- Article
Quantitative Evaluation of Displacement Fields in a Tailings Dam Physical Model Under Elevated Pore Water Pressure Using Digital Image Processing
- Abraham Armah,
- Mehrdad Razavi and
- Sandra Donkor
- + 2 authors
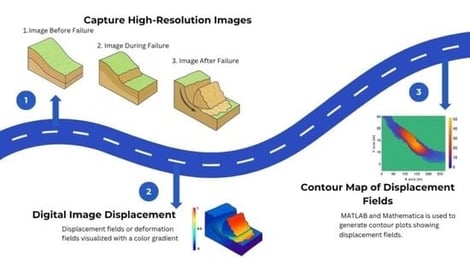
The mining industry still faces major environmental and socioeconomic problems as a result of tailings dam failures, which highlights the urgent need for improved monitoring and early-warning systems. This research offers practical recommendations for improved monitoring and safer design practices, in addition to investigating the use of digital image processing (DIP) as a non-invasive technique for tracking slope deformation in tailings dam models subjected to incremental pore water pressure increases. To replicate real-world conditions as closely as possible, a scaled laboratory embankment was built using coarse and fine tailings. During controlled pore-pressure loading, more than 500 high-resolution photos were taken, recording the entire deformation sequence from initial displacement to slope failure. The images were processed using Mathematica to generate pixel-by-pixel displacement fields and vector plots, providing a detailed visualization of deformation mechanisms. The findings demonstrated that DIP accurately detects and measures surface displacement, revealing the mechanisms, direction, and intensity of deformation. This study illustrates the extensive potential of DIP for real-time monitoring by directly connecting slope instability triggered by incremental pore water pressure with visual indications of slope deformation. While the results confirm the strong potential of DIP for deformation monitoring with a minimum detectable displacement of approximately 1.0 mm under controlled laboratory conditions, its field application may be affected by scale effects, variable lighting, and environmental occlusion. The mining industry benefits greatly from the insights gained through in-depth image analysis, which promotes safer tailings dam design and management. Overall, DIP can provide a reliable, scalable foundation for real-time deformation monitoring in operational tailings dams, where continuous image-based measurements can help identify early signs of instability and support proactive risk management.
22 February 2026