- Article
Cell Damage, Toxicity and Bacterial Diversity Shifts of Microcystis and Oscillatoria Cultures Treated with Bacterial Isolates
- Luyanda Lindelwa Ndlela,
- James Wesley-Smith and
- Monique Smit
- + 1 author
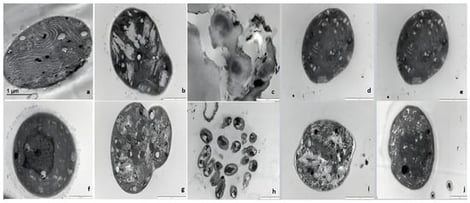
The mitigation of toxic cyanobacterial blooms is a much-researched and ongoing challenge. Seasonal influences, microbial diversity, and the wide range of cyanotoxins known to be associated with cyanobacterial blooms add layers of complexity to these environmental threats. Strategies to remediate blooms must avoid inducing widespread cell lysis and the release of cyanotoxins, which would compound rather than address the problem. Bacterial isolates have been found to be effective in bloom mitigation and can impact the diversity associated with the bloom. The present study reports on the exposure of non-axenic cultures of colonial Microcystis sp. and filamentous Oscillatoria sp. isolated from dams in South Africa to low ratios of four antagonistic bacterial isolates for 4 days. TEM was used to assess ultrastructural changes, HPLC to determine the relative concentrations of microcystin-LR and RR, and next-generation sequencing (NGS) to explore possible shifts in diversity from control samples as a result of exposure to the biological control bacterial isolates used. Ultrastructurally, Microcystis showed greater signs of stress than cells of Oscillatoria, with isolate 1 (Aeromonas lacus) having the least effect overall, whilst Isolate B (Lysinibacillus) and 3Y (Pseudomonas sp.) induced cell lysis in Microcystis. All isolates reduced the concentration of the toxic microcystin-LR, while the -RR variant often increased after 4 days. Minimal diversity shifts were noted in Microcystis-treated cultures, whilst those of Oscillatoria showed a greater diversity shift, indicating an increase in families containing isolates linked to bloom decline.
11 February 2026