- Article
Direct-to-Implant Breast Reconstruction of Large-Volume Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy Without Wise-Pattern Incision
- Kella L. Vangsness,
- Andre-Philippe Sam and
- Ronald M. Cornely
- + 1 author
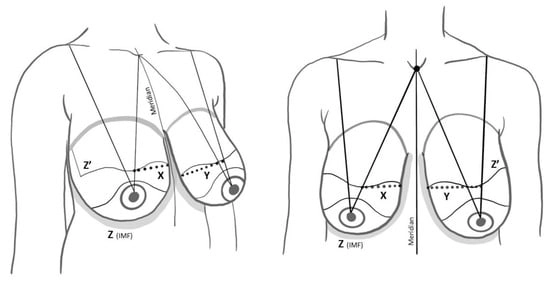
Background: Large-volume ptotic breasts are associated with incision complication rates in single-stage direct-to-implant pre-pectoral breast reconstruction. The aim is to propose an updated surgical approach for this patient population. Methods: A small retrospective case series of patients who underwent direct-to-implant breast reconstruction without a wise-pattern incision from 2019 to 2024 at a single academic institution. Results: Eight breasts from five patients fulfilled the inclusion criteria. One patient had minimal superior nipple–areolar complex ischemia with no additional postoperative complications identified. Conclusions: Refinement to a popular direct-to-implant breast reconstruction technique has the potential to decrease complication rates and improve aesthetic outcomes in large-volume ptotic breasts.
5 December 2025