- Article
Human–AI Complementarity in Peer Review: Empirical Analysis of PeerJ Data and Design of an Efficient Collaborative Review Framework
- Zhihe Yang,
- Xiaoyu Zhou and
- Yuxin Jiang
- + 4 authors
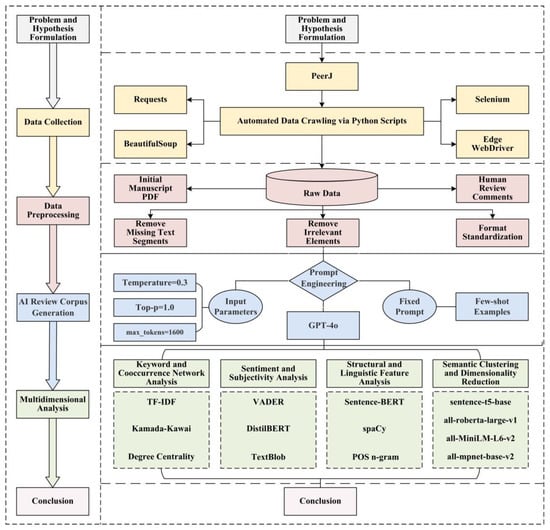
In response to the persistent imbalance between the rapid expansion of scholarly publishing and the constrained availability of qualified reviewers, an empirical investigation was conducted to examine the feasibility and boundary conditions of employing Large Language Models (LLMs) in journal peer review. A parallel corpus of 493 pairs of human expert reviews and GPT-4o-generated reviews was constructed from the open peer-review platform PeerJ Computer Science. Analytical techniques, including keyword co-occurrence analysis, sentiment and subjectivity assessment, syntactic complexity measurement, and n-gram distributional entropy analysis, were applied to compare cognitive patterns, evaluative tendencies, and thematic coverage between human and AI reviewers. The results indicate that human and AI reviews exhibit complementary functional orientations. Human reviewers were observed to provide integrative and socially contextualized evaluations, while AI reviews emphasized structural verification and internal consistency, especially regarding the correspondence between abstracts and main texts. Contrary to the assumption of excessive leniency, GPT-4o-generated reviews demonstrated higher critical density and functional rigor, maintaining substantial topical alignment with human feedback. Based on these findings, a collaborative human–AI review framework is proposed, in which AI systems are positioned as analytical assistants that conduct structured verification prior to expert evaluation. Such integration is expected to enhance the efficiency, consistency, and transparency of the peer-review process and to promote the sustainable development of scholarly communication.
19 December 2025