- Article
An Empirical Study on the Determinants of Customers’ Intentions to Switch to Smart Lockers as a Trending Last-Mile Logistics Channel
- Mona ElSemary,
- Nada Eman and
- Dana Corina Deselnicu
- + 1 author
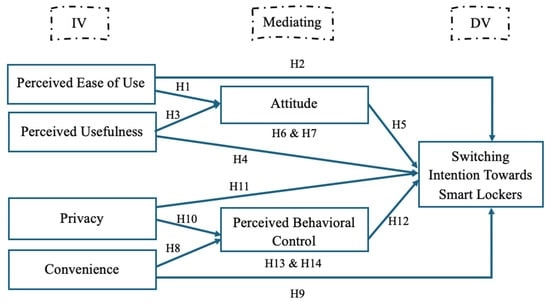
Background: nowadays, traditional delivery options are challenging to the urban last-mile logistics and sustainability goals. The purpose of this study is to investigate the practical factors that drive frequent e-shoppers to actively switch their intention from conventional delivery options to utilizing smart lockers. Methods: the hypothetical framework tested integrating constructs from the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB), and supplementary constructs such as privacy and convenience. Data were collected via a structured online questionnaire from 513 respondents in major Egyptian cities, including Alexandria and Cairo. The framework was tested using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) via SmartPLS 4.0 software to assess the relationship between constructs and switching intention. Results: the analysis confirms that switching intention to use smart lockers is positively driven by Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease of Use, Convenience, Privacy, and Perceived Behavioral Control. Notably, a positive attitude towards smart lockers was found to have a non-significant effect on the intention to switch in the Egyptian context. Conclusions: this research contributes to addressing the gap in the extant literature by focusing on analyzing the unique contextual determinants in the emerging last-mile logistics within a developing market context.
11 December 2025