- Article
Dose-Dependent Effect of Foliar ZnO Nanoparticles on the Physiology, Mineral Nutrition, and Redox Status of Coffea arabica Seedlings Under Soil Acidity
- Amilcar Valle-Lopez,
- Jegnes Benjamín Meléndez-Mori and
- Eyner Huaman
- + 1 author
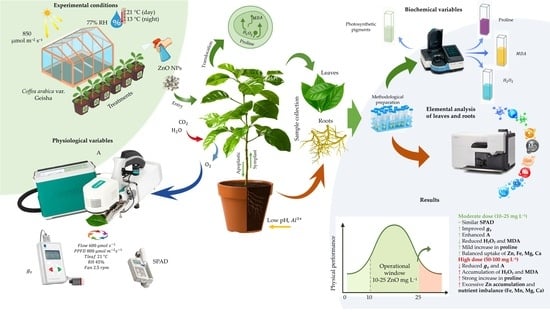
Soil acidity severely constrains coffee production by reducing nutrient availability and promoting aluminum toxicity and oxidative stress. Foliar zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) have been proposed as redox modulators that can improve nutrient homeostasis under abiotic stress. However, the safe and effective range of Coffea arabica L. remains unclear. In this study, seedlings were grown in acidic soil and sprayed twice with ZnO NPs at 10, 25, 50, and 100 mg L−1. Morphophysiological, biochemical, and ionomic parameters were evaluated fifty days after treatment. Moderate ZnO NPs doses led to intermediate stomatal conductance values, whereas net photosynthesis showed intermediate but non-significant responses only at 10–25 mg L−1, with higher doses (50–100 mg L−1) causing a marked decline. These doses did not significantly modify hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) or malondialdehyde (MDA) levels in leaves or roots. In contrast, the highest dose (100 mg L−1) induced a marked increase in H2O2 without affecting MDA, indicating a partial oxidative response rather than clear lipid peroxidation. Foliar analysis showed that 50 mg L−1 ZnO NPs significantly increased P compared with the optimal soil, while Ca and K remained statistically similar across treatments. Na in the optimal soil was comparable to the 10–25 mg L−1 ZnO NPs treatments, whereas Na at 50–100 mg L−1 ZnO NPs was significantly reduced and foliar Zn increased markedly with increasing nanoparticle dose. Proline accumulation reflected a dose-dependent osmotic adjustment, and chlorophyll ratios indicated adaptive photoprotection. Overall, foliar ZnO NPs mitigated acidity-induced stress through physiological and ionomic adjustment, with 10–25 mg L−1 identified as the physiologically safe range for C. arabica seedlings grown under acidic conditions.
10 December 2025