Gene Regulation in Comorbid Migraine and Myogenic Temporomandibular Disorder Pain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Comorbid Migraine and TMD Mouse Model
2.3. RNA-Seq and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. DEGs Associated with Ferroptosis
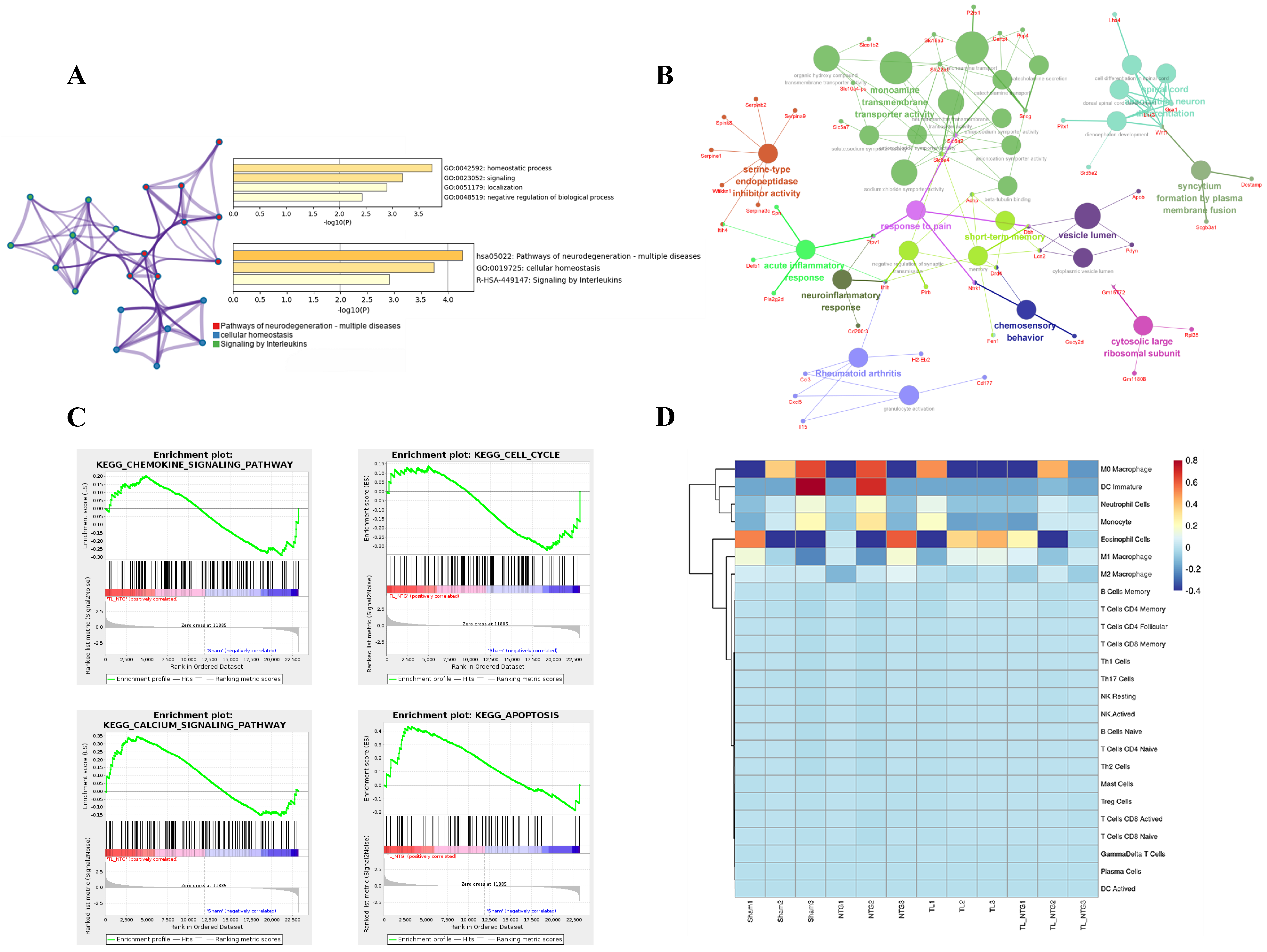
2.5. Enrichment and Immune Infiltration Analysis
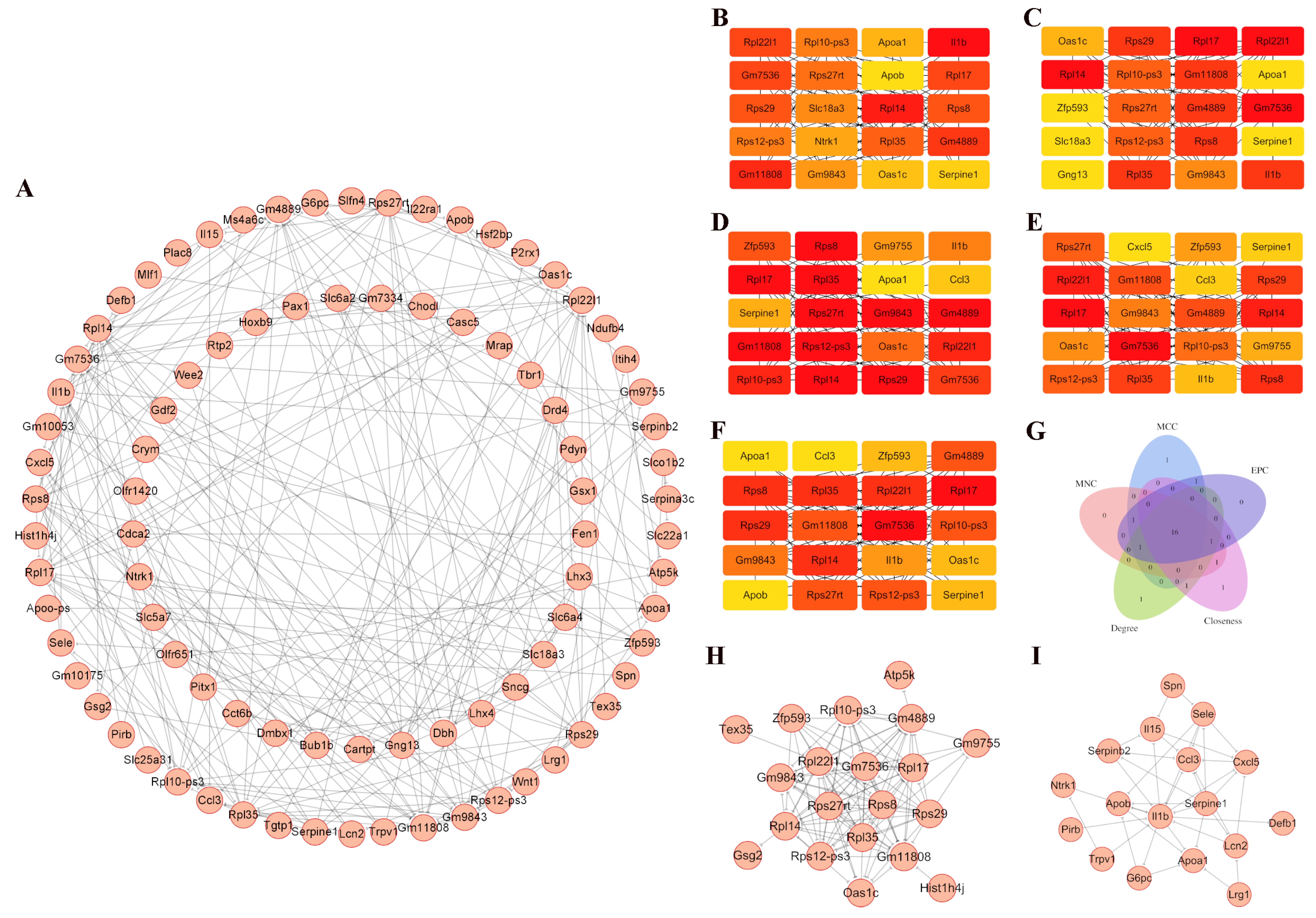
2.6. Generation of Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network
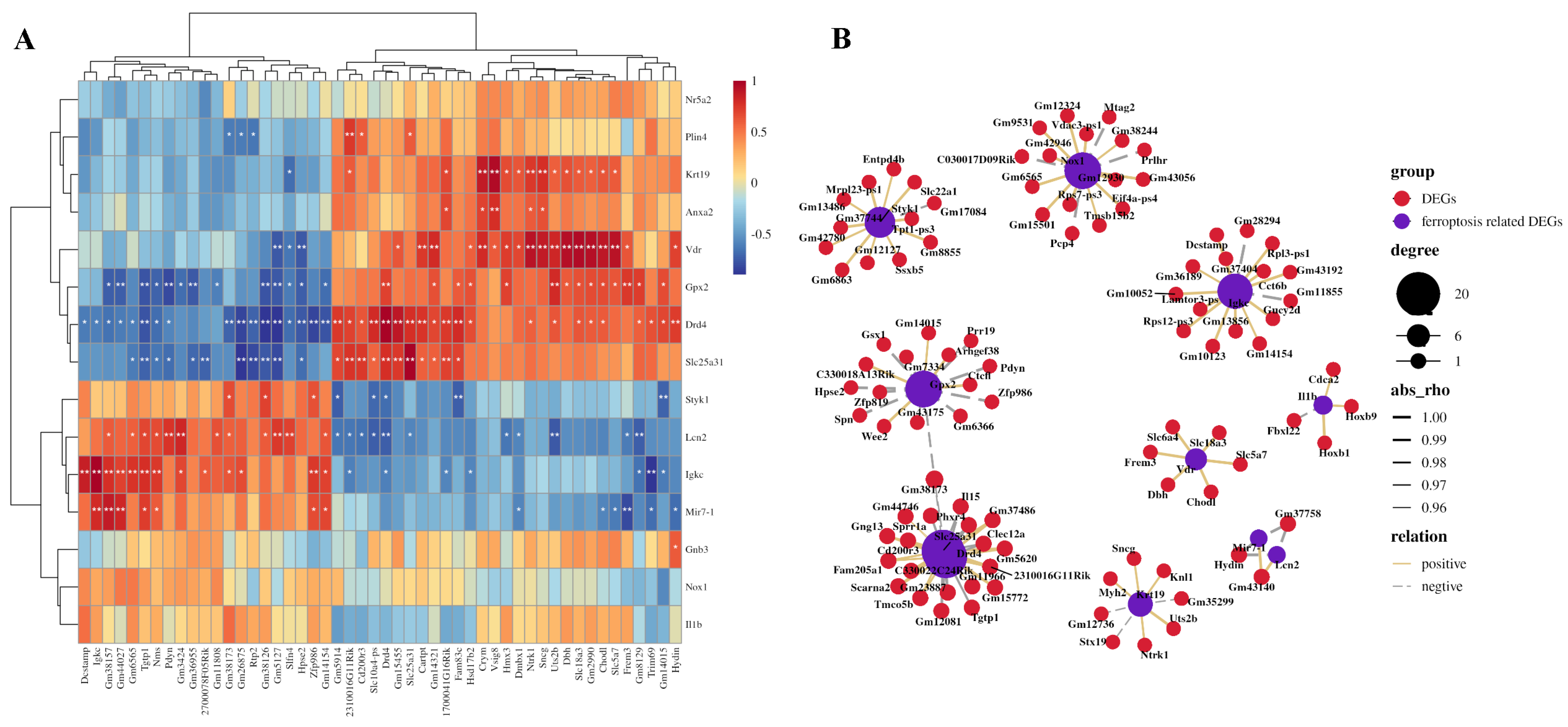
2.7. Construction of Ferroptosis-Related DEGs and Other DEGs Co-Expression Network
3. Results
3.1. Identification of DEGs Associated with Ferroptosis in the Comorbid Orofacial Pain
3.2. Immune Infiltration in the Comorbid Orofacial Pain
3.3. PPI Network in the Comorbid Orofacial Pain
3.4. Co-Expression Networks Between Ferroptosis-Related DEGs and Other DEGs
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasmussen, A.H.; Kogelman, L.J.A.; Kristensen, D.M.; Chalmer, M.A.; Olesen, J.; Hansen, T.F. Functional gene networks reveal distinct mechanisms segregating in migraine families. Brain 2020, 143, 2945–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Zheng, W.; Qu, M.; Xiao, C.C.; Chen, S.; Yao, Q.; Gong, W.; Tao, C.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, P.; et al. Kindlin-2 loss in condylar chondrocytes causes spontaneous osteoarthritic lesions in the temporomandibular joint in mice. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2022, 14, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauer, R.L.; Semidey, M.J. Diagnosis and treatment of temporomandibular disorders. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 91, 378–386. [Google Scholar]
- Kuć, J.; Szarejko, K.D.; Gołębiewska, M. The Prevalence and Overlaps of Temporomandibular Disorders in Patients with Myofascial Pain with Referral-A Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Liu, S.; Tang, Y.; Schmidt, B.L.; Dolan, J.C.; Bellinger, L.L.; Kramer, P.R.; Bender, S.D.; Tao, F. A Pre-Existing Myogenic Temporomandibular Disorder Increases Trigeminal Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide and Enhances Nitroglycerin-Induced Hypersensitivity in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Liu, S.; Crawford, J.; Tao, F. A female-specific role for trigeminal dynorphin in orofacial pain comorbidity. Pain 2023, 164, 2801–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, D.A.; Camparis, C.M.; Franco, A.L.; Fernandes, G.; Speciali, J.G.; Bigal, M.E. How to investigate and treat: Migraine in patients with temporomandibular disorders. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2012, 16, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale Braido, G.V.D.; Svensson, P.; Dos Santos Proença, J.; Mercante, F.G.; Fernandes, G.; de Godoi Gonçalves, D.A. Are central sensitization symptoms and psychosocial alterations interfering in the association between painful TMD, migraine, and headache attributed to TMD? Clin. Oral Investig. 2023, 27, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, D.; Monteiro, F.; Paço, M.; Vaz-Silva, M.; Lemos, C.; Alves-Ferreira, M.; Pinho, T. Genetic overlap between temporomandibular disorders and primary headaches: A systematic review. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2022, 58, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Reyes, M.; Klasser, G.; Akerman, S. An Update on Temporomandibular Disorders (TMDs) and Headache. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2023, 23, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dibello, V.; Lozupone, M.; Sardone, R.; Ballini, A.; Lafornara, D.; Dibello, A.; Vertucci, V.; Santarcangelo, F.; Maiorano, G.; Stallone, R.; et al. Temporomandibular Disorders as Contributors to Primary Headaches: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2023, 37, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Suzuki, S.; Shiina, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Hirata, K. Central Sensitization in Migraine: A Narrative Review. J. Pain Res. 2022, 15, 2673–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrillo, M.; Giudice, A.; Marotta, N.; Fortunato, F.; Di Venere, D.; Ammendolia, A.; Fiore, P.; de Sire, A. Pain Management and Rehabilitation for Central Sensitization in Temporomandibular Disorders: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessle, B.J. Peripheral and central mechanisms of orofacial inflammatory pain. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2011, 97, 179–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casale, R.; Atzeni, F.; Bazzichi, L.; Beretta, G.; Costantini, E.; Sacerdote, P.; Tassorelli, C. Pain in Women: A Perspective Review on a Relevant Clinical Issue that Deserves Prioritization. Pain Ther. 2021, 10, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maixner, W.; Fillingim, R.B.; Williams, D.A.; Smith, S.B.; Slade, G.D. Overlapping Chronic Pain Conditions: Implications for Diagnosis and Classification. J. Pain 2016, 17, T93–T107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lövgren, A.; Visscher, C.M.; Lobbezoo, F.; Yekkalam, N.; Vallin, S.; Wänman, A.; Häggman-Henrikson, B. The association between myofascial orofacial pain with and without referral and widespread pain. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2022, 80, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonato, L.L.; Quinelato, V.; De Felipe Cordeiro, P.C.; De Sousa, E.B.; Tesch, R.; Casado, P.L. Association between temporomandibular disorders and pain in other regions of the body. J. Oral Rehabil. 2017, 44, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Si, H.; Li, Z.; Bai, Q.; Tao, F. Transcriptomic Analysis of Trigeminal Ganglion and Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus Caudalis in Mice with Inflammatory Temporomandibular Joint Pain. J. Pain Res. 2022, 15, 1487–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Huang, F.; Lin, K.; Lin, S.W.; Wei, D.E.; Luo, D.S. Using RNA-Seq to Explore the Hub Genes in the Trigeminal Root Entry Zone of Rats by Compression Injury. Pain Physician 2021, 24, E573–E581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Tao, R.; Weng, X.; Sun, S.; Yang, Y.; Ying, B. Bioinformatics analysis of synovial fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the temporomandibular joint stimulated with IL-1β. Cytotechnology 2023, 75, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.H.; Min, C.; Yoo, D.M.; Yang, B.E.; Choi, H.G. Increased Risk of Migraine in Patients with Temporomandibular Disorder: A Longitudinal Follow-Up Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speciali, J.G.; Dach, F. Temporomandibular dysfunction and headache disorder. Headache 2015, 55, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chichorro, J.G.; Porreca, F.; Sessle, B. Mechanisms of craniofacial pain. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakkaphan, P.; Elias, L.-A.; Ravindranath, P.T.; Renton, T. Is Painful Temporomandibular Disord. A Real Headache Many Patients? Br. Dent. J. 2024, 236, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akerman, S.; Romero-Reyes, M. Preclinical studies investigating the neural mechanisms involved in the co-morbidity of migraine and temporomandibular disorders: The role of CGRP. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 5555–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hassany, L.; Haas, J.; Piccininni, M.; Kurth, T.; Maassen Van Den Brink, A.; Rohmann, J.L. Giving Researchers a Headache—Sex and Gender Differences in Migraine. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 549038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, C.H.; Pereira, D.D.; Pattussi, M.P.; Grossi, P.K.; Grossi, M.L. Gender differences in temporomandibular disorders in adult populational studies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Oral Rehabil. 2018, 45, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, A.; Cattaneo, R.; Marci, M.C.; Pietropaoli, D.; Ortu, E. Central Sensitization-Based Classification for Temporomandibular Disorders: A Pathogenetic Hypothesis. Pain Res. Manag. 2017, 2017, 5957076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Jin, S.; Chen, Y.; Guo, R. Ferroptosis in cancer therapy: A novel approach to reversing drug resistance. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Cao, F.; Yin, H.L.; Huang, Z.J.; Lin, Z.T.; Mao, N.; Sun, B.; Wang, G. Ferroptosis: Past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira-Santos, L.; Albino-Teixeira, A.; Pinho, D. Neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and their interplay in neuropathic pain: Focus on specialized pro-resolving mediators and NADPH oxidase inhibitors as potential therapeutic strategies. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 162, 105280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverria-Villalobos, M.; Tortorici, V.; Brito, B.E.; Ryskamp, D.; Uribe, A.; Weaver, T. The role of neuroinflammation in the transition of acute to chronic pain and the opioid-induced hyperalgesia and tolerance. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1297931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Guo, L.; Gao, R.; Yao, M.; Qu, X.; Sun, G.; Fu, Q.; Hu, C.; Han, G. Ferroptosis: A new regulatory mechanism in neuropathic pain. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1206851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kang, R.J.; Hyeon, S.J.; Ryu, H.; Joo, H.; Bu, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Suk, K. Lipocalin-2 Is a Key Regulator of Neuroinflammation in Secondary Traumatic and Ischemic Brain Injury. Neurotherapeutics 2023, 20, 803–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Torres, R. Role of interleukin-1beta during pain and inflammation. Brain Res. Rev. 2009, 60, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avenali, L.; Narayanan, P.; Rouwette, T.; Cervellini, I.; Sereda, M.; Gomez-Varela, D.; Schmidt, M. Annexin A2 regulates TRPA1-dependent nociception. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 14506–14516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, A.M.; Nagi, K.; Thillaiappan, N.B.; Sukumaran, V.; Akhtar, S. Vitamin D and Its Potential Interplay with Pain Signaling Pathways. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Guo, M.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, J.; Chen, L.; He, Z.; Xu, L.; Zha, Y. MicroRNA-7: A New Intervention Target for Inflammation and Related Diseases. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binshtok, A.M.; Wang, H.; Zimmermann, K.; Amaya, F.; Vardeh, D.; Shi, L.; Brenner, G.J.; Ji, R.R.; Bean, B.P.; Woolf, C.J.; et al. Nociceptors are interleukin-1beta sensors. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 14062–14073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, S.D.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Cavalli, E.; Bramanti, P.; Nania, R.; Fagone, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Petralia, M.C. Upregulation of IL-1 Receptor Antagonist in a Mouse Model of Migraine. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldbach-Mansky, R.; Dailey, N.J.; Canna, S.W.; Gelabert, A.; Jones, J.; Rubin, B.I.; Kim, H.J.; Brewer, C.; Zalewski, C.; Wiggs, E.; et al. Neonatal-Onset Multisystem Inflammatory Disease Responsive to Interleukin-1β Inhibition. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachmann, H.J.; Kone-Paut, I.; Kuemmerle-Deschner, J.B.; Leslie, K.S.; Hachulla, E.; Quartier, P.; Gitton, X.; Widmer, A.; Patel, N.; Hawkins, P.N. Use of Canakinumab in the Cryopyrin-Associated Periodic Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2416–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taru, V.; Szabo, G.; Mehal, W.; Reiberger, T. Inflammasomes in chronic liver disease: Hepatic injury, fibrosis progression and systemic inflammation. J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 895–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Long, T.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Qin, G.; Chen, L.; Zhou, J. Microglial NLRP3 inflammasome activation mediates IL-1β release and contributes to central sensitization in a recurrent nitroglycerin-induced migraine model. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klück, V.; Tim, L.; Janssen, M.; Comarniceanu, A.; Efdé, M.; Tengesdal, I.W.; Schraa, K.; Cleophas, M.C.P.; Scribner, C.L.; Skouras, D.B.; et al. Dapansutrile, an oral selective NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor, for treatment of gout flares: An open-label, dose-adaptive, proof-of-concept, phase 2a trial. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e270–e280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, J.F.; Lu, Z.B.; Fu, L.Q.; Tong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.F.; Mou, X.Z. The role of iron homeostasis and iron-mediated ROS in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 1895–1912. [Google Scholar]
- Song, E.; Ramos, S.V.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Botta, A.; Sung, H.K.; Turnbull, P.C.; Wheeler, M.B.; Berger, T.; Wilson, D.J.; et al. Holo-lipocalin-2-derived siderophores increase mitochondrial ROS and impair oxidative phosphorylation in rat cardiomyocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 1576–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, S.; Alhazmi, H.A.; Hassani, R.; Khuwaja, G.; Maheshkumar, V.P.; Aldahish, A.; Chidambaram, K. Role of ferroptosis pathways in neuroinflammation and neurological disorders: From pathogenesis to treatment. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Zhong, Z.; Gao, L.; Wu, X.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, G.; Liu, S. Focus on the Role of Inflammation as a Bridge between Ferroptosis and Atrial Fibrillation: A Narrative Review and Novel Perspective. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 25, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, R.; Liu, S.; Maltezos, H.; Tao, F. Gene Regulation in Comorbid Migraine and Myogenic Temporomandibular Disorder Pain. Genes 2025, 16, 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121435
Tao R, Liu S, Maltezos H, Tao F. Gene Regulation in Comorbid Migraine and Myogenic Temporomandibular Disorder Pain. Genes. 2025; 16(12):1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121435
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Ran, Sufang Liu, Hui Maltezos, and Feng Tao. 2025. "Gene Regulation in Comorbid Migraine and Myogenic Temporomandibular Disorder Pain" Genes 16, no. 12: 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121435
APA StyleTao, R., Liu, S., Maltezos, H., & Tao, F. (2025). Gene Regulation in Comorbid Migraine and Myogenic Temporomandibular Disorder Pain. Genes, 16(12), 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121435




