- 3.0Impact Factor
- 6.0CiteScore
- 20 daysTime to First Decision
The Impacts of Human Activities on the Functional Ecology of Coastal Microbial Communities
This special issue belongs to the section “Oceans and Coastal Zones“.
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
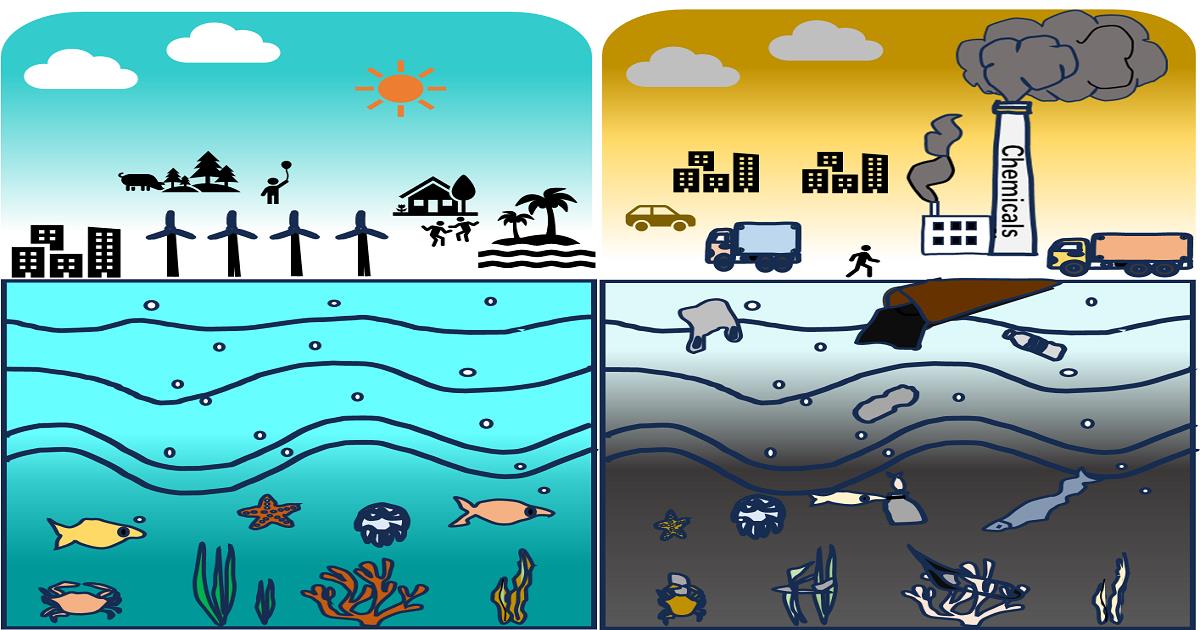
Marine microorganisms are fundamental to the health and sustainability of marine ecosystems, playing essential roles in nutrient cycling, carbon sequestration, and supporting biodiversity. However, the accelerating pace of human activities, such as industrial pollution, agricultural runoff, overfishing, climate change, and coastal development, is increasingly disrupting these vital microbial communities' diversity, structure, and functionality. These disruptions pose significant risks to marine ecological balance and these microorganisms' services, including biogeochemical cycling and environmental protection.
This Special Issue, entitled “The Impacts of Human Activities on the Functional Ecology of Coastal Microbial Communities", aims to address how anthropogenic influences affect microbial diversity and the broader marine ecological environment. It will explore the impact of pollutants, habitat loss, eutrophication, and climate-driven changes on microbial ecosystems from coastal areas to the deep ocean. Additionally, it seeks to highlight the role of new technologies, such as metagenomics, metatranscriptomics, single-cell genomics, and ecological modeling, in advancing our understanding of marine microbial dynamics. Contributions focusing on how human-induced changes in marine environments can be mitigated are encouraged. This Special Issue welcomes original research articles, reviews, and perspectives that provide novel insights into these pressing issues.
Dr. Qiuzhen Wang
Dr. Xinlong An
Prof. Dr. Guangyi Wang
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Water is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- human activities
- microbial communities
- marine pollution
- marine conservation
- climate change
- eutrophication
- metagenomics
- coastal ecosystems
- marine ecological balance
- deep sea
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- e-Book format: Special Issues with more than 10 articles can be published as dedicated e-books, ensuring wide and rapid dissemination.

