Abstract
Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) is a serine/threonine kinase that orchestrates multiple critical events during mitosis, including centrosome maturation, spindle assembly, kinetochore–microtubule attachment, and cytokinesis. Dysregulation and overexpression of PLK1 are frequently observed in various cancers, correlating with increased proliferation, metastatic potential, and poor prognosis, which highlights its potential as a therapeutic target. Traditional small-molecule inhibitors have predominantly focused on the ATP-binding site of the N-terminal kinase domain, effectively inducing mitotic arrest and apoptosis in tumor cells; however, these compounds often suffer from limited selectivity and off-target toxicity. The C-terminal Polo-box domain (PBD), responsible for substrate recognition and subcellular localization, has emerged as an alternative and highly selective target for inhibitor design, enabling the disruption of protein–protein interactions critical for PLK1 function. Here, we present a comprehensive review demonstrating the potential inhibition of several compounds against PLK1. This work establishes a foundation for future preclinical development of small molecule-based therapeutics against PLK1-dependent malignancies.
1. Introduction
Cancer remains one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide, and its treatment continues to pose a significant clinical challenge. Conventional therapeutic approaches, such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy, are often limited by acquired resistance, disease recurrence, and severe side effects that substantially compromise patients’ quality of life [1,2]. In this context, the design of drugs targeting specific molecular sites has emerged as a promising strategy, offering the potential to enhance therapeutic efficacy while minimizing associated toxicity [3,4,5].
During the cell cycle, a variety of molecular signals regulate the orderly progression of cell division through checkpoint controls at the G1/S and G2/M transitions, as well as during mitosis. These mechanisms enable the repair of DNA damage and ensure the fidelity of chromosomal replication and segregation. The proper execution of these processes relies on the coordinated activity of several nuclear serine/threonine kinases, including cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), polo-like kinases (PLKs), and Aurora kinases [6]. In cancer cells, these kinases are frequently deregulated, promoting uncontrolled proliferation and aberrant cell division [7,8].
Within these families, the polo-like kinases (PLKs) constitute a highly conserved group from yeast to humans, originally described in Drosophila melanogaster from a mitotic mutant characterized by abnormal spindle poles [9]. These proteins share a structural organization consisting of an N-terminal catalytic domain (CD), responsible for kinase activity, and a C-terminal polo-box domain (PBD), which mediates interactions with phosphorylated substrates and directs subcellular localization. In mammals, five members (PLK1–PLK5) have been identified, each exhibiting distinct functions in cell cycle progression and signaling processes [10,11].
Among these, Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) is the most extensively studied member and is regarded as a key regulator of the G2/M transition, mitosis, and cytokinesis. Its expression is low or undetectable in differentiated cells but markedly elevated in proliferating cells. In human tumors, PLK1 is consistently overexpressed, and its presence is associated with increased tumor aggressiveness, drug resistance, and poorer clinical outcomes [1,2,12]. These findings have established PLK1 as an attractive therapeutic target, since its pharmacological inhibition can induce cell-cycle arrest and selective apoptosis in cancer cells, whereas normal cells exhibit a lower dependency on this kinase for their survival [13].
The search for specific PLK1 inhibitors has led to multiple strategies, including compounds targeting the kinase domain (ATP-competitive inhibitors) and molecules directed toward the polo-box domain (PBD inhibitors). Both approaches present distinct advantages and limitations. Catalytic site inhibitors tend to exhibit high potency but limited selectivity due to structural conservation among kinases, whereas PBD inhibitors exploit more specific interactions, although they often display lower initial potency [14,15,16,17].
These findings support the relevance of PLK1 as an oncological target and highlight the importance of computational approaches in the rational design of inhibitors. This review aims to provide a detailed analysis of various aspects related to PLK1 as a therapeutic target, including its structural and functional biology, binding sites and inhibition mechanisms, representative compounds under clinical investigation, and computational studies contributing to the development of innovative anticancer strategies.
2. Polo-like Kinase 1: A Promising Therapeutic Target for Cancer Treatment
2.1. PLK1 Structure
The PLK1 (Figure 1) is a highly conserved serine/threonine kinase composed of 603 amino acids and has an approximate molecular mass of 66 kDa [18,19]. Its polypeptide sequence is organized into two clearly defined functional domains: an N-terminal kinase domain and a C-terminal PBD, each with distinct structural and functional characteristics [9,20].
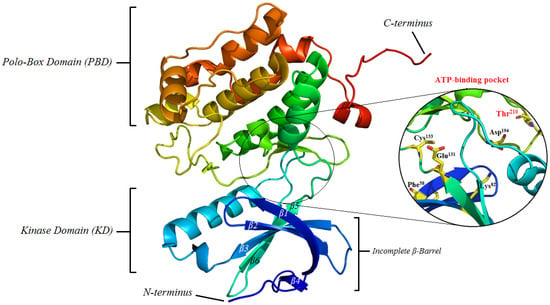
Figure 1.
Structure of Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) showing both the polo-box domain (PBD) and kinase domain (KD), as well as, its catalytic binding pocket. PDB id: 2RKU; PyMol version 0.99 was used to generate the cartoon style of illustration, colored by using rainbow style.
2.1.1. PLK1 Kinase Domain: Structural Organization and Crystallographic Evidence of the ATP Catalytic Site
The N-terminal kinase domain of PLK1, spanning approximately residues 49–310, contains all the elements required for catalytic activity, including Thr210 located within the activation (T-) loop. This threonine represents a critical residue within the catalytic domain of PLK1, and its phosphorylation is an essential step for the enzyme to achieve full activity. This post-translational modification is carried out by upstream regulatory kinases in the signaling hierarchy, with Aurora A in association with the cofactor Bora being primarily responsible for this event [9,21]. The incorporation of a phosphate group at this residue induces a conformational change that stabilizes the active structure of PLK1, enabling the protein to recognize and phosphorylate its substrates. As a result, the proper transition of the cell from the G2 phase to mitosis is facilitated, coordinating key processes such as centrosome maturation, mitotic spindle formation, and chromosomal segregation [22,23]. The architecture of this domain combines β-sheets and α-helices, forming an incomplete β-barrel composed of six antiparallel strands and several α-helix bundles at the C-terminal terminus, which provide structural stability and define the catalytic site where ligands and substrates bind for phosphorylation. Additional helices, such as αD and αG, are positioned strategically, suggesting a significant role in active site orientation and in interactions with regulatory proteins and mitotic cofactors [18,22,24].
The ATP-binding pocket is located at the interface between the N-lobe (predominantly β-sheets) and the C-lobe (α-helices), creating a narrow cavity that recognizes both the adenine base and the ribose-phosphate backbone. Its architecture is defined by a set of highly conserved residues that determine ATP affinity and selectivity against other kinases [21]. Among the most relevant residues are Lys82, which is involved in ATP anchoring and orientation; Glu131 and Asp194, essential components of the catalytic network that position the nucleotide and facilitate the phosphate transfer reaction; and Cys133 and Phe58, which influence the pocket topology and inhibitor selectivity. These residues have been repeatedly reported as hotspots in structural studies with co-crystallized inhibitors, such as BI-2536 [21,25,26].
The hinge region, which connects both lobes, provides donor and acceptor atoms capable of forming hydrogen bonding-interactions with the adenine moiety of ATP; these same sites are exploited by ATP-competitive inhibitors to mimic these interactions. Nearby residues, such as Phe58 and the so-called gatekeeper, contribute hydrophobic contacts that define the selectivity sub-pocket [27]. Moreover, Glu131 and Cys133 form a local network that shapes the geometry of the catalytic site, while Asp194 is directly integrated into the catalytic machinery. Together with the T-loop, phosphorylation of Thr210 is crucial: this event shifts the conformation of the T-loop, opens the catalytic site, and modulates the affinity for both ATP and inhibitors that discriminate between the active and inactive states of the enzyme [23,28,29].
Co-crystallization studies with representative inhibitors (BI-2536, volasertib/BI-6727, onvansertib/NMS-P937, GSK461364—see Figure 2) reveal a recurring pattern: most form between one and three hydrogen bonding-interactions with the hinge, mimicking the interaction of adenine, while aromatic fragments occupy an adjacent hydrophobic pocket that enhances inhibitory potency. Subtle variations, such as rotamers of Cys133 or the positioning of Phe58, account for differences in selectivity between PLK1 and other kinases in the family (PLK2 and PLK3) [30]. Similarly, phosphorylation of the T-loop induces a structural rearrangement that influences the affinity of conformationally selective inhibitors, which is crucial for rational drug design [31,32].
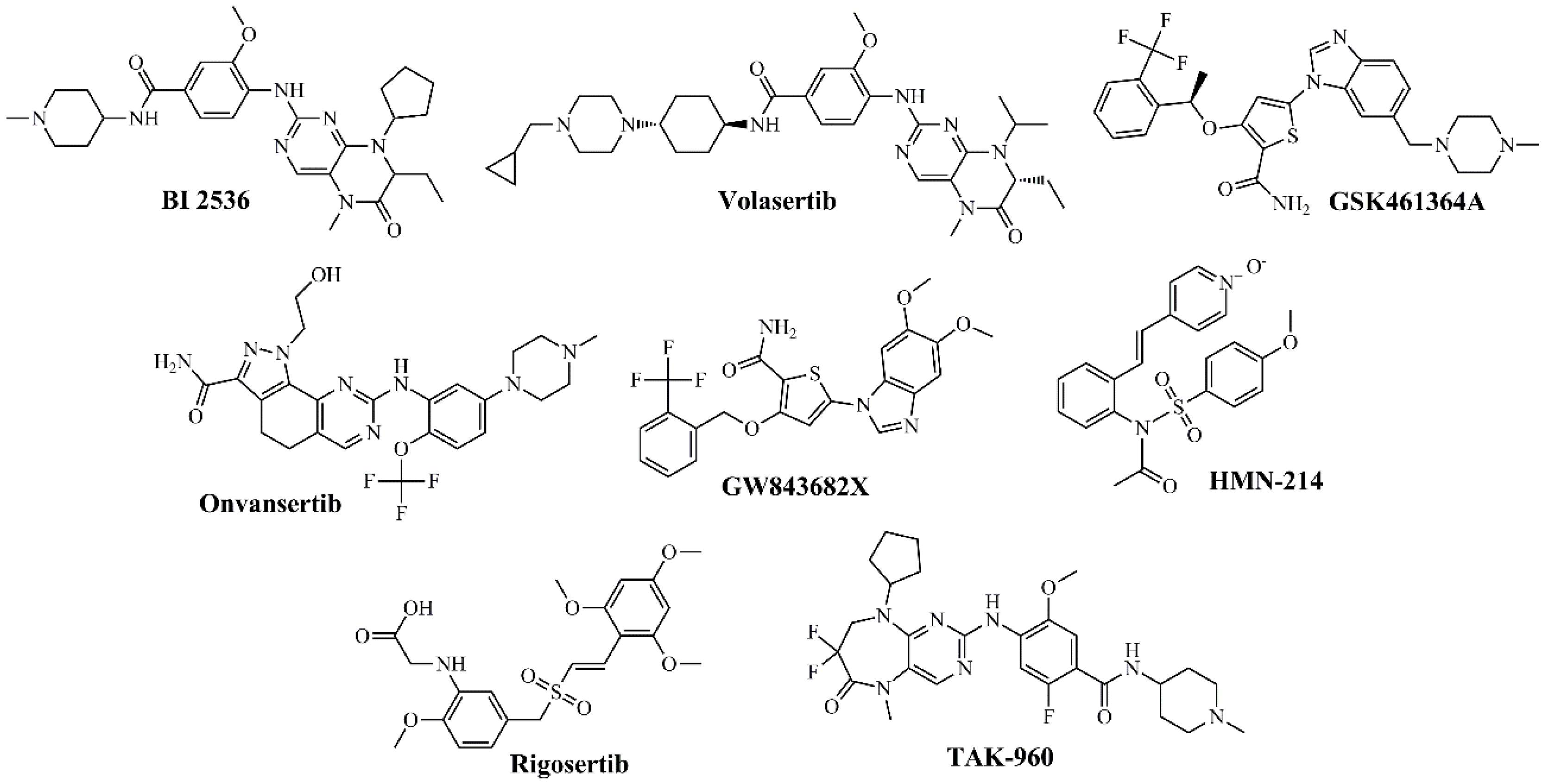
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of PLK1 kinase domain inhibitors.
Beyond the ATP-binding pocket, allosteric surfaces and variable regions at the termini and loops of the kinase domain have been identified, which participate in protein–protein interactions and can modulate the accessibility of the catalytic site [10,33]. These areas represent alternative targets for the development of allosteric modulators or bivalent inhibitors capable of simultaneously interacting with the kinase domain (KD) and PBD, thereby enhancing functional selectivity. In this context, recent research is exploring bivalent compounds and PBD-targeted ligands as innovative strategies to improve efficacy and reduce toxicity [33,34,35,36].
Structural advances in PLK1 and the detailed characterization of its binding sites have enabled an understanding of how classical inhibitors such as BI-2536, volasertib, GSK461364, and onvansertib interact with critical residues of the catalytic pocket, and have paved the way for the design of next-generation inhibitors with improved selectivity and more favorable safety profiles [28,32,37].
2.1.2. PLK1 Polo-Box Domain (PBD): Recognition of Phosphorylated Substrates and Crystallographic Evidence
The PBD, located in the C-terminal region of PLK1 (residues 345–603), constitutes a distinctive structural feature of the PLK family. This domain is composed of two subunits, PB1 and PB2, which adopt a conserved fold consisting of a six-stranded antiparallel β-sheet and an α-helix, exhibiting a high degree of structural similarity despite low sequence identity between them [18,24,38,39,40].
PBD functions as a spatial regulator, directing PLK1 to specific sites of action such as centrosomes, centromeres, the central mitotic spindle, and the midbody ring during cytokinesis, thereby ensuring the fidelity of cell division and preventing off-target phosphorylation [23,41]. Its primary function is to control the subcellular localization of PLK1 throughout the cell cycle, ensuring its presence at the centrosomes during interphase, at the central region of the mitotic spindle during anaphase, and subsequently at the midbody during cytokinesis. This precise localization is essential for proper chromosomal segregation and the correct coordination of mitotic events. Additionally, the PBD exerts an intramolecular regulatory role by interacting with the N-terminal kinase domain, blocking Thr210 phosphorylation under conditions that require temporary inhibition of catalytic activity, constituting an autoinhibitory mechanism [18,24,42,43].
From a molecular perspective, the PBD recognizes phosphorylated serine or threonine residues in target proteins through a consensus motif Ser-[pSer/pThr]-[Pro/X], where “X” corresponds to any amino acid [9]. This specificity depends on the prior phosphorylation of substrates by proline-directed kinases, such as Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPKs) or Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 1 (CDK1), thereby ensuring a phosphorylation-dependent interaction [44]. Phosphopeptide binding occurs at the interface between PB1 and PB2, establishing critical contacts with residues such as Trp414, Leu490, His538, and Lys540, which stabilize the interaction and facilitate the release of the kinase domain for the phosphorylation of specific proteins during mitosis [18,44,45,46].
Within the PBD, the residues forming the phosphate-binding groove are critical for substrate affinity and selectivity. Alterations in these residues, whether through point mutations or inhibitor binding, result in protein mislocalization and defects in mitotic progression [40,44,47].
X-ray crystallography has identified a previously uncharacterized hydrophobic pocket in PLK1, termed the ‘Tyr pocket’, whose characterization provides valuable insights into potential alternative binding sites for inhibitor design. This site, located adjacent to the phospho-substrate binding motif, is essential for cell cycle progression. Directed mutagenesis assays demonstrated that disruption of the pocket compromised cell viability and the proper discrimination of substrates such as Polo-Box domain-Interacting Protein 1 (PBIP1) and Neural precursor cell Expressed, Developmentally Downregulated 1 (NEDD1) [10]. Furthermore, using a rational design approach, Polotyrin was developed as an experimental inhibitor capable of occupying the Tyr pocket and reproducing the mitotic defects observed in the mutants. These findings are supported by crystal structures of the PLK1 PBD (PDB IDs: 3P37, 1Q4K [40], 5NEI, 5NMM), consolidating the Tyr pocket as a highly selective alternative site for the design of PLK1-targeted inhibitors [44].
2.2. Role of PLK1 in Mitosis Process
The kinase PLK1 plays an essential role in multiple mitotic processes, including mitotic entry, centrosome maturation, bipolar spindle assembly, chromosomal segregation, the G2/M transition, nuclear envelope breakdown, kinetochore localization, Golgi apparatus fragmentation, activation of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C), and cytokinesis [12,20]. These events depend on both the activity of its catalytic domain and the regulatory function of PBD, which mediates interactions with phosphorylated substrates and directs subcellular localization [9,10,20].
This enzyme associates with mitotic spindles during cell division, where it stabilizes kinetochore–microtubule interactions and promotes the metaphase-to-anaphase transition. Its inhibition induces apoptosis in various cancer types, including pancreatic, breast, bladder, and oropharyngeal carcinomas, underscoring its value as a therapeutic target [9,12].
Beyond mitotic regulation, PLK1 is involved in processes such as autophagy [48], apoptosis, and cytokine signaling. Additionally, it contributes to the assembly of the contractile ring at the equatorial plate during anaphase and to the control of mitotic exit, ensuring proper chromosomal segregation and progression into G1. It also promotes proliferation, cellular transformation, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition, processes associated with tumor progression [9,20,49].
The role of PLK1 changes dynamically throughout the cell cycle. During interphase, this kinase regulates procentriole elongation during centriole duplication, and its hyperactivity can lead to aberrant elongation, a phenomenon frequently observed in various cancer types [24,50]. During prophase, PLK1 contributes to the activation of the CDK1–Cyclin B complex, thereby promoting mitotic entry. During prometaphase and metaphase, it regulates proper kinetochore localization through two main mechanisms: first, the phosphorylation of Cytoplasmic Linker Protein 170 (CLIP-170) [51], which facilitates its recruitment; and second, the phosphorylation of Sgt1, which enables the formation of the Hsp90–Sgt1–MIS12 complex, essential for the assembly of the Nuclear Division Cycle 80 (NDC80) complex and for the stabilization of microtubules at the kinetochores [52]. During anaphase and telophase, PLK1 participates in APC/C activation, promoting sister chromatid segregation. Additionally, it phosphorylates Breast Cancer Type 2 Susceptibility Protein (BRCA2) at Thr207, facilitating the formation of a complex with Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and phosphorylated Budding Uninhibited By Benzimidazoles 1 Homolog (BUBR1), which ensures proper kinetochore–microtubule attachment. Finally, during cytokinesis, it regulates cleavage furrow formation through the HsCyk-4–Ect2 complex and remains associated with the contractile ring, thereby coordinating the completion of cell division [19].
Another mechanism regulated by PLK1 is the activation of the Cell Division Cycle 25 (Cdc25) phosphatases, particularly Cdc25C, whose phosphorylation promotes nuclear translocation and activation of the CDK1–Cyclin B complex, facilitating the G2/M transition. In parallel, it phosphorylates and inactivates the inhibitors Wee1 and Myt1, promoting their SCF/β-TrCP mediated degradation and supporting mitotic progression. Finally, direct phosphorylation of Cyclin B at the centrosomes contributes to the spatially controlled activation of the CDK1–Cyclin B complex [21,53].
Although the role of PLK1 in multiple cellular functions is well-established, its potential in cancer therapeutics remains under investigation. Numerous reports have demonstrated that tumor cell proliferation can be inhibited by blocking its expression, either through antibodies, RNA interference (RNAi), or PLK1 inhibitors [54,55].
2.3. PLK1 Overexpression and Implications in Tumor Metastasis
The enzyme PLK1 exhibits nuclear expression in various tissues, including the testes, endocrine tissues, lungs, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, kidney, bladder, muscle, skin, bone marrow, and lymphoid tissues; it is predominantly expressed in the nuclei of the testes, breast, and lymphoid tissues, whereas low expression levels have been reported in the human brain [20,56]. During the G1 phase, PLK1 mRNA is very low or absent, whereas it begins to accumulate during the S phase, reaching maximal expression in the G2/M phase [57]. PLK1 gene expression is regulated by transcriptional repressors during G1 and transcriptional activators during G2 [58,59]. PLK1 overexpression highlights the strong dependency of tumor cells on this kinase to complete mitosis and progress through the cell cycle. This elevated expression not only enhances uncontrolled proliferation but is also associated with increased tumor aggressiveness and post-treatment recurrence, reinforcing its clinical value as a biomarker of tumor progression [12,60].
Various studies have shown that PLK1 inhibitors induce mitotic arrest and apoptosis in tumor cells, whereas normal cells exhibit lower dependency on this enzyme, suggesting a favorable therapeutic window [60]. Furthermore, tumors with PLK1 overexpression are particularly sensitive to specific inhibitors, and their combination with chemotherapy or radiotherapy can enhance treatment efficacy [60]. Therapeutic agents targeting PLK1 can be directed toward two functionally distinct domains: the kinase domain and the C-terminal PBD [10].
From a pharmacological perspective, both domains offer opportunities for the development of small-molecule inhibitors. The kinase domain can be blocked at its ATP-binding site, directly suppressing the enzyme’s catalytic activity and halting the phosphorylation of multiple substrates essential for mitotic progression. On the other hand, the PBD functions as an interaction platform for phosphorylated peptide motifs of substrates [43]. This domain exhibits unique structural features: a hydrophobic region that accommodates these motifs and a positively charged region that contributes to binding specificity through electrostatic interactions [36,61,62,63]. In this context, the pharmacological exploitation of these properties has driven the design of inhibitors capable of interfering with PLK1 subcellular localization and protein–protein interactions, offering a more selective therapeutic approach with reduced risk of toxicity in normal cells.
2.4. PLK1 Inhibitors
As described, PLK1 performs multiple functions throughout the cell cycle and at various subcellular locations. Consequently, PLK1 inhibitors must be designed to block specific functions without interfering with unrelated activities. First-generation inhibitors target the N-terminal catalytic kinase domain. However, this region is highly conserved among different PLK subtypes and other kinases, increasing the risk of off-target effects. Additionally, the frequent emergence of mutations in the ATP-binding site has led to pharmacological resistance. To overcome these limitations, an alternative strategy has been developed that focuses on unique residues within the PLK1 kinase domain [12,64].
To minimize these challenges, inhibitors have been designed targeting the PBD, which is unique to the PLK family and characterized by a sequence that is far less conserved compared to the kinase domain [36,61,62,63]. This approach aims to achieve greater inhibitor selectivity, reducing the likelihood of adverse effects and improving efficacy against tumor cells that depend on PLK1 activity [18]. In the Supplementary Materials, Table S1 presents the main characteristics and specificities of both types of PLK1 inhibitors [17,20,32,35,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84].
2.4.1. ATP-Competitive Inhibitors
ATP-competitive inhibitors of the kinase domain represent the most extensively explored strategy to date. These molecules bind competitively to the ATP-binding pocket in the catalytic site, competing with the endogenous molecule and blocking the phosphorylation of essential substrates such as Cdc25C, leading to mitotic arrest and cellular apoptosis [63]. For this binding to occur, PLK1 must be in its active conformation with the binding site accessible [20,85]. These inhibitors share common binding interactions within the hinge region (Lys82, Glu131, Cys133, Asp194, and residues of the regulatory region), which contribute to the orientation and stabilization of the heterocyclic core. In most cases, the nitrogen atom of the central ring forms a hydrogen bond with the NH group of Cys133, while adjacent polar substituents interact with Glu131 and Asp194, anchoring the compound in a manner similar to endogenous ATP. Furthermore, the incorporation of lipophilic groups into the back pocket has been shown to enhance selectivity by exploiting less conserved cavities among kinases. Accordingly, modifications that extend the aromatic scaffold toward the αC or DFG-out loops tend to modulate affinity and confer more sustained kinetic profiles [86].
Several compounds have been developed in this category, including BI 2536 [65,66,67,68], BI 6727 (volasertib) [67,68], GSK461364A [67,68,75,76], NMS-P937 (onvansertib) [72,73], GW843682X [72,73], and HMN-214 [17,80,81]. Among these compounds, BI-2536—the first inhibitor to enter clinical trials—exhibited potent activity against PLK1 with acceptable selectivity. However, in phase I/II studies in lung and pancreatic cancer, it induced grades 3–4 neutropenia as a dose-limiting toxicity, with only modest efficacy. Pharmacokinetic analyses revealed a short half-life and poor tumor penetration, which ultimately limited its further development [25]. In contrast, BI 6727 (volasertib) progressed to phase III trials in acute myeloid leukemia. Although it initially showed responses when combined with cytarabine, the pivotal POLO-AML-2 study was discontinued in 2017 due to excessive hematological toxicity and an unfavorable risk–benefit ratio compared with standard therapy. Its clinical development is currently suspended [32,72,73,80,87]. Onvansertib, on the other hand, represents the second generation of PLK1 inhibitors, featuring an improved pharmacological and selectivity profile. It is currently under phase II clinical evaluation for metastatic colorectal cancer and relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia, demonstrating durable partial responses and improved tolerability. The most common adverse events are grades 1–2 neutropenia and anemia, with no severe thrombotic events reported [32,40,88]. Figure 2 shows the structures of the most representative compounds.
These inhibitors have demonstrated the ability to induce mitotic arrest and apoptosis in tumor cells, validating the role of PLK1 as a therapeutic target. However, their clinical application has been limited by a lack of selectivity, as the ATP-binding pocket is highly structurally conserved among different kinases, leading to hematological adverse effects and systemic toxicity, as previously noted [12,60,63].
2.4.2. Polo-Box Domain (PBD) Inhibitors
PBD inhibitors exert their mechanism of action by causing subcellular mislocalization of PLK1. They prevent binding to the centrosome and kinetochores, thereby inhibiting microtubule assembly as well as proper chromosome segregation at the kinetochores. In this way, PLK1 loses its function in cytokinesis, ultimately leading the cell to apoptosis [60,63].
Inhibitors targeting this region—such as polyoxindole, benzotriazole, and pSer/pThr-mimetic derivatives—act on a conformational interface between the PB1 and PB2 subdomains, where residues Tyr417, His538, and Trp414 play key roles. Effective ligands replicate the interaction pattern of natural phosphopeptides, establishing ionic contacts with the positively charged pocket and π–π stacking interactions with Tyr417. From a chemical standpoint, the success of PBD inhibitors depends on the incorporation of planar aromatic fragments that stabilize π-interactions and phosphomimetic groups capable of forming hydrogen bonds with basic residues in the surrounding environment. The flexibility of the substituent rings is critical for adapting the conformation to the polar environment of the PB1/PB2 pocket [89].
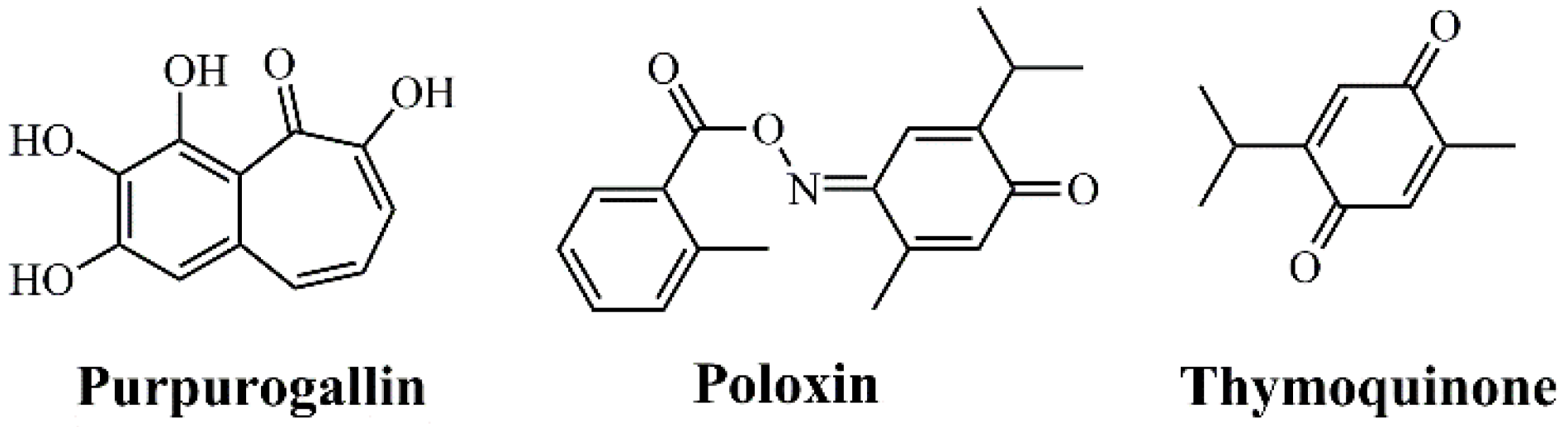
Three molecules have been described as representative inhibitors of the PLK1 PBD: Purpurogallin [17], Poloxin [35,67,82,83], and Thymoquinone [17,35,83,84] (Figure 3). Although still in preclinical stages, these compounds illustrate the feasibility of blocking protein–protein interactions critical for PLK1 function [17]. The advantage of PBD inhibitors lies in their superior specificity within the PLK family, reducing the likelihood of adverse effects compared to ATP-site inhibitors [63]. However, the development of PBD-specific drugs faces significant challenges due to the intrinsic difficulty of designing small molecules capable of blocking large-surface protein–protein interactions [60].
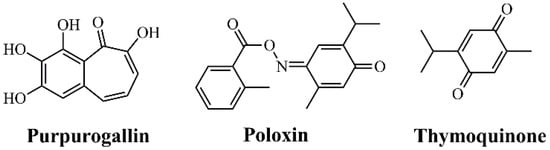
Figure 3.
Chemical structures of PLK1 Polo-Box Domain (PBD) inhibitors.
Recently, new PLK1 PBD inhibitors have been proposed, expanding therapeutic options beyond Purpurogallin, Poloxin, and Thymoquinone [63]. Among them, molecules such as bg-34 have been described, a cell-permeable inhibitor capable of inducing apoptosis through specific PBD blockade [87], and T521, which selectively interferes with the functions of this domain by covalently binding to critical lysine residues, causing mitotic defects and tumor suppression in xenograft models [83]. Additionally, MCC1019 demonstrated cytotoxicity in multiple cell lines with marked selectivity for PLK1 compared to PLK2/3 [88].
Furthermore, screening studies identified new chemical series in which several compounds induced mitotic arrest in HeLa cells with potencies in the micromolar range [90]. Inhibitors derived from marine natural products have also been proposed, characterized by pharmacophore models and in silico validation of stability and favorable ADMET properties [91]. Moreover, the so-called abbapolins, featuring a 2-(4-AlkylBenzamido) benzoic acid core, demonstrated the ability to block PBD-dependent interactions, promoting PLK1 degradation and cytotoxicity in tumor cells [92]. More recently, Allopole was described as an allosteric inhibitor that disrupts the substrate recognition mechanism by perturbing a regulatory loop of the PBD, representing an innovative strategy to modulate PBD-dependent functions [93]. These findings reinforce the potential of the PBD as a therapeutic target.
2.4.3. Perspectives on the Use of PLK1 Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy
Advances in computational tools, such as computer-aided molecular modeling using machine learning and artificial intelligence, high-throughput virtual screening, docking, and molecular dynamics, have enabled the identification of new candidates with optimized pharmacological profiles, paving the way for the development of more selective and potent inhibitors [94,95]. Looking ahead, the future of PLK1 inhibition will likely depend on combined approaches that integrate molecular optimization, complementary therapeutic modalities, and emerging strategies such as peptidomimetics, hybrid molecules, or PROTACs specifically targeting this kinase, establishing PLK1 as a central target in oncological treatment [63,96].
3. Contributions of Computational Studies to the Design of PLK1 Inhibitors
Reviewing the recent literature makes it evident that computational studies have transformed the approach to designing PLK1 inhibitors. These tools not only facilitate the identification of promising compounds but also provide a deep understanding of the molecular mechanisms governing enzyme activity. In this regard, the combination of approaches such as Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship (QSAR), machine learning, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics has enabled a more holistic strategy, capable of integrating multiple levels of analysis to optimize the selectivity, affinity, and pharmacokinetic properties of candidate molecules. This integrated approach has significantly accelerated the drug discovery process and increased the likelihood of success in developing targeted therapies against PLK1 [63,94,95,96].
3.1. Ligand-Based Drug Design (LBDD) Approaches
QSAR models have proven essential for establishing quantitative correlations between the chemical structure of compounds and their biological activity. In particular, 3D-QSAR approaches have recently been applied to the study of inhibitors targeting the PLK1 PBD domain, enabling the identification of critical residues involved in ligand–receptor interactions [95,97]. These methodologies not only facilitate the prediction of the biological activity of new compounds but also provide key insights into the structural determinants of binding, offering a rational basis for optimizing molecules to enhance their affinity and selectivity. Collectively, these advances highlight the potential of QSAR models as predictive tools capable of accelerating candidate selection, guiding structural modifications, and enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of future PLK1 inhibitors [91,96].
Moreover, machine-learning approaches represent a significant advancement in the prediction and screening of compound libraries. By training models on large databases of molecules with known activity, it becomes possible to identify complex patterns that are not evident through traditional methods [98]. This suggests that the ability to discern nonlinear relationships enables the prioritization of compounds with a high likelihood of success before conducting experimental assays, thereby optimizing both resources and time.
Predictive models based on machine-learning algorithms have been trained using large databases of compounds with known activity, enabling the identification of complex patterns that are not evident through traditional methods. These models have facilitated the virtual screening of compound libraries, accelerating the drug discovery process and reducing the need for extensive experimental assays [99,100].
3.2. Structure-Based Drug Design (SBDD) Approaches
Among these techniques, molecular docking has become an essential strategy for predicting ligand binding modes in catalytic sites or within the PBD. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations complement these findings by assessing the stability of protein–ligand complexes, their conformational flexibility, and the persistence of critical interactions over time [96,101,102,103].
Molecular docking is an in silico approach that predicts the preferred orientation and binding modes of an inhibitor within an active site, whether in the kinase domain or the PBD. This technique allows for the identification of key interactions between critical PLK1 residues and ligands, such as hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and ionic bonds, which contribute to complex stability. Furthermore, docking enables large-scale virtual screening of compound libraries, facilitating the selection of candidates with higher potential affinity and desirable pharmacological properties [63,99,104]. This approach is highly valuable, as it provides insights into which structural elements of the inhibitor are indispensable for activity, and which may be modified to enhance selectivity or reduce toxicity.
However, docking alone does not capture the true dynamics of the enzyme or ligand flexibility. In this context, MD simulations are indispensable, allowing for the assessment of how protein–ligand interactions are maintained or fluctuate under simulated solvation and temperature conditions, providing insights into conformational flexibility, the persistence of critical contacts, and the relative affinity of different inhibitors. MD studies have provided detailed information on binding mechanisms and potential alternative binding sites, which has been crucial for the design of more specific inhibitors. MD also facilitates the identification of protein regions that may contribute to selectivity against inhibitors, guiding the design of more effective and specific molecules [101,102,103,105]. Therefore, integrating MD with docking allows for the refinement of the most promising candidates and the elimination of those that, while appearing suitable in a static model, would exhibit low affinity or instability in a dynamic environment.
As can be seen, the combination of computational techniques not only enables the identification of compounds with high affinity but also allows for the optimization of pharmacokinetic properties and the reduction in adverse effects, bringing computational research closer to clinically relevant outcomes. These methodologies provide the capability to integrate structural, biochemical, and pharmacokinetic data into increasingly robust predictive models, facilitating the generation of mechanistic hypotheses that can be experimentally validated, reducing the number of failed assays and accelerating the drug discovery cycle [106,107]. Given this context, the development of specific PLK1 inhibitors has been significantly advanced through the use of advanced computational tools.
In recent years, several studies have explored flavonoids and other natural compounds as potential PLK1 inhibitors, highlighting their relevance in the development of anticancer therapies based on natural products [108,109]. The structural diversity of these metabolites facilitates the formation of hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic contacts, and electrostatic interactions, which can lead to effective inhibition of kinase activity and interference with critical cell cycle processes, such as chromatid segregation and kinetochore stability [91].
Virtual screenings of large sets of natural compounds have enabled the identification of flavonoids capable of interacting with both the catalytic domain and the PBD of PLK1. These molecules exhibit sufficient affinity to stabilize their interaction with the protein, suggesting that they could simultaneously modulate PLK1’s catalytic activity and subcellular localization [110].
Overall, in silico studies conducted by our group suggest that these flavonoids may exert a multi-targeted anticancer effect, as all of them have previously reported antitumor activity in the literature. Considering that PLK1 is expressed in various types of malignant cells, it is postulated that this protein could also serve as a specific target of these compounds, particularly in the case of hesperidin. This information is highly valuable, as, to date, no precedent exists for this type of analysis.
Other studies have extended this approach to marine sources and dual peptides, evaluating inhibitors simultaneously targeting the PBD domains of PLK1 and PLK4. These works have demonstrated that the combination of pharmacophore modeling, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulations enables the selection of candidates with high binding stability and specificity [62,91]. Additionally, research on bioactive compounds from plants such as Garcinia cowa and pteridinone derivatives has shown that integrating QSAR, network pharmacology, molecular docking, and MD simulations can predict critical interactions with PLK1 and guide experimental validation in tumor cells [96,111]. These studies confirm that the inhibitory activity observed in silico correlates with the reduction in key protein expression and the inhibition of cell proliferation, demonstrating that the combination of computational and experimental approaches is essential for identifying effective and selective natural inhibitors.
Furthermore, the integration of large-scale computational screenings, detailed structural modeling, and experimental validation not only enables the prioritization of molecules with the highest likelihood of success but also reduces the time and costs in the early stages of preclinical development. Moreover, this comprehensive approach provides valuable insights into protein–ligand interaction mechanisms, facilitating the rational design of more effective drugs with a lower risk of off-target effects.
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) is a master regulator of mitosis, orchestrating centrosome maturation, spindle assembly, chromosome segregation, and cytokinesis, with additional roles in apoptosis, autophagy, and signaling pathways relevant to tumorigenesis. Its overexpression in diverse cancers correlates with enhanced proliferation, aggressiveness, metastasis, and poor clinical outcomes, consolidating PLK1 as a high-value therapeutic target. The dual-domain architecture of PLK1, comprising the N-terminal kinase domain and the C-terminal Polo-box domain (PBD), provides distinct opportunities for pharmacological intervention. Although ATP-competitive inhibitors targeting the kinase domain have demonstrated antitumor efficacy, their clinical utility has been limited by hematological toxicity and narrow therapeutic windows, as evidenced by the clinical discontinuation of BI-2536 and volasertib. These findings highlight the intrinsic challenge of systemically inhibiting an essential mitotic kinase, underscoring the need to achieve greater selectivity and optimized pharmacological exposure. In contrast, PBD-targeted molecules offer a promising avenue for the selective modulation of PLK1 localization and protein–protein interactions, potentially reducing adverse effects. However, therapeutic targeting of the PBD remains challenging due to the shallow and highly polar nature of its binding surface, which limits ligand permeability and solubility. Recent advances in computational modeling, including molecular docking, molecular dynamics, QSAR, and machine-learning, have significantly accelerated the identification and optimization of PLK1 inhibitors. These tools enable a detailed understanding of ligand–protein interactions, allosteric sites, and conformational dynamics, guiding rational drug design and improving the probability of success in preclinical development. Moreover, emerging strategies—such as bivalent inhibitors targeting nucleophilic residues near the ATP-binding site, covalent PBD ligands that bridge the kinase domain and the PBD, and PROTAC-based degradation approaches—represent the new generation of PLK1-targeted therapies. These approaches aim to overcome the limitations of previous inhibitors by achieving greater selectivity, improved solubility, and reduced systemic toxicity. Looking forward, the integration of structural, biochemical, and computational insights promises to inform the design of next-generation PLK1 inhibitors with improved potency, specificity, and safety profiles. Continued exploration of dual-domain targeting, allosteric modulation, and combination therapies holds significant potential to translate PLK1 inhibition into effective cancer treatments. Collectively, PLK1 remains a central focus in oncology research, exemplifying how mechanistic understanding at the molecular level can drive innovation in targeted anticancer therapy.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3040023/s1.
Author Contributions
D.B.A.-H. contributed by collecting data, reviewing the literature, and writing both the draft and final version. Y.C.-C. contributed by providing ideas and the study concept; E.F.d.S.-J. contributed by performing the study organization and final revision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001 and by Move La America mobility program (Call for proposals nº 07/2024).
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Acknowledgments
Y. Cañizares-Carmenate thanks the support from Agencia Nacional de Investigación y Desarrollo (ANID) (Project number: 3250840). E.F. Silva-Júnior gives thanks for his PQ fellowship granted by the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), process number: 306323/2022-2. Additionally, the authors thank the Post-Graduation Program in Pharmaceutical Sciences at Federal University of Alagoas—Maceió, Brazil for being the host for the exchange student D.B. Aguado-Herrera.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BRCA2 | Breast Cancer Type 2 Susceptibility Protein |
| BUBR1 | Budding Uninhibited By Benzimidazoles 1 homolog |
| Cdc25 | Cell Division Cycle 25 |
| CDK1 | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 1 |
| CLIP-170 | Cytoplasmic Linker Protein 170 |
| KD | Kinase Domain |
| LBDD | Ligand-Based Drug Design |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| MD | Molecular Dynamics |
| NDC80 | Nuclear Division Cycle 80 |
| NEDD1 | Neural precursor cell Expressed, Developmentally Downregulated 1 |
| PBD | Polo-Box Domain |
| PBIP1 | Polo-Box Domain-Interacting Protein 1 |
| PLK1 | Polo-Like Kinase 1 |
| PP2A | Protein Phosphatase 2A |
| QSAR | Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship |
| SBDD | Structure-Based Drug Design |
References
- Zafar, A.; Khatoon, S.; Khan, M.J.; Abu, J.; Naeem, A. Advancements and Limitations in Traditional Anti-Cancer Therapies: A Comprehensive Review of Surgery, Chemotherapy, Radiation Therapy, and Hormonal Therapy. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Yang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, M.; Takehiro, K.; Zhan, M.; Yang, L.; Wang, H. Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies in Overcoming Chemotherapy Resistance in Cancer. Mol. Biomed. 2025, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Solimini, N.L.; Elledge, S.J. Principles of Cancer Therapy: Oncogene and Non-Oncogene Addiction. Cell 2009, 136, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Tyagi, P.; Singh, P.; Rajkumar; Singh, A.P. Recent Advancement in Drug Designing as Small Molecules in Targeted Cancer Therapy: Challenges and Future Directions. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2025, 25, 1364–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Li, J.; Yan, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, W.; Chu, E.; Wei, N. Emerging Roles of Aurora-A Kinase in Cancer Therapy Resistance. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 2826–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malumbres, M.; Barbacid, M. Cell Cycle, CDKs and Cancer: A Changing Paradigm. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Khoshbakht, T.; Hussen, B.M.; Dong, P.; Gassler, N.; Taheri, M.; Baniahmad, A.; Dilmaghani, N.A. A Review on the Role of Cyclin Dependent Kinases in Cancers. BioMed Cent. 2022, 22, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T. Recent Progress on the Localization of PLK1 to the Kinetochore and Its Role in Mitosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapagai, D.; Strebhardt, K.; Wyatt, M.D.; McInnes, C. Structural Regulation of PLK1 Activity: Implications for Cell Cycle Function and Drug Discovery. Cancer Gene Ther. 2025, 32, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ma, P.; Wang, S.; Li, N. Pan-Cancer Analysis of Polo-like Kinase Family Genes Reveals Polo-like Kinase 1 as a Novel Oncogene in Kidney Renal Papillary Cell Carcinoma. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strebhardt, K. Multifaceted Polo-like Kinases: Drug Targets and Antitargets for Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 643–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, N.Q.; Theodorakis, P.E.; Li, M.S. Fast Estimation of the Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability by Pulling a Ligand through a Lipid Membrane. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 3057–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Song, M.; Huang, C.; Yu, Q.; Jiang, G.; Jin, G.; Jia, X.; Shi, Z. Effectiveness, Safety and Pharmacokinetics of Polo-like Kinase 1 Inhibitors in Tumor Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raab, M.; Becker, S.; Sanhaji, M. Targeting Polo-like Kinase 1: Advancements and Future Directions in Anti-Cancer Drug Discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2024, 19, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Lee, H.; Oliva, P.; Kirsch, K.; Kim, B.; Ahn, J.I.; Alverez, C.N.; Gaikwad, S.; Krausz, K.W.; O’Connor, R.; et al. Structural Optimization and Anticancer Activity of Polo-like Kinase 1 (Plk1) Polo-Box Domain (PBD) Inhibitors and Their Prodrugs. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2023, 6, 422–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, R.N.; Park, J.-E.; Kim, E.-H.; Shin, S.Y.; Cheong, C.; Lee, K.S.; Bang, J.K. Plk1-Targeted Small Molecule Inhibitors: Molecular Basis for Their Potency and Specificity. Mol. Cells 2011, 32, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, I.; Basheer, N.; Hasan, G.M.; Afzal, M.; Hassan, M.I. Polo-like Kinase 1 as an Emerging Drug Target: Structure, Function and Therapeutic Implications. J. Drug Target. 2021, 29, 168–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlén, Å.; Martin, C.; Miron, S.; Julien, M.; Theillet, F.-X.X.; Ropars, V.; Sessa, G.; Beaurepere, R.; Boucherit, V.; Duchambon, P.; et al. Proper Chromosome Alignment Depends on BRCA2 Phosphorylation by PLK1. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, S.S. Caracterización Molecular de Los Mecanismos de Resistencia a Inhibidores de Polo-like Kinasa 1 En Cáncer Colorrectal. Papel de Simvastatina Como Modulador de La Resistencia. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fassolari, M. Estudio Funcional de La Familia de Enzimas Aurora Quinasa en Trypanosoma cruzi. Ph.D. Thesis, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Shen, C.; Wang, T.; Quan, J. Structural Basis for the Inhibition of Polo-like Kinase 1. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macůrek, L.; Lindqvist, A.; Lim, D.; Lampson, M.A.; Klompmaker, R.; Freire, R.; Clouin, C.; Taylor, S.S.; Yaffe, M.B.; Medema, R.H. Polo-like Kinase-1 Is Activated by Aurora A to Promote Checkpoint Recovery. Nature 2008, 455, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xing, X.; Guan, P.; Song, S.; You, G.; Xia, C.; Liu, T. Recent Progress in Agents Targeting Polo-like Kinases: Promising Therapeutic Strategies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 217, 113314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steegmaier, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Baum, A.; Lénárt, P.; Petronczki, M.; Krššák, M.; Gürtler, U.; Garin-Chesa, P.; Lieb, S.; Quant, J.; et al. BI 2536, a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of Polo-like Kinase 1, Inhibits Tumor Growth In Vivo. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kim, J. PLK-1 Targeted Inhibitors and Their Potential against Tumorigenesis. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Mei, S.; Liu, J.; Huang, J.; Yue, H.; Ge, T.; Wang, K.; He, X.; Gu, Y.-C.; Hu, C.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Novel Dihydropteridone Derivatives Possessing Oxadiazoles Moiety as Potent Inhibitors of PLK1. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 251, 115242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, O.; Kim, H.; No, K.T. Leveraging the Fragment Molecular Orbital Method to Explore the PLK1 Kinase Binding Site and Polo-Box Domain for Potent Small-Molecule Drug Design. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, Y.-J.; Lin, C.-Y.; Ma, S.; Erikson, R.L. Functional Studies on the Role of the C-Terminal Domain of Mammalian Polo-like Kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2002, 99, 1984–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.-F.; Qian, W.; Li, F.; Yang, R.-H.; Wang, N.; Zheng, C.-B.; Li, C.-Y.; Gu, X.-R.; Yang, L.-M.; Liu, J.; et al. Discovery of ZFD-10 of a Pyridazino[4,5-b]Indol-4(5H)-One Derivative as an Anti-ZIKV Agent and a ZIKV NS5 RdRp Inhibitor. Antiviral Res. 2023, 214, 105607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothe, M.; Kohls, D.; Low, S.; Coli, R.; Rennie, G.R.; Feru, F.; Kuhn, C.; Ding, Y.H. Selectivity-Determining Residues in Plk1. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2007, 70, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, D.; Steegmaier, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Grauert, M.; Baum, A.; Quant, J.; Haslinger, C.; Garin-Chesa, P.; Adolf, G.R. BI 6727, A Polo-like Kinase Inhibitor with Improved Pharmacokinetic Profile and Broad Antitumor Activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3094–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Hymel, D.; Burke, T.R., Jr.; Lee, K.S. Current Progress and Future Perspectives in the Development of Anti-Polo-like Kinase 1 Therapeutic Agents. F1000Research 2017, 6, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raab, M.; Sanhaji, M.; Pietsch, L.; Béquignon, I.; Herbrand, A.K.; Süß, E.; Gande, S.L.; Caspar, B.; Kudlinzki, D.; Saxena, K.; et al. Modulation of the Allosteric Communication between the Polo-Box Domain and the Catalytic Domain in Plk1 by Small Compounds. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 1921–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reindl, W.; Yuan, J.; Krämer, A.; Strebhardt, K.; Berg, T. Inhibition of Polo-like Kinase 1 by Blocking Polo-Box Domain-Dependent Protein-Protein Interactions. Chem. Biol. 2008, 15, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, K.; Tamamura, H.; Burke, T.R. Affinity Enhancement of Polo-like Kinase 1 Polo Box Domain-Binding Ligands by a Bivalent Approach Using a Covalent Kinase-Binding Component. RSC Chem. Biol. 2024, 5, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjertsen, B.T.; Schöffski, P. Discovery and Development of the Polo-like Kinase Inhibitor Volasertib in Cancer Therapy. Leukemia 2015, 29, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowery, D.M.; Lim, D.; Yaffe, M.B. Structure and Function of Polo-like Kinases. Oncogene 2005, 24, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Soung, N.-K.; Johmura, Y.; Kang, Y.H.; Liao, C.; Lee, K.S.H.; Park, C.H.; Nicklaus, M.C.; Lee, K.S.H. Polo-Box Domain: A Versatile Mediator of Polo-like Kinase Function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 1957–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.-Y.; Lowe, E.D.; Sinclair, J.; Nigg, E.A.; Johnson, L.N. The Crystal Structure of the Human Polo-like Kinase-1 Polo Box Domain and Its Phospho-Peptide Complex. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 5757–5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petronczki, M.; Lénárt, P.; Peters, J.M. Polo on the Rise-from Mitotic Entry to Cytokinesis with Plk1. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Park, J.-E.; Kang, Y.H.; Kim, T.-S.; Bang, J.K. Mechanisms Underlying Plk1 Polo-Box Domain-Mediated Biological Processes and Their Physiological Significance. Mol. Cells 2014, 37, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archambault, V.; Glover, D.M. Polo-like Kinases: Conservation and Divergence in Their Functions and Regulation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Mahen, R.; Rossmann, M.; Stokes, J.E.; Hardwick, B.; Huggins, D.J.; Emery, A.; Kunciw, D.L.; Hyvönen, M.; Spring, D.R.; et al. A Cryptic Hydrophobic Pocket in the Polo-Box Domain of the Polo-like Kinase PLK1 Regulates Substrate Recognition and Mitotic Chromosome Segregation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfatah, S.; Berg, A.; Böckers, M.; Efferth, T. A Selective Inhibitor of the Polo-Box Domain of Polo-like Kinase 1 Identified by Virtual Screening. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 16, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elia, A.E.H.; Cantley, L.C.; Yaffe, M.B. Proteomic Screen Finds PSer/PThr-Binding Domain Localizing Plk1 to Mitotic Substrates. Science 2003, 299, 1228–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.M.; Moulaei, T.; Lim, D.; Bang, J.K.; Park, J.E.; Shenoy, S.R.; Liu, F.; Kang, Y.H.; Liao, C.; Soung, N.K.; et al. Structural and Functional Analyses of Minimal Phosphopeptides Targeting the Polo-Box Domain of Polo-like Kinase 1. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.; Yan, H.; Du, J.; Chen, X.; Shao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Lin, N.; Yang, B.; et al. PLK1 (Polo like Kinase 1)-Dependent Autophagy Facilitates Gefitinib-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Degrading COX6A1 (Cytochrome c Oxidase Subunit 6A1). Autophagy 2021, 17, 3221–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalous, J.; Aleshkina, D. Multiple Roles of PLK1 in Mitosis and Meiosis. Cells 2023, 12, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Farmer, V.; Shukla, A.; James, J.; Gruskin, R.; Kiriyama, S.; Loncarek, J. Centriole Maturation Requires Regulated Plk1 Activity during Two Consecutive Cell Cycles. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 206, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, X.S.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Turner, J.R.; Liu, X.S. Phosphorylation of CLIP-170 by Plk1 and CK2 Promotes Timely Formation of Kinetochore–Microtubule Attachments. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 2953–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Targeting Polo-Like Kinases: A Promising Therapeutic Approach for Cancer Treatment. Transl. Oncol. 2015, 8, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colicino, E.G.; Hehnly, H. Regulating a Key Mitotic Regulator, Polo-like Kinase 1 (PLK1). Cytoskeleton 2018, 75, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spankuch-Schmitt, B.; Bereiter-Hahn, J.; Kaufmann, M.; Strebhardt, K. Effect of RNA Silencing of Polo-Like Kinase-1 (PLK1) on Apoptosis and Spindle Formation in Human Cancer Cells. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 1863–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.Q.; Lasky, K.; Shinde, V.; Stringer, B.; Qian, M.G.; Liao, D.; Liu, R.; Driscoll, D.; Nestor, M.T.; Amidon, B.S.; et al. MLN0905, a Small-Molecule PLK1 Inhibitor, Induces Antitumor Responses in Human Models of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 2045–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, J.M.; Wyatt, M.D.; McInnes, C. Inhibitors of the PLK1 Polo-Box Domain: Drug Design Strategies and Therapeutic Opportunities in Cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2023, 18, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmit, T.L.; Zhong, W.; Setaluri, V.; Spiegelman, V.S.; Ahmad, N. Targeted Depletion of Polo-Like Kinase (Plk) 1 Through Lentiviral ShRNA or a Small-Molecule Inhibitor Causes Mitotic Catastrophe and Induction of Apoptosis in Human Melanoma Cells. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 2843–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, T.; Asaoka, M.; Katsuta, E.; Li, Y.; Takabe, K. Abstract 5252: High Expression of PLK1, Polo-like Kinase 1, Is Significantly Associated with DNA Repair Deficiency, Inactivated TP53, and Worse Prognosis in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 11, 5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratmann, J.A.; Sebastian, M. Polo-like Kinase 1 Inhibition in NSCLC: Mechanism of Action and Emerging Predictive Biomarkers. Lung Cancer Targets Ther. 2019, 10, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, R.; Wang, Y.; Pan, L.; Luan, F.; Fu, G. PLK1 in Cancer Therapy: A Comprehensive Review of Immunomodulatory Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yan, F.; Huo, X.; Niu, M.-M. Discovery of a Potent PLK1-PBD Small-Molecule Inhibitor as an Anticancer Drug Candidate through Structure-Based Design. Molecules 2019, 24, 4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Wu, H.; Liu, H.; Dong, H.; Niu, M.M.; Shi, K.; Wang, F. Discovery of Novel Dual-Targeting Inhibitors against PLK1-PBD and PLK4-PB3: Structure-Guided Pharmacophore Modelling, Virtual Screening, Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics Simulation, and Biological Evaluation. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2025, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, Q.; Wang, X. PLK1, A Potential Target for Cancer Therapy. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarhan, R.M.; Harb, H.S.; Abou Warda, A.E.; Salem-Bekhit, M.M.; Shakeel, F.; Alzahrani, S.A.; Madney, Y.M.; Boshra, M.S. Efficacy of the Early Treatment with Tocilizumab-Hydroxychloroquine and Tocilizumab-Remdesivir in Severe COVID-19 Patients. J. Infect. Public Health 2022, 15, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, A.; Mross, K.; Steinbild, S.; Hedbom, S.; Unger, C.; Kaiser, R.; Trommeshauser, D.; Munzert, G. Phase I Study of the Plk1 Inhibitor BI 2536 Administered Intravenously on Three Consecutive Days in Advanced Solid Tumours. Curr. Oncol. 2012, 19, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mross, K.; Dittrich, C.; Aulitzky, W.E.; Strumberg, D.; Schutte, J.; Schmid, R.M.; Hollerbach, S.; Merger, M.; Munzert, G.; Fleischer, F.; et al. A Randomised Phase II Trial of the Polo-like Kinase Inhibitor BI 2536 in Chemo-Nave Patients with Unresectable Exocrine Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas-a Study within the Central European Society Anticancer Drug Research (CESAR) Collaborative Network. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutteridge, R.E.A.; Ndiaye, M.A.; Liu, X.; Ahmad, N. Plk1 Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy: From Laboratory to Clinics. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, H. Current Clinical Trials with Polo-like Kinase 1 Inhibitors in Solid Tumors. Anticancer. Drugs 2013, 24, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, D.W.; Diamond, J.R.; Lam, E.T.; Weekes, C.D.; Astling, D.P.; Anderson, R.T.; Leong, S.; Gore, L.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Vogler, B.W.; et al. Phase I Study of Oral Rigosertib (ON 01910.Na), a Dual Inhibitor of the PI3K and Plk1 Pathways, in Adult Patients with Advanced Solid Malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1656–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumireddy, K.; Reddy, M.V.R.; Cosenza, S.C.; Nathan, R.B.; Baker, S.J.; Papathi, N.; Jiang, J.; Holland, J.; Reddy, E.P. ON01910, a Non-ATP-Competitive Small Molecule Inhibitor of Plk1, Is a Potent Anticancer Agent. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navada, S.C.; Fruchtman, S.M.; Odchimar-Reissig, R.; Demakos, E.P.; Petrone, M.E.; Zbyszewski, P.S.; Holland, J.F.; Silverman, L.R. A Phase 1/2 Study of Rigosertib in Patients with Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) and MDS Progressed to Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2018, 64, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, D.H.; Barzi, A.; Ridinger, M.; Samu€elsz, E.; Subramanian, R.A.; Croucher, P.J.P.; Smeal, T.; Kabbinavar, F.F.; Lenz, H.J. Onvansertib in Combination with FOLFIRI and Bevacizumab in Second-Line Treatment of KRAS-Mutant Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Phase Ib Clinical Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 2039–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, G.J.; Jameson, G.; Von Hoff, D.D.; Valsasina, B.; Davite, C.; Di Giulio, C.; Fiorentini, F.; Alzani, R.; Carpinelli, P.; Di Sanzo, A.; et al. Phase I Dose Escalation Study of NMS-1286937, an Orally Available Polo-Like Kinase 1 Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2018, 36, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, D.; Meredith, W.O.; Weber, I.K.; Price, M.R.; Birtwistle, M.R. Predicting Anti-Cancer Drug Combination Responses with a Temporal Cell State Network Model. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2023, 19, e1011082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmos, D.; Barker, D.; Sharma, R.; Brunetto, A.T.; Yap, T.A.; Taegtmeyer, A.B.; Barriuso, J.; Medani, H.; Degenhardt, Y.Y.; Allred, A.J.; et al. Phase I Study of GSK461364, a Specific and Competitive Polo-like Kinase 1 Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3420–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmartin, A.G.; Bleam, M.R.; Richter, M.C.; Erskine, S.G.; Kruger, R.G.; Madden, L.; Hassler, D.F.; Smith, G.K.; Gontarek, R.R.; Courtney, M.P.; et al. Distinct Concentration-Dependent Effects of the Polo-like Kinase 1-Specific Inhibitor GSK461364A, Including Differential Effect on Apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6969–6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, G.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Breuer, E.K.; Kim, C.K. Combination Treatment of Polo-Like Kinase 1 and Tankyrase-1 Inhibitors Enhances Anticancer Effect in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Xiang, W.; Liu, X.; Jiang, M.; Hu, J. Proteasome Activation Is Critical for Cell Death Induced by Inhibitors of Polo-like Kinase 1 (PLK1) in Multiple Cancers. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 972, 176558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, L.; Yisha, Z.; Gu, A.; Liu, T. Polo-like Kinase 1 Inhibition Modulates Urinary Tract Smooth Muscle Contraction and Bladder Cell Transcriptional Programs. Cytoskeleton 2025, 82, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilamakuri, R.; Rouse, D.C.; Agarwal, S. Inhibition of Polo-like Kinase 1 by HMN-214 Blocks Cell Cycle Progression and Inhibits Neuroblastoma Growth. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, L.L.; Taylor, C.; Pilkington, D.L.; Cohen, J.L.; Von Hoff, D.D. A Phase I Pharmacokinetic Study of HMN-214, a Novel Oral Stilbene Derivative with Polo-like Kinase-1-Interacting Properties, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5182–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Sanhaji, M.; Krmer, A.; Reindl, W.; Hofmann, M.; Kreis, N.N.; Zimmer, B.; Berg, T.; Strebhardt, K. Polo-Box Domain Inhibitor Poloxin Activates the Spindle Assembly Checkpoint and Inhibits Tumor Growth in Vivo. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 2091–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Si, S. Identification of a Novel Polo-like Kinase 1 Inhibitor That Specifically Blocks the Functions of Polo-Box Domain. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 1234–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Song, Y.; Rehse, P.H. Thymoquinone Blocks PSer/PThr Recognition by Plk1 Polo-Box Domain as a Phosohate Mimic. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, P.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, M.; Wang, M.; Cai, P.; Huang, Y.; Song, Y. PLK1 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. Ann. Med. Surg. 2025, 87, 4165–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkard, M.E.; Santamaria, A.; Jallepalli, P.V. Enabling and Disabling Polo-like Kinase 1 Inhibition through Chemical Genetics. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 978–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasrao, G.; Park, J.E.; Kim, S.; Ahn, M.; Cheong, C.; Nam, K.Y.; Gunasekaran, P.; Hwang, E.; Kim, N.H.; Shin, S.Y.; et al. Design and Synthesis of a Cell-Permeable, Drug-like Small Molecule Inhibitor Targeting the Polo-Box Domain of Polo-like Kinase 1. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfatah, S.; Berg, A.; Huang, Q.; Yang, L.J.; Hamdoun, S.; Klinger, A.; Greten, H.J.; Fleischer, E.; Berg, T.; Wong, V.K.W.; et al. MCC1019, a Selective Inhibitor of the Polo-Box Domain of Polo-like Kinase 1 as Novel, Potent Anticancer Candidate. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.S.; Śledź, P.; Lang, S.; Stubbs, C.J.; Spring, D.R.; Abell, C.; Best, R.B. Using Ligand-Mapping Simulations to Design a Ligand Selectively Targeting a Cryptic Surface Pocket of Polo-Like Kinase 1. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10078–10081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Chen, F.; Zhuo, X.; Guo, X.; Yun, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lai, L. Discovery of Novel Polo-Like Kinase 1 Polo-Box Domain Inhibitors to Induce Mitotic Arrest in Tumor Cells. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 7089–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Zheng, C.; Tan, H.; Luo, L. Identification of PLK1-PBD Inhibitors from the Library of Marine Natural Products: 3D QSAR Pharmacophore, ADMET, Scaffold Hopping, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Study. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, J.; Mcinnes, C.; Wyatt, M.D. Non-Peptidic, Polo Box Domain-Targeted Inhibitors of PLK1 Block Kinase Activity, Induce Its Degradation and Target Resistant. Cells 2023, 64, 9916–9925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Kirsch, K.; Lee, H.; Oliva, P.; Ahn, J.I.; Ravishankar, H.; Zeng, Y.; Fox, S.D.; Kirby, S.A.; Badhwar, P.; et al. Specific Inhibition of an Anticancer Target, Polo-like Kinase 1, by Allosterically Dismantling Its Mechanism of Substrate Recognition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2305037120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Shehri, Z.S.; Alshehri, F.F. Machine Learning-Based Virtual Screening and Molecular Modeling Reveal Potential Natural Inhibitors for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Crystals 2025, 15, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhujbal, S.P.; Kim, H.; Bae, H.; Hah, J.-M. Design and Synthesis of Aminopyrimidinyl Pyrazole Analogs as PLK1 Inhibitors Using Hybrid 3D-QSAR and Molecular Docking. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er-rajy, M.; El Fadili, M.; Imtara, H.; Saeed, A.; Ur Rehman, A.; Zarougui, S.; Abdullah, S.A.; Alahdab, A.; Parvez, M.K.; Elhallaoui, M. 3D-QSAR Studies, Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamic Simulation, and ADMET Proprieties of Novel Pteridinone Derivatives as PLK1 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Life 2023, 13, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, J.; Wang, T.; Feng, Y. Drug Design and Molecular Docking Simulations of Polo-like Kinase 1 Inhibitors Based on QSAR Study. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 21134–21145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caba, K.; Tran-Nguyen, V.K.; Rahman, T.; Ballester, P.J. Comprehensive Machine Learning Boosts Structure-Based Virtual Screening for PARP1 Inhibitors. J. Cheminform. 2024, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luttens, A.; Cabeza de Vaca, I.; Sparring, L.; Brea, J.; Martínez, A.L.; Kahlous, N.A.; Radchenko, D.S.; Moroz, Y.S.; Loza, M.I.; Norinder, U.; et al. Rapid Traversal of Vast Chemical Space Using Machine Learning-Guided Docking Screens. Nat. Comput. Sci. 2025, 5, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Huang, Y.; Yang, M.; He, L.; Yu, Q.; Cai, Y.; Shen, J.; Lu, B. Machine Learning-Based Cell Death Marker for Predicting Prognosis and Identifying Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Prostate Cancer. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohimani, H.; Gurevich, A.; Mikheenko, A.; Garg, N.; Nothias, L.-F.; Ninomiya, A.; Kentaro Takada, P.C.D.; Pevzner, P.A. Molecular Dynamics for All. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 176, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Ma, X.; Yang, H.; Luan, Y.; Ai, H. Molecular Engineering and Activity Improvement of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: Insights from 3D-QSAR, Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2022, 116, 108239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, S.A.; Dror, R.O. Molecular Dynamics Simulation for All. Neuron 2018, 99, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito-Verza, A.; Musacchio, A.; Conti, D. Decoding the Language of PLK1 Docking Motifs and Activation Mechanisms. Trends Cell Biol. 2025, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Guan, L.; Wang, Y.; Niu, M.-M.; Ruan, Y.; Xu, C.; Yang, L. Discovery of a Novel PLK1 Inhibitor with High Inhibitory Potency Using a Combined Virtual Screening Strategy. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2025, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadybekov, A.V.; Katritch, V. Computational Approaches Streamlining Drug Discovery. Nature 2023, 616, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahin, R.; Jaafreh, S.; Azzam, Y. Tracking Protein Kinase Targeting Advances: Integrating QSAR into Machine Learning for Kinase-Targeted Drug Discovery. Futur. Sci. OA 2025, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlAjmi, M.F.; Rehman, M.T.; Hussain, A.; Rather, G.M. Pharmacoinformatics Approach for the Identification of Polo-like Kinase-1 Inhibitors from Natural Sources as Anti-Cancer Agents. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Malik, J.; Singh, G. Investigation of Flavonoids Derivatives as PLK-1 Targeted Inhibitor and Their Potential Against Lung Tumorigenesis: In-Silico Molecular Docking. Sch. Acad. J. Pharm. 2025, 14, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawale, F.; Iwaloye, O.; Elekofehinti, O.O. Virtual Screening of Natural Compounds as Selective Inhibitors of Polo-like Kinase-1 at C-Terminal Polo Box and N-Terminal Catalytic Domain. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 13606–13624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, M.; Chen, W.; Sun, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, B.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J. Integrating Network Pharmacology, Bioinformatics, and Experimental Validation to Unveil the Molecular Targets and Mechanisms of Galangin for Treating Hepatocellular Carcinoma. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2024, 24, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).