Immunopathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Interplay of Innate and Adaptive Immunity, Microbiome Dysbiosis, and Emerging Therapeutic Targets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
3. Gender-Based Variations
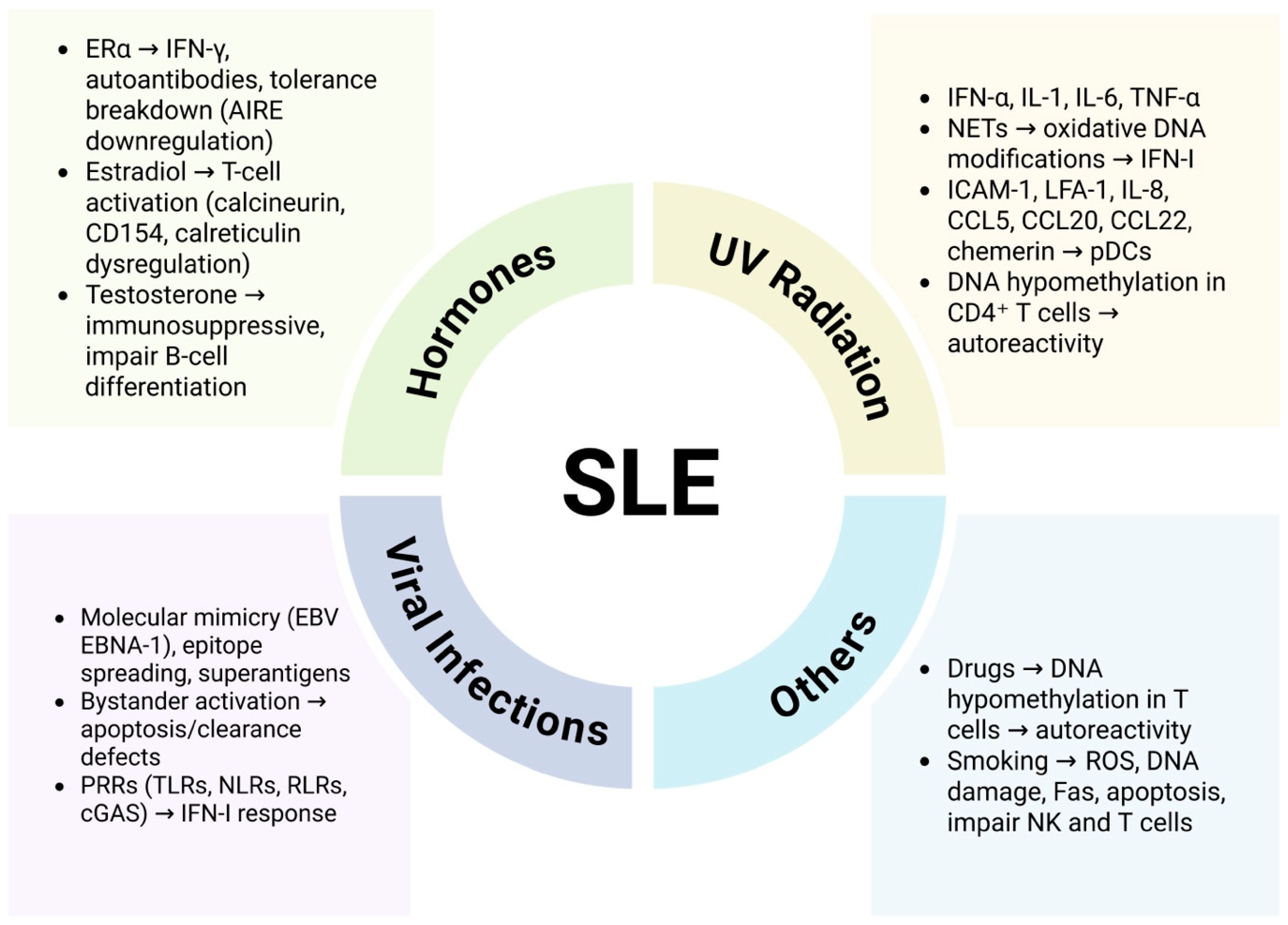
4. Environmental Predisposition to SLE
4.1. Hormonal Involvement
4.2. Effect of UV Radiations
4.3. Viral Infections
4.4. Drug Induced Lupus (DIL)
4.5. Alcoholism and Cigarette Smoking
5. Genetic Predisposition to SLE
6. Immune Dysregulation in SLE Pathogenesis
6.1. Innate Immune Dysregulation in SLE
6.2. Adaptive Immune System
6.2.1. T Cells
6.2.2. B Cell Dysfunction and Autoreactivity
7. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in SLE
8. Conclusions
9. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Justiz Vaillant, A.A.; Goyal, A.; Varacallo, M.A. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fava, A.; Petri, M. Systemic lupus erythematosus: Diagnosis and clinical management. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 96, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Barrat, F.J.; Crow, M.K.; Ivashkiv, L.B. Interferon target-gene expression and epigenomic signatures in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tsokos, G.C. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2110–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Boumpas, D.T. Advances in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): A case for optimism. Mediterr. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 28, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Moore, E.; Reynolds, J.A.; Davidson, A.; Gallucci, S.; Morel, L.; Rao, D.A.; Young, H.A.; Putterman, C. Promise and complexity of lupus mouse models. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Baethge, C.; Goldbeck-Wood, S.; Mertens, S. SANRA—A Scale for the Quality Assessment of Narrative Review Articles. Methodology 2019, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Barber, M.R.W.; Drenkard, C.; Falasinnu, T.; Hoi, A.; Mak, A.; Kow, N.Y.; Svenungsson, E.; Peterson, J.; Clarke, A.E.; Ramsey-Goldman, R. Global epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 515–532, Erratum in Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 642. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-021-00690-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rees, F.; Doherty, M.; Grainge, M.J.; Lanyon, P.; Zhang, W. The worldwide incidence and prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 1945–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falasinnu, T.; Chaichian, Y.; Bass, M.B.; Simard, J.F. The Representation of Gender and Race/Ethnic Groups in Randomized Clinical Trials of Individuals with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2018, 20, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Albrecht, K.; Troll, W.; Callhoff, J.; Strangfeld, A.; Ohrndorf, S.; Mucke, J. Sex- and gender-related differences in systemic lupus erythematosus: A scoping review. Rheumatol. Int. 2025, 45, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alonso, M.D.; Martínez-Vázquez, F.; Riancho-Zarrabeitia, L.; de Terán, T.D.; Miranda-Filloy, J.A.; Blanco, R.; González-Juanatey, C.; Llorca, J.; González-Gay, M.A. Sex differences in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus from Northwest Spain. Rheumatol. Int. 2013, 34, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, D.; Ansar Ahmed, S. The Immune System Is a Natural Target for Estrogen Action: Opposing Effects of Estrogen in Two Prototypical Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2016, 6, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Abdolahpour, S.; Abdolahi, N.; Aghaei, M.; Azadeh, H.; Farazmandfar, T. The Effect of Estradiol and Testosterone Levels Alone or in Combination with Their Receptors in Predicting the Severity of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Cohort Study. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2025, 50, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Constantin, A.; Baicus, C. Estradiol in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Acta Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ward, J.M.; Rider, V.; Abdou, N.I.; Kimler, B. Estradiol differentially regulates calreticulin: A potential link with abnormal T cell function in systemic lupus erythematosus? Lupus 2013, 22, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, H.A.; Suh, C.H.; Jung, J.Y. Sex hormones affect the pathogenesis and clinical characteristics of systemic lupus erythematosus. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 906475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pan, Q.; Chen, J.; Guo, L.; Lu, X.; Liao, S.; Zhao, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, H. Mechanistic insights into environmental and genetic risk factors for systemic lupus erythematosus. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 1241–1254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stannard, J.N.; Reed, T.J.; Myers, E.; Lowe, L.; Sarkar, M.K.; Xing, X.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Kahlenberg, J.M. Lupus Skin Is Primed for IL-6 Inflammatory Responses through a Keratinocyte-Mediated Autocrine Type I Interferon Loop. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Quaglia, M.; Merlotti, G.; De Andrea, M.; Borgogna, C.; Cantaluppi, V. Viral Infections and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: New Players in an Old Story. Viruses 2021, 13, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Deacy, A.M.; Gan, S.K.E.; Derrick, J.P. Superantigen Recognition and Interactions: Functions, Mechanisms and Applications. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 731845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kanduc, D.; Shoenfeld, Y. From Anti-EBV Immune Responses to the EBV Diseasome via Cross-reactivity. Glob. Med. Genet. 2020, 7, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pan, Q.; Liu, Z.; Liao, S.; Ye, L.; Lu, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.Z.; Liu, H. Current mechanistic insights into the role of infection in systemic lupus erythematosus. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, Y.; Acosta-Ampudia, Y.; Monsalve, D.M.; Chang, C.; Gershwin, M.E.; Anaya, J.M. Bystander activation and autoimmunity. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 103, 102301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzsimmons, L.; Kelly, G.L. EBV and Apoptosis: The Viral Master Regulator of Cell Fate? Viruses 2017, 9, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, Z.; Chang, C.; Peng, M.; Lu, Q. Translating epigenetics into clinic: Focus on lupus. Clin. Epigenet. 2017, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Crowl, J.T.; Gray, E.E.; Pestal, K.; Volkman, H.E.; Stetson, D.B. Intracellular Nucleic Acid Detection in Autoimmunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 35, 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Eisenächer, K.; Steinberg, C.; Reindl, W.; Krug, A. The role of viral nucleic acid recognition in dendritic cells for innate and adaptive antiviral immunity. Immunobiology 2008, 212, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Houen, G.; Trier, N.H. Epstein-Barr Virus and Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 587380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Poole, B.D.; Scofield, R.H.; Harley, J.B.; James, J.A. Epstein-Barr virus and molecular mimicry in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity 2006, 39, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaglio, A.; Grayson, P.C.; Fenaroli, P.; Gianfreda, D.; Boccaletti, V.; Ghiggeri, G.M.; Moroni, G. Drug-induced lupus: Traditional and new concepts. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Sawalha, A.H. Drug-induced lupus erythematosus: An update on drugs and mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2018, 30, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Solhjoo, M.; Goyal, A.; Chauhan, K. Drug-Induced Lupus Erythematosus. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441889/ (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Bojinca, V.C.; Bojinca, M.; Gheorghe, M.; Birceanu, A.; Iosif, C.I.; Balanescu, S.M.; Balanescu, A.R. Stevens-Johnsons syndrome or drug-induced lupus—A clinical dilemma: A case report and review of the literature. Biomed. Rep. 2018, 9, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Barbhaiya, M.; Lu, B.; Sparks, J.A.; Malspeis, S.; Chang, S.; Karlson, E.W.; Costenbader, K.H. Influence of Alcohol Consumption on the Risk of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Among Women in the Nurses’ Health Study Cohorts. Arthritis Care Res. 2016, 69, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wirleitner, B.; Schroecksnadel, K.; Winkler, C.; Schennach, H.; Fuchs, D. Resveratrol suppresses interferon-gamma-induced biochemical pathways in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro. Immunol. Lett. 2005, 100, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Quintela, A.; Alende, R.; Gude, F.; Campos-Franco, J.; Rey, J.; Meijide, L.M.; Fernandez-Merino, C.; Vidal, C. Serum levels of immunoglobulins (IgG, IgA, IgM) in a general adult population and their relationship with alcohol consumption, smoking and common metabolic abnormalities. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 151, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Murr, C.; Widner, B.; Wirleitner, B.; Fuchs, D. Neopterin as a marker for immune system activation. Curr. Drug Metab. 2002, 3, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyohara, C.; Washio, M.; Horiuchi, T.; Asami, T.; Ide, S.; Atsumi, T.; Kobashi, G.; Tada, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Kyushu Sapporo SLE (KYSS) Study Group. Cigarette smoking, alcohol consumption, and risk of systemic lupus erythematosus: A case-control study in a Japanese population. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, M.H.Y.; Ng, I.A.T.; Cheung, M.W.L.; Mak, A. Association Between Cigarette Smoking and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: An Updated Multivariate Bayesian Metaanalysis. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 47, 1514–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speyer, C.B.; Costenbader, K.H. Cigarette smoking and the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Barbhaiya, M.; Tedeschi, S.K.; Lu, B.; Malspeis, S.; Kreps, D.; Sparks, J.A.; Karlson, E.W.; Costenbader, K.H. Cigarette smoking and the risk of systemic lupus erythematosus, overall and by anti-double stranded DNA antibody subtype, in the Nurses’ Health Study cohorts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hong, C.H.; Lee, C.H.; Yu, H.S.; Huang, S.K. Benzopyrene, a major polyaromatic hydrocarbon in smoke fume, mobilizes Langerhans cells and polarizes Th2/17 responses in epicutaneous protein sensitization through the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 36, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, C.Y.; Wang, P.Y.; Chen, K.Y.; Tseng, C.C.; Wu, C.C.; Ou, T.T.; Yen, J.H. HLA-DR genotypes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in Taiwan. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2023, 86, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Molineros, J.E.; Looger, L.L.; Zhou, X.J.; Kim, K.; Okada, Y.; Ma, J.; Qi, Y.Y.; Kim-Howard, X.; Motghare, P.; et al. High-density genotyping of immune-related loci identifies new SLE risk variants in individuals with Asian ancestry. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Molineros, J.E.; Looger, L.L.; Kim, K.; Okada, Y.; Terao, C.; Sun, C.; Zhou, X.J.; Raj, P.; Kochi, Y.; Suzuki, A.; et al. Amino acid signatures of HLA Class-I and II molecules are strongly associated with SLE susceptibility and autoantibody production in Eastern Asians. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Guga, S.; Wang, Y.; Graham, D.C.; Vyse, T.J. A review of genetic risk in systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 19, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamitaki, N.; Sekar, A.; Handsaker, R.E.; de Rivera, H.; Tooley, K.; Morris, D.L.; Taylor, K.E.; Whelan, C.W.; Tombleson, P.; Loohuis, L.M.O.; et al. Complement genes contribute sex-biased vulnerability in diverse disorders. Nature 2020, 582, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- da Costa, M.G.; Poppelaars, F.; van Kooten, C.; Mollnes, T.E.; Tedesco, F.; Würzner, R.; Trouw, L.A.; Truedsson, L.; Daha, M.R.; Roos, A.; et al. Age and Sex-Associated Changes of Complement Activity and Complement Levels in a Healthy Caucasian Population. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ha, E.; Bae, S.C.; Kim, K. Recent advances in understanding the genetic basis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin. Immunopathol. 2021, 44, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.Y.; Morris, D.L.; Sheng, Y.; Cui, Y.; et al. Independent Replication on Genome-Wide Association Study Signals Identifies IRF3 as a Novel Locus for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yin, X.; Kim, K.; Suetsugu, H.; Bang, S.Y.; Wen, L.; Koido, M.; Ha, E.; Liu, L.; Sakamoto, Y.; Jo, S.; et al. Meta-analysis of 208370 East Asians identifies 113 susceptibility loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhao, J.; Ma, J.; Deng, Y.; Kelly, J.A.; Kim, K.; Bang, S.-Y.; Lee, H.-S.; Li, Q.-Z.; Wakeland, E.K.; Qiu, R.; et al. A missense variant in NCF1 is associated with susceptibility to multiple autoimmune diseases. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Meroni, P.L.; Penatti, A.E. Epigenetics and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Unmet Needs. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 50, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreté-Bonastre, A.G.; Martínez-Gallo, M.; Morante-Palacios, O.; Calvillo, C.L.; Calafell-Segura, J.; Rodríguez-Ubreva, J.; Esteller, M.; Cortés-Hernández, J.; Ballestar, E. Disease activity drives divergent epigenetic and transcriptomic reprogramming of monocyte subpopulations in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farivar, S.; Aghamaleki, F.S. Effects of Major Epigenetic Factors on Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Iran. Biomed. J. 2018, 22, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y. An updated review on abnormal epigenetic modifications in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2025, 15, 1501783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cheng, Y.; Liu, L.; Ye, Y.; He, Y.; Hu, W.; Ke, H.; Guo, Z.Y.; Shao, G. Roles of macrophages in lupus nephritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1477708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Murray, P.J. Macrophage Polarization. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 541–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, A.L.; Schiller, S.M.; Keegan, W.J.; Ammons, M.C.B.; Eilers, B.; Tripet, B.; Copié, V. Quantitative 1H NMR Metabolomics Reveal Distinct Metabolic Adaptations in Human Macrophages Following Differential Activation. Metabolites 2019, 9, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ahamada, M.M.; Jia, Y.; Wu, X. Macrophage Polarization and Plasticity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 734008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kaewraemruaen, C.; Ritprajak, P.; Hirankarn, N. Dendritic cells as key players in systemic lupus erythematosus. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 38, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, R.; High, A.A.; Slaughter, C.A.; Finkelstein, D.; Rehg, J.E.; Redecke, V.; Häcker, H. A20-binding inhibitor of NF-κB (ABIN1) controls Toll-like receptor-mediated CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β activation and protects from inflammatory disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E998–E1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bengtsson, A.A.; Rönnblom, L. Role of interferons in SLE. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 31, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumurkhuu, G.; Montano, E.; Jefferies, C. Innate Immune Dysregulation in the Development of Cardiovascular Disease in Lupus. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2019, 21, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhao, M.; Jia, S. Macrophage: Key player in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1080310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, F.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, L.; Xu, J. TIPE2 Alleviates Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Through Regulating Macrophage Polarization. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horuluoglu, B.; Bayik, D.; Kayraklioglu, N.; Goguet, E.; Kaplan, M.J.; Klinman, D.M. PAM3 supports the generation of M2-like macrophages from lupus patient monocytes and improves disease outcome in murine lupus. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 99, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Salemme, R.; Peralta, L.N.; Meka, S.H.; Pushpanathan, N.; Alexander, J.J. The Role of NETosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Cell Immunol. 2019, 1, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Reshetnyak, T.; Nurbaeva, K.; Ptashnik, I.; Kudriaeva, A.; Belogurov, A.; Lila, A.; Nasonov, E. Markers of NETosis in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Lai, Y.; Nallapothula, D.; Singh, R.R. Diverse Roles of NETosis in the Pathogenesis of Lupus. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 895216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fu, X.; Liu, H.; Huang, G.; Dai, S.S. The emerging role of neutrophils in autoimmune-associated disorders: Effector, predictor, and therapeutic targets. MedComm 2021, 2, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Smith, C.K.; Vivekanandan-Giri, A.; Tang, C.; Knight, J.S.; Mathew, A.; Padilla, R.L.; Gillespie, B.W.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; Liu, X.; Subramanian, V.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular trap–derived enzymes oxidize high-density lipoprotein: An additional proatherogenic mechanism in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 2532–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Patiño-Trives, A.M.; Pérez-Sánchez, C.; Pérez-Sánchez, L.; Luque-Tévar, M.; Ábalos-Aguilera, M.C.; Alcaide-Ruggiero, L.; la Rosa, I.A.-D.; Román-Rodríguez, C.; Seguí, P.; Espinosa, M.; et al. Anti-dsDNA Antibodies Increase the Cardiovascular Risk in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Promoting a Distinctive Immune and Vascular Activation. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 2417–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuitino, L.; Obreque, J.; Gajardo-Meneses, P.; Villarroel, A.; Crisóstomo, N.; Francisco, I.F.S.; Valenzuela, R.A.; Méndez, G.P.; Llanos, C. Heme-Oxygenase-1 Is Decreased in Circulating Monocytes and Is Associated with Impaired Phagocytosis and ROS Production in Lupus Nephritis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lever, J.M.; Boddu, R.; George, J.F.; Agarwal, A. Heme Oxygenase-1 in Kidney Health and Disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 25, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Athanassiadou, V.; Plavoukou, S.; Grapsa, E.; Detsika, M.G. The Role of Heme Oxygenase-1 as an Immunomodulator in Kidney Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sarma, J.V.; Ward, P.A. The complement system. Cell Tissue Res. 2011, 343, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Weinstein, A.; Alexander, R.V.; Zack, D.J. A Review of Complement Activation in SLE. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2021, 23, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Martin, M.; Blom, A.M. Complement in removal of the dead—Balancing inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 274, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.L.; Birmingham, D.J.; Rovin, B.H. Expanding the Role of Complement Therapies: The Case for Lupus Nephritis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Macedo, A.C.; Isaac, L. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Deficiencies of Early Components of the Complement Classical Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, X.X.; Lee, J.D.; Kemper, C.; Woodruff, T.M. The Complement Receptor C5aR2: A Powerful Modulator of Innate and Adaptive Immunity. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 3339–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Haas, M.; Quigg, R.J. Complement factor H deficiency accelerates development of lupus nephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wilson, H.R.; Medjeral-Thomas, N.R.; Gilmore, A.C.; Trivedi, P.; Seyb, K.; Farzaneh-Far, R.; Gunnarsson, I.; Zickert, A.; Cairns, T.D.; Lightstone, L.; et al. Glomerular membrane attack complex is not a reliable marker of ongoing C5 activation in lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sakata, K.; Nakayamada, S.; Miyazaki, Y.; Kubo, S.; Ishii, A.; Nakano, K.; Tanaka, Y. Up-Regulation of TLR7-Mediated IFN-α Production by Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jenks, S.A.; Cashman, K.S.; Zumaquero, E.; Marigorta, U.M.; Patel, A.V.; Wang, X.; Tomar, D.; Woodruff, M.C.; Simon, Z.; Bugrovsky, R.; et al. Distinct Effector B Cells Induced by Unregulated Toll-like Receptor 7 Contribute to Pathogenic Responses in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Immunity 2018, 49, 725–739.e6, Erratum in Immunity 2020, 52, 203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2019.12.005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tilstra, J.S.; John, S.; Gordon, R.A.; Leibler, C.; Kashgarian, M.; Bastacky, S.; Nickerson, K.M.; Shlomchik, M.J. B cell–intrinsic TLR9 expression is protective in murine lupus. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3172–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Accapezzato, D.; Caccavale, R.; Paroli, M.P.; Gioia, C.; Nguyen, B.L.; Spadea, L.; Paroli, M. Advances in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hjorton, K.; Hagberg, N.; Israelsson, E.; Jinton, L.; Berggren, O.; Sandling, J.K.; Thörn, K.; Mo, J.; DISSECT Consortium; Eloranta, M.L.; et al. Cytokine production by activated plasmacytoid dendritic cells and natural killer cells is suppressed by an IRAK4 inhibitor. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Corzo, C.A.; Varfolomeev, E.; Setiadi, A.F.; Francis, R.; Klabunde, S.; Senger, K.; Sujatha-Bhaskar, S.; Drobnick, J.; Do, S.; Suto, E.; et al. The kinase IRAK4 promotes endosomal TLR and immune complex signaling in B cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Sci. Signal. 2020, 13, eaaz1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiecki, M.; Colonna, M. The multifaceted biology of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Soni, C.; Perez, O.A.; Voss, W.N.; Pucella, J.N.; Serpas, L.; Mehl, J.; Ching, K.L.; Goike, J.; Georgiou, G.; Ippolito, G.C.; et al. Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells and Type I Interferon Promote Extrafollicular B Cell Responses to Extracellular Self-DNA. Immunity 2020, 52, 1022–1038.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gautam, P.; Sharma, A.; Bhatnagar, A. Global histone modification analysis reveals hypoacetylated H3 and H4 histones in B Cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Immunol. Lett. 2021, 240, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liao, J.; Wu, R.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, P.; Luo, S. Deficiency of p53 Causes the Inadequate Expression of miR-1246 in B Cells of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2022, 209, 1492–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Luo, S.; Wu, R.; Li, Q.; Zhang, G. MiR-301a-3p Advances IRAK1-Mediated Differentiation of Th17 Cells to Promote the Progression of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus via Targeting PELI1. J. Healthc. Eng. 2021, 2021, 2982924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, M.; Yang, B.; Deng, D. Targeting of EIF4EBP1 by miR-99a-3p affects the functions of B lymphocytes via autophagy and aggravates SLE disease progression. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 10291–10305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, J.; Peng, L.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, Q.; Yin, F.; Liu, M.; Luo, X.; He, C.; He, Y. HDAC1 potentiates CD4+ T cell activation by inhibiting miR-124 and promoting IRF1 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell. Immunol. 2021, 362, 104284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Day, J.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Wicks, I.P.; Louis, C. Natural killer cells in inflammatory autoimmune diseases. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2021, 10, e1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hervier, B.; Beziat, V.; Haroche, J.; Mathian, A.; Lebon, P.; Ghillani-Dalbin, P.; Musset, L.; Debré, P.; Amoura, Z.; Vieillard, V. Phenotype and function of natural killer cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: Excess interferon-γ production in patients with active disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1698–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-González, D.J.; Gómez-Martin, D.; Layseca-Espinosa, E.; Baranda, L.; Abud-Mendoza, C.; Alcocer-Varela, J.; González-Amaro, R.; Monsiváis-Urenda, A.E. Analysis of the regulatory function of natural killer cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 191, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Voynova, E.N.; Skinner, J.; Bolland, S. Expansion of an atypical NK cell subset in mouse models of systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kurata, I.; Matsumoto, I.; Sumida, T. T follicular helper cell subsets: A potential key player in autoimmunity. Immunol. Med. 2020, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zumaquero, E.; Stone, S.L.; Scharer, C.D.; Jenks, S.A.; Nellore, A.; Mousseau, B.; Rosal-Vela, A.; Botta, D.; Bradley, J.E.; Wojciechowski, W.; et al. IFNγ induces epigenetic programming of human T-bethi B cells and promotes TLR7/8 and IL-21 induced differentiation. eLife 2019, 8, e41641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Koga, T.; Ichinose, K.; Kawakami, A.; Tsokos, G.C. The role of IL-17 in systemic lupus erythematosus and its potential as a therapeutic target. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes, J.L.; Fernandez-Ruiz, R.; Niewold, T.B. T Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 47, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Raphael, I.; Nalawade, S.; Eagar, T.N.; Forsthuber, T.G. T cell subsets and their signature cytokines in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Cytokine 2015, 74, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mao, Y.M.; Zhao, C.N.; Leng, J.; Leng, R.X.; Ye, D.Q.; Zheng, S.G.; Pan, H.F. Interleukin-13: A promising therapeutic target for autoimmune disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019, 45, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, P.; Rodríguez-Carrio, J.; Caminal-Montero, L.; Mozo, L.; Suárez, A. A pathogenic IFNα, BLyS and IL-17 axis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fischer, K.; Przepiera-Będzak, H.; Sawicki, M.; Walecka, A.; Brzosko, I.; Brzosko, M. Serum Interleukin-23 in Polish Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Association with Lupus Nephritis, Obesity, and Peripheral Vascular Disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 9401432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zickert, A.; Amoudruz, P.; Sundström, Y.; Rönnelid, J.; Malmström, V.; Gunnarsson, I. IL-17 and IL-23 in lupus nephritis—Association to histopathology and response to treatment. BMC Immunol. 2015, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lin, J.; Yue, L.H.; Chen, W.Q. Decreased plasma IL-22 levels and correlations with IL-22-producing T helper cells in patients with new-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand. J. Immunol. 2014, 79, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chang, C.; Lu, L.; Lau, C.S.; Lu, Q. Th9 cells and IL-9 in autoimmune disorders: Pathogenesis and therapeutic potentials. Hum. Immunol. 2017, 78, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Li, Q.; Yang, X.; Li, M. Interleukin-9 Is Associated with Elevated Anti-Double-Stranded DNA Antibodies in Lupus-Prone Mice. Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rajendiran, A.; Tenbrock, K. Regulatory T cell function in autoimmune disease. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2021, 4, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mohr, A.; Atif, M.; Balderas, R.; Gorochov, G.; Miyara, M. The role of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in human autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 197, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Arnaud, L.; Chasset, F.; Martin, T. Immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus: An update. Autoimmun. Rev. 2024, 23, 103648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolouri, N.; Akhtari, M.; Farhadi, E.; Mansouri, R.; Faezi, S.T.; Jamshidi, A.; Mahmoudi, M. Role of the innate and adaptive immune responses in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 71, 537–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Yu, D.; Wang, Y.; Luo, N.; Han, G.; Yang, B. Interferon-α activates interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 to induce regulatory T-cell apoptosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, 1172–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherlinger, M.; Guillotin, V.; Douchet, I.; Vacher, P.; Boizard-Moracchini, A.; Guegan, J.-P.; Garreau, A.; Merillon, N.; Vermorel, A.; Ribeiro, E.; et al. Selectins impair regulatory T cell function and contribute to systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabi4994, Erratum in Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabl7656. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.abl7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsokos, G.C.; Lo, M.S.; Reis, P.C.; Sullivan, K.E. New insights into the immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 716–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Wang, S.; Zhou, M.; Huang, Y.; Fu, R.; Guo, C.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J.; Gaskin, F.; Fu, S.M.; et al. The ratio of circulating follicular T helper cell to follicular T regulatory cell is correlated with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 183, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhao, J.; Li, L.; Feng, X.; Yin, H.; Fan, X.; Gao, C.; Zhao, M.; Lu, Q. Blockade of OX40/OX40L signaling using anti-OX40L alleviates murine lupus nephritis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2024, 54, e2350915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchen, J.; Simon, Q.; Chapart, L.; Thaminy, M.K.; Vibhushan, S.; Saveanu, L.; Lamri, Y.; Saidoune, F.; Pacreau, E.; Pellefigues, C.; et al. PD-L1- and IL-4-expressing basophils promote pathogenic accumulation of T follicular helper cells in lupus. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yuan, S.; Zeng, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Li, W.; He, Z.; Ye, J.; Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Lin, X.; et al. Phenotypical changes and clinical significance of CD4+/CD8+ T cells in SLE. Lupus Sci. Med. 2022, 9, e000660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Katsuyama, E.; Suarez-Fueyo, A.; Bradley, S.J.; Mizui, M.; Marin, A.V.; Mulki, L.; Krishfield, S.; Malavasi, F.; Yoon, J.; Sui, S.J.H.; et al. The CD38/NAD/SIRTUIN1/EZH2 Axis Mitigates Cytotoxic CD8 T Cell Function and Identifies Patients with SLE Prone to Infections. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 112–123.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, H.; Adamopoulos, I.E.; Moulton, V.R.; Stillman, I.E.; Herbert, Z.; Moon, J.J.; Sharabi, A.; Krishfield, S.; Tsokos, M.G.; Tsokos, G.C. Systemic lupus erythematosus favors the generation of IL-17 producing double negative T cells. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Song, K.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X. An update on genetic susceptibility in lupus nephritis. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 210, 108272, Erratum in Clin. Immunol. 2020, 215, 108389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2020.108389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Chen, J. The Role of γδ T Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 2932531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rastogi, I.; Jeon, D.; Moseman, J.E.; Muralidhar, A.; Potluri, H.K.; McNeel, D.G. Role of B cells as antigen presenting cells. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 954936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Canny, S.P.; Jackson, S.W. B Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: From Disease Mechanisms to Targeted Therapies. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 47, 395–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kil, L.P.; de Bruijn, M.J.W.; van Nimwegen, M.; Corneth, O.B.J.; van Hamburg, J.P.; Dingjan, G.M.; Thaiss, F.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Elewaut, D.; Delsing, D.; et al. Btk levels set the threshold for B-cell activation and negative selection of autoreactive B cells in mice. Blood 2012, 119, 3744–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, J.A.; Wu, Q.; Yang, P.; Luo, B.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Mattheyses, A.L.; Sanz, I.; Chatham, W.W.; Hsu, H.C.; et al. Cutting Edge: Intracellular IFN-β and Distinct Type I IFN Expression Patterns in Circulating Systemic Lupus Erythematosus B Cells. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 2203–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hamilton, J.A.; Hsu, H.; Mountz, J.D. Autoreactive B cells in SLE, villains or innocent bystanders? Immunol. Rev. 2019, 292, 120–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, H.; Wu, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, P.; Zhu, Z.; Luo, B.; Hsu, H.-C.; Mountz, J.D. Cutting Edge: Defective follicular exclusion of apoptotic antigens due to marginal zone macrophage defects in autoimmune BXD2 mice. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 4465–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, J.H.; New, J.S.; Xie, S.; Yang, P.; Wu, Q.; Li, J.; Luo, B.; Ding, Y.; Druey, K.M.; Hsu, H.; et al. Extension of the germinal center stage of B cell development promotes autoantibodies in BXD2 mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 2703–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Taylor, E.B.; Barati, M.T.; Powell, D.W.; Turbeville, H.R.; Ryan, M.J. Plasma Cell Depletion Attenuates Hypertension in an Experimental Model of Autoimmune Disease. Hypertension 2018, 71, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, T.; Mei, Y.; Li, Z. Research Progress on Regulatory B Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7948687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cai, X.; Zhang, L.; Wei, W. Regulatory B cells in inflammatory diseases and tumor. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 67, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaniv, G.; Twig, G.; Shor, D.B.; Furer, A.; Sherer, Y.; Mozes, O.; Komisar, O.; Slonimsky, E.; Klang, E.; Lotan, E.; et al. A volcanic explosion of autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: A diversity of 180 different antibodies found in SLE patients. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Bañuelos, E.; Fava, A.; Andrade, F. An update on autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2022, 35, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, X.; Xia, Y. Anti-double Stranded DNA Antibodies: Origin, Pathogenicity, and Targeted Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Augusto, J.-F.; Truchetet, M.-E.; Charles, N.; Blanco, P.; Richez, C. IgE in lupus pathogenesis: Friends or foes? Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.Y.; Dai, Y.; Rosen, C.E.; Schmitt, M.M.; Dong, M.X.; Ferré, E.M.; Liu, F.; Yang, Y.; González-Hernández, J.A.; Meffre, E.; et al. High-throughput identification of autoantibodies that target the human exoproteome. Cell Rep. Methods 2022, 2, 100172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, Y.; Loignon, R.C.; Julien, A.S.; Marcoux, G.; Allaeys, I.; Lévesque, T.; Rollet-Labelle, E.; Benk-Fortin, H.; Cloutier, N.; Melki, I.; et al. Anti-mitochondrial autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus and their association with disease manifestations. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Caielli, S.; Athale, S.; Domic, B.; Murat, E.; Chandra, M.; Banchereau, R.; Baisch, J.; Phelps, K.; Clayton, S.; Gong, M.; et al. Oxidized mitochondrial nucleoids released by neutrophils drive type I interferon production in human lupus. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 697–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, L.; Qing, P.; Yang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y. Gut Microbiome and Metabolites in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Link, Mechanisms and Intervention. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 686501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tong, Y.; Marion, T.; Schett, G.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y. Microbiota and metabolites in rheumatic diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Wen, X.; Liu, R.; Xu, K. Microbial dysbiosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: A scientometric study. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1319654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ali, A.Y.; Zahran, S.A.; Eissa, M.; Kashef, M.T.; Ali, A.E. Gut microbiota dysbiosis and associated immune response in systemic lupus erythematosus: Impact of disease and treatment. Gut Pathog. 2025, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Azzouz, D.; Omarbekova, A.; Heguy, A.; Schwudke, D.; Gisch, N.; Rovin, B.H.; Caricchio, R.; Buyon, J.P.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Silverman, G.J. Lupus nephritis is linked to disease-activity associated expansions and immunity to a gut commensal. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- de Oliveira, D.G.; Machado, A.; Lacerda, P.C.; Karakikla-Mitsakou, Z.; Vasconcelos, C. Systemic lupus erythematosus and the gut microbiome: To look forward is to look within—A systematic review and narrative synthesis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2025, 24, 103921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmant, B.D.; Fonseca, D.C.; Prudêncio, A.P.A.; Rocha, I.M.; Callado, L.; Alves, J.T.M.; Torrinhas, R.S.M.d.M.; Borba, E.F.; Waitzberg, D.L. Megamonas funiformis, Plasma Zonulin, and Sodium Intake Affect C3 Complement Levels in Inactive Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gronke, K.; Nguyen, M.; Fuhrmann, H.; de Souza, N.S.; Schumacher, J.; Pereira, M.S.; Löschberger, U.; Brinkhege, A.; Becker, N.J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Translocating gut pathobiont Enterococcus gallinarum induces T H 17 and IgG3 anti-RNA–directed autoimmunity in mouse and human. Sci. Transl. Med. 2025, 17, eadj6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiling, T.M.; Dehner, C.; Chen, X.; Hughes, K.; Iñiguez, A.J.; Boccitto, M.; Ruiz, D.Z.; Renfroe, S.C.; Vieira, S.M.; Ruff, W.E.; et al. Commensal orthologs of the human autoantigen Ro60 as triggers of autoimmunity in lupus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaan2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Parodi, E.; Novi, M.; Bottino, P.; La Porta, E.; Merlotti, G.; Castello, L.M.; Gotta, F.; Rocchetti, A.; Quaglia, M. The Complex Role of Gut Microbiota in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis: From Pathogenetic Factor to Therapeutic Target. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vitale, A.M.; Paladino, L.; Bavisotto, C.C.; Barone, R.; Rappa, F.; de Macario, E.C.; Cappello, F.; Macario, A.J.L.; Gammazza, A.M. Interplay between the Chaperone System and Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Pathogenesis: Is Molecular Mimicry the Missing Link between Those Two Factors? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Toumi, E.; Goutorbe, B.; Plauzolles, A.; Bonnet, M.; Mezouar, S.; Militello, M.; Mege, J.-L.; Chiche, L.; Halfon, P. Gut microbiota in systemic lupus erythematosus patients and lupus mouse model: A cross species comparative analysis for biomarker discovery. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 943241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- He, J.; Chan, T.; Hong, X.; Zheng, F.; Zhu, C.; Yin, L.; Dai, W.; Tang, D.; Liu, D.; Dai, Y. Microbiome and Metabolome Analyses Reveal the Disruption of Lipid Metabolism in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brown, J.; Robusto, B.; Morel, L. Intestinal Dysbiosis and Tryptophan Metabolism in Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Guo, M.; Wang, H.; Xu, S.; Zhuang, Y.; An, J.; Su, C.; Xia, Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, Z.Z.; Liu, Q.; et al. Alteration in gut microbiota is associated with dysregulation of cytokines and glucocorticoid therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 1758–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, A.; Li, S.; Yu, J.J.; Shao, W.-H. Immunopathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Interplay of Innate and Adaptive Immunity, Microbiome Dysbiosis, and Emerging Therapeutic Targets. Pathophysiology 2025, 32, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32040061
Ahmed A, Li S, Yu JJ, Shao W-H. Immunopathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Interplay of Innate and Adaptive Immunity, Microbiome Dysbiosis, and Emerging Therapeutic Targets. Pathophysiology. 2025; 32(4):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32040061
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Arslan, Siru Li, Jane J. Yu, and Wen-Hai Shao. 2025. "Immunopathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Interplay of Innate and Adaptive Immunity, Microbiome Dysbiosis, and Emerging Therapeutic Targets" Pathophysiology 32, no. 4: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32040061
APA StyleAhmed, A., Li, S., Yu, J. J., & Shao, W.-H. (2025). Immunopathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Interplay of Innate and Adaptive Immunity, Microbiome Dysbiosis, and Emerging Therapeutic Targets. Pathophysiology, 32(4), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32040061





