- Article
Evaluation of Pharmacist-Developed Educational Leaflets for Women’s Health: A Pre–Post Study of Knowledge and Perceived Usefulness
- Weronika Guzenda,
- Zuzanna Berdzińska and
- Magdalena Waszyk-Nowaczyk
- + 3 authors
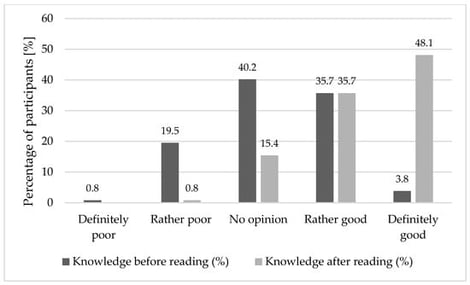
Background: Written educational materials are widely used in community pharmacies to support patient education, and available evidence suggests their effectiveness in improving short-term knowledge. However, there remains a need for well-documented, practice-oriented evaluations of pharmacist-developed materials in real-world community pharmacy settings. The aim of this study was to evaluate the immediate impact of a pharmacist-developed educational leaflet on women’s health knowledge and its perceived usefulness, clarity, and acceptability. Methods: This study evaluated pharmacist-developed educational leaflets addressing women’s health topics using a pre–post study design. The study was conducted in Poland and involved 266 adult women. All participants completed a five-question knowledge test before and immediately after reading the educational leaflet, followed by a self-assessment of perceived usefulness, clarity, and visual appeal. Descriptive statistics were performed to summarize the results. Results: A statistically significant increase in knowledge was observed after exposure to the educational material, with mean scores rising from 2.8 ± 1.2 to 4.6 ± 0.7 (out of 5, p < 0.001). The greatest improvements were noted in topics related to sexually transmitted infection self-testing and pregnancy testing. Most participants rated the leaflet as useful, comprehensible, attractive, and engaging, with higher ratings reported among younger and better-educated respondents. Conclusions: Pharmacist-developed educational leaflets can support short-term knowledge acquisition and are perceived positively by women across age groups. These findings highlight the potential role of community pharmacies in delivering accessible written health education, while underscoring the need for future studies to assess long-term knowledge retention, behavioral outcomes, and topic-specific, targeted materials.
5 February 2026