Abstract
Zinc is an essential micronutrient that plays critical roles in numerous physiological processes, including bone homeostasis. The majority of zinc in the human body is stored in bone. Zinc is not only a component of bone but also an essential cofactor of many proteins involved in microstructural stability and bone remodeling. There are two types of membrane zinc transporter proteins identified in mammals: the Zrt- and Irt-like protein (ZIP) family and the zinc transporter (ZnT) family. They regulate the influx and efflux of zinc, accounting for the transport of zinc through cellular and intracellular membranes to maintain zinc homeostasis in the cytoplasm and in intracellular compartments, respectively. Abnormal function of certain zinc transporters is associated with an imbalance of bone homeostasis, which may contribute to human bone diseases. Here, we summarize the regulatory roles of zinc transporters in different cell types and the mechanisms underlying related pathological changes involved in bone diseases. We also present perspectives for further studies on bone homeostasis-regulating zinc transporters.
1. Introduction
Bone is the main supporting framework of the body and is characterized by its nature of rigidity and self-healing ability [1]. It provides protection for soft organs and a stable environment for the marrow, which is responsible for hemopoiesis and fat storage [2,3]. Bone is a highly dynamic tissue that undergoes constant physiological activities to remove old, injured or microdamaged bone and replace it with newly formed bone that is mechanically stronger in promoting or preserving bone strength and adapting to changing biomechanical forces [4]. Healthy bones are always in homeostasis, and disturbance of homeostasis causes various bone diseases, such as osteoporosis and osteoarthritis (OA) [5,6,7]. Bone homeostasis involves multiple coordinated cellular and molecular events that revolve around three main types of bone cells: osteoblasts, osteocytes and osteoclasts [8]. Osteoblasts are large cuboidal cells that lie along the bone surface and are responsible for osteogenesis, contributing to bone matrix synthesis and subsequent mineralization [9]. Osteoblasts produce and secrete cellular products during bone formation, are trapped in lacunae and eventually transform into osteocytes [10]. Osteocytes are the most abundant cell type in bone, and they serve as the primary mechanosensor and respond to hormone cues [11,12]. Osteoclasts are large multinucleated cells that are responsible for osteoclastogenesis, accounting for bone destruction and resorption [13]. Osteoblasts originate from mesenchymal stem/stromal cells, whereas osteoclasts are derived from monocyte fusion and have more than one nucleus [14]. Chondrocytes are another type of cell that is very important for bone; they are the only cell type found in the cartilage and are responsible for cartilaginous matrix production and maintenance [15]. Bone homeostasis is synergistically regulated by a series of regulatory factors and sophisticated signaling pathways [16,17,18].
Bone itself is also an important reservoir for diverse metal ions, cytokines, and growth factors [19]. As an essential metal element, zinc plays indispensable roles in the growth and development of humans and other animals [7,20,21,22]. In humans, bone contains approximately 30% of the total body zinc, which has been shown to decrease during aging [23,24]. Zinc deficiency caused by different pathological conditions was found to give rise to bone growth retardation, suggesting that zinc is of great importance for the development, growth, and health of bone [25]. The majority of zinc in the body is stored in the skeleton and enriched in the osteoid layer, where inorganic mineral salts are deposited [26]. Specifically, zinc is found to occur in the mineral component, probably in hydroxyapatite or in complex with fluoride, which might improve the crystallinity of apatite [27,28,29]. In addition to being one of the components of bone, zinc also acts as an activator or coactivator of a variety of proteins involved in bone homeostasis in the form of zinc fingers or zinc clusters [30,31,32]. For instance, zinc acts as a coactivator of runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2), which is the earliest determinant of osteogenic differentiation, and its downstream target gene Osterix, which is itself a zinc finger motif-containing transcription factor [25,33].
There has been growing interest in the potential roles of zinc in bone homeostasis and bone diseases. The transport of zinc through cellular and intracellular membranes is of great significance for maintaining zinc homeostasis, suggesting that homeostasis-regulating zinc transporters could be very important in the regulation of physiological and pathological processes in bone. In mammals, there are two types of zinc transporter genes: the Slc39a family of importers encodes Zrt- and Irt-like proteins (ZIPs), and the Slc30a family of exporters encodes zinc transporters (ZnTs). The ZIP family mediates zinc influx from extracellular fluid or intracellular vesicles into the cytoplasm, and the ZnT family promotes zinc efflux from cells or influx into intracellular vesicles from the cytoplasm. In mammalian genomes, a total of 14 members of the ZIP family (ZIP1–ZIP14) and 10 members of the ZnT family (ZnT1–ZnT10) have been identified [34]. Most ZIP proteins are homo- or heterodimers with eight transmembrane domains, and the N-terminal and C-terminal regions are located extracellularly, with a histidine-rich loop between the third and fourth transmembrane domains [23,35,36,37]. ZnT transporters have six transmembrane domains with their termini inside the cytoplasm, and there is a long histidine-rich loop between transmembrane domains IV and V, which is the binding site of zinc ions [34,38]. Herein, we review the biological functions of six members of the ZIP family and two members of the ZnT family that play regulatory roles in bone homeostasis, the imbalance of which might lead to certain bone diseases (Table 1).

Table 1.
Zrt- and Irt-like protein (ZIP) and zinc transporter (ZnT) proteins in bone physiology and pathology.
2. Roles of ZIP Transporters in Bone
2.1. ZIP1, ZIP2 and ZIP3
Zrt/Irt-like proteins 1, 2 and 3 (ZIP1, ZIP2, and ZIP3) are multipass membrane zinc transporter proteins that are responsible for mammalian zinc homeostasis by mediating zinc uptake into the cytoplasm [58,59]. Osteoblasts are known to be the primary functional cells for bone formation. ZIP1 was found to be expressed early in mouse embryo development, at E15.5 in osteoblasts and later in ameloblasts and odontoblasts, indicating that ZIP1 is closely related to bone formation [60]. Additionally, ZIP1 is located in the cytoplasmic membrane and mediates zinc influx during mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) differentiation into osteoblasts [40]. ZIP1 expression was induced upon osteogenic differentiation of multipotent human MSCs and osteoblast progenitor MC3T3-E1 cells in vitro, accompanied by an increase in intracellular zinc uptake [39,40,41]. Moreover, ZIP1-mediated zinc influx gave rise to higher expression of the osteogenic master regulators Runx2 and Osterix. Enhancement of Runx2 and Osterix expression further modulated transcriptional expression of ZIP1 by directly binding to the response elements in the promoter. These processes resulted in a series of intertwined feed-forward loops that induced zinc influx and osteogenic differentiation and promoted bone apatite formation [41,61,62]. On the other hand, ZIP1 is also expressed in osteoclasts, and overexpression of ZIP1 inhibited mature osteoclast activity by exerting a negative impact on the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, which is essential for osteoclast differentiation and activity [63]. Thus, ZIP1 could play regulatory roles in stimulating osteogenesis and suppressing osteoclastogenesis in vitro. Although ZIP1 is widely expressed in mouse tissues, no visible bone phenotype was observed in ZIP1 knockout mice fed a normal diet; however, a decreased embryonic survival rate was found upon feeding with a low-zinc diet, but no obvious bone phenotype was revealed [42,43,44].
Unlike that of ZIP1, the expression of ZIP2 and ZIP3 is low in tissues, and few studies have been published on the roles of ZIP2 and ZIP3 in osteogenesis or osteoclastogenesis in vitro. Although ZIP2 expression has been reported to correlate with hormones, no obvious bone phenotypes appeared in homozygous ZIP2 knockout mice with an adequate dietary zinc supply [43,44,45]. Similarly, ZIP3 knockout mice; double ZIP1 and ZIP3 knockout mice; and even triple ZIP1, ZIP2, and ZIP3 knockout mice exhibited no differences in the content of bone zinc and no bone deformity, but the triple knockout mice exhibited a higher risk of malformations under the condition of dietary zinc deficiency [42,43,44]. These interesting phenomena imply that there might be other compensatory pathways that contribute to the process of zinc uptake in vivo.
2.2. ZIP8
Zrt/Irt-like protein 8 (ZIP8) is an 8-transmembrane transporter that is present on the cytoplasmic membrane or intracellular vesicles of various types of cells [64,65]. Zinc supplementation or overexpression of ZIP8 in osteoblasts could improve zinc homeostasis, which helps to protect against intermittent hypoxia (IH) exposure in vitro [66]. IH-treated osteoblasts exhibited reductions in mineralization and zinc content, accompanied by decreased expression of ZIP8, Runx2, Col1α1, and other osteogenesis-associated genes, which could be recovered by zinc supplementation or ZIP8 overexpression [66]. Notably, IH-treated animals displayed significantly impaired insulin production and bone fragility due to an imbalance of zinc homeostasis [67,68].
Recently, ZIP8-mediated zinc influx has been revealed to be essential for the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis [46]. OA is characterized by cartilage degradation, synovitis, osteophyte formation, and sclerosis of subchondral bone. Tissue destruction is caused by proteins named matrix-degrading enzymes, which are produced by cartilage cells. Matrix-degrading enzymes need zinc to function, implying that zinc levels play an important role in OA [69]. ZIP8 expression was found to be increased in chondrocytes from OA patients or OA mouse models, resulting in increased intracellular zinc concentrations [46,47,70]. ZIP8 is embedded in the plasma membrane of cartilage cells and is involved in transporting zinc into these cells from the outside environment. Mechanistically, zinc influx through ZIP8 activates the nuclear localization of a transcription-activating protein, metal-regulatory transcription factor-1 (MTF1), which in turn upregulates the expression of zinc-dependent metalloprotease matrix-degrading enzymes (MMP3, MMP9, MMP12, MMP13) and ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 5 (ADAMTS5), induces the destruction of the cartilage extracellular matrix and exacerbates the pathogenesis of OA [46,48,71]. Moreover, overexpression or transgenic manipulation of ZIP8 or MTF1 in chondrocytes causes OA pathogenesis in mice. It is worth noting that the pathogenesis of OA caused by overexpression of ZIP8 was significantly inhibited in MTF1-deficient mice, whereas the pathogenesis of OA caused by overexpression of MTF1 was not affected in ZIP8-deficient mice. This clearly shows that MTF1 is a downstream mediator of ZIP8 in the pathogenesis of OA. In contrast, chondrocyte-specific deficiency of ZIP8 or MTF1 ameliorated cartilage destruction in OA mice [46]. Furthermore, the zinc-ZIP8-MTF1 axis could reciprocally activate hypoxia-inducible factor 2α (HIF-2α), one of the key regulatory factors of endochondral osteogenesis and OA-related cartilage degeneration, to amplifying catabolic signals and accelerating cartilage destruction [49,72,73]. Therefore, the zinc-ZIP8-MTF1 axis might be a novel drug target for the treatment of OA.
2.3. ZIP13
Zrt- and Irt-like protein 13 (ZIP13) possesses an 8-transmembrane structure and acts as a zinc-influx transporter, moving zinc from the subcellular compartment into the cytosol [74]. ZIP13 is located in the Golgi apparatus and intracellular vesicles and mainly plays roles in mesenchyme-originating cells [51,74,75,76]. ZIP13 can respond to and be regulated by zinc concentrations. This process might contribute to the influx of stored zinc from vesicles to the cytosol, meeting the requirement for zinc in order to activate enzymes and related metabolic reactions under zinc-restricted conditions [76,77]. ZIP13 was found to be expressed in osteoblasts of the tibia and alveolar bone, in the proliferative zone of the growth plate, in odontoblasts of the forming dentin crown in molars, and in fibroblasts of the reticular layer of the skin [51,78,79].
The spondylocheiro dysplastic form of Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (SCD-EDS) is an inherited connective tissue and bone disease caused by a homozygous mutation of the ZIP13 gene [50,77]. Zinc deficiency can cause bone growth retardation and increase the risk of skin fragility [80,81]. Many clinical features of SCD-EDS patients are similar to symptoms of zinc deficiency in humans or animal models, such as osteogenesis imperfecta, skin inelasticity, and systemic growth retardation, which is also recapitulated in ZIP13-knockout mice [50,51]. Mice with ZIP13 deletion exhibited impaired bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4)/transforming growth factor β (TGF-β)/Smad signaling in the corresponding tissues. Bone morphogenetic proteins and TGF-β signaling are known to play important roles in cell proliferation and differentiation and are highly correlated with the development of bone and various tissues [82]. Ablation of ZIP13 initiated dysregulation of a variety of differentiation-related marker genes leading to inadequate maturation of osteoblasts, chondrocytes, odontoblasts and fibroblasts; these markers included 1) Runx2 and Msh homeobox 2 (Msx2), which are involved in skeletogenesis; 2) Indian hedgehog (Ihh), Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (Fgfr3) and SRY-box transcription factor 9 (Sox9), which are responsible for differentiation of chondrocytes; and 3) Collagen type I alpha 2 (Col1α2), which is responsible for fibroblast differentiation [51,75]. Furthermore, the valosin-containing protein (VCP)-dependent ubiquitin proteasome pathway accelerates the degradation of the pathological mutant ZIP13 protein, reduces the level of functional protein, and leads to vertebral dysplasia in SCD-EDS [78,83].
2.4. ZIP14
ZIP14 is most closely related to ZIP8, which is known to be localized to the plasma membrane and to function in the transport of Zn2+, Fe2+, and Mn2+ [84,85,86]. ZIP14 is important for mammalian development and was found to be highly expressed in the pituitary gland and bone, which are responsible for the production of growth hormone and bone elongation [52,53]. ZIP14 is highly expressed in chondrocytes in the proliferation zone of growth plates and contributes to endochondral ossification, which accounts for longitudinal lengthening of bones. Loss of ZIP14 in mice results in dwarfism, scoliosis, osteopenia and shortening of the long bones caused by abnormal chondrogenesis and endochondral ossification [52,53]. At the same time, intracellular zinc concentrations in the growth plate proliferation zone as well as zinc concentrations and 3′,5′-Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels in pituitary cells of ZIP14 knockout mice were significantly reduced, and these effects were important for maintaining the homeostasis of G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)-mediated signal transduction. Further research on the underlying mechanisms revealed that zinc transport mediated by ZIP14 could prevent cAMP degradation by inhibiting phosphodiesterase (PDE) activity, through which ZIP14 facilitates the GPCR/cAMP/cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) signaling pathways [52,53]. The expression of ZIP14 is stable during osteogenic differentiation of mouse MSCs, whereas it increases during the mineralization stage. ZIP14 knockout mice exhibited markedly reduced trabecular bone mass that was greatly amplified with aging [87]. In humans, hyperostosis cranialis interna (HCI) is a genetic disease related to a missense mutation (P.L441R) in the ZIP14 gene, which was confirmed by whole-exome sequencing [88]. P.L441R-ZIP14 leads to incorrect localization of ZIP14 in osteoblasts, thus increasing the accumulation of unstable cellular zinc and abnormal cellular zinc homeostasis, causing excessive bone growth in the skull [54]. Notably, ZIP14L438R osteoblast-specific knock-in mice, which have a missense mutation in the mouse ZIP14 gene, exhibit no effects on the calvariae but have a severe femoral phenotype characterized by a sharp increase in cortical thickness, similar to the underlying pathology of HCI patients. Conditional osteoblast ZIP14-mutation knock-in mice have a significant increase in cortical thickness and a decreased midshaft due to enhanced intimal formation caused by significantly enhanced cAMP/CREB and nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) signaling activity, which plays an important role in bone and inflammatory processes; however, conditional osteoclast ZIP14-mutation knock-in mice display no significant difference in skeletal phenotype.
3. Role of ZnT Transporters in Bone
The zinc transporter (ZnT)/Slc30 family is a subfamily responsible for zinc efflux, in contrast to the function of the (ZIP)/Slc39 subfamily [89]. Few studies have been reported on the relationship between the ZnT family and bone, except for ZnT5 and ZnT7. ZnT5 expressed after transfection in HeLa cells was reported to localize to Golgi membranes, mediating zinc efflux from the cytosol to the Golgi compartment [90]. ZnT7 is localized to the Golgi apparatus and unique vesicular compartments [91]. The activity of tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNAP) was significantly reduced in DT40 cells in the absence of both ZnT5 and ZnT7 [92,93]. As a zinc-requiring membrane-bound enzyme, TNAP is crucial for bone mineralization. Decreased TNAP activity inevitably leads to impaired mineralization of the bone matrix, which mimics the skeletal defects of infantile hypophosphatasia [94]. Mice with ZnT5 deficiency displayed poor growth, osteopenia and heart failure [55]. Specifically, ZnT5 knockout mice manifest bone abnormalities, including lower bone density due to impairment of osteoblast maturation [55]. However, the roles of ZnT5 in bone and the related mechanisms are largely elusive. The ZnT7 protein is abundantly expressed in mouse osteoblast MC3T3-E1 cells [57] and is a crucial component of the functional activities of MSCs [56]. ZnT7 prevented MC3T3-E1 cells from undergoing apoptosis induced by oxidative stress by reducing the accumulation of intracellular cationic zinc [57]. On the other hand, the expression of ZnT7 decreased upon osteogenic induction of MSCs. Downregulation of ZnT7 expression by small interfering RNA (siRNA) increased the levels of osteogenesis-associated markers such as alkaline phosphatase (ALP), collagen I and osteocalcin, whereas overexpression of ZnT7 exerted the opposite effects. Further study demonstrated that ZnT7 could interfere with Wnt/β-catenin signaling, a key pathway involved in osteogenesis [56]. ZnT5 and ZnT7 might play opposite roles in osteogenesis; however, the underlying mechanism still needs to be explored.
4. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Zinc is an important element for bone development, regeneration, and homeostasis, which has been gradually recognized in recent years [95]. However, zinc is incapable of passing through the cell membrane freely, and transporter-mediated influx and efflux of zinc are required for zinc homeostasis in cells. Since the discovery of zinc transporters, accumulating evidence has demonstrated that mutation and disorder of ZIP and ZnT transporter proteins are related to certain aspects of bone physiology or disease [96]. In this review, eight zinc transporters, namely, ZIP1, ZIP2, ZIP3, ZIP8, ZIP13, ZIP14, ZnT5, and ZnT7, were characterized to illuminate the relationship between zinc transporters and bone homeostasis (Figure 1). Different members of the ZIP and ZnT families synergize with zinc to participate in the processes of osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis. The ZIP8-mediated zinc signaling axis in chondrocytes is an essential regulator of OA pathogenesis; dysfunction of the ZIP13, ZIP14, or ZnT5 gene gives rise to bone deformity in mice and humans. Mutations in zinc transporter genes may lead to genetic disease or increase the risk of disease. However, studies related to the role of zinc transporters in the pathogenesis of bone diseases are relatively rare, and further investigation is needed to gain a deeper understanding, which might facilitate the development of zinc supplements for bone diseases, zinc-containing bone repair materials, and molecular therapies targeting zinc signaling pathways. In addition, recent studies suggest that zinc transporters can transport not only zinc but also trace elements such as iron, manganese, and cadmium, which makes the functions of zinc transporters in bone more complex and diverse. Whether a specific zinc transporter transports other divalent metal ions, whether the same zinc transporter regulates bone development by coordinating the steady-state metabolism of different trace elements, and whether the transport function of a zinc transporter for multiple trace elements is independent or balanced are important scientific issues to be further studied.
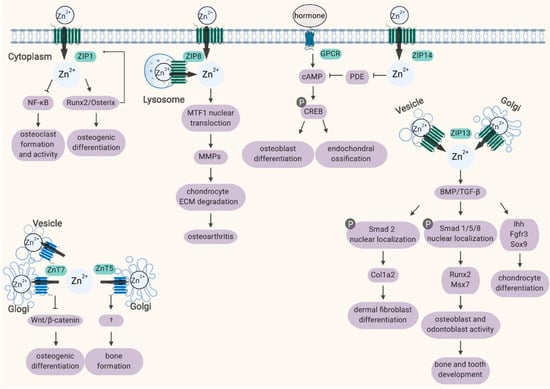
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the subcellular localization and biological processes of ZIP and ZnT proteins involved in bone homeostasis. Refer to the text for a detailed description. Abbreviations: MTF1, metal-regulatory transcription factor-1; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; GPCR, G protein-coupled receptor; PDE, phosphodiesterase; CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein; BMP, bone morphogenetic protein.
Funding
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFA0703100), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81770882), Shenzhen Science and Technology Research Funding (KQJSCX20180330170052049 and 20170502171625936), Guangdong Special Support Program (2017TQ04R394).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| ZIP | Zrt- and Irt-like protein |
| ZnT | zinc transporter |
| MSCs | mesenchymal stem cells |
| OA | osteoarthritis |
| MTF1 | metal-regulatory transcription factor-1 |
| Runx2 | runt-related transcription factor 2 |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa B |
| ADAMTS5 | ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 5 |
| Msx2 | msh homeobox 2 |
| Ihh | Indian hedgehog |
| Fgfr3 | fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 |
| Sox9 | SRY-box transcription factor 9 |
| Col1α2 | collagen type I alpha 2 |
| MMPs | matrix metalloproteinases |
| VCP | valosin-containing protein |
| cAMP | 3′,5′-Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| NFAT | nuclear factor of activated T cells |
| ALP | alkaline phosphatase |
| siRNA | small interfering RNA |
| PDE | phosphodiesterase |
| GPCR | G protein-coupled receptor |
| CREB | cAMP response element-binding protein |
| BMP | bone morphogenetic protein |
| SCD-EDS | spondylocheiro dysplastic form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome |
| HCI | hyperostosis cranialis interna |
| BMP | bone morphogenetic protein |
References
- Uthgenannt, B.A.; Kramer, M.H.; Hwu, J.A.; Wopenka, B.; Silva, M.J. Skeletal self-repair: Stress fracture healing by rapid formation and densification of woven bone. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2007, 22, 1548–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontikoglou, C.; Deschaseaux, F.; Sensebe, L.; Papadaki, H.A. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: Biological properties and their role in hematopoiesis and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2011, 7, 569–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, C.J.; Ackert-Bicknell, C.; Rodriguez, J.P.; Pino, A.M. Marrow fat and the bone microenvironment: Developmental, functional, and pathological implications. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2009, 19, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeman, E.; Delmas, P.D. Bone quality--the material and structural basis of bone strength and fragility. New Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2250–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gur, A.; Colpan, L.; Cevik, R.; Nas, K.; Jale Sarac, A. Comparison of zinc excretion and biochemical markers of bone remodelling in the assessment of the effects of alendronate and calcitonin on bone in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Clin. Biochem. 2005, 38, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, D.J.; Spector, T.D. The role of bone metabolism in osteoarthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2003, 5, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relea, P.; Revilla, M.; Ripoll, E.; Arribas, I.; Villa, L.F.; Rico, H. Zinc, biochemical markers of nutrition, and type I osteoporosis. Age Ageing 1995, 24, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florencio-Silva, R.; Sasso, G.R.; Sasso-Cerri, E.; Simoes, M.J.; Cerri, P.S. Biology of Bone Tissue: Structure, Function, and Factors That Influence Bone Cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 421746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano-Lopes, J.; Canhao, H.; Fonseca, J.E. Osteoblasts and bone formation. Acta Reumatol. Port. 2007, 32, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Franz-Odendaal, T.A.; Hall, B.K.; Witten, P.E. Buried alive: How osteoblasts become osteocytes. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 2006, 235, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.L.; Kumbar, S.G.; Laurencin, C.T. Chapter II.6.7—Bone Tissue Engineering. In Biomaterials Science, 3rd ed.; Ratner, B.D., Hoffman, A.S., Schoen, F.J., Lemons, J.E., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 1194–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Potts, J.T.; Gardella, T.J. Chapter 6—Parathyroid Hormone and Calcium Homeostasis. In Pediatric Bone, 2nd ed.; Glorieux, F.H., Pettifor, J.M., Jüppner, H., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 109–140. [Google Scholar]
- Teitelbaum, S.L. Bone resorption by osteoclasts. Science 2000, 289, 1504–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagiri, T.; Takahashi, N. Regulatory mechanisms of osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation. Oral Dis. 2002, 8, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkiraju, H.; Nohe, A. Role of Chondrocytes in Cartilage Formation, Progression of Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Regeneration. J. Dev. Biol. 2015, 3, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bab, I.; Smoum, R.; Bradshaw, H.; Mechoulam, R. Skeletal lipidomics: Regulation of bone metabolism by fatty acid amide family. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.H.; Guo, L.J.; Yuan, L.Q.; Xie, H.; Zhou, H.D.; Wu, X.P.; Liao, E.Y. Adiponectin stimulates human osteoblasts proliferation and differentiation via the MAPK signaling pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2005, 309, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, B.L. The mechanisms of estrogen regulation of bone resorption. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 1203–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taichman, R.S. Blood and bone: Two tissues whose fates are intertwined to create the hematopoietic stem-cell niche. Blood 2005, 105, 2631–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploysangam, A.; Falciglia, G.A.; Brehm, B.J. Effect of marginal zinc deficiency on human growth and development. J. Trop. Pediatrics 1997, 43, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, N.F. Dietary zinc and iron sources, physical growth and cognitive development of breastfed infants. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 358s–360s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Li, D. Zinc and Zinc Transporters: Novel Regulators of Ventricular Myocardial Development. Pediatric Cardiol. 2018, 39, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambe, T.; Tsuji, T.; Hashimoto, A.; Itsumura, N. The Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Roles of Zinc Transporters in Zinc Homeostasis and Metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 749–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M. Role of zinc in bone formation and bone resorption. J. Trace Elem. Exp. Med. 1998, 11, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M. Role of nutritional zinc in the prevention of osteoporosis. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 338, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haumont, S. Distribution of zinc in bone tissue. J. Histochem. Cytochem. Off. J. Histochem. Soc. 1961, 9, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappalainen, R.; Knuuttila, M.; Lammi, S.; Alhava, E.M. Fluoride content related to the elemental composition, mineral density and strength of bone in healthy and chronically diseased persons. J. Chronic Dis. 1983, 36, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, E.J.; Messer, H.H. Turnover of bone zinc during normal and accelerated bone loss in rats. J. Nutr. 1981, 111, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, G.R. Distribution of zinc in the avian growth plate. J. Bone Min. Res. 1990, 5, 162. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.C.; Wein, M.N.; Oukka, M.; Hofstaetter, J.G.; Glimcher, M.J.; Glimcher, L.H. Regulation of adult bone mass by the zinc finger adapter protein Schnurri-3. Science 2006, 312, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, E.; Kiviranta, R.; Wu, M.; Saito, H.; Yamana, K.; Correa, D.; Atfi, A.; Baron, R. Zinc finger protein 521, a new player in bone formation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1192, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, S.; Yamauchi, M.; Wakisaka, S.; Ooshima, T.; Amano, A. Zinc-finger transcription factor odd-skipped related 2 is one of the regulators in osteoblast proliferation and bone formation. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2007, 22, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Zhou, X.; Kunkel, G.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, J.M.; Behringer, R.R.; de Crombrugghe, B. The novel zinc finger-containing transcription factor osterix is required for osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Cell 2002, 108, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Kambe, T. The Functions of Metallothionein and ZIP and ZnT Transporters: An Overview and Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagishi, T.; Hara, T.; Fukada, T. Recent Advances in the Role of SLC39A/ZIP Zinc Transporters In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.; Eide, D.J. The SLC39 family of zinc transporters. Mol. Aspects Med. 2013, 34, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; Fellner, M.; Zhang, C.; Sui, D.; Hu, J. Crystal structures of a ZIP zinc transporter reveal a binuclear metal center in the transport pathway. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Fu, D. Structure of the zinc transporter YiiP. Science 2007, 317, 1746–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Goto, M.; Uchiyama, S.; Nakagawa, T. Effect of zinc on gene expression in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells: Enhancement of Runx2, OPG, and regucalcin mRNA expressions. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 312, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Sahu, S.N.; Khadeer, M.A.; Bai, G.; Franklin, R.B.; Gupta, A. Overexpression of the ZIP1 zinc transporter induces an osteogenic phenotype in mesenchymal stem cells. Bone 2006, 38, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, T.; Yu, Z.; Ma, K.; Yang, M.; Liu, Q.; Pan, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; et al. Runx2/Osterix and Zinc Uptake Synergize to Orchestrate Osteogenic Differentiation and Citrate Containing Bone Apatite Formation. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufner-Beattie, J.; Huang, Z.L.; Geiser, J.; Xu, W.; Andrews, G.K. Mouse ZIP1 and ZIP3 genes together are essential for adaptation to dietary zinc deficiency during pregnancy. Genesis 2006, 44, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambe, T.; Geiser, J.; Lahner, B.; Salt, D.E.; Andrews, G.K. Slc39a1 to 3 (subfamily II) Zip genes in mice have unique cell-specific functions during adaptation to zinc deficiency. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 294, R1474–R1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brommage, R.; Liu, J.; Hansen, G.M.; Kirkpatrick, L.L.; Potter, D.G.; Sands, A.T.; Zambrowicz, B.; Powell, D.R.; Vogel, P. High-throughput screening of mouse gene knockouts identifies established and novel skeletal phenotypes. Bone Res. 2014, 2, 14034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, K.; Wan, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L. Zip1, Zip2, and Zip8 mRNA expressions were associated with growth hormone level during the growth hormone provocation test in children with short stature. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 155, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jeon, J.; Shin, M.; Won, Y.; Lee, M.; Kwak, J.S.; Lee, G.; Rhee, J.; Ryu, J.H.; Chun, C.H.; et al. Regulation of the catabolic cascade in osteoarthritis by the zinc-ZIP8-MTF1 axis. Cell 2014, 156, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Kim, D.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, M.S.; Chun, C.-H.; Jin, E.-J. MicroRNA-488 regulates zinc transporter SLC39A8/ZIP8 during pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. J. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 20, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, V.B. Osteoarthritis: The zinc link. Nature 2014, 507, 441–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Won, Y.; Shin, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Chun, J.S. Reciprocal activation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-2alpha and the zinc-ZIP8-MTF1 axis amplifies catabolic signaling in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giunta, C.; Elcioglu, N.H.; Albrecht, B.; Eich, G.; Chambaz, C.; Janecke, A.R.; Yeowell, H.; Weis, M.; Eyre, D.R.; Kraenzlin, M.; et al. Spondylocheiro dysplastic form of the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome--an autosomal-recessive entity caused by mutations in the zinc transporter gene SLC39A13. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 82, 1290–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukada, T.; Civic, N.; Furuichi, T.; Shimoda, S.; Mishima, K.; Higashiyama, H.; Idaira, Y.; Asada, Y.; Kitamura, H.; Yamasaki, S.; et al. The zinc transporter SLC39A13/ZIP13 is required for connective tissue development; its involvement in BMP/TGF-beta signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S.; Tsukamoto, M.; Saito, M.; Hojyo, S.; Fukada, T.; Takami, M.; Furuichi, T. Disruption of the mouse Slc39a14 gene encoding zinc transporter ZIP14 is associated with decreased bone mass, likely caused by enhanced bone resorption. FEBS Open Bio. 2018, 8, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojyo, S.; Fukada, T.; Shimoda, S.; Ohashi, W.; Bin, B.H.; Koseki, H.; Hirano, T. The zinc transporter SLC39A14/ZIP14 controls G-protein coupled receptor-mediated signaling required for systemic growth. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickx, G.; Borra, V.M.; Steenackers, E.; Yorgan, T.A.; Hermans, C.; Boudin, E.; Waterval, J.J.; Jansen, I.D.C.; Aydemir, T.B.; Kamerling, N.; et al. Conditional mouse models support the role of SLC39A14 (ZIP14) in Hyperostosis Cranialis Interna and in bone homeostasis. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Matsuda, K.; Itoh, M.; Kawaguchi, H.; Tomoike, H.; Aoyagi, T.; Nagai, R.; Hori, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Tanaka, T. Osteopenia and male-specific sudden cardiac death in mice lacking a zinc transporter gene, Znt5. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002, 11, 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, F.; Yang, W.L.; Lu, X.F.; Wang, W.B. Effects of zinc transporter on differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to osteoblasts. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 154, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Xiang, L.; Yang, M.; Zhang, X.; Guo, B.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Cao, J. ZnT7 can protect MC3T3-E1 cells from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerinot, M.L. The ZIP family of metal transporters. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2000, 1465, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotz, N.; Fox, T.; Connolly, E.; Park, W.; Guerinot, M.L.; Eide, D. Identification of a family of zinc transporter genes from Arabidopsis that respond to zinc deficiency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7220–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lioumi, M.; Ferguson, C.A.; Sharpe, P.T.; Freeman, T.; Marenholz, I.; Mischke, D.; Heizmann, C.; Ragoussis, J. Isolation and characterization of human and mouse ZIRTL, a member of the IRT1 family of transporters, mapping within the epidermal differentiation complex. Genomics 1999, 62, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, L.C.; Chellaiah, M.A.; Zou, J.; Reynolds, M.A.; Franklin, R.B. In vitro BMP2 stimulation of osteoblast citrate production in concert with mineralized bone nodule formation. J. Regen. Med. Tissue Eng. 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, R.B.; Chellaiah, M.; Zou, J.; Reynolds, M.A.; Costello, L.C. Evidence that Osteoblasts are Specialized Citrate-producing Cells that Provide the Citrate for Incorporation into the Structure of Bone. Open Bone J. 2014, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Khadeer, M.A.; Sahu, S.N.; Bai, G.; Abdulla, S.; Gupta, A. Expression of the zinc transporter ZIP1 in osteoclasts. Bone 2005, 37, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkitkasemwong, S.; Wang, C.Y.; Mackenzie, B.; Knutson, M.D. Physiologic implications of metal-ion transport by ZIP14 and ZIP8. Biomet. Int. J. Role Met. Ions Biol. Biochem. Med. 2012, 25, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydemir, T.B.; Liuzzi, J.P.; McClellan, S.; Cousins, R.J. Zinc transporter ZIP8 (SLC39A8) and zinc influence IFN-gamma expression in activated human T cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Elnabawi, O.; Shin, D.; Pae, E.K. Transient Intermittent Hypoxia Exposure Disrupts Neonatal Bone Strength. Front. Pediatrics 2016, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, C.M.; Shea, S.A.; Stone, K.L.; Cauley, J.A.; Rosen, C.J.; Redline, S.; Karsenty, G.; Orwoll, E.S. Obstructive sleep apnea and metabolic bone disease: Insights into the relationship between bone and sleep. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2015, 30, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pae, E.K.; Kim, G. Insulin production hampered by intermittent hypoxia via impaired zinc homeostasis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.C.; Jackson, M.T.; Smith, M.M.; Smith, S.M.; Penm, S.; Lord, M.S.; Whitelock, J.M.; Little, C.B.; Melrose, J. Ablation of Perlecan Domain 1 Heparan Sulfate Reduces Progressive Cartilage Degradation, Synovitis, and Osteophyte Size in a Preclinical Model of Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 868–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaventura, P.; Lamboux, A.; Albarede, F.; Miossec, P. A Feedback Loop between Inflammation and Zn Uptake. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu-Bryan, R.; Terkeltaub, R. Emerging regulators of the inflammatory process in osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.S.; Chun, J.S. Upregulation of lipocalin-2 (LCN2) in osteoarthritic cartilage is not necessary for cartilage destruction in mice. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2017, 25, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.A.; Simon, M.C. Biology of hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha in development and disease. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin, B.H.; Fukada, T.; Hosaka, T.; Yamasaki, S.; Ohashi, W.; Hojyo, S.; Miyai, T.; Nishida, K.; Yokoyama, S.; Hirano, T. Biochemical characterization of human ZIP13 protein: A homo-dimerized zinc transporter involved in the spondylocheiro dysplastic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 40255–40265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.G.; Bin, B.H. Different Actions of Intracellular Zinc Transporters ZIP7 and ZIP13 Are Essential for Dermal Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.; Walker, J.M.; Wang, F.; Park, J.G.; Palmer, A.E.; Giunta, C.; Rohrbach, M.; Steinmann, B.; Eide, D.J. Promotion of vesicular zinc efflux by ZIP13 and its implications for spondylocheiro dysplastic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E3530–E3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusanic, M.; Dekomien, G.; Lucke, T.; Vorgerd, M.; Weis, J.; Epplen, J.T.; Kohler, C.; Hoffjan, S. Novel Nonsense Mutation in SLC39A13 Initially Presenting as Myopathy: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Mol. Syndromol. 2018, 9, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin, B.H.; Hojyo, S.; Hosaka, T.; Bhin, J.; Kano, H.; Miyai, T.; Ikeda, M.; Kimura-Someya, T.; Shirouzu, M.; Cho, E.G.; et al. Molecular pathogenesis of spondylocheirodysplastic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome caused by mutant ZIP13 proteins. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 1028–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, B.H.; Bhin, J.; Seo, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, E.; Park, K.; Choi, D.H.; Takagishi, T.; Hara, T.; Hwang, D.; et al. Requirement of Zinc Transporter SLC39A7/ZIP7 for Dermal Development to Fine-Tune Endoplasmic Reticulum Function by Regulating Protein Disulfide Isomerase. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1682–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambidge, K.M.; Krebs, N.F. Zinc deficiency: A special challenge. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambidge, M. Human zinc deficiency. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1344s–1349s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Deng, C.; Li, Y.P. TGF-beta and BMP signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, B.H.; Hojyo, S.; Ryong Lee, T.; Fukada, T. Spondylocheirodysplastic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (SCD-EDS) and the mutant zinc transporter ZIP13. Rare Dis. 2014, 2, e974982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Gao, J.; Enns, C.A.; Knutson, M.D. ZRT/IRT-like protein 14 (ZIP14) promotes the cellular assimilation of iron from transferrin. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 32141–32150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Y.; Jenkitkasemwong, S.; Duarte, S.; Sparkman, B.K.; Shawki, A.; Mackenzie, B.; Knutson, M.D. ZIP8 is an iron and zinc transporter whose cell-surface expression is up-regulated by cellular iron loading. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 34032–34043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liuzzi, J.P.; Aydemir, F.; Nam, H.; Knutson, M.D.; Cousins, R.J. Zip14 (Slc39a14) mediates non-transferrin-bound iron uptake into cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13612–13617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydemir, T.B.; Troche, C.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.H.; Teran, O.Y.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Cousins, R.J. Aging amplifies multiple phenotypic defects in mice with zinc transporter Zip14 (Slc39a14) deletion. Exp. Gerontol. 2016, 85, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, J.J.; Scaf, J.J.; Huygen, P.L.; Cruysberg, J.R.; Verhagen, W.I. Hyperostosis cranialis interna. A new hereditary syndrome with cranial-nerve entrapment. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmiter, R.D.; Huang, L. Efflux and compartmentalization of zinc by members of the SLC30 family of solute carriers. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2004, 447, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambe, T.; Narita, H.; Yamaguchi-Iwai, Y.; Hirose, J.; Amano, T.; Sugiura, N.; Sasaki, R.; Mori, K.; Iwanaga, T.; Nagao, M. Cloning and characterization of a novel mammalian zinc transporter, zinc transporter 5, abundantly expressed in pancreatic beta cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 19049–19055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschke, C.P.; Huang, L. ZnT7, a novel mammalian zinc transporter, accumulates zinc in the Golgi apparatus. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 4096–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Ishihara, K.; Migaki, H.; Matsuura, W.; Kohda, A.; Okumura, K.; Nagao, M.; Yamaguchi-Iwai, Y.; Kambe, T. Zinc transporters, ZnT5 and ZnT7, are required for the activation of alkaline phosphatases, zinc-requiring enzymes that are glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored to the cytoplasmic membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Ishihara, K.; Migaki, H.; Ishihara, K.; Nagao, M.; Yamaguchi-Iwai, Y.; Kambe, T. Two different zinc transport complexes of cation diffusion facilitator proteins localized in the secretory pathway operate to activate alkaline phosphatases in vertebrate cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 30956–30962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedde, K.N.; Blair, L.; Silverstein, J.; Coburn, S.P.; Ryan, L.M.; Weinstein, R.S.; Waymire, K.; Narisawa, S.; Millan, J.L.; MacGregor, G.R.; et al. Alkaline phosphatase knock-out mice recapitulate the metabolic and skeletal defects of infantile hypophosphatasia. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 1999, 14, 2015–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukada, T.; Kambe, T. Welcome to the World of Zinc Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levaot, N.; Hershfinkel, M. How cellular Zn2+ signaling drives physiological functions. Cell Calcium 2018, 75, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).