- Article
Systematic Investigation of the Solvation Structure in THF-Based Localized High-Concentration Electrolytes
- Yoonha Hwang,
- Yeo Jin An and
- Minjeong Shin
- + 1 author
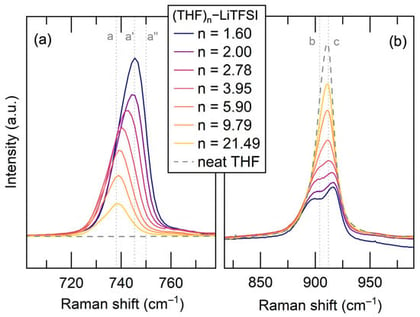
Understanding Li+ solvation structure is critical for the rational design of high- and localized high-concentration electrolytes. Here, we present a systematic investigation of tetrahydrofuran (THF)-based electrolytes with lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (LiTFSI) using Raman spectroscopy and 7Li nuclear magnetic resonance to investigate the local solvation structures. By varying the THF:LiTFSI molar ratio, we observed a transition of Li+ solvation from solvent-separated ion pairs to contact ion pairs and aggregates, accompanied by increased structural heterogeneity and constrained local dynamics. Raman spectroscopy captures the evolution of Li+–anion coordination with increasing salt concentration, while 7Li NMR chemical shifts, line widths, and relaxation times provide complementary insight into changes in the electronic environment and symmetry of Li+ coordination. Electrolyte structure is further examined by introducing a hydrofluoroether co-solvent into a concentrated (THF)2–LiTFSI electrolyte. Raman results show that the local Li+–TFSI− coordination structure is preserved upon 1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl-2,2,3,3-tetrafluoropropyl ether (TTE) addition, whereas NMR reveals subtle modifications of the ion-rich solvation clusters. These results provide fundamental insight into Li+ solvation and electrolyte localization, offering general design principles for advanced electrolyte systems.
14 February 2026