Journal Description
Kinases and Phosphatases
Kinases and Phosphatases
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on every aspect of post-translational modifications in all biological systems, from bacteria to humans, covering a wide range of disciplines, including biochemistry, molecular biology, structural biology, cell biology, medicinal chemistry, pharmacology, cellular pathology, and clinical disciplines, and is published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 22.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 1.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
SPINET-KSP: A Multi-Modal LLM-Graph Foundation Model for Contextual Prediction of Kinase-Substrate-Phosphatase Triads
Kinases Phosphatases 2026, 4(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases4010003 - 22 Jan 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Reversible protein phosphorylation is an important regulatory mechanism in cellular signalling and disease, regulated by the opposing actions of kinases and phosphatases. Modern computer methods predict kinase–substrate or phosphatase–substrate interactions in isolation and lack specificity for biological conditions, neglecting triadic regulation. We present
[...] Read more.
Reversible protein phosphorylation is an important regulatory mechanism in cellular signalling and disease, regulated by the opposing actions of kinases and phosphatases. Modern computer methods predict kinase–substrate or phosphatase–substrate interactions in isolation and lack specificity for biological conditions, neglecting triadic regulation. We present SPINET-KSP, a multi-modal LLM–Graph foundation model engineered for the prediction of kinase–substrate–phosphatase (KSP) triads with contextual awareness. SPINET-KSP integrates high-confidence interactomes (SIGNOR, BioGRID, STRING), structural contacts obtained from AlphaFold3, ESM-3 sequence embeddings, and a 512-dimensional cell-state manifold with 1612 quantitative phosphoproteomic conditions. A heterogeneous KSP graph is examined utilising a cross-attention Graphormer with Reversible Triad Attention to mimic kinase–phosphatase antagonism. SPINET-KSP, pre-trained on 3.41 million validated phospho-sites utilising masked phosphorylation modelling and contrastive cell-state learning, achieves an AUROC of 0.852 for kinase-family classification (sensitivity 0.821, specificity 0.834, MCC 0.655) and a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.712 for phospho-occupancy prediction. In distinct 2025 mass spectrometry datasets, it identifies 72% of acknowledged cancer-resistance triads within the top 10 rankings and uncovers 247 supplementary triads validated using orthogonal proteomics. SPINET-KSP is the first foundational model for simulating context-dependent reversible phosphorylation, enabling the targeting of dysregulated kinase-phosphatase pathways in diseases.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinases and Arginine Kinase in Trypanosoma cruzi: Versatile Enzymes at the Crossroads of Metabolism, Stress Adaptation, and Drug Development
by
Chantal Reigada, Melisa Sayé, Fabio Augusto Digirolamo and Mariana Reneé Miranda
Kinases Phosphatases 2026, 4(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases4010002 - 9 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Trypanosoma cruzi is the protozoan parasite responsible for Chagas disease, a neglected tropical disease caused by trypanosomatids. Its success as pathogen relies on remarkable metabolic adaptability, stress tolerance, and complex interactions with mammalian hosts. Among the proteins contributing to these processes, nucleoside diphosphate
[...] Read more.
Trypanosoma cruzi is the protozoan parasite responsible for Chagas disease, a neglected tropical disease caused by trypanosomatids. Its success as pathogen relies on remarkable metabolic adaptability, stress tolerance, and complex interactions with mammalian hosts. Among the proteins contributing to these processes, nucleoside diphosphate kinases (NDPKs) and arginine kinase (AK) have emerged as central enzymes for parasite metabolism. NDPKs, beyond their canonical role in nucleotide homeostasis, are implicated in DNA repair and oxidative stress responses and are also secreted enzymes. AK, on the other hand, serves as a unique energy-buffering system absent in mammals, supporting parasite growth and adaptation to oxidative and metabolic stresses, including modulation of host immunity. Both enzymes display distinct subcellular localizations all along the parasite and through the life cycle, linking them to multiple roles important for parasite biology and survival. Recent studies have highlighted the impact of interfering these enzymes with several compounds on the viability of the organisms, suggesting new avenues to explore them as drug targets. This review provides a general overview of NDPKs and AK in T. cruzi, aiming to underline their relevance to a broader context of trypanosomatids. Their study not only broadens our understanding of parasite biology but also opens perspectives for applied research, including therapeutic alternatives for Chagas and related diseases.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Crystallographic Fragment Screening with CK2α’, an Isoform of Human Protein Kinase CK2 Catalytic Subunit, and Its Use to Obtain a CK2α’/Heparin Complex Structure
by
Christian Werner, Tatjana Barthel, Hugo Harasimowicz, Christelle Marminon, Manfred S. Weiss, Marc Le Borgne and Karsten Niefind
Kinases Phosphatases 2026, 4(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases4010001 - 4 Jan 2026
Abstract
CK2α and CK2α’, two paralogous members of the human kinome, are catalytic subunits of protein kinase CK2. Together with the regulatory subunit CK2β, they form heterotetrameric holoenzymes. CK2 is the subject of efforts to develop effective and selective inhibitors. For this, secondary binding
[...] Read more.
CK2α and CK2α’, two paralogous members of the human kinome, are catalytic subunits of protein kinase CK2. Together with the regulatory subunit CK2β, they form heterotetrameric holoenzymes. CK2 is the subject of efforts to develop effective and selective inhibitors. For this, secondary binding sites remote from the canonical ATP/GTP cavity are critical. A crystallographic fragment screening with CK2α’ crystals and an established molecular fragment collection was performed to identify new ligands at known or novel sites. It resulted in fourteen CK2α’/fragment structures. Five fragments were found at the CK2β interface of CK2α’ and three fragments at the established αD pocket, which exhibits subtle differences between CK2α and CK2α’; comparative co-crystallisations with CK2α showed that one of them binds to the αD pocket of CK2α’ exclusively. No fragments bound at the substrate-binding region of CK2α’, but a CK2α’ structure with dp10, a decameric section of the substrate-competitive inhibitor heparin, and the indenoindole-type ATP-competitive inhibitor 4w was determined. A comparison with a published CK2α/dp10 structure revealed features consistent with reports about substrate specificity differences between the isoenzymes: dp10 binds to CK2α’ and CK2α with opposite strand orientations, and the local conformations of the isoenzymes in the helix αD region are significantly different.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Past, Present and Future of Protein Kinase CK2 Research—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
A Critical Assessment of Computer-Aided Approaches for Identifying FAK Inhibitors
by
Patricia A. Quispe, Daniel Lietha, Ignacio E. León and Martin J. Lavecchia
Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3(4), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3040027 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) is a key regulator of tumor cell migration and survival, and its persistent overexpression in aggressive cancers has motivated ongoing efforts to identify novel small-molecule inhibitors. Despite this interest, progress in discovering new potent scaffolds has been limited. In
[...] Read more.
Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) is a key regulator of tumor cell migration and survival, and its persistent overexpression in aggressive cancers has motivated ongoing efforts to identify novel small-molecule inhibitors. Despite this interest, progress in discovering new potent scaffolds has been limited. In this work, we applied a multistep computational workflow followed by experimental testing to refine hit selection and reduce the false positives typically associated with docking. DrugBank and several commercial libraries were screened using Exponential Consensus Ranking (ECR) docking, and molecular dynamics simulations were used to assess pose stability and interaction persistence. A subset of predicted binders was then tested in MG-63 (bone cancer) and MDA-MB-231 (breast cancer) cells using cell viability and wound-healing assays, followed by direct autophosphorylation assays with recombinant FAK. Several repurposed compounds, including clofazimine and tafamidis, produced clear dose-dependent effects on cell migration, although their inhibitory activity in biochemical assays remained weak (

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Differential Expression of STK35L1-Associated Transcription Factors in Plasmodium Infection During the Liver Stage of Malaria
by
Arpana Yadav, Phulwanti Kumari Sharma, Mayuree Hazarika, Pragya Gehlot, Saloni Bage, Mahesh Saini, Kritika Gaur, Acham Parambath Aswathi, Malti Thakur, Devesh Madhukar Sawant, Agam Prasad Singh, Daniela Brünnert and Pankaj Goyal
Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3(4), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3040026 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Malaria remains one of the devastating illnesses, and drug-resistant malaria has incurred enormous societal costs. A few host kinases are vital for the liver stage malaria and might be promising drug targets against drug-resistant malaria. STK35L1 is one of the host kinases that
[...] Read more.
Malaria remains one of the devastating illnesses, and drug-resistant malaria has incurred enormous societal costs. A few host kinases are vital for the liver stage malaria and might be promising drug targets against drug-resistant malaria. STK35L1 is one of the host kinases that is highly upregulated during the liver stage of malaria, and the knockdown of STK35L1 significantly suppresses Plasmodium sporozoite infection. In this study, we retrieved the promoter region of STK35L1 based on 5′ complete transcripts, transcription start sites, and cap analysis of gene expression tags. Furthermore, we identify transcriptionally active regions by analyzing CpG islands, histone acetylation (H3K27ac), and histone methylation (H3K4me3). It suggests that the identified promoter region is active and has cis-regulatory elements and enhancer regions. We identified various putative transcription factors (TFs) from the various high-throughput ChIP data that might bind to the promoter region of STK35L1. These TFs were differentially regulated during the infection of Plasmodium sporozoites in HepG2 cells. Our molecular modeling study suggests that, except for SMAD3, the identified TFs may be directly bound to the promoter. Together, the data suggest that these TFs may play a role in sporozoite infection and in regulating STK35L1 expression during the liver stage of malaria.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Differential Expression of AURKA, AURKB, and PLK1 Modulates Clinical Outcomes and Survival in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
by
Anna Karolyna da Costa Machado, Beatriz Maria Dias Nogueira, Deivide de Sousa Oliveira, Caio Bezerra Machado, Flávia Melo Cunha de Pinho Pessoa, Leidivan Sousa Cunha, Igor Valentim Barreto, Isabelle Magalhães Farias, Rodrigo Monteiro Ribeiro, Ana Paula Lopes Moreira, Kaira Mara Cordeiro de Albuquerque, Mateus de Paula Gomes, Fabiana Aguiar Carneiro Silva, Lívia Andrade Gurgel, Gésio Eduardo Antas Rodrigues, Ricardo Parente Garcia Vieira, André Salim Khayat, Ana Virgínia Soares Van Den Berg, Manoel Odorico de Moraes Filho, Maria Elisabete Amaral de Moraes and Caroline Aquino Moreira-Nunesadd
Show full author list
remove
Hide full author list
Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3(4), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3040025 - 3 Dec 2025
Abstract
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is one of the most aggressive types of leukemia, represented by the clonal proliferation of hematopoietic precursors, which mainly promotes quantitative and differentiation alterations, as well as normal hematopoiesis suppression. Throughout leukemogenesis, modifications may occur in several elements that
[...] Read more.
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is one of the most aggressive types of leukemia, represented by the clonal proliferation of hematopoietic precursors, which mainly promotes quantitative and differentiation alterations, as well as normal hematopoiesis suppression. Throughout leukemogenesis, modifications may occur in several elements that make up cellular signaling pathways; among these, AURKA, AURKB, and PLK1 are key related regulators of mitotic progression and cellular proliferation. This study investigated the hematological profile and the expression of the AURKA, AURKB, and PLK1 genes in a cohort of individuals with AML, in order to understand their roles in the pathophysiology of the disease. The analyses revealed a significant hypoexpression of AURKA in the bone marrow of AML individuals compared to the control group (p = 0.0254) and AURKB showed no significant difference in bone marrow and peripheral blood samples. It was also observed a hyperexpression of PLK1 in bone marrow (p < 0.0001) and in peripheral blood (p = 0.0144). Our results also point to PLK1 as a potential biomarker for AML, since its hyperexpression did not differ with respect to gender, risk stratification, or age of the individuals. Finally, survival analyses indicate that AURKA expression in the bone marrow is associated with a protective factor and increased survival, and that those with higher expression of the three target genes had a lower mortality rate (p = 0.043).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Kinases in Cancer and Other Diseases, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The 14-3-3 Protein Family, Beyond the Kinases and Phosphatases
by
Exequiel E. Barrera, Marina Uhart and Diego M. Bustos
Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3(4), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3040024 - 28 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Eukaryotic phosphorylation of serine and threonine residues is a central regulatory mechanism in cell signalling, carried out by more than 500 kinases and a diverse array of phosphatases. Traditionally understood as a two-component system driven by writers (kinases) and erasers (phosphatases), this regulatory
[...] Read more.
Eukaryotic phosphorylation of serine and threonine residues is a central regulatory mechanism in cell signalling, carried out by more than 500 kinases and a diverse array of phosphatases. Traditionally understood as a two-component system driven by writers (kinases) and erasers (phosphatases), this regulatory network is now appreciated to involve additional proteins that modulate or interpret phosphorylation-dependent changes. Among them, the 14-3-3 protein family has emerged as a prominent example due to its ability to bind phosphorylated serine/threonine motifs—typically located within intrinsically disordered regions—and influence the activity, stability, or localization of its partners. In this review, we discuss the importance, evolution, structure, and dynamics of 14-3-3 proteins, as well as their interactions with small molecules—both natural and designed—that bind to them. We highlight several underexplored aspects of their molecular behaviour, integrate recent discoveries, and emphasize how these insights contribute to a broader understanding of phosphorylation-dependent regulation across eukaryotes.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Polo-like Kinase 1 (PLK1) Inhibitors Targeting Anticancer Activity
by
Dina Bárbara Aguado-Herrera, Yudith Cañizares-Carmenate and Edeildo Ferreira da Silva-Júnior
Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3(4), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3040023 - 12 Nov 2025
Abstract
Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) is a serine/threonine kinase that orchestrates multiple critical events during mitosis, including centrosome maturation, spindle assembly, kinetochore–microtubule attachment, and cytokinesis. Dysregulation and overexpression of PLK1 are frequently observed in various cancers, correlating with increased proliferation, metastatic potential, and poor
[...] Read more.
Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) is a serine/threonine kinase that orchestrates multiple critical events during mitosis, including centrosome maturation, spindle assembly, kinetochore–microtubule attachment, and cytokinesis. Dysregulation and overexpression of PLK1 are frequently observed in various cancers, correlating with increased proliferation, metastatic potential, and poor prognosis, which highlights its potential as a therapeutic target. Traditional small-molecule inhibitors have predominantly focused on the ATP-binding site of the N-terminal kinase domain, effectively inducing mitotic arrest and apoptosis in tumor cells; however, these compounds often suffer from limited selectivity and off-target toxicity. The C-terminal Polo-box domain (PBD), responsible for substrate recognition and subcellular localization, has emerged as an alternative and highly selective target for inhibitor design, enabling the disruption of protein–protein interactions critical for PLK1 function. Here, we present a comprehensive review demonstrating the potential inhibition of several compounds against PLK1. This work establishes a foundation for future preclinical development of small molecule-based therapeutics against PLK1-dependent malignancies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Human Protein Kinases: Development of Small-Molecule Therapies—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Bioinformatic Investigation of Regulatory Elements in the Core Promoters of CK2 Genes and Pseudogene
by
Nicholas G. Wilson, Jesse S. Basra and Isabel Dominguez
Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3(4), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3040022 - 4 Nov 2025
Abstract
Protein kinase CK2 is an important regulator of cell, embryo, and organism function whose transcript levels are often dysregulated in disease. Previous studies have primarily focused on the regulation of CK2 gene expression via the proximal promoter. Here, we analyzed the core promoter
[...] Read more.
Protein kinase CK2 is an important regulator of cell, embryo, and organism function whose transcript levels are often dysregulated in disease. Previous studies have primarily focused on the regulation of CK2 gene expression via the proximal promoter. Here, we analyzed the core promoter of the CK2 genes and pseudogene to assess the structure and potential regulatory elements. Our analysis showed that CSNK2A1 contained 14 exons, rather than 13 exons as previously reported. Using FANTOM5 and DBTTS data, we found that transcription start sites were broadly distributed across a 100-nucleotide region in the CK2 gene core promoters, consistent with “broad” class promoter architecture. Using these databases, we found a dissimilar transcription start site usage between adult and cancer tissues compared to fetal tissues for each of the CK2 gene promoters. A further analysis of the CK2 gene core promoter subregions showed instances of core promoter subregion switching. All CK2 gene core promoters contained canonical and non-canonical initiator motifs, suggesting their potential as dual-initiator core promoters, while CSNK2A3 only had canonical initiator motifs. Additionally, all CK2 gene core promoters contain DCE motifs and pause buttons. In contrast, Wnt/β-catenin target genes c-MYC and CCND1 had DPEs, which can be regulated by protein kinase CK2. Collectively, our data provides new insights into the transcriptional regulation of CK2 genes and opens new avenues for research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Past, Present and Future of Protein Kinase CK2 Research—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Metal–Organic Frameworks for Enzyme Modulation in Protein Kinase and Phosphatase Regulation—Mechanisms and Biomedical Applications
by
Azizah Alamro and Thanih Balbaied
Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3(4), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3040021 - 30 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) have been increasingly recognized as promising platforms for enzyme modulation, owing to their tunable porosity, high surface area, and versatile chemical functionality. In this review, the potential of MOFs for the inhibition and modulation of protein kinases and phosphatases—key regulators
[...] Read more.
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) have been increasingly recognized as promising platforms for enzyme modulation, owing to their tunable porosity, high surface area, and versatile chemical functionality. In this review, the potential of MOFs for the inhibition and modulation of protein kinases and phosphatases—key regulators of cellular signaling and disease progression—is examined. The structural fundamentals of MOFs are outlined, followed by a discussion of common synthesis strategies, including solvothermal, microwave-assisted, sonochemical, and mechanochemical methods. Emphasis is placed on how synthesis conditions influence critical features such as particle size, crystallinity, surface chemistry, and functional group accessibility, all of which impact biological performance. Four primary mechanisms of MOF–enzyme interaction are discussed: surface adsorption, active site coordination, catalytic mimicry, and allosteric modulation. Each mechanism is linked to distinct physicochemical parameters, including pore size, surface charge, and metal node identity. Special focus is given to biologically relevant metal centers such as Zr4+, Ce4+, Cu2+, Fe3+, and Ti4+, which have been shown to contribute to both MOF stability and enzymatic inhibition through Lewis acid or redox-mediated mechanisms. Recent in vitro studies are reviewed, in which MOFs demonstrated selective inhibition of disease-relevant enzymes with minimal cytotoxicity. Despite these advancements, several limitations have been identified, including scalability challenges, limited physiological stability, and potential off-target effects. Strategies such as post-synthetic modification, green synthesis, and biomimetic surface functionalization are being explored to overcome these barriers. Through an integration of materials science, coordination chemistry, and molecular biology, this review aims to provide a comprehensive perspective on the rational design of MOFs for targeted enzyme inhibition in therapeutic contexts.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mass Spectrometry and 3D Modeling Indicate the SBK2 Kinase Phosphorylates Splicing Factor SRSF7 to Regulate Cardiac Development
by
Mark Bouska, Eduardo Callegari, Daniela Paez and Xuejun Wang
Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3(4), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3040020 - 23 Sep 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
SH3 Domain Binding Kinase Family Member 2 (SBK2) is a critical kinase in atrial cardiomyocyte differentiation. However, its phospho-targets, its role in ventricle function, and its role in cardiac disease progression are unknown. Notably, SBK2 has been shown to be downregulated in the
[...] Read more.
SH3 Domain Binding Kinase Family Member 2 (SBK2) is a critical kinase in atrial cardiomyocyte differentiation. However, its phospho-targets, its role in ventricle function, and its role in cardiac disease progression are unknown. Notably, SBK2 has been shown to be downregulated in the ventricular myocardium of several mouse models that recapitulate human desmin-related cardiomyopathies. To restore SBK2 expression, adenoviruses were constructed to promote cardiomyocyte-restricted SBK2 expression and injected at postnatal day 0. This significantly increased ejection fraction at 1 month of age relative to control hearts. However, in 3-month nontransgenic (NTG) and desmin-related cardiomyopathy hearts, the overexpression of SBK2 opposed increases in ejection fraction and left ventricular posterior wall thickness. These findings provide the first in vivo evidence that SBK2 plays a vital role in left ventricular function. To elucidate the molecular mechanism behind the physiological effects of SBK2 on the heart, we performed mass spectrometry combined with phospho-enrichment on ventricular tissue with and without SBK2 overexpression. We identified multiple phosphorylation sites on SBK2 and used AlphaFold3 to model how this phosphorylation likely affects SBK2’s role in phosphorylating the splicing factor SRSF7. We propose a novel mechanism by which SBK2 regulates splicing to promote cardiomyocyte development.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Critical Look at the Crystal Structures of cAMP-Dependent Protein Kinases
by
Alexander Wlodawer, Pawel Rubach, Zbigniew Dauter, Wojciech Dec, Wladek Minor, Dariusz Brzezinski and Mariusz Jaskolski
Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3(3), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3030019 - 11 Sep 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
We have evaluated the quality of all 325 deposits in the PDB (as of December 2024) that correspond to (or contain) the catalytic domain of cAMP-dependent protein kinases (PKA). Detailed analysis was possible for 289 deposits of crystal structures that included not only
[...] Read more.
We have evaluated the quality of all 325 deposits in the PDB (as of December 2024) that correspond to (or contain) the catalytic domain of cAMP-dependent protein kinases (PKA). Detailed analysis was possible for 289 deposits of crystal structures that included not only the atomic coordinates but also structure factors. These structures represent 35 years of studies, and it is not surprising that the more recent structures are generally of better quality than the older ones. We did not encounter deposits with very severe problems, although some minor problems were found. To assess whether a uniform method of structure re-refinement, as implemented in the pipeline and website PDB-REDO, leads to significant improvement of structural models, we compared structure quality indicators for the originally refined structures and their counterparts resulting from PDB-REDO refinement. The re-refinement procedure significantly improved only some older structures, while its success was generally limited. We paid particular attention to the quality of small-molecule ligands, finding that most of them fit the electron density very well. This type of analysis helps identify the highest quality structures among many deposits for certain protein families and, thus, could be extended to other groups of proteins as well.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Digital Twin-Based Multiscale Models for Biomarker Discovery in Kinase and Phosphatase Tumorigenic Processes
by
Sara Sadat Aghamiri and Rada Amin
Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3(3), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3030018 - 31 Aug 2025
Cited by 2
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Digital twin is a mathematical model that virtually represents a physical object or process and predicts its behavior at future time points. These simulation models enable a deeper understanding of tumorigenic processes and improve biomarker discovery in cancer research. Tumor microenvironment is marked
[...] Read more.
Digital twin is a mathematical model that virtually represents a physical object or process and predicts its behavior at future time points. These simulation models enable a deeper understanding of tumorigenic processes and improve biomarker discovery in cancer research. Tumor microenvironment is marked by dysregulated signaling pathways, where kinases and phosphatases serve as critical regulators and promising sources for biomarker discovery. These enzymes operate within multiscale and context-dependent processes where spatial and temporal coordination determine cellular outcomes. Digital Twin technology provides a platform for multimodal and multiscale modeling of kinase and phosphatase processes at the patient-specific level. These models have the potential to transform biomarker validation processes, enhance the prediction of therapeutic responses, and support precision decision-making. In this review, we present the major alterations affecting kinases and phosphatase functions within the tumor microenvironment and their clinical relevance as biomarkers, and we address how digital twins in oncology can augment and refine each stage of the biomarker discovery pipeline. Introducing this emerging technology for cancer biomarker discovery will assist in accelerating its adoption and translation into precision diagnostics and targeted therapies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Past, Present and Future of Protein Kinase CK2 Research
by
Mauro Salvi and Maria Ruzzene
Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3(3), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3030017 - 19 Aug 2025
Abstract
The first described instance of protein kinase activity dates back more than half a century [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Past, Present and Future of Protein Kinase CK2 Research)
Open AccessReview
Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) Agonists and Protein Kinase Regulation in NAFLD and NASH: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential
by
Ayan Saha, Emily Wood, Luna Omeragic, Maya Minkara, Kethain Marma, Shipan Das Gupta and Jannatul Ferdoush
Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3(3), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3030016 - 11 Jul 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a common metabolic condition characterized by hepatic lipid deposits, insulin resistance, and inflammation which may progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and fibrosis. Protein kinases play an important role in NAFLD development by regulating metabolic and inflammatory pathways.
[...] Read more.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a common metabolic condition characterized by hepatic lipid deposits, insulin resistance, and inflammation which may progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and fibrosis. Protein kinases play an important role in NAFLD development by regulating metabolic and inflammatory pathways. Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), protein kinase C (PKC), AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT, and mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) are all involved in NAFLD and NASH progression. Emerging evidence indicates that Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) agonists have therapeutic potential by modulating bile acid metabolism, lipid balance, and inflammatory responses. This review examines the mechanistic interplay between FXR agonists and important protein kinases in NAFLD and NASH. FXR agonists activate AMPK, which promotes fatty acid oxidation and reduces hepatic steatosis. They also regulate MAPK signaling, which reduces c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK)- and p38 MAPK-mediated inflammation. Furthermore, FXR agonists activate the PI3K/AKT pathway, enhancing insulin sensitivity and modulating mTOR signaling to reduce hepatic fibrosis. Clinical studies in NAFLD/NASH indicate that FXR agonists confer metabolic and anti-inflammatory benefits, although optimizing efficacy and minimizing adverse effects remain challenging. Future studies should focus on combination therapies targeting FXR alongside specific kinases to improve therapeutic outcomes. This review highlights the potential of FXR agonists to modulate protein kinase signaling, opening new avenues for targeted NAFLD/NASH therapy.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Regulation of Mouse CK2α (Csnk2a1) Promoter Expression In Vitro and in Cell Lines
by
Gregory A. Imbrie, Nicholas G. Wilson, David C. Seldin and Isabel Dominguez
Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3(3), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3030015 - 4 Jul 2025
Cited by 3
Abstract
CK2α is a kinase important for essential cellular and biological processes. CK2α is ubiquitously expressed, albeit at different tissue levels, and its transcript levels are dysregulated in disease. However, there is limited knowledge on the regulation of CK2α gene expression. The best one
[...] Read more.
CK2α is a kinase important for essential cellular and biological processes. CK2α is ubiquitously expressed, albeit at different tissue levels, and its transcript levels are dysregulated in disease. However, there is limited knowledge on the regulation of CK2α gene expression. The best one studied, the human CSNK2A1 (CK2α) gene promoter, contains uncharacterized binding motifs for NF-κB. Our goal was to investigate the role of NF-κB in Csnk2a1 promoter regulation. We cloned the mouse Csnk2a1 promoter which had significant sequence homology with the human CSNK2A1 promoter. Using promoter deletions, we identified a minimal promoter region containing transcription factor motifs (NF-κB, Ets-1, Sp1) consistent with those published for the CSNK2A1 promoter. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays demonstrated specific NF-κB subunit binding to the minimal promoter. NF-κB subunit transfection and extracellular NF-κB stimulation in non-tumor cell lines led to increased transactivation of the mouse minimal promoter. These data, together with data on the regulation of NF-κB by CK2 kinase activity, suggest a positive-feedback loop between CK2α and NF-κB. Non-tumor cell line re-plating and increased percent confluence upregulated Csnk2a1 transcript levels which differed from tumor cell line published data. In summary, Csnk2a1 promoter is regulated by NF-κB signaling and during cellular proliferation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Past, Present and Future of Protein Kinase CK2 Research)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Protein Kinases in Mediating Phage-Bacteria Interactions
by
Yong Everett Zhang
Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3(3), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3030014 - 25 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Protein kinases and phosphatases are essential for post-translational regulation, enabling bacteria to adapt to environmental stresses and modulate virulence. While prior reviews have broadly covered their roles in stress response, antibiotic resistance, and virulence, this article updates specifically on the roles of histidine
[...] Read more.
Protein kinases and phosphatases are essential for post-translational regulation, enabling bacteria to adapt to environmental stresses and modulate virulence. While prior reviews have broadly covered their roles in stress response, antibiotic resistance, and virulence, this article updates specifically on the roles of histidine kinases (HKs) and serine/threonine kinases (STKs) in mediating phage-bacteria interactions. A key aspect is phage-encoded kinases, which hijack bacterial signalling by phosphorylating and disrupting host processes to promote infection. Despite their importance, significant gaps remain in understanding these regulatory networks. This microreview highlights both the unresolved mechanisms and the therapeutic potential of targeting kinase pathways—for instance, by disrupting phage evasion strategies or enhancing phage-based antimicrobial therapies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Fucosylation-Mediated Suppression of Lipid Droplet Accumulation Induced by Low-Level L-Fucose Administration in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
by
Tomoya Nakamura, Tomohiko Nakao, Yuri Kominami, Miho Ito, Teruki Aizawa, Yusuke Akahori and Hideki Ushio
Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3(3), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3030013 - 24 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Obesity causes lifestyle-related diseases such as hypertension and type 2 diabetes and has become a global health concern. L-fucose (Fuc), a monosaccharide that can be derived from brown algae, has been shown to strongly suppress lipid droplet accumulation in 3T3-L1 murine adipocytes at
[...] Read more.
Obesity causes lifestyle-related diseases such as hypertension and type 2 diabetes and has become a global health concern. L-fucose (Fuc), a monosaccharide that can be derived from brown algae, has been shown to strongly suppress lipid droplet accumulation in 3T3-L1 murine adipocytes at high concentrations via the activation of AMP-activated kinase (AMPK). Although low concentrations of Fuc also exhibited similar effects, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. In this study, we investigated the effects of low-level Fuc on lipid metabolism, focusing on the role of fucosylation. Low-level Fuc did not induce AMPK phosphorylation but suppressed lipid droplet accumulation. This suppressive effect was abolished by co-treatment with the fucosylation inhibitor 2F-Peracetyl-Fucose (2F-PAF), suggesting that fucosylation plays a key role in the observed metabolic regulation. Furthermore, proteomic analysis combined with click chemistry pulldown suggested that proteins involved in the regulation of lipid metabolism, such as acetoacetyl-CoA synthetase enzymes and catalytic subunit alpha of cAMP-dependent protein kinase, are fucosylated or interact with fucose. These findings provide novel insights into the anti-obesity mechanisms of Fuc and highlight the physiological significance of protein fucosylation in adipocyte lipid metabolism.
Full article
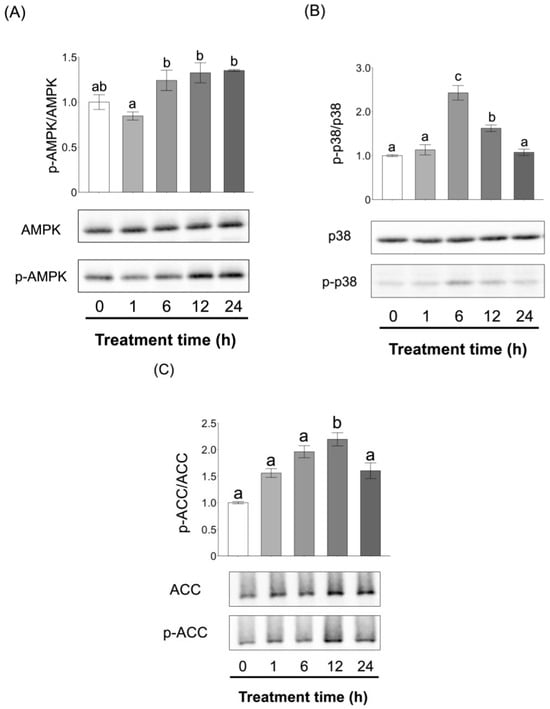
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Multifaceted Role of STK35/STK35L1 in Human Diseases: A Time for Critical Appraisal
by
Arpana Yadav, Kritika Gaur, Phulwanti Kumari Sharma, Pragya Gehlot, Saloni Bage, Mahesh Saini, Daniela Brünnert and Pankaj Goyal
Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3(2), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3020012 - 23 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Dysregulation of protein kinases is associated with developmental defects and various human diseases. The human kinome comprises 518 kinases, including several orphan kinases whose functions remain to be fully characterized. The NKF4 family, which includes STK35L1 and PDIK1L, is one such uncharacterized kinase
[...] Read more.
Dysregulation of protein kinases is associated with developmental defects and various human diseases. The human kinome comprises 518 kinases, including several orphan kinases whose functions remain to be fully characterized. The NKF4 family, which includes STK35L1 and PDIK1L, is one such uncharacterized kinase family. STK35L1, also known as Clik1, was initially identified as a nuclear kinase associated with actin fibers. Subsequent studies have demonstrated that STK35L1 plays critical roles in cellular processes such as cell cycle regulation, migration, angiogenesis, the DNA damage response, and related processes such as spermatogenesis. STK35L1 has also been implicated in various developmental processes and its knockout mice exhibited defects in the testis, ovary, and eye. STK35L1 acts as a central regulator of the fundamental cellular functions, and its dysregulation leads to various diseases. Research has established that STK35L1 regulates tumor growth and proliferation in cancers such as osteosarcoma, colorectal cancer, and acute myeloid leukemia. Notably, it also affects chemosensitivity in colorectal cancer and metabolism in acute myeloid leukemia. Additionally, STK35L1 is crucial for the infection of hepatocytes by Plasmodium sporozoites during the liver stage of Malaria. This review discusses the current understanding of STK35L1, highlighting its role in various diseases.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Comparative Kinetic Study on Alkaline Phosphatase Thermal Inactivation in Different Milk Types
by
Anastasia Tzereme, Michalis Koureas, Athanasios Manouras, Eleni Malissiova, Georgia Soultani, Konstantina Poulianiti and Eleni Gogou
Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3(2), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3020011 - 16 May 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has raised concerns regarding the use of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) as a pasteurization marker in non-cow milk due to compositional differences. This study investigates the thermal inactivation kinetics of ALP in six milk species (cow, sheep, goat,
[...] Read more.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has raised concerns regarding the use of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) as a pasteurization marker in non-cow milk due to compositional differences. This study investigates the thermal inactivation kinetics of ALP in six milk species (cow, sheep, goat, donkey, buffalo and camel) to assess its reliability as an indicator. The thermal inactivation of ALP in different milk types was evaluated by heating samples at 63–75 °C at various times, then measuring residual enzyme activity using a spectrophotometric method. The results revealed a sharp increase in ALP inactivation with rising temperatures, consistent with previous findings on the enzyme’s thermal sensitivity. Notably, donkey milk exhibited the highest ALP inactivation at 72 °C, probably due to lower fat content compared to the rest of milk types studied, while camel milk showed the lowest inactivation rate constant (kT) at 75 °C, highlighting its higher heat resistance compared to bovine milk. These findings highlight potential limitations of using the ALP test to verify pasteurization in non-bovine milk, which is directly linked to microbial safety, as well as the preservation of nutritional and sensory characteristics. This study reinforces the importance of considering milk composition, particularly fat and protein structures, in optimizing pasteurization conditions for diverse milk varieties.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biology, Biomolecules, Cancers, Cells, IJMS, Pharmaceuticals, Kinases and Phosphatases
Kinases in Cancer and Other Diseases, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Jonas Cicenas, Anna M. CzarneckaDeadline: 31 August 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Kinases and Phosphatases
Human Protein Kinases: Development of Small-Molecule Therapies—2nd Edition
Guest Editor: Alison D. AxtmanDeadline: 28 February 2026
Special Issue in
Kinases and Phosphatases
Kinases and Phosphatases in Alzheimer's Disease
Guest Editor: Alberto OuroDeadline: 30 April 2026
Special Issue in
Kinases and Phosphatases
Uncovering the Substrate Landscape: Emerging Methods in PTM Enzyme Target Discovery
Guest Editor: Kyle K. BiggarDeadline: 30 April 2026
Special Issue in
Kinases and Phosphatases
Past, Present and Future of Protein Kinase CK2 Research—2nd Edition
Guest Editors: Mauro Salvi, Maria RuzzeneDeadline: 30 June 2026







