- Article
Inhibitory Effects of Hydrogen Peroxide on Prorocentrum donghaiense Lu Under Varying Light Conditions and Iron Ion Environments
- Pengyu Liang,
- Ziqing Zhong and
- Qilin Zheng
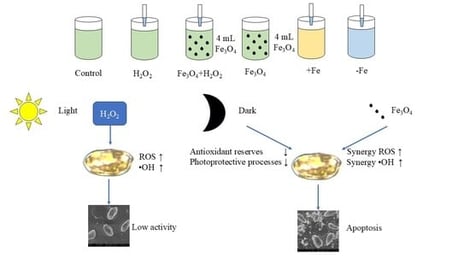
Light and antioxidant systems play a crucial role in the life activities of algal cells. This study investigates the algicidal efficacy of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) against the harmful algal bloom (HAB)-forming dinoflagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense Lu, with a focus on the modulating roles of light conditions and iron ion environments. Within 180 min, dark-adapted cells showed 78% greater viability loss than light-exposed ones, and Fe3O4 nanoparticles synergistically enhanced H2O2 inhibition. Imaging and cytometry confirmed cell damage, including membrane rupture. Mechanistically, H2O2 penetrated cells, induced severe oxidative stress, suppressed photosynthesis, and compromised membrane integrity. Darkness likely exacerbated toxicity by depleting antioxidant reserves. This study elucidates an apoptosis-like pathway underlying H2O2-induced cell death and highlights the critical influence of ambient light on treatment efficiency. These findings reveal an apoptosis-like death pathway and highlight ambient light’s critical role, suggesting that optimized nighttime H2O2 application with nanomaterial synergists could improve HAB control strategies.
2 February 2026