Effect of Current Density on Shear Performance and Fracture Behavior of Cu/Sn-58Bi/Cu Solder Joints
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
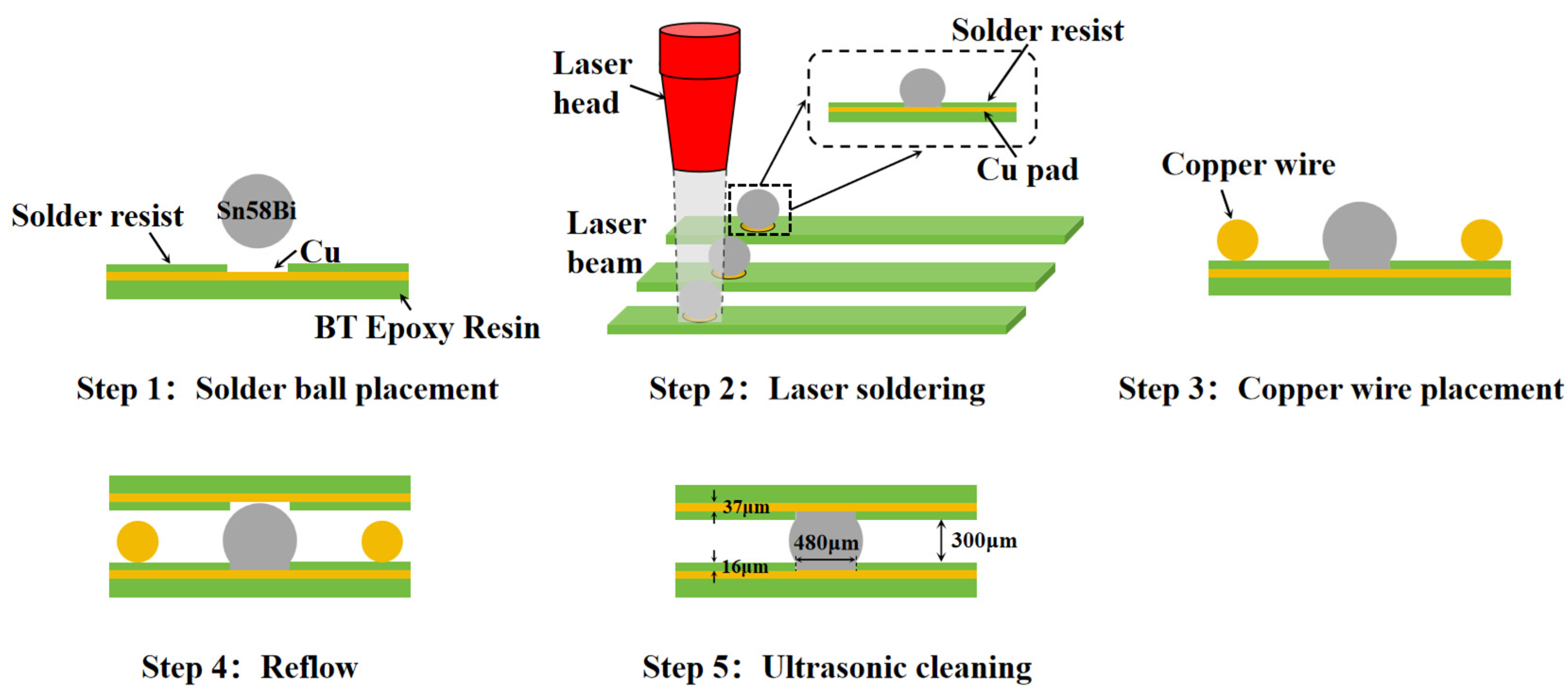
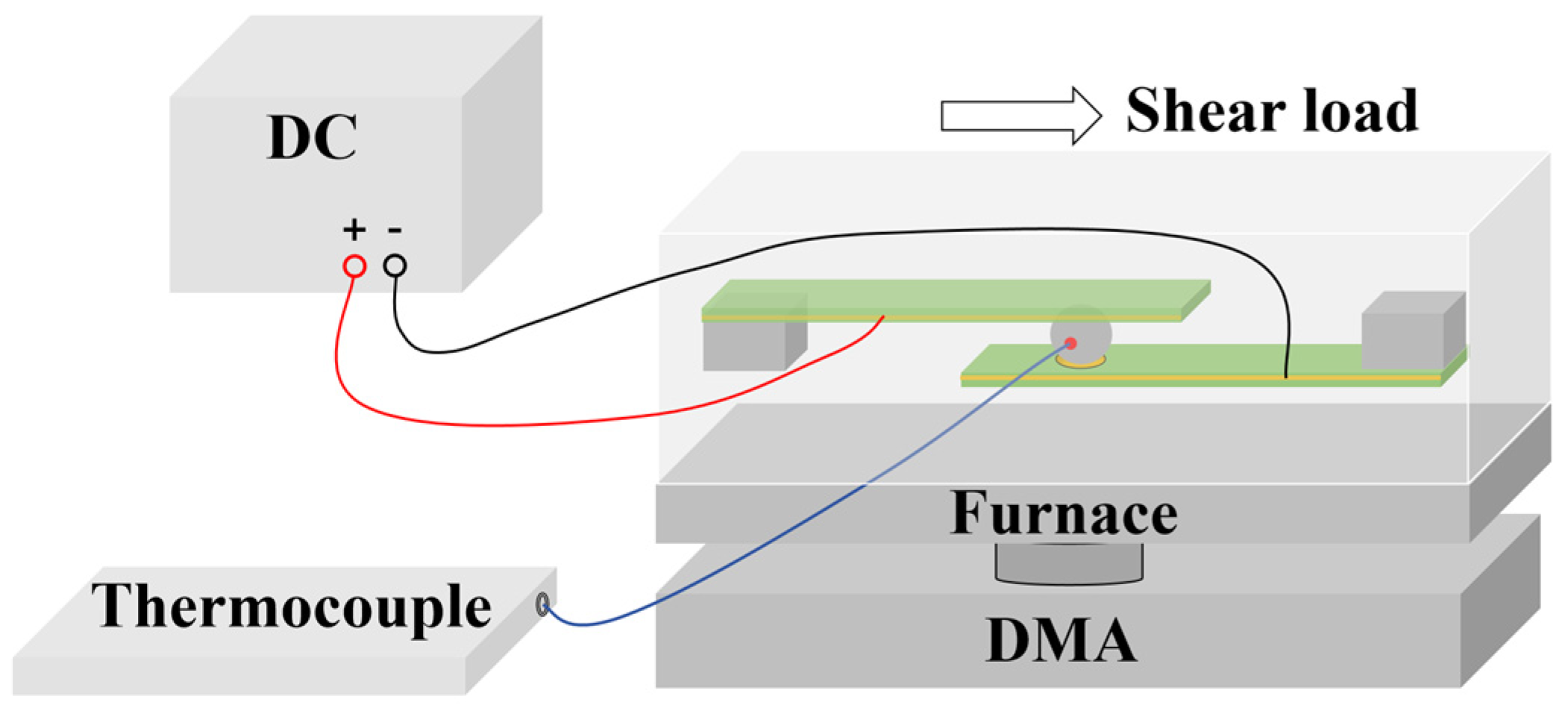
2.1. Experimental Methods
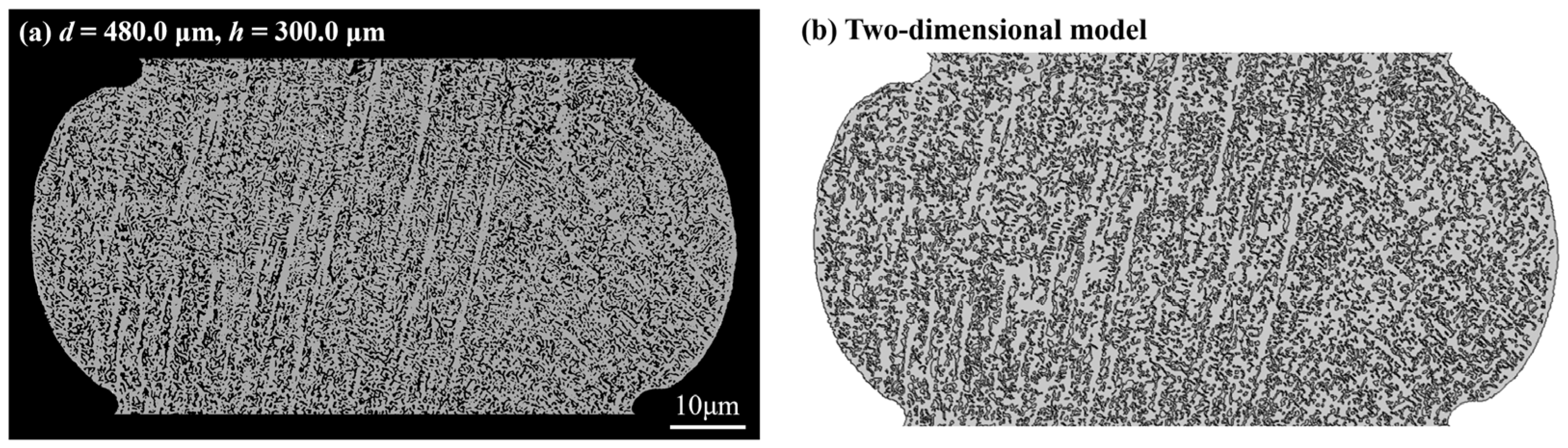
2.2. Finite Element Methods
3. Results
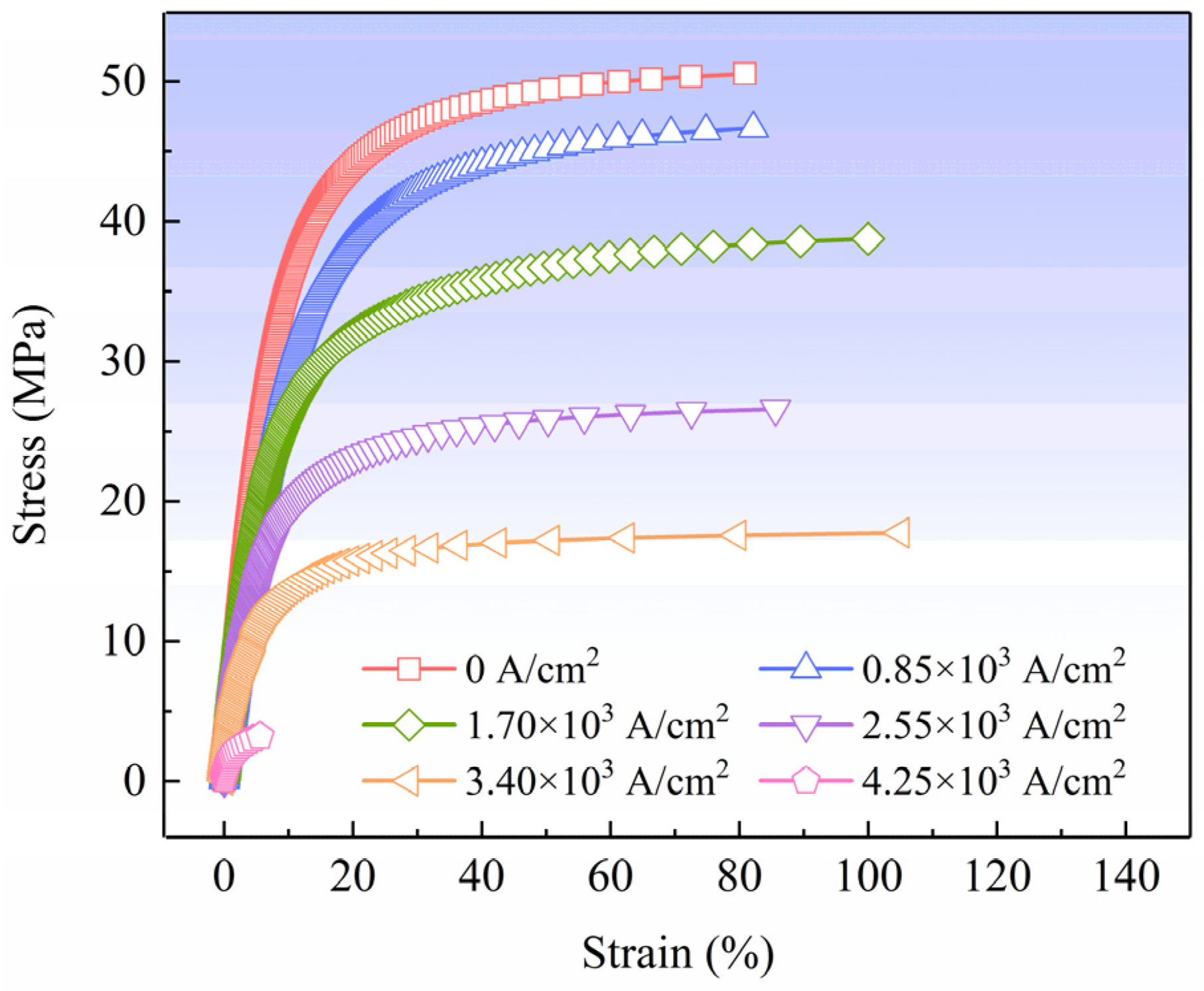
3.1. Deformation of Solder Joints Under Current Loading
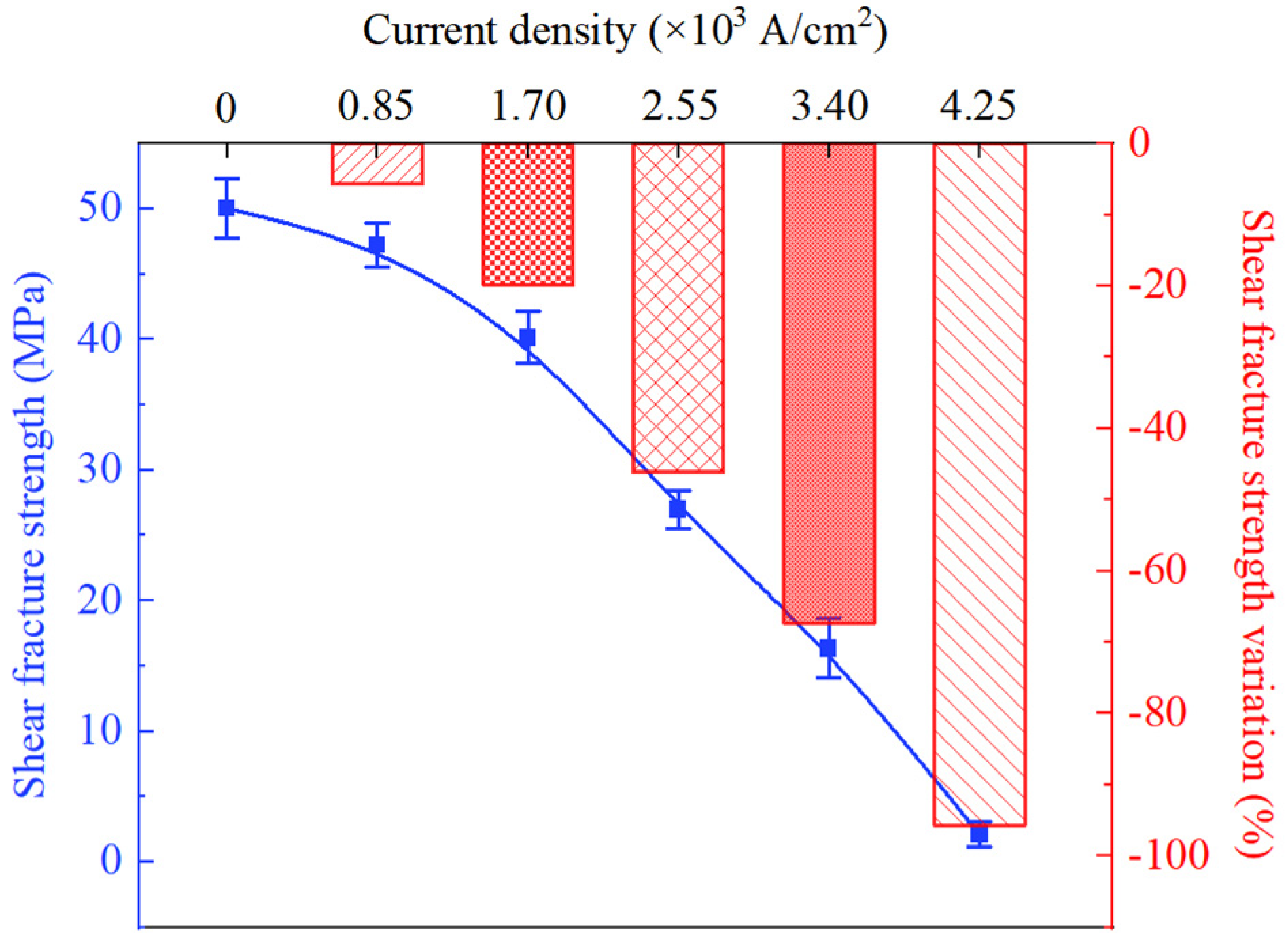
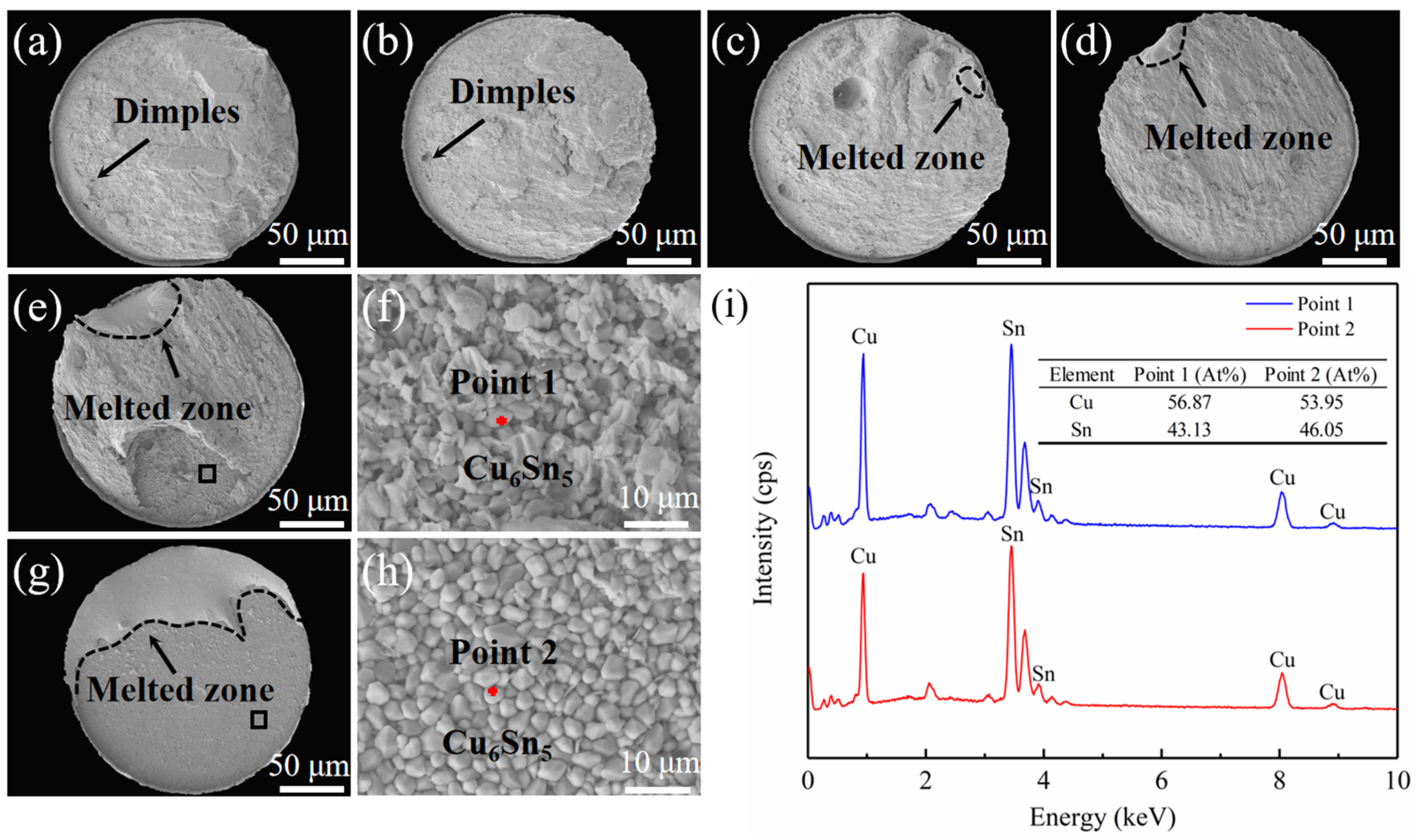
3.2. Fracture Behavior of Solder Joints Under Current Loading
4. Discussion
4.1. Mechanism of Degradation in Shear Performance of Solder Joints Under Current Loading
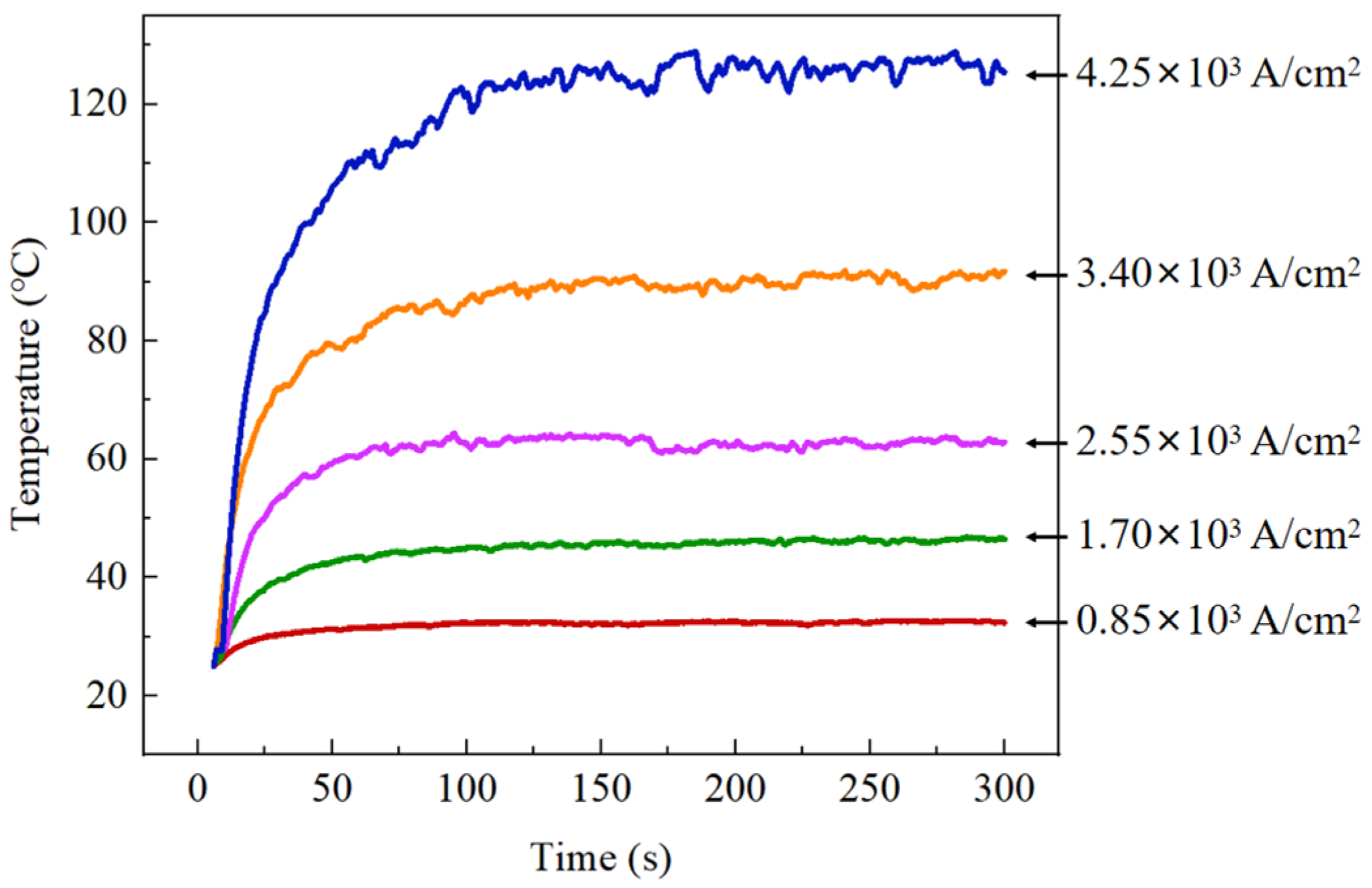
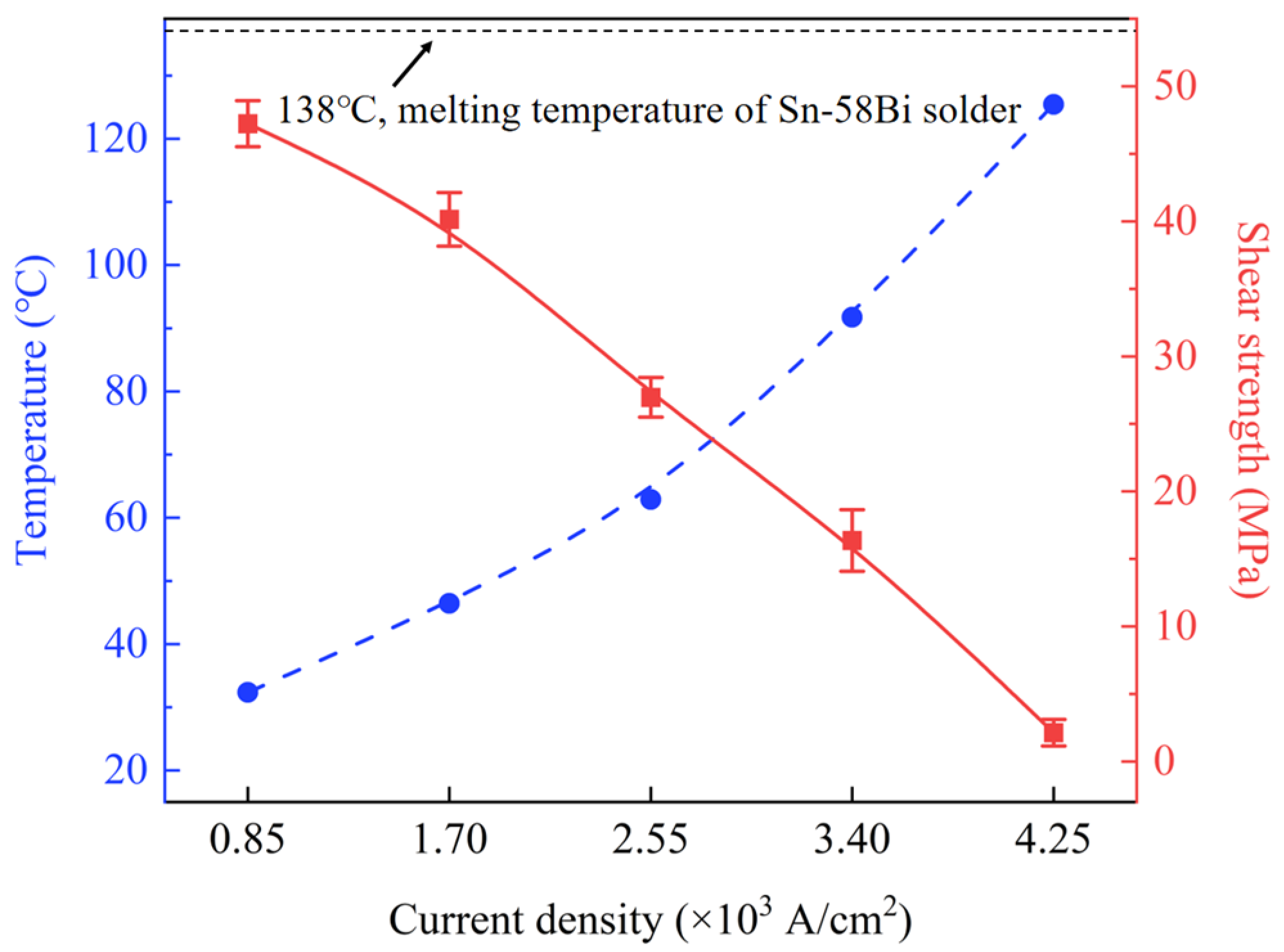
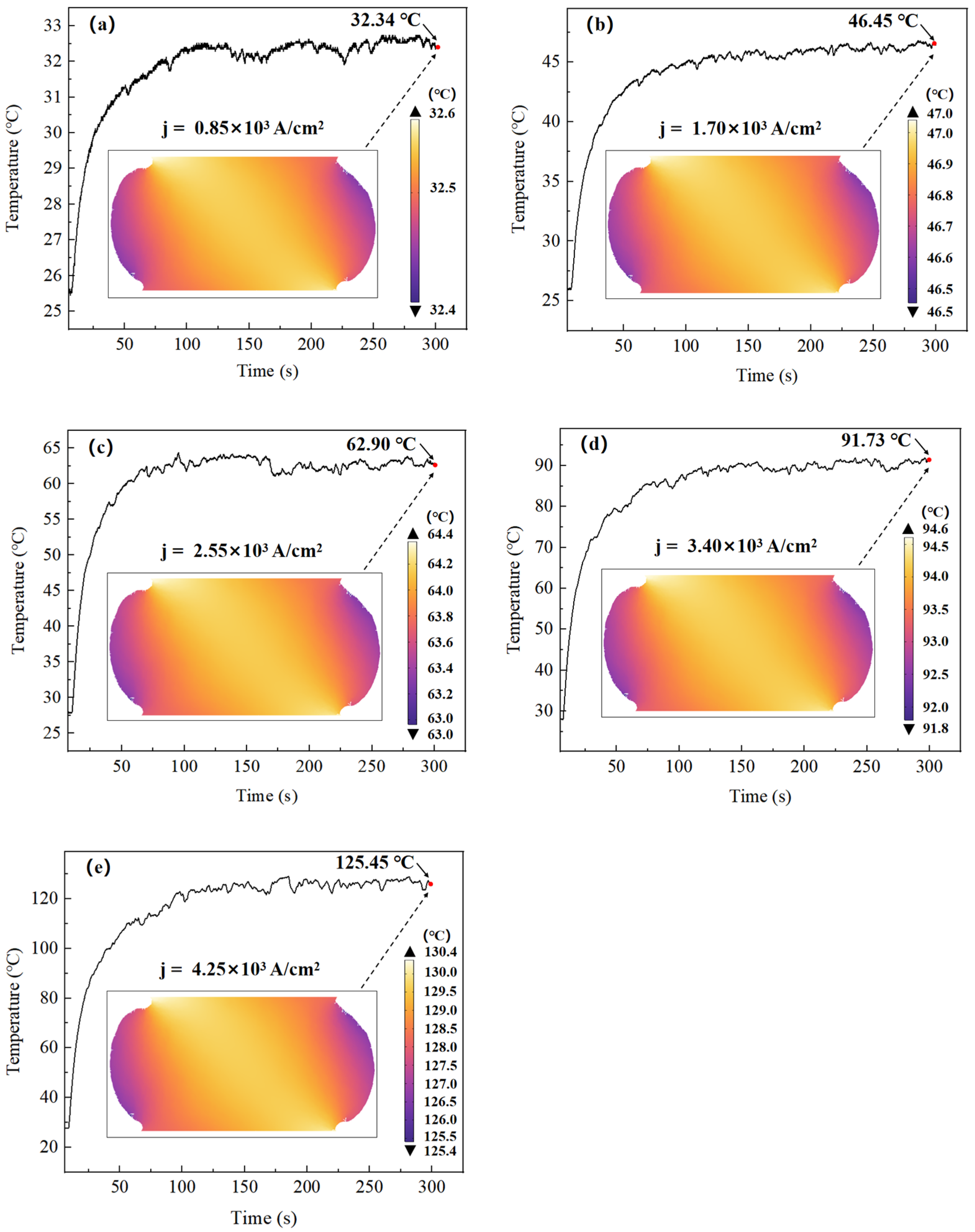
4.1.1. Overall Temperature Rise Caused by Joule Heating Effect and Material Softening
4.1.2. Non-Thermal Strengthening Mechanism of Electron Wind in Low-Current Range
4.2. Evolution Mechanism of Fracture Behavior in Solder Joints Under Current Loading
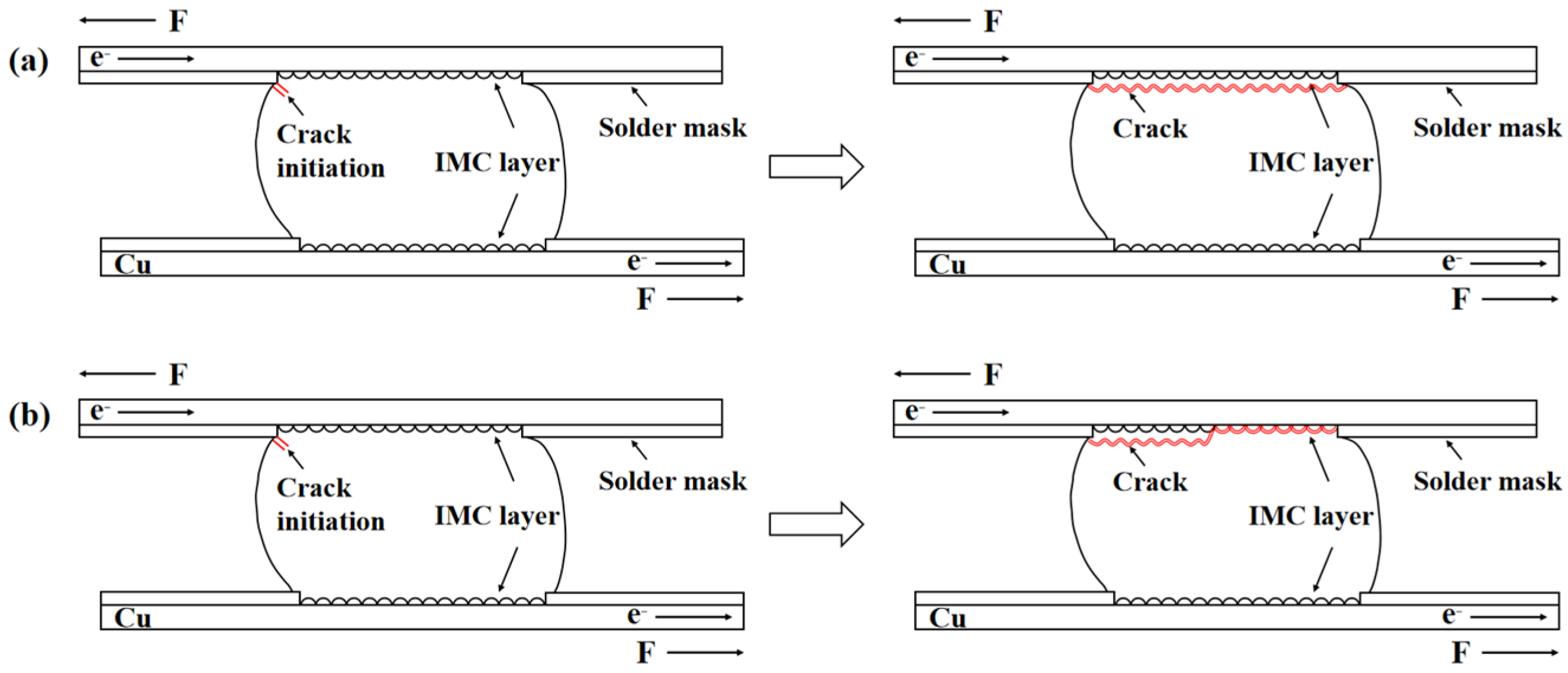
4.2.1. Interface Strain Mismatch and Fracture Mechanism Transition
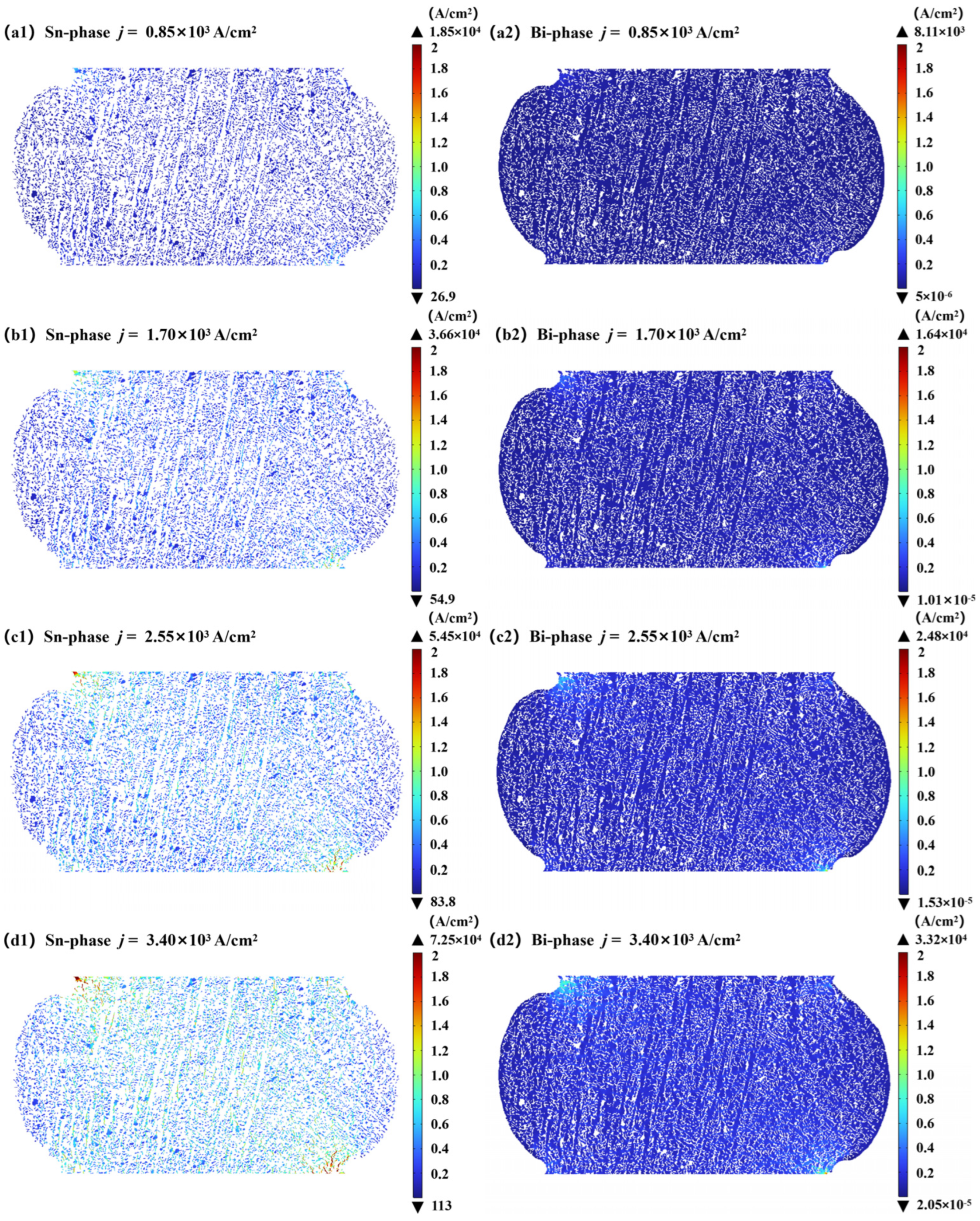
4.2.2. Microcurrent Concentration and Local Property Evolution
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- As current density increases from 0 A/cm2 to 4.25 × 103 A/cm2, the shear strength of the Cu/Sn-58Bi/Cu solder joints shows a steadily declining trend. The degradation mechanism primarily involves overall temperature rise and material softening due to the Joule heating effect, coupled with the weak strengthening effect of non-thermal electron wind in low current ranges, being masked by thermal effects as current increases. At current densities ≥3.40 × 103 A/cm2, the solder joint temperature approaches the melting point, making thermal softening the dominant factor in strength degradation.
- (2)
- Increasing current density significantly alters the fracture path and mode: under no-current or low-current conditions, fracture occurs within the solder matrix, exhibiting ductile fracture; as current density increases (≥3.40 × 103 A/cm2), the fracture location gradually shifts to the solder/IMC interface, with fracture surfaces exhibiting mixed ductile-brittle characteristics and localized exposure of Cu6Sn5 IMC; when current density reaches 4.25 × 103 A/cm2, brittle fracture at the interface becomes dominant.
- (3)
- Arising from the divergent electrical conductivities of its constituent Sn and Bi phases, the solder joint exhibits a markedly heterogeneous current distribution, as evidenced by finite element simulations. Significant current crowding effects occur at the Sn-rich phase and the solder/IMC interface, where local current densities far exceed the set value. This triggers intense Joule heating effects and thermal-mechanical mismatch strain. This coupled action causes thermal softening in the interface region, significantly reducing the interface bonding strength and inducing strain localization. This, in turn, promotes microcrack nucleation and propagation at the interface, ultimately leading to shear strength degradation and shifting the fracture path toward the interface.
- (4)
- The solder/IMC interface, characterized by material property differences (e.g., mismatched thermal expansion coefficients) and current concentration effects, becomes a stress and strain concentration zone—a sensitive region for crack initiation. A marked deterioration in interfacial bond strength occurs with higher current density, resulting in a transition of fracture mode from bulk ductile to interfacial brittle failure.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, H.B.; Li, W.Y.; Zhou, M.B.; Zhang, X.P. Low Cycle Fatigue Performance of Ball Grid Array Structure Cu/Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu/Cu Solder Joints. Microelectron. Reliab. 2014, 54, 2911–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tu, K.N. Low Melting Point Solders Based on Sn, Bi, and In Elements. Mater. Today Adv. 2020, 8, 100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illés, B.; Géczy, A.; Tafferner, Z.; Skwarek, A.; Krammer, O. Low-Temperature Soldering (LTS) in the Electronics Industry: A Brief Review. In Proceedings of the 2025 International Spring Seminar on Electronics Technology (ISSE), Budapest, Hungary, 14–18 May 2025; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, W.; Pan, K. Abnormal Shear Performance of Microscale Ball Grid Array Structure Cu/Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu/Cu Solder Joints with Increasing Current Density. Crystals 2022, 12, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Jing, S.; Heng, Y.; Yao, Y.; Tu, K.N.; Liu, Y. Electromigration in Three-Dimensional Integrated Circuits. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2023, 10, 021309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Chan, Y.C.; Wu, F. Failure Mechanisms of Solder Interconnects under Current Stressing in Advanced Electronic Packages: An Update on the Effect of Alternating Current (AC) Stressing. Microelectron. Reliab. 2018, 91, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Tong, H.M.; Tu, K.N. Electromigration and Thermomigration in Pb-Free Flip-Chip Solder Joints. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2010, 40, 531–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Qin, H.; He, S.; Li, W.; Wei, S. Creep Performance of Phase-Inhomogeneous Cu/Sn–58Bi/Cu Solder Joints with Increasing Current Density. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 16167–16182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Pan, K. Effect of Electric Current Stressing on Mechanical Performance of Solders and Solder Joints: A Review. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 17533–17562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Y.; Zhang, X.P.; Qin, H.B.; Mai, Y.W. Joule Heating Dominated Fracture Behavior Change in Micro-Scale Cu/Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu/Cu(Ni) Joints under Electro-Thermal Coupled Loads. Microelectron. Reliab. 2018, 82, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Liu, T.; Li, W.; Yue, W.; Yang, D. Influence of Microstructure Inhomogeneity on the Current Density and Temperature Gradient in Microscale Line-Type Sn58Bi Solder Joints under Current Stressing. Microelectron. Reliab. 2020, 115, 113995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadian, F.; Panta, S.; Flores, J.; Cotts, E.J. The Failure of Sn-Bi-Based Solder Joints Due to Current Stressing. J. Electron. Mater. 2023, 52, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadian, F.; Flores, J.; Cotts, E. The Variation of the Electrical Resistance and Microstructure of SnBi Based Solder Joints with Current Stressing. JOM J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. (TMS) 2022, 74, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Mo, L.; Hu, F.; Li, W.; Wei, S. Synergistic Effect of Thermomigration and Electric Current Stressing on Damping Capacity of Sn58Bi Solder. Vacuum 2025, 231, 113760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.H.; Liang, C.L.; Lin, K.L.; Wu, A.T. High Dislocation Density of Tin Induced by Electric Current. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 127210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Tian, Y.; Liu, W.; Wu, W.; Wang, C. TEM Observation of Interfacial Compounds of SnAgCu/ENIG Solder Bump after Laser Soldering and Subsequent Hot Air Reflows. Mater. Lett. 2016, 163, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straubinger, D.; Hurtony, T.; Géczy, A. Impact of Electromigration and Isothermal Ageing on Lead-Free Solder Joints of Chip-Sized SMD Components. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, W.; Pan, K. Shear Performance of Microscale Ball Grid Array Structure Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu Solder Joints with Different Surface Finish Combinations under Electro-Thermo-Mechanical Coupled Loads. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 4924–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Iwata, N. Formation and Growth of Intermetallic Compound Layers at the Interface during Laser Soldering Using Sn–Ag Cu Solder on a Cu Pad. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 215, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunwar, A.; Shang, S.; Råback, P.; Wang, Y.; Givernaud, J.; Chen, J.; Ma, H.; Song, X.; Zhao, N. Heat and Mass Transfer Effects of Laser Soldering on Growth Behavior of Interfacial Intermetallic Compounds in Sn/Cu and Sn-3.5Ag0.5/Cu Joints. Microelectron. Reliab. 2018, 80, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Guo, Z.; Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Su, X. Investigation of the Microstructure, Thermal Properties, and Mechanical Properties of Sn-Bi-Ag and Sn-Bi-Ag-Si Low Temperature Lead-Free Solder Alloys. Coatings 2023, 13, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chan, Y.C. Effect of Silver (Ag) Nanoparticle Size on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Sn58Bi–Ag Composite Solders. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 645, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Zhou, W.; Tsuchiya, K. Effect of Bi Additions on the Microstructure Evolution and Surface Instability during Room-Temperature Aging of Sn Alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2025, 60, 11529–11547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Li, S.; Li, Z.; Wu, G.; Zhu, P.; Dong, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wu, B.; Zhao, B.; et al. Coupled Effect of Ag and In Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Sn–Bi Lead-Free Solder Alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 5902–5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Engineering ToolBox. Linear Thermal Expansion Coefficients of Materials. 2003. Available online: https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/linear-expansion-coefficients-d_95.html. (accessed on 27 July 2025).
- Tian, R.; Hang, C.; Tian, Y.; Feng, J. Brittle Fracture Induced by Phase Transformation of Ni-Cu-Sn Intermetallic Compounds in Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu/Ni Solder Joints under Extreme Temperature Environment. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 777, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, W.K.; Ning, X.; Ke, C.B.; Zhou, M.B.; Zhang, X.P. Current Density Dependent Shear Performance and Fracture Behavior of Micro-Scale BGA Structure Cu/Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu/Cu Joints under Coupled Electromechanical Loads. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 15184–15197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.L.; Lin, K.L. The Microstructure and Property Variations of Metals Induced by Electric Current Treatment: A Review. Mater. Charact. 2018, 145, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Liu, L.; He, S.; Yan, H.; Li, W.; Qin, H. Shear Performance of Cu/Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu/Cu Joints with Same Solder Volume and Different Heights at Increasing Current Density. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 24906–24919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Mo, L.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Qin, H.; He, S. Minor Ag Induced Shear Performance Alternation in BGA Structure Cu/SnBi/Cu Solder Joints under Electric Current Stressing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 6111–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Materials Properties | Materials Elements | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sn | Bi | Cu | |
| Density/(kg·m−3) | |||
| Coefficient of thermal expansion/(1·K−1) | 13.3 × 10−6 [25] | ||
| Poisson’s ratio | |||
| Electrical conductivity/(S·m−1) | |||
| Thermal conductivity/(W·m−1·K−1) | 67.0 | 401.0 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, K.; Chen, Z.; Liu, M.; Ke, Z.; Wang, B.; He, K.; Huang, W.; He, S. Effect of Current Density on Shear Performance and Fracture Behavior of Cu/Sn-58Bi/Cu Solder Joints. Crystals 2025, 15, 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110945
Pan K, Chen Z, Liu M, Ke Z, Wang B, He K, Huang W, He S. Effect of Current Density on Shear Performance and Fracture Behavior of Cu/Sn-58Bi/Cu Solder Joints. Crystals. 2025; 15(11):945. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110945
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Kailin, Zimeng Chen, Menghao Liu, Zhanglong Ke, Bo Wang, Kaixuan He, Wei Huang, and Siliang He. 2025. "Effect of Current Density on Shear Performance and Fracture Behavior of Cu/Sn-58Bi/Cu Solder Joints" Crystals 15, no. 11: 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110945
APA StylePan, K., Chen, Z., Liu, M., Ke, Z., Wang, B., He, K., Huang, W., & He, S. (2025). Effect of Current Density on Shear Performance and Fracture Behavior of Cu/Sn-58Bi/Cu Solder Joints. Crystals, 15(11), 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110945






