Abstract
Colaconema daviesii has been described as an epi-endophyte of red algae. However, it has also been observed in vitro to colonize thalli of Macrocystis pyrifera, a giant kelp classified as a foundational organism of coastal marine ecosystems. This study aimed to determine, through co-cultivations, how C. daviesii affects the early stages of M. pyrifera, specifically gametophyte and sporophyte development. Determined were growth, oogonia formation, and gametophyte fertility, as well as sporophyte growth rate and survival. The results showed that the presence of C. daviesii negatively altered oogonia production and gametophyte fertility. Moreover, the survival of young sporophytes in co-cultures decreased. These findings demonstrate that the early developmental stages of M. pyrifera could be susceptible to infestation by a filamentous red alga, with negative consequences on fitness.
1. Introduction
In recent years, species from the genus Colaconema have been reported in different regions of the world as filamentous endophytes associated with commercially related red algae species. This includes Colaconema infestans in Brazil, found on Kappaphycus alvarezii thalli [1], and Colaconema formosanum in Taiwan, infecting Sarcodia suae [2]. In Chile, studies report Colaconema daviesii growing epi-endophytically on the thalli of the edible seaweed Chondracanthus chamissoi [3,4], marking the first record of C. daviessi in the southeastern Pacific. In all cases, the presence of Colaconema species negatively affects host fitness, causing severe morphological damage [1,2,3]. In addition to discoloration and thalli breakage, culture loss can occur. Therefore, producers worldwide have concerns about the impacts that endophytic and epiphytic algae exert on commercially important seaweeds [5,6]. These relationships can particularly affect the production of quality biomass, which has the potential to cause negative economic consequences [7].
In the case of C. daviesii, infestation on C. chamissoi is mediated through monospores, with a rapid development of filaments on host thalli, negatively affecting growth and survival [4]. Moreover, this species has been reported on different organisms, being found in association with brown algae, seagrasses, and invertebrates [8,9,10], suggesting that it might have a broad host spectrum. This idea has been reinforced through observations made by our laboratory; presumably due to cross-contamination, C. daviesii filaments grew under indoor cultivation conditions on sporophytes (1–3 cm) of Macrocystis pyrifera, resulting in loss of the young kelps. Another study reported contamination by C. cf. infestans of a land-based Asparagopsis taxiformis cultivation, which impacted productivity and product quality [11]. This evidence demonstrates the potential for Colaconema species to pose a significant threat to seaweed aquaculture, even in controlled environments.
There are currently several efforts to consolidate the commercial cultivation of C. chamissoi along the South Pacific coast [12,13]. The preferred cultivation technologies are based on the fragmentation of thalli obtained directly from donor populations and transference to different cultivation areas along the coasts of Chile and Peru [12,13,14,15]. Considering the report by [4], where C. chamissoi-infested thalli showed no obvious early signs of C. daviesii presence, these translocations may represent a potential vector for the transfer of this epi-endophyte alga.
Alerts as to the scarce biosecurity measures in aquaculture have been raised, especially in the case of seaweeds, where a lack of knowledge and regulation represents a risk to the industry [16]. The movement of cultivated seaweeds without quarantine measures could facilitate the proliferation of harmful epiphytes/endophytes, diseases, and pests, either within crops or into local seaweed populations [17]. For this reason, the scientific community views epiphytes and endophytes as an emerging threat to the conservation of community-structuring species such as kelps [18], which are recognized for having long and flexible fronds and for playing a crucial role in coastal marine ecosystems worldwide [19,20,21]. Indeed, kelps influence the availability of light, substrate, and food, and are fundamental in the carbon cycle [22,23], oxygen production, and the biogeochemical balance of the planet [24]. However, kelp forests face various threats, such as overgrazing, pollution, overexploitation, and climate change [17,23,25,26,27].
To date, relationships with and the potential negative effects of endophytes and epiphytes or pathogens have primarily focused on the macroscopic phases of brow-algae life cycles [17,28,29,30,31], with abundant reports worldwide and in different kelp species [17,32]. Few cases have demonstrated the susceptibility of kelp gametophytes/early sporophytes to invasion by endophytes and pathogens [33,34,35,36], and only in very few instances have the consequences of such interactions been evidenced. Malformations, such as calluses, inflammations in the cortex, and tissue discoloration, can exist in young sporophytes of Nereocystis, Macrocystis, and Laminaria when infected by filaments of the endophytic alga Streblonema spp. [37]. Similarly, ref. [33] reported that the pathogens Eurychasma dicksonii and Quitridio polysiphoniae can infect juvenile sporophytes of various brown algae species, leading to thalli death.
There is no doubt about the importance of gametophytes and the early stages of development for the persistence of kelp forests, and projected environmental changes in the future ocean appear to be potential threats to gametogenesis and sporophyte development [23]. However, almost nothing is known about the positive or negative interactions of the early developmental stages of kelps with epiphytic/endophytic algae or pathogens [33]. These could become another threat to kelp conservation, especially considering that these interactions are expected to become more frequent and the consequences more severe in the future [25].
The present study explored the effects of the filamentous alga C. daviesii, recognized as an aggressive endophyte [3,4], on the early developmental stages of M. pyrifera. Through co-cultivation experiments of M. pyrifera in the presence of C. daviesii, we evaluated impacts to gametophyte oogonia formation, fertility, and growth, in addition to the growth and survival of juvenile sporophytes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture Preparation
Biological material was collected in September 2023 from Algarrobo (33°21′38″ S 71°40′5″ W) in central Chile. Sporophylls with sori of M. pyrifera were obtained and treated according to previously reported protocols [27]. At the same collection site, the sori were separated and washed with a 9% iodine solution dissolved in seawater and then cleaned with 5% alcohol. The sori were transported in a cooler at 10 °C to the Laboratorio de Estudio y Producción de Algas Marinas located in Santiago, Chile. After a partial dehydration period of three hours, the sori were cut into 2 cm2 pieces, and five pieces were introduced into two airtight plastic containers with 250 mL of filtered seawater (1 µm) enriched with the Von Stoch medium (4 mL/L) for the release of spores. After 48 h, the sori pieces were removed, and the spores were cultivated in the containers until the formation of gametophytes, with maintenance under a L:D photoperiod of 12:12 h, a temperature of 16 °C, and a photon flux density of 40 µmol m−2 s−1; the culture medium was renewed every five days. Daily monitoring was carried out to observe gametophyte development. After 12 to 15 days, differentiation between male and female gametophytes was possible, and after 20 days, the first sporophytes appeared. This biological material was used for all subsequent experiments.
In the case of C. daviesii, a permanent culture has existed in our laboratory since isolation and molecular identification four years ago [3,4]. For the present study, two 8 L containers of filtered seawater (1 µm) were maintained under controlled conditions of 16 °C, a photon flux density of 40 µmol m−2 s−1, a L:D photoperiod of 12:12 h, and a density of 1 g L−1. The seawater was renewed weekly, and filaments of C. daviesii were collected to confirm the presence of filaments with monospores (Figure 1), as previously described [3].
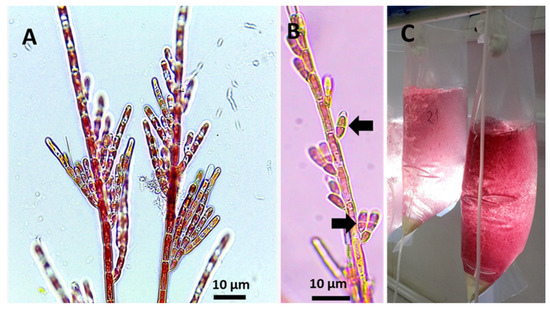
Figure 1.
(A): Filaments of C. daviesii cultivated in vitro. (B): Reproductive thalli of C. daviesii with the formation of monosporangia (arrows), and (C): Filaments of C. daviesii maintained in culture column systems providing the biological stocks used for experiments.
2.2. Co-Cultivation Experiments
To evaluate the growth rate, oogonium formation, and fertility of M. pyrifera gametophytes in the presence of C. daviesii, an experiment was conducted consisting of control and co-culture treatments, with each including five 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks. Each flask was filled with 100 mL of filtered seawater (1 μm) enriched with the von Stosch culture medium (4 mL/L). The cultivation conditions were the same as those previously described for the maintenance of the C. daviesii and M. pyrifera cultures. The seawater and culture media were replaced every 5 days, and the experiments lasted 21 days. A solution containing gametophytes was added to both the control and co-culture treatments, ensuring a final concentration in each container of 1000 gametophytes mL−1. For the co-culture treatment, 0.1 g of C. daviesii filaments exhibiting monospores were added. Aeration was provided through bubbling to all containers in both treatments, thus keeping the cultures in suspension.
2.3. Data Collection
Gametophyte growth rate was determined by taking 1 mL aliquots from each container of the control and co-culture treatments at the start of the experiment and then on day 21. From each sample, images of 20 randomly chosen female gametophytes were captured and analyzed with the ImageJ software v1.53. Then, the area (µm2) of the gametophytes was calculated. The growth rate was calculated using the following formula:
where A1 is the final area (µm2), A0 is the initial area (µm2), and t is the time in days.
Oogonium formation in female gametophytes was quantified at day 15. For this, 1 mL aliquots were obtained and observed under an inverted field microscope. The results were expressed as the percentage of female gametophytes containing oogonia relative to the total number of female gametophytes found in three fields of observation.
Fertility was recorded on day 21. For this, 1 mL aliquots were obtained and observed under an inverted field microscope, and the number of sporophytes and available female gametophytes was counted using the following expression:
To evaluate the growth rate and survival of M. pyrifera sporophytes in the presence of C. daviesii, another experiment was conducted with control and co-culture treatments. Each group comprised five Erlenmeyer flasks containing 400 mL of filtered seawater (1 μm) enriched with the von Stosch medium (8 mL/L). In this experiment, the concentration of the von Stosch culture medium was increased, using the recommended 100% (8 mL/L) for seawater enrichment. This was performed with the aim of preventing a drop in available nutrients. Sporophytes ranging from 1 to 4 mm in length were selected from stock cultures, and 30 sporophytes were added to each flask in both the control and co-culture treatments. As with the previous experiment, C. daviesii filaments (0.1 g; reproductive and monospore containing) were added to the co-culture treatment. To evaluate growth, five sporophytes were randomly selected from each culture container at the start of the experiment and on day 35. These were photographed, and the growth rate was calculated as described before.
Sporophyte survival was expressed as the percentage of living thalli at the end of the experiment with respect to the initial number of inoculated thalli. Thalli with up to 60% of the surface showing signs of necrosis, discoloration, and detachment of biomass were considered dead.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
To evaluate the effect of the control and co-culture treatments on the growth rate, oogonium formation, and fertility of gametophytes, as well as the growth rate and survival of sporophytes, a t-test was conducted for two paired samples.
3. Results
During the cultivation period, gametophytes grew and formed oogonia that were fertilized to form early sporophytes, both in the control and co-culture treatments. However, in the co-culture treatment, both the gametophytes and early sporophytes exhibited depigmentation and, in some cases, cellular rupturing and content loss (Figure 2A,B). In the control treatment gametophytes and early sporophytes with the typical pigmentation were observed, without showing any damage or loss of cellular content (Figure 2C,D). Regarding the co-culture, it was noted that small filaments of C. daviesii developed from spores attached to both early sporophytes (Figure 2E) and gametophytes (Figure 2F) of M. pyrifera. Similarly, C. daviesii filaments on young sporophyte fronds were observed.
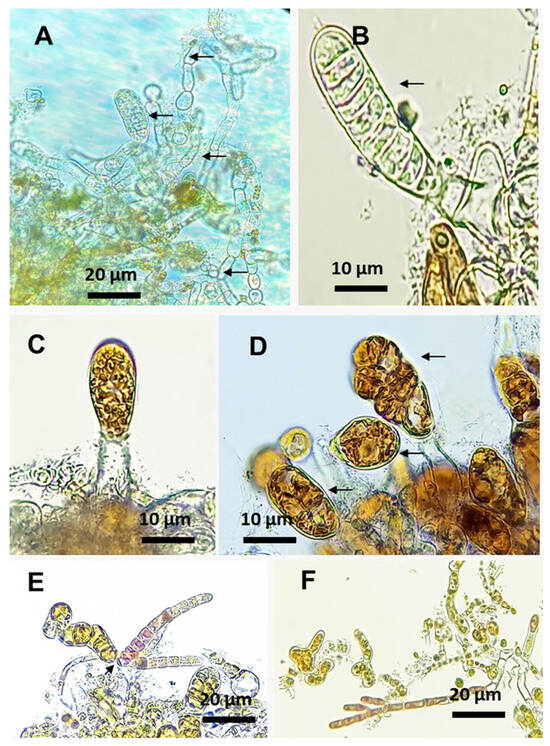
Figure 2.
M. pyrifera gametophytes after 21 days of cultivation. (A,B): M. pyrifera gametophytes and sporophytes showing depigmentation (arrows) when maintained in co-culture. (C,D): Control treatment with M. pyrifera sporophytes (arrows). (E,F): Co-culture with C. daviesii filaments attached to early sporophytes (arrow) and gametophytes, respectively.
The growth rate of the gametophytes in the control treatment and the co-culture were not different (t-test; p = 0.958), reaching 1.86 ± 0.89% d−1 and 1.87 ± 0.99% d−1, respectively (Figure 3A). Oogonium formation showed a difference between the control group and the co-culture. In the control treatment, 64.39 ± 10.02% of the gametophytes presented oogonium formation, while in the co-culture, a lower value of 41.36 ± 10% was recorded (Figure 3B). This difference was statistically significant (t-test: p = 0.003). Fertility was also different (t-test; p = 0.001589) between both groups (Figure 3C). The control treatment exhibited a fertility of 24.99 ± 4.76%, higher than that of the co-culture, which was 15.69 ± 3.44%.
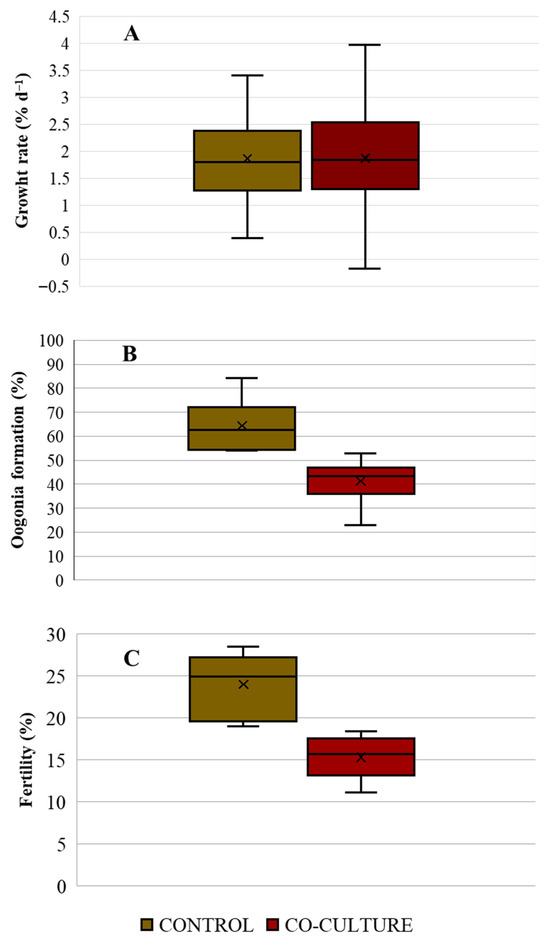
Figure 3.
(A): Growth rate (% d−1) of gametophytes; (B): Oogonium formation (%); and (C) Fertility (%) of M. pyrifera gametophytes maintained under control (brown) and C. daviesii co-culture (red) treatments (n = 5).
After 35 days of cultivation, depigmentation symptoms were observed in the young sporophytes of M. pyrifera maintained in co-culture (Figure 4A), along with the loss of thallus fragments. On the other hand, the control treatment presented healthy sporophytes with the characteristic brown pigmentation of the species (Figure 4B).

Figure 4.
Petri dishes showing sporophytes of M. pyrifera after 35 days of cultivation. (A): Depigmented thalli with tissue loss from the co-culture treatment. (B): Thalli of M. pyrifera grown in the control treatment with healthy sporophytes and the characteristic brown pigmentation.
The growth rate of M. pyrifera sporophytes in the control and co-culture treatments slightly differed, with maximum values of 7.44 ± 2.09% d−1 and 6.68 ± 2.24% d−1, respectively (Figure 5A). However, this difference was not significant (t-test; p = 0.177). In contrast, the survival of M. pyrifera sporophytes from the control treatment was higher (80 ± 17.8%) than that recorded in the co-culture (34.6 ± 8.7%) (Figure 5B). This difference was statistically significant (t-test; p = 0.01).
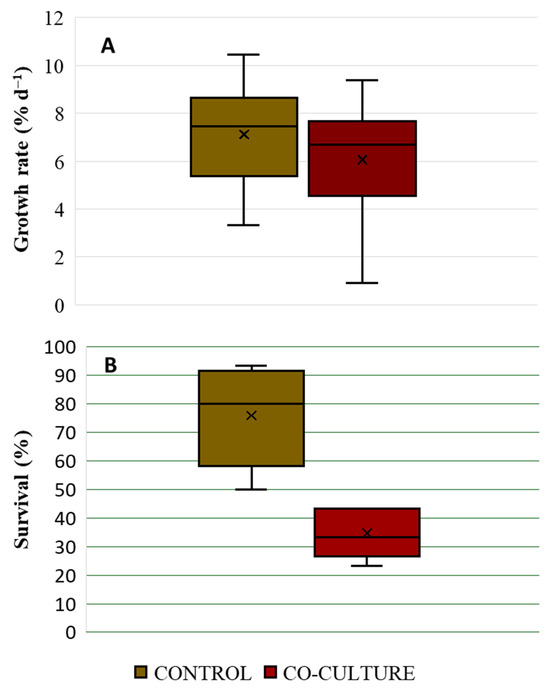
Figure 5.
(A): Growth rate (% day−1) and (B): Survival (%) of M. pyrifera sporophytes cultivated in control (brown) and C. daviesii co-culture (red) treatments (n = 5).
4. Discussion
Both kelp gametophytes and sporophytes can be superficially or internally infected by various classes of organisms, such as viruses, bacteria, fungi, and endophytic algae, among others [17,31,35,36]. The endophytic algae of kelps are most often filamentous brown algae [32]. The results of the present study showed that although C. daviesii was not observed as an endophyte growing inside the thallus, it can colonize gametophytes and young sporophytes. Furthermore, the interaction had negative effects on gametophytes and young sporophytes, highlighting potential consequences for M. pyrifera. In this regard, some studies have addressed the biological interactions between algae (preferably endophytes) and other pathogens, such as Oomycetes, with the early developmental stages of kelps [33,35,36,37,38]. This evidence indicates that these relationships are common [33] and that an infection can occur at a very early stage of development [34]. An example of this was reported by [35], where early gametophytes and sporophytes of M. pyrifera were infected by Anisolpidium ectocarpii after nine days of cultivation. Similarly, species of Eurychasma dicksonii (Oomycota) and Chytridium polysiphoniae (Chytridiomycota) can infect gametophytes and early sporophytes of Lessonia trabeculata and M. pyrifera. Furthermore, ref. [34] report that sporophytes of Saccharina latissima (>5 cm) are infected very early in life by Laminarionema elsbetiae.
In the present study, during co-culturing, the growth of M. pyrifera gametophytes was not affected by the presence of C. daviesii. However, there was a decrease in oogonium formation and fertility, with sporophyte formation reduced. These results are the first evidence of interference by a red filamentous alga on the fertility of M. pyrifera gametophytes at a very early stage of development. Previous studies have shown that the presence of endophytes can affect the reproductive output of adult sporophyte kelps by the infection and coverage of sporophylls or sori; reducing the reproductive area; or directly by inhibiting sori production ([17,29] and references therein). Until now, however, there were no reports on the negative effects of potentially harmful organisms on the sexual reproduction of the microscopic phase.
Young sporophyte growth during the experimental period in the co-culture was only slightly lower than in the control treatment. Nonetheless, survival was significantly lower in the presence of C. daviesii. We believe these results are not due to a lack of culture nutrients as a higher concentration of the enrichment solution was incorporated and the renewal period was shortened from 7 to 5 days, as has been employed in different co-culture studies including kelps or other marine algae species [4,31]. Therefore, we propose that lower survival could be due to an activation of energy-costing defense reactions resulting in decreases in the growth and physiological performance of the young sporophytes, as has been evidenced in different kelps [31,38]. However, this hypothesis needs to be confirmed.
In this context, the mere presence of C. daviesii in the co-cultures or the colonization of the thalli by filaments (derived from spores), even when not representing an extensive interaction due to no evidence of filaments inside the thalli, may be sufficient for recognition of a potential invasion. This suggests that Colaconema may release exogenous compounds (allelopathic elicitors) into the culture medium, which could potentially be enriched and cause detrimental effects on Macrocystis, thus activating the defense responses and innate immunity, as has been demonstrated in macroalgae [39]. Especially in kelps, the activation of defense reactions could consume energy, triggering a decrease in growth during interactions with the invader [31]. The idea of recognizing an exogenous elicitor, which has been defined as highly conserved patterns found only in the invader [31,39], is a potential way of M. pyrifera recognizing an invasion. This idea is supported by similar observations that showed C. daviesii only superficially infests (as an epiphyte), without penetrating the tissue of its host (C. chamissoi), causing a negative effect on growth and leading to the death of the thalli [4]. Therefore, we could speculate that in both cases, the detection of a specific exogenous elicitor present in C. daviesii would trigger energy-costing defense reactions that similarly affect both host species. While the defense pathways of M. pyrifera to the presence of infestation by C. daviesii are still unknown, these could involve an oxidative burst, as this mechanism has been proposed in macroalgae as the earliest conserved response after the recognition of invasion [40,41].
5. Conclusions
The results obtained demonstrate that the presence of C. daviesii could represent a potential threat to the microscopic and early stages of M. pyrifera. Of particular note was the negative effect on the sexual reproduction of the microscopic phases, with consequences that are still difficult to project for the maintenance of kelp populations, where gametophytes are key and highly vulnerable in a scenario of changing biotic and abiotic conditions [23]. Likewise, attention should be given to the aquaculture of C. chamissoi as a potential vector that could disseminate species such as C. daviesii along the coastlines of Chile and Peru. Many of the areas available for the cultivation of this species share the environment with kelp populations along the east coast of the South Pacific [42]. Biosecurity measures and the production of quality seeds free of potential pathogens should be implemented as soon as possible to ensure sustainable aquaculture.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. D.V.: conceptualization, investigation, visualization, Software, writing—original draft, Methodology. C.B.: Conceptualization, Supervision, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by ANID—Subdirección de Investigación Aplicada—FONDEF ID21I10054.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that supports the results of the present research study are available when solicited to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We extend our gratitude to LEPAM (Laboratory of Studies and Production of Marine Algae), where the present work was conducted. We also appreciate the support from CIMARQ (Center for Marine Research), where the cultivation of C. daviesii was carried out. This work was supported by ANID—Subdirección de Investigación Aplicada—FONDEF ID21I10054.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Araújo, P.; Schmidt, É; Kreusch, M.; Kano, C.; Guimarães, S.; Bouzon, Z.; Fujii, M.; Yokoya, N. Ultrastructural, morphological, and molecular characterization of Colaconema infestans (Colaconematales, Rhodophyta) and its host Kappaphycus alvarezii (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta) cultivated in the Brazilian tropical region. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 1953–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Yeh, H. Molecular and morphological characterization of Colaconema formosanum sp. nov. (Colaconemataceae, Rhodophyta)—A new endophytic filamentous red algal species from Taiwan. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, V.; Meynard, A.; Contreras-Porcia, L.; Bulboa, C. Molecular identification, growth, and reproduction of Colaconema daviesii (Rhodophyta; Colaconematales) endophyte of the edible red seaweed Chondracanthus chamissoi. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 3533–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, V.; Alvear, P.; Bulboa, C. Infestation by Colaconema daviesii (Rhodophyta, Colaconematales) of haploid and diploid thalli of edible red seaweed Chondracanthus chamissoi (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales): Effects on growth and survival. J. Appl. Phycol. 2024, 36, 2039–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, G.; Faisan, J.; Cottier-Cook, E.; Gachon, C.; Hurtado, A.; Lim, P.; Matoju, I.; Msuya, F.; Bass, D.; Brodie, J. A review of reported seaweed diseases and pests in aquaculture in Asia. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2020, 51, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, D.; Ingle, K.; Mathew, D.; Dhimmar, A.; Sahastrabudhe, H.; Sahu, S.; Krishnan, M.; Shinde, P.; Ganesan, M.; Mantri, V. Epiphytism, diseases and grazing in seaweed aquaculture: A comprehensive review. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 1345–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vairappan, C.; Chung, C.; Hurtado, A.; Soya, F.; Lhonneur, G.; Critchley, A. Distribution and symptoms of epiphyte infection in major carrageenophyte-producing farms. J. Appl. Phycol. 2008, 20, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poza, M.; Gauna, C.; Escobar, J.; Parodi, E. Temporal dynamics of algal epiphytes on Leathesia marina and Colpomenia sinuosa macrothalli (Phaeophyceae). Mar. Biol. Res. 2018, 14, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, G.; Hanyuda, T.; Kawai, H. Benthic Marine Algae on Japanese Tsunami Marine Debris; Oregon State University: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- García, V.; Bárbara, I.; Días, P. Biodiversity of epiphytic macroalgae (Chlorophyta, Ochrophyta, and Rhodophyta) on leaves of Zostera marina in the northwestern Iberian Peninsula. An. Jard. Bot. Madr. 2019, 76, 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Theobald, E.J.; Kumar, M.; Jackson, T.L.; Rule, M.B.; Diaz-Pulido, G.; Jackson, E.L. Fighting the red devil: Infestation of Asparagopsis taxiformis (Rhodophyta, Bonnemaisoniales) by the epiphyte Colaconema cf. infestans (Rhodophyta, Colaconematales). Phycologia 2025, 64, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchiavello, J.; Sepúlveda, C.; Basaure, H.; Sáez, F.; Yañez, D.; Marín, C.; Vega, L. Suspended culture of Chondracanthus chamissoi (Rhodophyta: Gigartinales) in Caleta Hornos (northern Chile) via vegetative propagation with secondary attachment discs. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbaiza, S.; Castañeda-Franco, M.; Baltazar Guerrero, P.; Bulboa, C. Tree-line system: A sea bottom cultivation technology to improve the biomass production of edible seaweed Chondracanthus chamissoi (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta). J. World Aquac. Soc. 2025, 56, e70007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaure, H.; Macchiavello, J.; Sepúlveda, C.; Sáez, F.; Yañez, D.; Vega, L.; Marín, C. Sea bottom culture of Chondracanthus chamissoi (Rhodophyta: Gigartinales) by vegetative propagation at Puerto Aldea, Tongoy Bay (Northern Chile). Aquac. Res. 2020, 52, 2025–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyarzo, S.; Ávila, M.; Alvear, P.; Remoncellez, J.; Contreras-Porcia, L.; Bulboa, C. Secondary attachment disc of edible seaweed Chondracanthus chamissoi (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales): Establishment of permanent thalli stock. Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, C.; Bustamante, D.; Calderon, M.; Gauna, C.; Hayashi, L.; Robledo, D.; Murúa, P. Biosecurity baseline for a sustainable development of seaweed aquaculture in Latin America. Mar. Policy 2024, 159, 105933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murúa, P.; Garvetto, A.; Egan, S.; Gachon, C. The reemergence of phycopathology: When algal biology meets ecology and biosecurity. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2023, 61, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggert, A.; Peters, A.F.; Küpper, F.C. The potential impacts of climate change on endophyte infections in kelp sporophytes. In Seaweeds and Their Role in Globally Changing Environments; Israel, A., Einav, R., Seckbach, J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 139–154. [Google Scholar]
- Smale, D.; Burrows, M.; Moore, P.; O’Connor, N.; Hawkins, S. Threats and knowledge gaps for ecosystem services provided by kelp forests: A northeast Atlantic perspective. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 4016–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teagle, H.; Hawkins, S.; Moore, P.; Smale, D. The role of kelp species as biogenic habitat formers in coastal marine ecosystems. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2017, 492, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyarzo-Miranda, C.; Otaíza, R.; Bellorín, A.; Vega, J.; Tala, F.; Lagos, N.; Bulboa, C.; Contreras-Porcia, L. Seaweed restocking along the Chilean coast: History, present, and inspiring recommendations for sustainability. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 10624814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckman, J.; Duggins, D.; Sewell, A. Ecology of understory kelp environments. Effects of kelps on flow and particle transport near the bottom. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1989, 129, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenhof, R.; Champion, C.; Dworjanyn, S.; Wernberg, T.; Minne, A.; Layton, C.; Bolton, J.; Reed, D.; Coleman, M. Kelp gametophytes in changing oceans. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 2022, 60, 335–372. [Google Scholar]
- Frieder, C.; Nam, S.; Martz, T.; Levin, L. High temporal and spatial variability of dissolved oxygen and pH in a nearshore California kelp forest. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 3917–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvell, C.; Mitchell, C.; Ward, J.; Altizer, S.; Dobson, A.; Ostfeld, R.; Samuel, M. Climate warming and disease risks for terrestrial and marine biota. Science 2002, 296, 2158–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filbee-Dexter, K.; Scheibling, R. Sea urchin barrens as alternative stable states of collapsed kelp ecosystems. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 495, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyarzo-Miranda, C.; Latorre, N.; Meynard, A.; Rivas, J.; Bulboa, C.; Contreras-Porcia, L. Coastal pollution from the industrial park Quintero Bay of central Chile: Effects on abundance, morphology, and development of the kelp Lessonia spicata (Phaeophyceae). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lein, T.; Sjøtun, K.; Wakili, S. Mass-occurrence of a brown filamentous endophyte in the lamina of the kelp Laminaria hyperborea (Gunnerus) Foslie along the southwestern coast of Norway. Sarsia 1991, 76, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A. Field and culture studies of Streblonema macrocystis sp. nov. (Ectocapales, Phaeophyceae) from Chile, a sexual endophyte of giant kelp. Phycologia 1991, 30, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellertsdottir, E.; Peters, A. High prevalence of infection by endophytic brown algae in populations of Laminaria spp. (Phaeophyceae). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 146, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Bernard, M.; Rousvoal, S.; Corre, E.; Markov, G.; Peters, A.; Leblanc, C. Different early responses of Laminariales to an endophytic infection provide insights about kelp host specificity. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 742469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, M.; Strittmatter, M.; Murúa, P.; Heesch, S.; Cho, G.; Leblanc, C.; Peters, A. Diversity, biogeography and host specificity of kelp endophytes with a focus on the genera Laminarionema and Laminariocolax (Ectocarpales, Phaeophyceae). Eur. J. Phycol. 2019, 54, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Küpper, F.; Küpper, H. Infection experiments reveal broad host ranges of Eurychasma dicksonii (Oomycota) and Chytridium polysiphoniae (Chytridiomycota), two eukaryotic parasites in marine brown algae (Phaeophyceae). Phycol. Res. 1999, 47, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, M.; Rousvoal, S.; Jacquemin, B.; Ballenghien, M.; Peters, A.; Leblanc, C. qPCR-based relative quantification of the brown algal endophyte Laminarionema elsbetiae in Saccharina latissima: Variation and dynamics of host–endophyte interactions. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 2901–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachon, C.; Strittmatter, M.; Badis, Y.; Fletcher, K.; West, P.; Müller, D. Pathogens of brown algae: Culture studies of Anisolpidium ectocarpii and A. rosenvingei reveal that the Anisolpidiales are uniflagellated oomycetes. Eur. J. Phycol. 2017, 52, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murúa, P.; Patiño, D.; Leiva, F.; Muñoz, L.; Müller, D.; Küpper, F.; Peters, A. Gall disease in the alginophyte Lessonia berteroana: A pathogenic interaction linked with host adulthood in a seasonal-dependant manner. Algal Res. 2019, 39, 101435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apt, K. Etiology and development of hyperplasia induced by Streblonema sp. (Phaeophyta) on members of the Laminariales (Phaeophyta). J. Phycol. 1988, 24, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heesch, S.; Peters, A. Scanning electron microscopy observation of host entry by two brown algae endophytic in Laminaria saccharina (Laminariales, Phaeophyceae). Phycol. Res. 1999, 47, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, F. Pathogen-induced defense and innate immunity in macroalgae. Biol. Bull. 2007, 213, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberger, F.; Friedlander, M.; Hoppe, H. Oligoagars elicit a physiological response in Gracilaria conferta (Rhodophyta). J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potin, P.; Bouarab, K.; Salaün, J.P.; Pohnert, G.; Kloareg, B. Biotic interactions of marine algae. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2002, 5, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuba, D.; Guardia-Luzon, K.; Cevallos, B.; Ramos-Larico, S.; Neira, E.; Pons, A.; Avila-Peltroche, J. Ecosystem services provided by kelp forests of the Humboldt current system: A comprehensive review. Coasts 2022, 2, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).