- Article
Trust in News Media Across Asia: A Multilevel Analysis of Individual and Societal Factors
- Ke Du and
- Zhe Xu
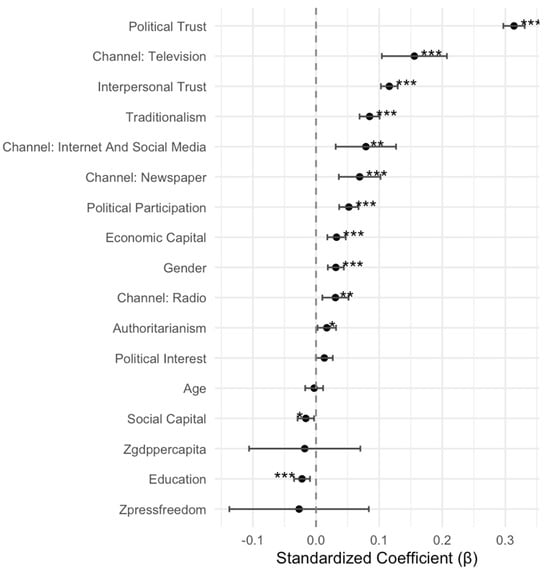
Despite extensive scholarly attention, the exploration of individual-level determinants of news media trust still offers substantial room for further research, particularly from non-Western perspectives. This article moves beyond traditional political and media-related perspectives by incorporating individual capital and cultural values into the analysis of media trust. Using data from the fifth wave of the Asian Barometer Survey (14 countries and territories, N = 25,321), this study employs Hierarchical Linear Modeling (HLM) to examine the effects of four key factors on news media trust in Asia. The findings suggest that individual-level characteristics, including economic capital, traditional values, and authoritarian values, contribute to trust in news media in Asia, whereas social capital has a negative influence. These associations even remain significant after controlling for some political factors. Additionally, authoritarian values shape news media trust through a moderating mechanism, weakening the influence of political trust while reinforcing the role of interpersonal trust. At the societal level, GDP per capita and press freedom influence news media trust in Asia primarily through cross-level interactions rather than direct effects. These findings highlight the complex interaction between societal and individual determinants in shaping news media trust.
4 January 2026