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rind, N.A.; Rind, K.H.; Dahot, M.U.; Faiza, H.; Aksoy, Ö.; Shar, A.H.; Jatoi, A.H. Production of limonoids through callus and cell suspension cultures of chinaberry (Melia azedarach L.). Bangladesh J. Bot. 2021, 50, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillberg, S.; Finnern, R. Plant molecular farming for the production of valuable proteins—Critical evaluation of achievements and future challenges. J. Plant Physiol. 2021, 258, 153359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillberg, S.; Raven, N.; Spiegel, H.; Rasche, S.; Buntru, M. Critical analysis of the commercial potential of plants for the production of recombinant proteins. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvathy, S.T. Engineering plants as platforms for production of vaccines. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 707–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, D.R. What are the most powerful immunogen design vaccine strategies? Reverse vaccinology 2.0 shows great promise. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a030262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.; Maselko, M. Transgene biocontainment strategies for molecular farming. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, P.N.; Shrivastava, N.; Padh, H. Production of heterologous proteins in plants: Strategies for optimal expression. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghag, S.B.; Adki, V.S.; Ganapathi, T.R.; Bapat, V.A. Plant platforms for efficient heterologous protein production. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2021, 26, 546–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, K.I.; Aftab, T. Plant Molecular Farming: Applications and New Directions; Springer: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Strugnell, R.; Zepp, F.; Cunningham, A.; Tantawichien, T. Vaccine antigens. Perspect. Vaccinol. 2011, 1, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, V.P. Codon optimization in the production of recombinant biotherapeutics: Potential risks and considerations. BioDrugs 2018, 32, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummari, D.; Palakolanu, S.R.; Kishor, P.K.; Bhatnagar-Mathur, P.; Singam, P.; Vadez, V.; Sharma, K.K. An update and perspectives on the use of promoters in plant genetic engineering. J. Biosci. 2020, 45, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, E.G.; Elorriaga, E.; Liu, Y.; Duduit, J.R.; Yuan, G.; Tsai, C.J.; Tuskan, G.A.; Ranney, T.G.; Yang, X.; Liu, W. Plant promoters and terminators for high-precision bioengineering. BioDesign Res. 2023, 5, 0013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Nasim, N.; Pudhuvai, B.; Koul, B.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Sethi, L.; Dey, N. Plant synthetic promoters: Advancement and prospective. Agriculture 2023, 13, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Guglielmo, Z.M.; Fernandez Da Silva, R. Principales promotores utilizados en la transformación genética de plantas. Rev. Colomb. Biotechnol. 2016, 18, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborda-Mansilla, J.; García-Ruiz, E. Advancements in Golden Gate Cloning: A Comprehensive Review. In Golden Gate Cloning: Methods and Protocols; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 481–500. [Google Scholar]
- Marillonnet, S.; Werner, S. Golden Gate Cloning of Multigene Constructs Using the Modular Cloning System MoClo. In Golden Gate Cloning: Methods and Protocols; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 21–39. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Huard, J.; Bayer, E.M.; Wattelet-Boyer, V. Versatile cloning strategy for efficient multigene editing in Arabidopsis. Bio-Protocol 2024, 14, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliga, P. Plastid transformation in higher plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004, 55, 289–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shreni Agrawal, E.R. A review: Agrobacterium-mediated gene transformation to increase plant productivity. J. Phytopharm. 2022, 11, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi-Dargahlou, S.; Pouresmaeil, M. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated plant transformation: A review. Mol. Biotechnol. 2024, 66, 1563–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanford, J.C. Biolistic plant transformation. Physiol. Plant. 1990, 79, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, B.; Citovsky, V. Biolistic approach for transient gene expression studies in plants. In Biolistic DNA Delivery in Plants: Methods and Protocols; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 125–139. [Google Scholar]
- Husaini, A.M.; Abdin, M.Z.; Parray, G.A.; Sanghera, G.S.; Murtaza, I.; Alam, T.; Srivastava, D.K.; Farooqi, H.; Khan, H.N. Vehicles and ways for efficient nuclear transformation in plants. GM Crops 2010, 1, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca Paixao, J.F.; Déléris, A. Epigenetic control of T-DNA during transgenesis and pathogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2025, 197, kiae583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, C.; Luo, W.; Ji, Q.; Eggenberger, A.L.; Chicowski, A.S.; Xu, W.; Sandhu, R.; Lee, K.; Whitham, S.A.; Qi, Y.; et al. Enhancing biolistic plant transformation and genome editing with a flow guiding barrel. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, P.; Anumalla, S.; Sharma, S. Role of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in transgenic plant development. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2023, 120, 3493–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivashakarappa, K.; Marriboina, S.; Dumenyo, K.; Taheri, A.; Yadegari, Z. Nanoparticle-mediated gene delivery techniques in plant systems. Front. Nanotechnol. 2025, 7, 1516180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, N.; Kumari, K.; Hooda, V. The role of nanoparticles in transforming plant genetic engineering: Advancements, challenges and future prospects. Funct. Integr. Genomics 2025, 25, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musini, A.; Deepu, P.G.; Vaishnavi, R.; Harikrishna, K.; Harihara, J. Nanoparticles in Plant Transformation. In Plant-Based Nanoparticle Synthesis for Sustainable Agriculture; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2025; pp. 46–60. [Google Scholar]
- Viegas, C.; Patrício, A.B.; Prata, J.M.; Nadhman, A.; Chintamaneni, P.K.; Fonte, P. Solid lipid nanoparticles vs. nanostructured lipid carriers: A comparative review. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, L.M.; Kaur, P.; Stanton, D.; Grosser, J.W.; Dutt, M. A cationic lipid mediated CRISPR/Cas9 technique for the production of stable genome edited citrus plants. Plant Methods 2022, 18, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghuthaymi, M.A.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, Z.; Khan, S.H.; Ahmed, F.K.; Faiz, S.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A. Exosome/liposome-like nanoparticles: New carriers for CRISPR genome editing in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Pereira, E.O.; Conley, A.J.; Richman, A.S.; Menassa, R. Green biofactories: Recombinant protein production in plants. Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 2010, 4, 242–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Kerbler, S.M.; Fernie, A.R.; Zhang, Y. Plant cell cultures as heterologous bio-factories for secondary metabolite production. Plant Commun. 2021, 2, 100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedhammar, M.; Karlström, A.E.; Hober, S. Chromatographic Methods for Protein Purification; Royal Institute of Technology: Stockholm, Sweden, 2006; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Walls, D. Protein Chromatography; Loughran, S.T., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 275–303. [Google Scholar]
- Margolin, E.; Chapman, R.; Williamson, A.L.; Rybicki, E.P.; Meyers, A.E. Production of complex viral glycoproteins in plants as vaccine immunogens. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 1531–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirilo, T.M.; de Oliveira, A.L.G.; Pinto, J.C.; da Rocha Rihs, J.B.; Ruas, A.C.L.; Siqueira, W.F.; Cirilo, T.M.; de Oliveira, A.L.G.; Pinto, J.C.; da Rocha Rihs, J.B.; et al. Assessing the efficacy of modified plant vaccine antigens in animal immunization: A systematic review. Food Biosci. 2025, 66, 106178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.C.; Verma, D.; Singh, N.D.; Herzog, R.; Daniell, H. Oral delivery of human biopharmaceuticals, autoantigens and vaccine antigens bioencapsulated in plant cells. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 782–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakas, I.; Tonk, F.A. Plants that can be used as plant-based edible vaccines, current situation and recent developments. Virol. Immunol. J. 2022, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekoah, Y.; Shulman, A.; Kizhner, T.; Ruderfer, I.; Fux, L.; Nataf, Y.; Shaaltiel, Y. Large-scale production of pharmaceutical proteins in plant cell culture—The protalix experience. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.; Asghar, N.; Munir, N.; Aftab, M.; Naz, S. Genetic transformation of carrot (Daucus carota L.) to express hepatitis B surface antigen gene for edible vaccine of HBV. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2020, 30, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, R.; Assem, S.K.; Omar, O.A.; Khalil, A.A.; Basry, M.A.; Waly, F.R.; Samir, N.; El-Kholy, A.A. Expressing the immunodominant projection domain of infectious bursal disease virus fused to the fragment crystallizable of chicken IgY in yellow maize for a prospective edible vaccine. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 118, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Grbic, V.; Ma, S.; Tian, L. Evaluation of somatic embryos of alfalfa for recombinant protein expression. Plant Cell Rep. 2015, 34, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaini, P.A.; Haddad, K.R.; Feinberg, N.G.; Ophir, Y.; Nandi, S.; McDonald, K.A.; Dandekar, A.M. Leveraging walnut somatic embryos as a biomanufacturing platform for recombinant proteins and metabolites. BioTech 2024, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Tang, J.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, H. Enhancing somatic embryogenesis and genetic transformation through overexpression of MdWOX4 in apple. Hortic. Plant J. 2025, 11, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Alejo, N. The uses of somatic embryogenesis for genetic transformation. In Somatic Embryogenesis: Fundamental Aspects and Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 415–434. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; He, Y.; Hu, Z.; Xu, W.; Xia, J.; Guo, C.; Zhang, J. Characterization and expression analysis of AcSERK2, a somatic embryogenesis and stress resistance related gene in pineapple. Gene 2012, 500, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, S.; Heath, R.L.; Clarke, A.E. A chimeric arabinogalactan protein promotes somatic embryogenesis in cotton cell culture. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, H.; Kotake, T.; Nakagawa, N.; Sakurai, N.; Nevins, D.J. Expression and function of cell wall-bound cationic peroxidase in asparagus somatic embryogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Ren, H.; Xie, H.; Ma, Z.; Chen, F. Identification and characterization of bZIP-type transcription factors involved in carrot (Daucus carota L.) somatic embryogenesis. Plant J. 2009, 60, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.B.; Abranches, R.; Fischer, R.; Sack, M.; Holland, T. Putting the spotlight back on plant suspension cultures. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarshana, M.R.; Plesha, M.A.; Uratsu, S.L.; Falk, B.W.; Dandekar, A.M.; Huang, T.K.; McDonald, K.A. A chemically inducible cucumber mosaic virus amplicon system for expression of heterologous proteins in plant tissues. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2006, 4, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, K.A.; Hong, L.M.; Trombly, D.M.; Xie, Q.; Jackman, A.P. Production of human α-1-antitrypsin from transgenic rice cell culture in a membrane bioreactor. Biotechnol. Prog. 2005, 21, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trexler, M.M.; McDonald, K.A.; Jackman, A.P. A cyclical semicontinuous process for production of human α1-antitrypsin using metabolically induced plant cell suspension cultures. Biotechnol. Prog. 2005, 21, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Ikura, K.; Ueda, M.; Sasaki, R. Characterization of a human glycoprotein (erythropoietin) produced in cultured tobacco cells. Plant Mol. Biol. 1995, 27, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.K.; McDonald, K.A. Bioreactor engineering for recombinant protein production in plant cell suspension cultures. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 45, 168–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damaj, M.B.; Jifon, J.L.; Woodard, S.L.; Vargas-Bautista, C.; Barros, G.O.; Molina, J.; Mandadi, K.K. Unprecedented enhancement of recombinant protein production in sugarcane culms using a combinatorial promoter stacking system. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egertsdotter, U.; Ahmad, I.; Clapham, D. Automation and scale up of somatic embryogenesis for commercial plant production, with emphasis on conifers. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mignon, E.; Werbrouck, S. Somatic embryogenesis as key technology for shaping the rubber tree of the future. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shohael, A.M.; Murthy, H.N.; Hahn, E.-J. Pilot-scale culture of somatic embryos of Eleutherococcus senticosus in air-lift bioreactors for the production of eleutherosides. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 36, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salma, U.; Kundu, S.; Gantait, S. Conserving biodiversity of a potent anticancer plant, Catharanthus roseus, through in vitro biotechnological intercessions: Substantial progress and imminent prospects. In Anti-Cancer Plants: Natural Products and Biotechnological Implements; Akhtar, M.S., Swamy, M.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 83–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.-B.; Park, J.-S.; Park, Y.-I.; Song, I.-J.; Lee, H.-J.; Cho, H.S.; Jeon, J.-H.; Kim, H.-S. Development of systems for the production of plant-derived biopharmaceuticals. Plants 2020, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, T.; Merecz-Sadowska, A.; Picot, L.; Brčić Karačonji, I.; Wieczfińska, J.; Śliwiński, T.; Sitarek, P. Genetic manipulation and bioreactor culture of plants as a tool for industry and its applications. Molecules 2022, 27, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malabadi, R.B.; Chalannavar, R.K.; Kolkar, K.P. Plant cell totipotency: Plant tissue culture applications—An updated review. World J. Adv. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2025, 16, 112–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzyszowska, M.; Samiec, M. Generation of monogenetic cattle by different techniques of embryonic cell and somatic cell cloning: Applications to biotechnological, agricultural, nutritional, biomedical and transgenic research. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2021, 21, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-X.; Nong, F.-T.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Yan, C.-X.; Gu, Y.; Song, P.; Sun, X.-M. Strategies for efficient production of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli: Alleviating the host burden and enhancing protein activity. Microb. Cell Fact. 2022, 21, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baschieri, S.; Menassa, R.; Klement, E.; Donini, M. Editorial: Plant-production platforms for veterinary biopharmaceuticals. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 858043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namasivayam, P. Acquisition of embryogenic competence during somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2007, 90, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairu, M.W.; Aremu, A.O.; Van Staden, J. Somaclonal variation in plants: Causes and detection methods. Plant Growth Regul. 2011, 63, 147–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nic-Can, G.I.; Galaz-Ávalos, R.M.; De-la-Peña, C.; Alcazar-Magaña, A.; Wrobel, K.; Loyola-Vargas, V.M. Somatic embryogenesis: Identified factors that lead to embryogenic repression. A case of species of the same genus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opabode, J.T. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of plants: Emerging factors that influence efficiency. Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2006, 1, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Veluthambi, K.; Gupta, A.K.; Sharma, A. The current status of plant transformation technologies. Curr. Sci. 2003, 84, 368–380. [Google Scholar]
- Belaffif, M.B.; Brown, M.C.; Marcial, B.; Baysal, C.; Swaminathan, K. New strategies to advance plant transformation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2025, 91, 103241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viji, M.; Maheswari, P.; Karuppanapandian, T.; Manoharan, K. Effect of polyethylene glycol and mannitol on somatic embryogenesis of pigeonpea, Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 10340–10349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fernando, S.C.; Gamage, C.K.A. Abscisic acid induced somatic embryogenesis in immature embryo explants of coconut (Cocos nucifera L.). Plant Sci. 2000, 151, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto de Souza Vandenberghe, L.; Murawski de Mello, A.F.; Matte Borges Machado, C.; Biagini, G.; Gruening de Mattos, P.B.; Negreiros Piazenski, I.; Manica Candelario, J.P.; Soccol, C.R. Alternative proteins production: Current scenario, bioreactor types, and scale-up strategies. Syst. Microbiol. Biomanuf. 2025, 5, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, A. Plant-Based Bioreactors: A Sustainable Approach for Large-Scale Production of Therapeutic Proteins and Vaccines. Eur. J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2025, 1, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathy, M. Plants as bioreactors-a review. Adv. Tech. Biol. Med. 2016, 4, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, E.; Ramos-Vega, A.; Monreal-Escalante, E.; Almazán, C.; Angulo, C. Overview of Recombinant Tick Vaccines and Perspectives on the Use of Plant-Made Vaccines to Control Ticks of Veterinary Importance. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ramos-Vega, A.; Monreal-Escalante, E.; Dumonteil, E.; Bañuelos-Hernández, B.; Angulo, C. Plant-made vaccines against parasites: Bioinspired perspectives to fight against Chagas disease. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2021, 20, 1373–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monreal-Escalante, E.; Ramos-Vega, A.; Angulo, C.; Bañuelos-Hernández, B. Plant-based vaccines: Antigen Design, Diversity, and strategies for high Level production. Vaccines 2022, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, E.; Angulo, C. Plant-Made Vaccines Targeting Enteric Pathogens-Safe Alternatives for Vaccination in Developing Countries. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2025, 122, 457–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo, E.; Angulo, C. Perspectives on the use of the CRISPR system in plants to improve recombinant therapeutic protein production. J. Biotechnol. 2025, 405, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

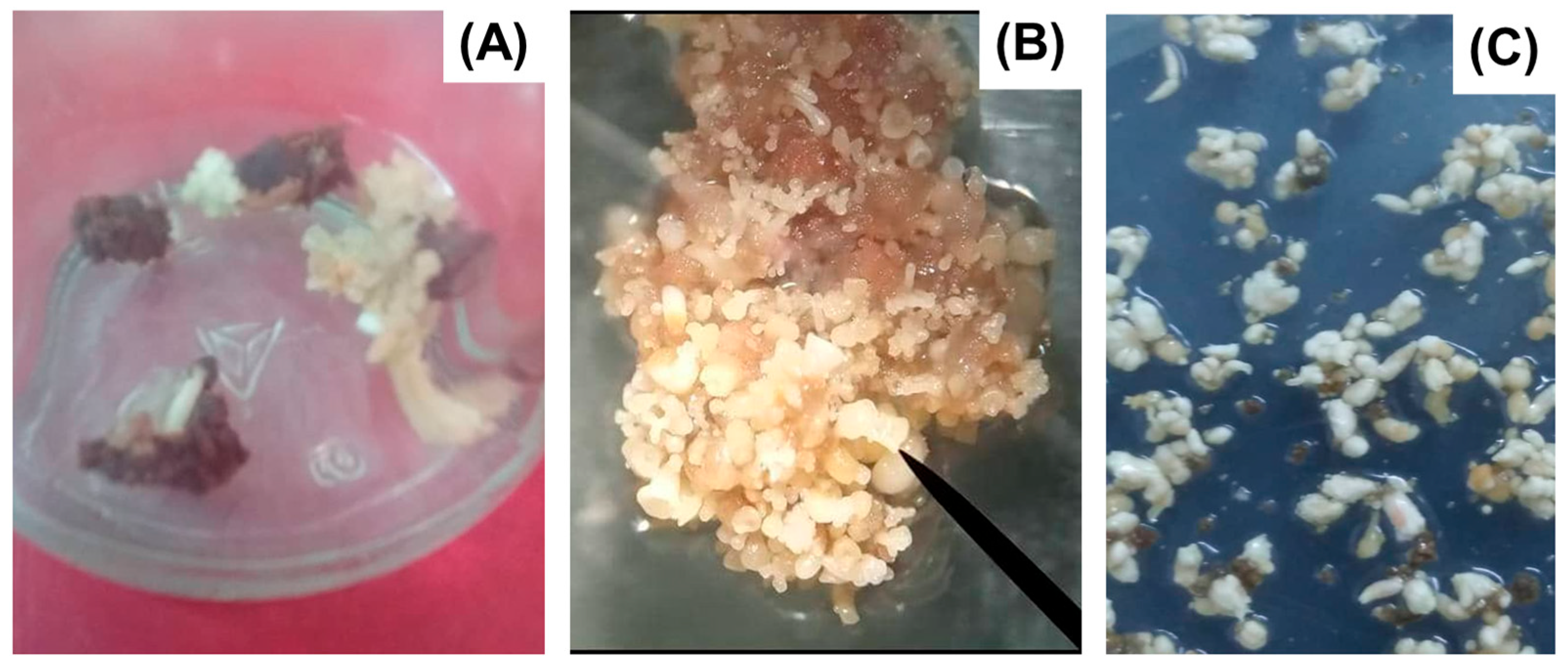
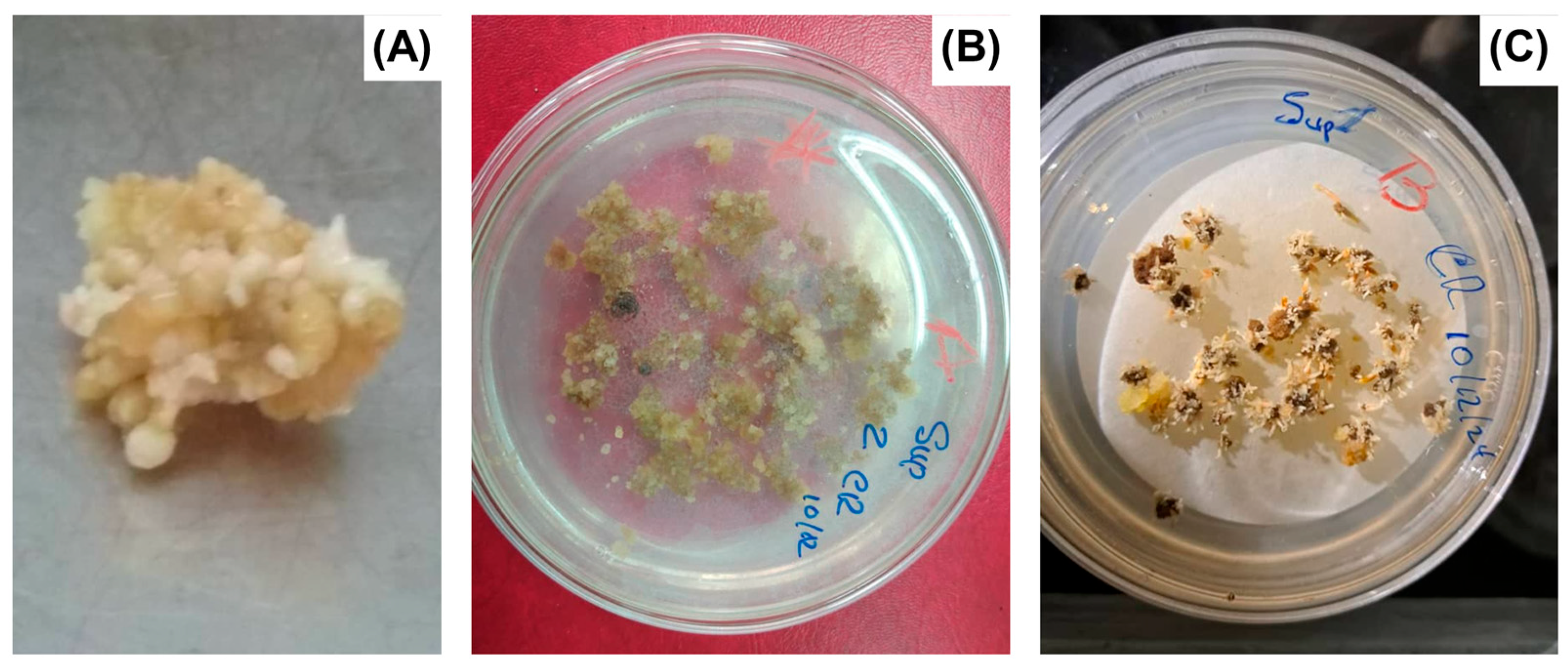
| Plant Species (Crop) | Protein/Product | SE System | Application(s) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medicago sativa L. (alfalfa) | β-glucuronidase (GUS); cholera toxin B subunit (CTB); human interleukin-13 (hIL-13) | Indirect, from embryogenic callus derived from Agrobacterium-transformed plants | Oral vaccine (CTB), therapeutic (hIL-13), reporter (GUS) | [84] |
| Juglans spp. hybrid Paradox J1 (J. hindsii × J. regia) | RBD and Spike ectodomain of SARS-CoV-2; betanin | Repetitive direct (REC) without callus; embryos in DKW; Agrobacterium transformation | Antigens for diagnostics/vaccines; antioxidant food pigment | [85] |
| Malus domestica cv. ‘Gala’ (apple) | Reporter genes GUS and GFP; MdPDS editing (CRISPR/Cas9) | Leaves; SE mediated by auxins | SE platform for transformation/gene editing and germplasm improvement | [86] |
| Daucus carota L. (carrot) | Cholera toxin B subunit (CTB) | Indirect, from callus in hypocotyls; Agrobacterium transformation | Oral vaccine antigen (cholera) | [87] |
| Ananas comosus cv. Shenwan (pineapple,) | AcSERK2 (receptor-like kinase 2) | Induced with 2,4-D in basal leaf callus; unicellular origin | Early marker of embryogenic competence; role in stress response | [88] |
| Gossypium hirsutum cv. ‘Coker 315′ (cotton) | GhPLA1 (chimeric AGP, PL1 domain); AGP fractions | Indirect SE from hypocotyls: callus with 2,4-D + kinetin | SE promoter; improved regeneration and transformation | [89] |
| Asparagus officinalis L. cv. Y6 (asparagus) | Dehydrodiconiferyl alcohol (DDCA; neolignan); enzyme AoPOX1 | Embryogenic callus suspension in MS ± 2,4-D | Role in cell division/differentiation (via neolignans/DCG) and as lignin precursor | [90] |
| Daucus carota L. (carrot) | Transcription factors CAREB1/CAREB2 (bZIP; binding to ABRE of Dc3 promoter) | Somatic embryos in MS in 35S:CAREB1 lines (Agrobacterium transformation) | ABA/sucrose-dependent regulatory framework of SE; role in maturation/dormancy | [91] |
| Eleutherococcus senticosus (Siberian ginseng) | Heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit of E. coli (LTB) | Transgenic somatic embryos obtained by Agrobacterium transformation of embryogenic cells | Antigen/adjuvant for edible vaccine; continuous production platform in bioreactor | [9] |
| Nicotiana tabacum cv. BY-2 (tobacco) | Various biotherapeutics (e.g., Taliglucerase alfa; HAS and hGH) | Suspension cultures derived from callus/embryogenic tissue | Recombinant protein production (vaccines, antibodies, and therapeutic enzymes) in GMP-compatible plant cell systems | [92] |
| Oryza sativa (rice) | Various biotherapeutics (e.g., mAbs and HBsAg) | Suspension cultures derived from callus/embryogenic tissue | Recombinant protein production (vaccines, antibodies, and therapeutic enzymes) in GMP-compatible plant cell systems | [92] |
| Daucus carota (carrot) | Various biotherapeutics (e.g., GM-CSF and hGH) | Suspension cultures derived from callus/embryogenic tissue | Recombinant protein production (vaccines, antibodies, and therapeutic enzymes) in GMP-compatible plant cell systems | [92] |
| Oryza sativa (rice) | Human serum albumin (HSA) | Transgenic suspension culture derived from callus/embryogenic tissue | Hypoalbuminemia/pharmaceutical | [93] |
| Oryza sativa (rice) | Human α1-antitrypsin (AAT) | Transgenic suspension derived from embryogenic callus | Emphysema (replacement therapy) | [94,95] |
| Nicotiana tabacum cv. BY-2 (tobacco) | Human erythropoietin (EPO) | BY-2 suspension line (derived from callus) | Tissue protection/therapeutic | [96] |
| Nicotiana tabacum cv. BY-2 (tobacco) | Human growth hormone (hGH); Human interferon α2b (IFN-α2b) | BY-2 suspension line (derived from callus) | Hormone therapy; Antiviral/immunomodulator | [97] |
| Saccharum spp. hybrids (sugarcane) | Bovine lysozyme (BvLz) | Embryogenic callus derived from rolled leaf disks and callus | Production of antimicrobial enzymes for food/cosmetic/agricultural use | [98] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramírez-Mosqueda, M.A.; Cadena-Zamudio, J.D.; Cruz-Cruz, C.A.; Aguirre-Noyola, J.L.; Barbón, R.; Gómez-Kosky, R.; Angulo, C. Somatic Embryogenesis: A Biotechnological Route in the Production of Recombinant Proteins. BioTech 2025, 14, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14040093
Ramírez-Mosqueda MA, Cadena-Zamudio JD, Cruz-Cruz CA, Aguirre-Noyola JL, Barbón R, Gómez-Kosky R, Angulo C. Somatic Embryogenesis: A Biotechnological Route in the Production of Recombinant Proteins. BioTech. 2025; 14(4):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14040093
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamírez-Mosqueda, Marco A., Jorge David Cadena-Zamudio, Carlos A. Cruz-Cruz, José Luis Aguirre-Noyola, Raúl Barbón, Rafael Gómez-Kosky, and Carlos Angulo. 2025. "Somatic Embryogenesis: A Biotechnological Route in the Production of Recombinant Proteins" BioTech 14, no. 4: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14040093
APA StyleRamírez-Mosqueda, M. A., Cadena-Zamudio, J. D., Cruz-Cruz, C. A., Aguirre-Noyola, J. L., Barbón, R., Gómez-Kosky, R., & Angulo, C. (2025). Somatic Embryogenesis: A Biotechnological Route in the Production of Recombinant Proteins. BioTech, 14(4), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14040093







