- Article
Design and Performance Optimization of a Micro Piezoelectric–Electromagnetic Hybrid Energy Harvester for Self-Powered Wireless Sensor Nodes
- Kesheng Wang,
- Junyan Lv and
- Wenqiang Yu
- + 5 authors
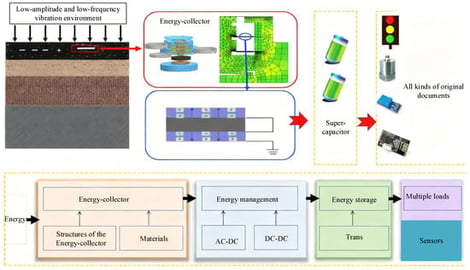
In low-amplitude and low-frequency vibration environments, the energy harvesting efficiency of self-powered wireless sensor nodes is insufficient, limiting their long-term autonomous operation. To address this issue, a micro piezoelectric–electromagnetic hybrid energy harvester is designed, aiming to enhance energy capture efficiency through structural integration and parameter optimization. The study is conducted entirely through numerical simulations. A coaxial integrated architecture is adopted, combining a piezoelectric cantilever beam array with an electromagnetic induction module. The piezoelectric layer uses lead magnesium niobate–lead titanate (PMN-PT) solid solution material with a thickness of 0.2 mm. The electromagnetic module employs copper wire coils with a diameter of 0.08 mm, winding 1500–3000 turns, paired with N52-type neodymium–iron–boron (NdFeB) permanent magnets. To improve energy conversion efficiency, the optimization parameters include the length-to-thickness ratio of the cantilever beam, the mass of the tip mass, the number of coil turns, and the spacing of the permanent magnets. Each parameter is set at four levels for orthogonal experiments. A multi-physics coupling model is established using ANSYS Workbench 2023, covering structural dynamics, piezoelectric effects, and the electromagnetic induction module. The mesh size is set to 0.1 mm. The energy output characteristics are analyzed under vibration frequencies of 0.3–12 Hz and amplitudes of 0.2–1.0 mm. Simulation results show that the optimized hybrid harvester achieves 45% higher energy conversion efficiency than a single piezoelectric structure and 31% higher than a traditional separated hybrid structure within the 0.3–12 Hz low-frequency range. Under a 6 Hz frequency and 0.6 mm amplitude, the output power density reaches 3.5 mW/cm3, the peak open-circuit voltage is 4.1 V, and the peak short-circuit current is 1.3 mA. Under environmental conditions of 20–88% humidity and −15–65 °C temperature, the device maintains over 94% stability in energy output. After 1.2 million vibration cycles, structural integrity remains above 96%, and energy conversion efficiency decreases by no more than 5%. The proposed coaxial hybrid structure and multi-parameter orthogonal optimization method effectively enhance energy harvesting performance in low-amplitude, low-frequency environments. The simulation design parameters and analysis procedures provide a reference for the development of similar micro hybrid energy harvesters and support the performance optimization of self-powered wireless sensor nodes.
9 February 2026