- Systematic Review
The Evolution and Role of Breast Dressing Following Aesthetic and Oncoplastic Breast Surgery: A Systematic Literature Review
- Edoardo Caimi,
- Arianna Balza and
- Riccardo Di Giuli
- + 5 authors
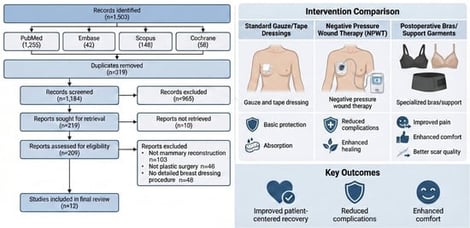
Background: Breast surgery, both aesthetic and reconstructive, has evolved significantly over the years. Postoperative care is vital for patient recovery, with surgical dressings playing a crucial role in minimizing complications, including infections and bleeding. This review aims to evaluate the safety, comfort, and effectiveness of different durations for wearing surgical dressings after breast surgery. It also explores the use of negative pressure wound dressings and postoperative bras to enhance surgical outcomes. Methods: A comprehensive review of literature published from 2003 to 2024. Studies focusing on breast dressing techniques after mammary reconstruction and aesthetic surgery in plastic surgery were included. Results: Of 1503 initially identified articles, 12 were deemed relevant and included in this review. The findings suggest that prolonged dressing wear, up to 6 days postsurgery, may reduce cutaneous colonization without affecting infection rates in aesthetic breast surgery. Additionally, negative pressure wound therapy demonstrates promise in reducing overall wound complications and mastectomy flap necrosis. The utilization of specific postoperative bras is shown to improve patient comfort, mobility, and security, contributing to pain reduction and aesthetic outcomes. Conclusions: The lack of consensus on dressing selection and duration calls for further research in breast surgery postoperative care. Extended dressing wear, negative pressure therapy, and customized postoperative bras show potential in reducing complications, providing new avenues to enhance patient outcomes in the field of plastic surgery. Addressing these issues can lead to improved patient satisfaction and surgical results.
3 February 2026